gaz et plasmas 🌬️
chaos et fourmis 🐜
Cermics
Oct 14, 2024
Thomas Borsoni
postdoc \(1^{ere}\) année
ma thèse
mon postdoc

Contributions around the Boltzmann equation and some of its variants
supervisé par
Laurent Boudin & Laurent Desvillettes
au Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions
Sorbonne Université
ma thèse :
Mesoscopic
Microscopic
Macroscopic
(statistical)
description of gases
Density of molecules: \(f \equiv f_{t,x}(v)\)
The original Boltzmann equation
Statistical description of a monoatomic gas
[A. Greg: Kinetic theory of gases, wikipedia.]
advection
collisions
(e.g. \(\mathrm{Ar} \) )

[A. Greg: Kinetic theory of gases, wikipedia.]
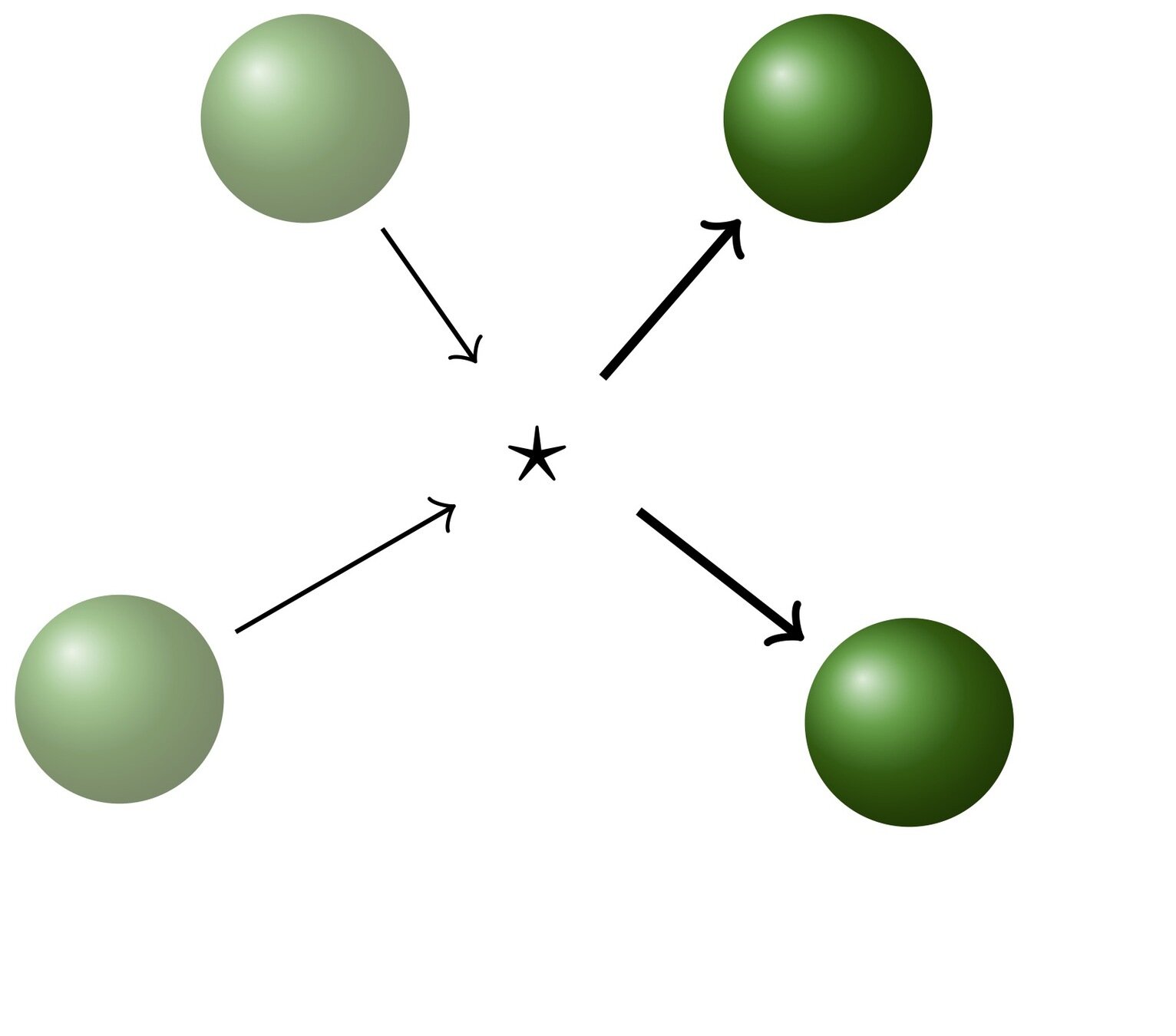
Focus on collisions
the Homogeneous Boltzmann equation
Density of molecules: \(f_t(v)\)

\(x \)
advection
\(+ \, v \cdot \nabla_x f\)
















Entropy and equilibrium
The Boltzmann entropy:
2. \(D(g) = 0 \iff g =M \) a Maxwellian:
characterization of equilibria
Boltzmann's H Theorem
1. If \(f \equiv f_t(v)\) solves
\(2^{nd}\) principle of thermodynamics
\((HB)\)
then
original
monoatomic molecules


polyatomic molecules



Part \(\mathrm{I}.1\)

Part \(\mathrm{ I}.2\)
polyatomic with
resonant collisions
fermions




Part \(\mathrm{II}\)
e.g. \(\mathrm{Ar}\)
e.g. \(\mathrm{N_2}\), \(\mathrm{H_2O}\)
e.g. \(\mathrm{CO_2}\)
e.g. \(\mathrm{e^-}\)


My work
- Modelling
- Analysis
- Simulations
- Functional analysis
- PDEs
Transfer of entropy inequalities
from Boltzmann to BOLTZMANN-Fermi-Dirac
(Partie \(\mathrm{II}\) de ma thèse)
Distribution of electrons in semi-conductors

The Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
Boltzmann for fermions
the Boltzmann equation
(homogeneous)
conservation of mass, momentum, energy

\(f \equiv f_t(v)\) density of molecules

1. Dissipation of the Boltzmann entropy
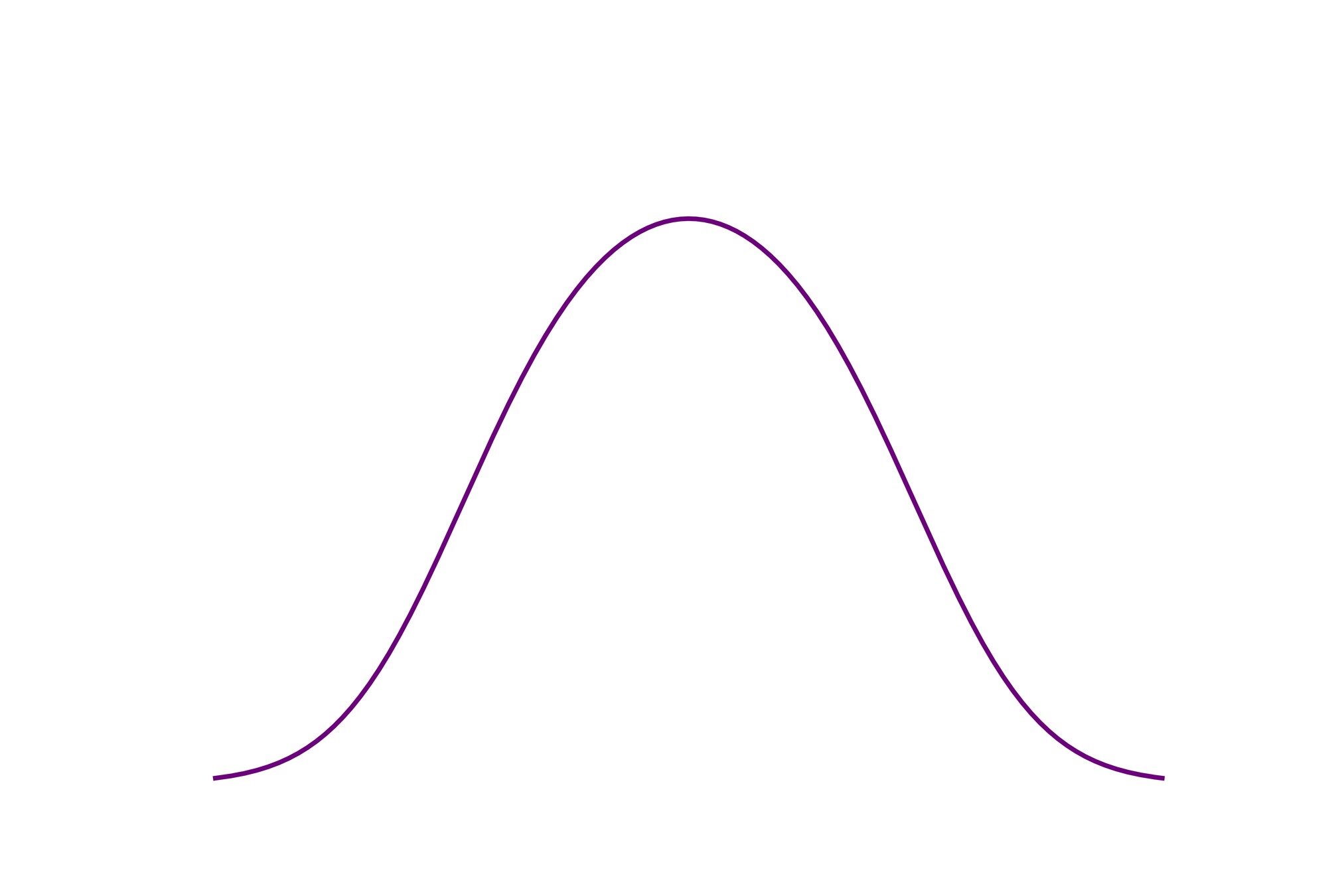
2. Equilibria: Maxwellian (Gibbs) distribution
H Theorem:

the Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac equation
Fermions -> Pauli exclusion principle -> quantum parameter \(\delta>0\) :
1. Dissipation of the Fermi-Dirac entropy
2. Equilibria: Fermi-Dirac statistics
H Theorem:
(+ saturated state: )
(homogeneous )
conservation of mass, momentum, energy
additional feature
\(f \equiv f_t(v)\) density of fermions
Fermi-Dirac entropy
Boltzmann entropy
Equilibrium: Fermi-Dirac statistics
Equilibrium: Maxwellian
entropies and equilibria
Boltzmann


Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
Fermi-Dirac entropy
Equilibrium: Fermi-Dirac statistics
Equilibrium: Maxwellian
entropies and equilibria
Boltzmann


Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac


entropy \(\displaystyle H : h \mapsto \int \Phi(h)\) \(\Phi\) \(\mathcal{C}^2\) st. convex
equilibrium
Boltzmann entropy
\(D(g) \gtrsim {H(g|M^g)}^{1+\alpha}\)
\(D(g) \geqslant C H(g|M^g)\)
the entropy method
Relative entropy to equilibrium:
\(H(f_t|M^{f_0}) \lesssim t^{-1/\alpha}\)
\(H(f_t|M^{f_0}) \lesssim e^{-Ct} \)
Csiszár-Kullback-Pinsker
Boltzmann
Toscani, Villani
Landau
LAndau-Fermi-Dirac
Desvillettes, Villani
Alonso, Bagland Desvillettes, Lods
Boltzmann-FERMI-DIRAC
known entropy inequalities
\(D_{\textcolor{green}{0}, land}(g) \gtrsim H_{\textcolor{green}{0}}(g|M_{\textcolor{green}{0}}^g)^{1 + \textcolor{grey}{\alpha}}\)
c'est moi
Main IDea
entropy inequality for Boltzmann
entropy inequality for Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
known
new!
(Toscani, Villani)
transfer of inequalities
We know:
entropy inequality for Boltzmann
entropy inequality for Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
We want:
Fermi-Dirac dissipation of \(f\)
Boltzmann dissipation of \( \displaystyle \frac{f}{1-\textcolor{purple}{\delta} f} \)
\( \gtrsim\)
?
as soon as all terms make sense
Boltzmann relative entropy to equilibrium of \(\displaystyle \frac{f}{1-\textcolor{purple}{\delta} f}\)
Fermi-Dirac relative entropy to equilibrium of \(f\)
Theorem 1.
For all
such that
and
and
comparison of relative entropies
[B.]
Let
Then \(R_g\) is nonincreasing on \(\R_+\).
Proposition.
and
Proof of the theorem
proof of the proposition
Key elements:
- Taylor representation of the relative entropy to eq.
- general link between entropy and equilibrium
- fact that \(x \mapsto -\left(\frac{x}{1+\delta x} \right)^2\) is decreasing
Other technicalities:
- differentiability on \(\R_+^*\)
- continuity at \(\delta = 0\)
general considerations
specific use of Fermi-Dirac features
Show \(R_g' \leq 0\) on \(\R_+^*\) and \(R_g\) \(\mathcal{C}^0\) on \(\R_+ \)
Relaxation to equilibrium for Boltzmann-fermi-dirac
\(p \in [1,\infty), \, k \geq 0\), and with \(C,\eta\) explicit and uniform in \(\delta \leqslant \delta^{\rm in}\).
Theorem 2.
with Lods
Let \(0\leqslant f^{\rm in} \in L^1_3(\R^3)\). Then \(\exists \delta^{\rm in} > 0\) such that \(\forall \delta \in (0,\delta^{\rm in})\), if \(f^{\delta} \) sol. to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac w/ cut-off hard potentials,
(\(\delta\) is the quantum parameter)
then
\(p \in [1,\infty), \, k \geq 0\), and with \(C,\eta\) explicit and uniform in \(\delta \leqslant \delta^{\rm in}\).
Relaxation to equilibrium for Boltzmann-fermi-dirac
Theorem 2.
[B., Lods]
Let \(0\leqslant f^{\rm in} \in L^1_3(\R^3)\). Then \(\exists \delta^{\rm in} > 0\) such that \(\forall \delta \in (0,\delta^{\rm in})\), if \(f^{\delta} \) sol. to Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac w/ cut-off hard potentials,
(\(\delta\) is the quantum parameter)
Proof's core ingredients:
- \(L^{\infty}\)-bound on \(f^{\delta}\) independent of \(\delta\)
- Entropy/entropy production inequality
- Control of moments
- Maxwellian lower-bound
- Csiszar-Kullback-Pinsker inequality
then
Proposition.
(general entropy)
\(\displaystyle H(f) = \int\Phi(f)\), \(\Phi \; \; \mathcal{C}^2\) st. convex, \(M^f\) equilibrium, and
For any \(f\), any \(p \in [1,2]\) and \(\varpi\) weight,
Corollary.
For any \(0\leq f \in L^1_2\cap L \log L(\R^3)\), \(p \in [1,2]\) and \(\varpi : \R^3 \to \R_+\),
(Boltzmann entropy)
\(\displaystyle H_0\) Boltzmann entropy and \(M_0^f\) Maxwellian.
[simplified]
Bonus: extended Csiszàr-Kullback-Pinsker inequalities
chaos et fourmis 🐜
mon postdoc :
Cermics
Part \(\mathrm{I}\):
Part \(\mathrm{II}\):
Propagation of chaos, mean-field limits for SPDEs
- Proba
- Analysis
- SPDEs
Traffic behavior in Argentine ants:
Recovering microscopic model from experiments
- Modelling (micro / meso)
- Parameter estimation
- Simulations




Merci pour votre attention !



🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜🐜
Proposition.
For all
such that
and
Classical / Fermi-Dirac equivalence
For Boltzmann/BFD (& Landau/LFD) dissipations:
entropy inequality for Boltzmann
entropy inequality for Boltzmann-Fermi-Dirac
[TB]
\(\R^3 \times \textcolor{orange}{\R^3 \times \N \times \N \times \N}\)
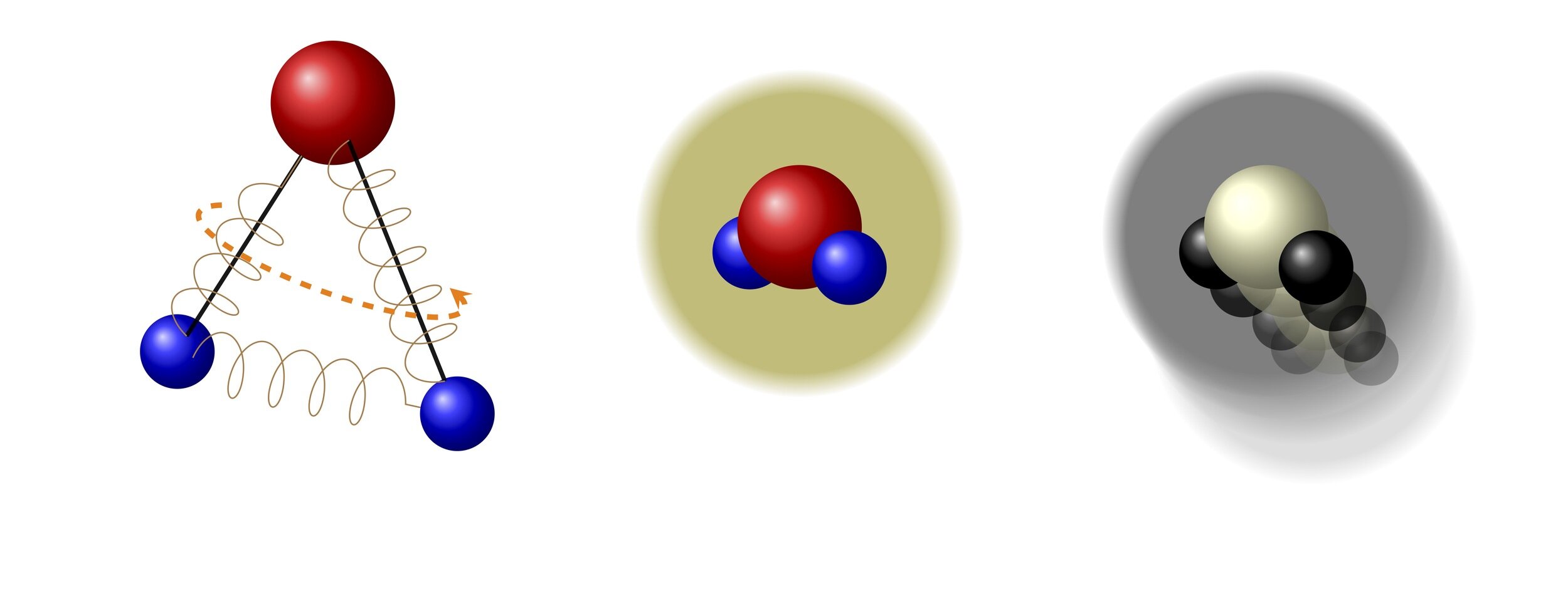
\(\mathrm{I}.1\). internal structure of polyatomic molecules: rotation, vibration,...
state of the molecule
space of states
energy of the molecule
An example:

\(\R^3 \times \textcolor{orange}{\mathcal{E}}\)
\(\mathrm{I}.1\). internal structure of polyatomic molecules: general setting
state of the molecule
space of states
energy of the molecule
\((\mathcal{E}, \mu)\)
\(\varepsilon : \mathcal{E} \to \R\)
2. Internal energy function:
existence of fundamental energy level
finiteness of the partition function
\(\bar{\varepsilon} := \varepsilon - \inf_{\mu} {\varepsilon}\) (\( : \mathcal{E} \to \R_+\))
1. Space of internal states:
3 points of view: parallel with probability theory
polyatomic internal structure
probability theory setting
\( (\Omega, \; \mathbb{P}) \) space of events
\( X : \Omega \to \R \) real random var.
\( (\mathcal{E}, \; \mu) \) space of internal states
\( \bar{\varepsilon} : \mathcal{E} \to \R_+ \) energy function
\( (\R, \, \mathbb{P}_X)\) space of outcomes
\( \mathbb{P}_X\) on \(\R\) law of \(X\)
\( (\R_+, \, \mu_{\bar{\varepsilon}}) \) space of energy levels
\( \mu_{\bar{\varepsilon}}\) on \(\R_+\) energy law


\( ((0,1), \, \mathrm{Leb})\) space of quantiles
\( F^{\leftarrow}_{\mathbb{P}_X}\) quantile function
\( ((0,q^+), \, \mathrm{Leb}) \) space of energy quantiles
\( F^{\leftarrow}_{\mu_{\bar{\varepsilon}}}\) energy quantile function
Simulations
Computations
Modelling