COMP3010: Algorithm Theory and Design
Daniel Sutantyo, Department of Computing, Macquarie University
3.1 Permutations and Combinations
Search space
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
- The set of all possible solution is known as the search space or solution space
- When we are brute forcing, we simply go through all possible solution and pick the correct one
- Obviously, we need to be able to generate all possible solutions, and to do this we need to employ techniques from combinatorial mathematics (which for us is just permutations and combinations)
- references: CLRS, Appendix C, Section C.1
Rule of Sum
- The number of ways to choose one element from one or more disjoint sets is the sum of the cardinalities of the sets
- example: a character on the number plate can either be a number of a letter, how many choices do you have?
- set of 1-digit numbers: \(\{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9\}\), cardinality is 10
- set of letters: \(\{A,B,C,\dots,Y,Z\}\), cardinality is 26
- number of choices: 26 + 10 = 36 choices
- example: a character on the number plate can either be a number of a letter, how many choices do you have?
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Rule of Product
- The number of ways to choose an ordered pair is the number of ways of choosing the first element multiplied by the number of ways of choosing the second element
- example: a single character followed by a one-digit integer (e.g. \(A9, C5, Z3\)), has \(26 * 10 = 260\) combinations
- example: there are 100 2-digit numbers (from 00 to 99)
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
- A permutation of a finite set \(S\) is an ordered sequenceof all elements of \(S\) such that each element appears exactly once
- example: The set \(\{a,b,c\}\) has six possible permutations:
- \(abc, acb, bac, bca, cab, cba\)
- example: The set \(\{a,b,c\}\) has six possible permutations:
- The number of permutations of a set with \(n\) elements is \(n!\)
- for the first element in the sequence, you have \(n\) choices
- for the second element, you have \((n-1)\) choices, and so on
- hence number of choices = \(n*(n-1)*\cdots*1 = n!\)
Permutation
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Permutation
- Given a set of size \(n\), if you only want permutations of length \(k\) (called \(\text{$k$-permutation}\)) then:
- for the first element in the sequence, you have \(n\) choices
- for the second element, you have \((n-1)\) choices,
- but you only want \(k\) elements, so you stop after choosing \(k\) elements
(for the last element, you have \(n-k+1\) choices)
\[n * (n-1) * \cdots * (n-k+1) = \frac{n!}{(n-k)!}\]
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Permutation
- Example: Given the set\(\{a,b,c,d\}\), how many permutations of 3 elements?
- 4 choices for the first element, 3 choices for the second one, and 2 choices for the last, i.e. a total of 24 permutations:
- \(abc,acb,bac,bca,cab,cba\)
- \(abd,adb,bad,bda,dab,dba\)
- \(acd,adc,cad,cda,dac,dca\)
- \(bcd,bdc,cbd,cdb,dbc,dcb\)
- 4 choices for the first element, 3 choices for the second one, and 2 choices for the last, i.e. a total of 24 permutations:
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Combination
- Given a set \(S\), how many combinations of unique elements in the set can you make?
- in permutation, the order matter: \(abc\), \(acb\), \(bca\), \(bac\), \(cab\), \(cba\) are all different
- but if we just want a combination of 3 elements where ordering does not matter, then there is only one: \(abc\)
- For each combination of \(k\) elements, there are \(k!\) permutations
- so if you want the number of combinations of \(k\) elements, divide the number of permutations with \(k!\)
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Combination
- \(abc,acb,bac,bca,cab,cba\)
- \(abd,adb,bad,bda,dab,dba\)
- \(acd,adc,cad,cda,dac,dca\)
- \(bcd,bdc,cbd,cdb,dbc,dcb\)
- \(\{a,b,c\}\)
- \(\{a,b,d\}\)
- \(\{a,c,d\}\)
- \(\{b,c,d\}\)
- Thus, the number of combination of \(k\) elements is
\[\frac{n!}{k!(n-k)!} = \binom{n}{k}\]
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Combination
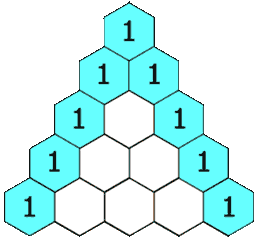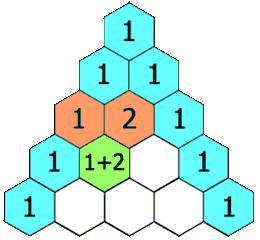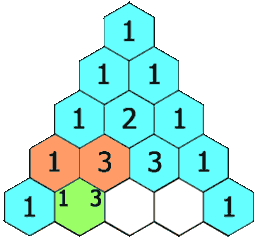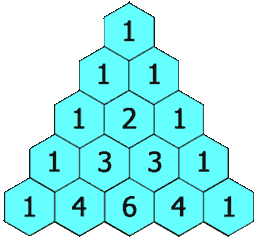
1 4 6 4 1
a b c d
a b c d
a b c
a b d
a c d
b c d
a b
a c
a d
b c
b d
c d
a
b
c
d
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Combination
1 4 6 4 1
1 3 3 1
\(2^3 = 8\)
1 5 10 10 5 1
\(2^5 =32\)
\(2^4 = 16\)
a b c d
\(\frac{0}{1}\)
- The total number of combinations is always \(2^n\) because for each item, you can either choose it, or not choose it
a d
b c d
c
1 0 0 1
\(\frac{0}{1}\)
\(\frac{0}{1}\)
\(\frac{0}{1}\)
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 0
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Combination
\[(x+y)^4 = x^4 + 4x^3y + 6x^2y^2 + 4xy^3 + y^3\]
\[(x+y)^n = \sum_{k=0}^n \binom{n}{k} x^ky^{n-k}\]
- You also use this for binomial expansion
\[(x+y)^3 = x^3 + 3x^2y + 3x2y^2 + 1y^3 \]
\[(x+y)^2 = x^2 + 2xy + y^2 \]
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Example
- Question: In how many ways can you choose three distinct numbers from the set \(\{1,2,\dots,99\}\) so that their sum is even?
- Case 1: All numbers are even
- \(\binom{49}{3}\) possibilities since there are 49 even numbers
- Case 2: Two odd numbers, one even number
- \(\binom{50}{2} * 49\)
- Total answer: \(\binom{49}{3} + 49 * \binom{50}{2}\)
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Example
- Question: How many ways can you seat \(n\) guests on a circular dining table? (assume two seatings arrangements are the same if one can be rotated from the other)
\((n-1)!\) ways (why not \(n!\) ?)
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations
Final remarks
-
The most important takeaway from permutations and combinations is that you understand that the total number of permutation is \(n!\) and the total number of combinations is \(2^n\)
- this is where we get \(O(n!)\) and \(O(2^n)\)
3.1 - Permutations and Combinations