<info 340/>
React Router
Tim Carlson
Spring 2024
View of the Day
-
React Libraries (react-bootstrap)
-
Single Page Applications (lecture)
-
React Router (code demo)
-
URL Parameters (lecture + code demo)
-
Firebase Hosting (demo)

Project Draft 2
What we are looking for: Refactored Draft 1 into a React App
Converted the HTML/CSS from draft 1 into a published React app. Began to add interactive functionality.
- App is built: Ran create-react-app, etc. See assignment for details
- ~90% of content rendered: "most" of your app should be there (main page at least, Components for everything else)
- Has Components w/ props and data: Organize your Components! Can hard-code sample data for now
- Has 1 feature almost implemented: Includes event handling and state manipulation
- Fixes issues from draft 1: You're revising the HTML/CSS, fix problems while you're at it!
-
Published to Firebase hosting: get that working this draft
(see assignment for details; demo today!)
Our chat app so far...
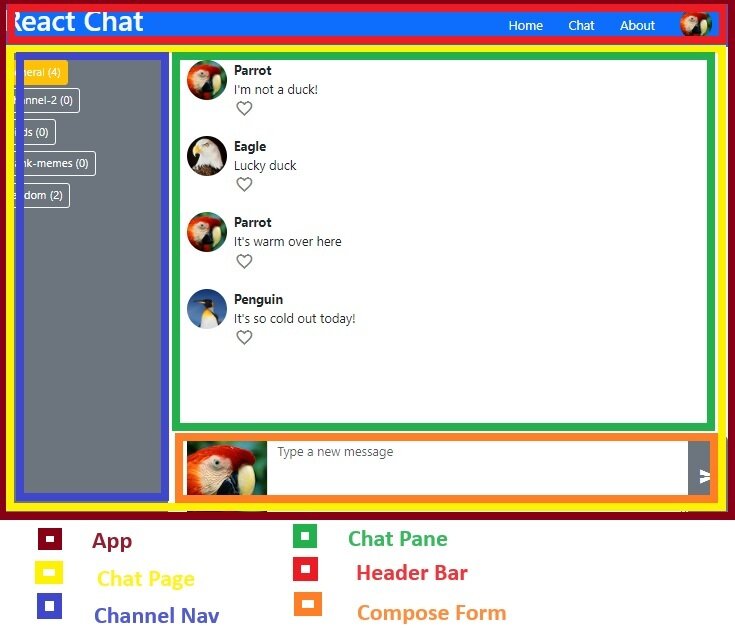
Demo- Chat Page
import React, {useState} from 'react';
import { HeaderBar } from './HeaderBar.js';
...etc
function App(props) {
const [messageStateArray, setMessageStateArray] = useState(INITIAL_HISTORY);
const [currentUser, setCurrentUser] = useState(DEFAULT_USERS[1]) //initialize;
const addMessage = function(userObj, messageText, channel) {
const newMessage = {
"userId": userObj.userId,
... etc
}
const newArray = [...messageStateArray, newMessage];
setMessageStateArray(newArray); //update state & re-render
}
const changeUser = (newUserObj) => {setCurrentUser(newUserObj);}
return (
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<HeaderBar currentUser={currentUser} />
<ChatPage
currentUser={currentUser} messageArray={messageStateArray} addMessageFunction={addMessage} />
{/* <SignInPage currentUser={currentUser} changeUserFunction={changeUser} />
<Static.WelcomePage />
<Static.AboutPage />
<Static.ErrorPage /> */}
</div>
);
}
App Component start
import React from 'react';
import _ from 'lodash';
import { ChannelList } from './ChannelList.js';
import { ChatPane } from './ChatPane.js';
export default function ChatPage(props) {
const {currentUser, messageArray, addMessageFunction} = props;
const channelNames = ["general", "channel-2", "birds", "dank-memes", "random"];
const currentChannel = "general";
//count how many messages are in each channel (using external library)
const channelCounts = _.countBy(messageArray, 'channel')
return (
<div className="row flex-grow-1">
<div className="col-3">
<ChannelList channelNames={channelNames} channelCounts={channelCounts} currentChannel={currentChannel} />
</div>
<div className="col d-flex flex-column">
<ChatPane
currentUser={currentUser}
messageArray={messageArray}
addMessageFunction={addMessageFunction}
/>
</div>
</div>
)
}Chat Page Component
import React from 'react';
import Dropdown from 'react-bootstrap/Dropdown';
import DEFAULT_USERS from '../data/users.json';
export default function SignInPage(props) {
const { currentUser, changeUserFunction} = props;
const handleClick = (event) => {
...etc }
const userButtons = DEFAULT_USERS.map((userObj) => {
...etc })
return (
<div className="card bg-light">
<div className="container card-body">
<p className="lead">Pick a user:</p>
<div>
<Dropdown>
<Dropdown.Toggle variant="light">
<img src={currentUser.userImg} alt={currentUser.userName + " avatar"} />
</Dropdown.Toggle>
<Dropdown.Menu>
{userButtons}
</Dropdown.Menu>
</Dropdown>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}Signin Page Component
export default function App(props) {
...
return (
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<HeaderBar currentUser={currentUser} />
{/* <ChatPage currentUser={currentUser} /> */}
{/* <SignInPage currentUser={currentUser} loginCallback={loginUser} /> */}
<Static.WelcomePage />
<Static.AboutPage />
<Static.ErrorPage />
</div>
);
}3 other static Components
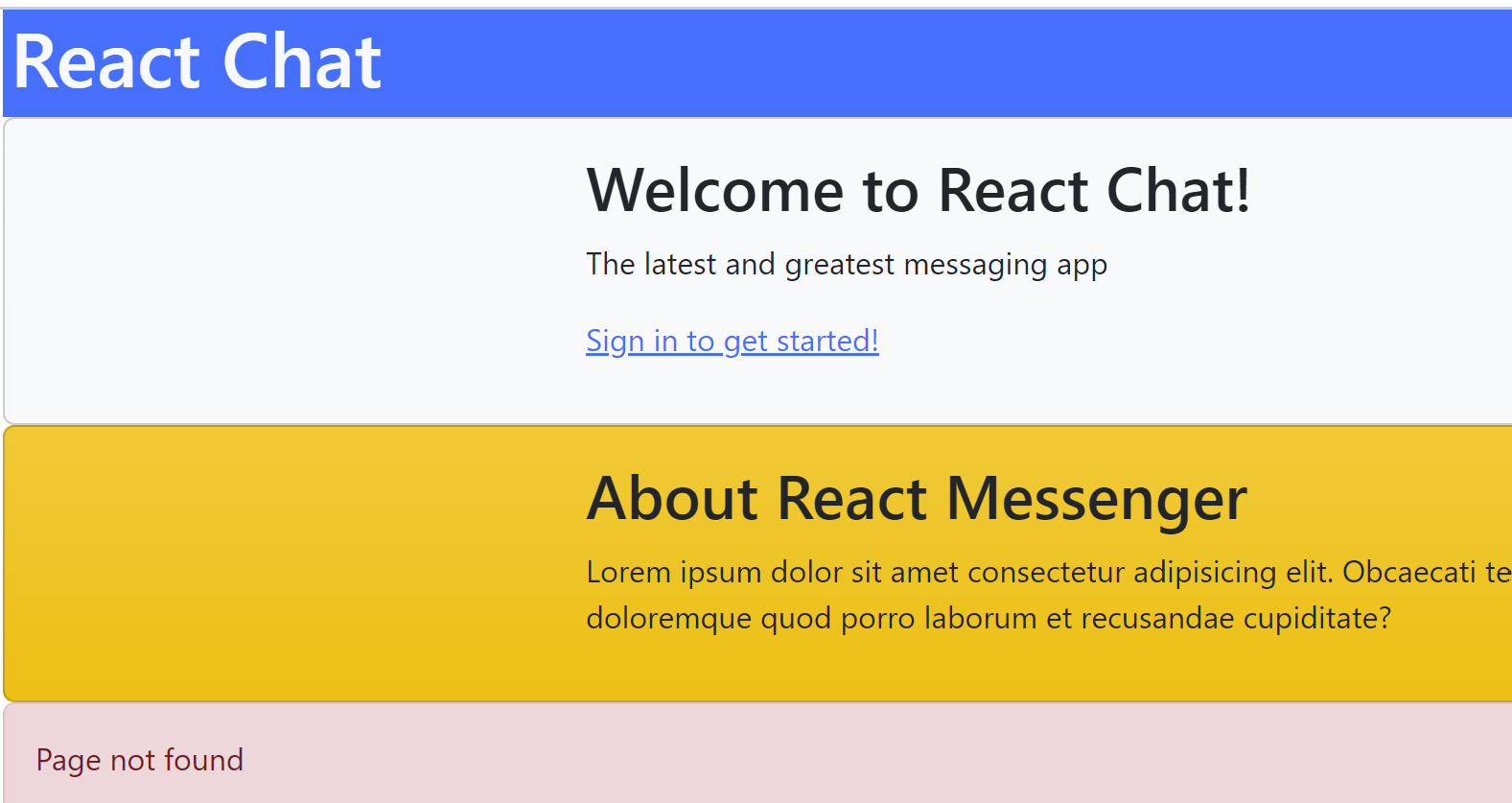
Single-Page Applications
Client-Side Routing
Render a different component depending on the URL.
"IF the current url MATCHES a route, render this Component!"
function App(props) {
//pick a component based on the URL
let componentToRender = null;
if(currentUrl === '/home'){ //pseudocode comparison with URL
componentToRender = <HomePage />;
}
else if(currentUrl === '/about'){
componentToRender = <AboutPage />;
}
//render that component
return <div>{componentToRender}</div>;
}React Libraries
React components are structured to be self-contained, re-usable elements... so there are lots of pre-defined components online you can use!
In order to use a component in your app:
- Find it! (via npm, google, etc). Read the documentation
- Install it!
npm install lib-name - Import it!
import { ComponentName } from 'lib-name'- (import structure may vary per library)
- Render it!
<ComponentName />- Remember to pass any expected props!
react-router
A library of React Components that can determine which other components to render based on the current URL.
Install Library
Import Components
//in App.js
import { Routes, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
# Install library (on command line)
npm install react-router-domas of Nov 2021

Router Versions
The version we're targeting (version 6.23.1)
Adds data apis (not using)
BrowserRouter
The BrowserRouter component will keep track of the current URL in its state, and re-renders descendent components if that changes.
//index.js
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import App from './components/App.js'
//render the App *inside* of the BrowserRouter
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>
);BrowserRouter
Add the BrowserRouter around our <App> in index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-dom/client';
//import CSS
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css';
import './index.css';
import App from './components/App';
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
// root.render(<App />);
// Slide 16
root.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>
);import BrowserRouter
Wrap the <App> in the BrowserRouter Component
Routes
Pass elements in a Route Component to specify that they should only render when the URL matches a particular path. All routes go inside of a Routes element, which chooses which to "match" based on the URL
function App(props) {
return (
<Routes> {/* the collection of routes to match */}
{/* if currentUrlPath === "home" */}
<Route path="home" element={<HomePage />} />
{/* if currentUrlPath === "about" */}
<Route path="about" element={<AboutPage />} />
</Routes>
);
}Routes/Route
...
import { Routes, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
export default function App(props) {
const [currentUser, setCurrentUser] = useState(DEFAULT_USERS[1])
const loginUser = (userObj) => { setCurrentUser(userObj); }
return (
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<HeaderBar currentUser={currentUser} />
<Routes>
<route path="home" element={<Static.WelcomePage />} />
<route path="chat" element={<ChatPage
currentUser={currentUser} />} />
<route path="signin" element={<SignInPage
currentUser={currentUser} loginCallback={loginUser} />} />
<route path="about" element={<Static.AboutPage />} />
<route path="error" element={<Static.ErrorPage />} />
</Routes>
</div>
);
}import Routes, Route
<Routes> wrap <Route>'s
if "chat" render <ChatPage>
Routes/Route
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<HeaderBar currentUser={currentUser} />
<Routes>
<Route index element={<Static.WelcomePage />} />
<Route path="chat" element={<ChatPage
currentUser={currentUser} />} />
<Route path="signin" element={<SignInPage
currentUser={currentUser} loginCallback={loginUser} />} />
<Route path="about" element={<Static.AboutPage />} />
<Route path="*" element={<Static.ErrorPage />} />
</Routes>
</div>"*" is a catchall
'index' route rather than " path='/' "
Links
Use a Link element (in place of an <a>) to create state-based links between routes.
function Nav() {
return (
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
{/* replaces anchor element */}
<Link to="home">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="about">About</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
);
}Links
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';
export function HeaderBar(props) {
const currentUser = props.currentUser;
return (
<header className="text-light bg-primary px-1 d-flex justify-content-between">
<h1>React Chat</h1>
<ul className="nav nav-pills">
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/chat">Chat</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/about">About</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/signin">
<img src={currentUser.userImg} alt={currentUser.userName + " avatar"} />
</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</header>
)import
change 'a' to 'Link'
change 'href' to 'to'
Nesting Routes
The Route path corresponds to a segment of a URL, with nested Route elements corresponding to each segment. Nested Routes will render in place of an Outlet component
function App(props) {
return (
<Routes>
<Route path="user" element={<UserLayout />} >
<Route path="profile" element={<UserProfile />} />
<Route path="favorites" element={<FavoriteItems />} />
</Route>
<Route path="items" element={ <ItemList />} />
</Routes>
);
}function UserLayout(props) {
render (
<div className="user-layout">
<h1>User Page</h1>
<Outlet /> {/* will be replaced with <UserProfile/>, etc */}
</div>
)
}Nesting Routes (App changes)
...
import { Routes, Route, Outlet } from 'react-router-dom';
...
export default function App(props) {
... return (
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<Routes>
<Route index element={<Static.WelcomePage />} />
<Route path="app" element={<AppLayout currentUser={currentUser} />}>
<Route path="chat" element={<ChatPage currentUser={currentUser} />} />
<Route path="signin" element={<SignInPage
currentUser={currentUser} loginCallback={loginUser} />} />
<Route path="about" element={<Static.AboutPage />} />
<Route path="*" element={<Static.ErrorPage />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
</div>
);
}
function AppLayout(props) {
return (
<>
<HeaderBar currentUser={props.currentUser} />
<Outlet />
</>
)
}nested Routes
/app
Shows whichever nested path route matches
import Outlet
/app/chat
Nesting Routes (static pages)
import React from 'react';
export function WelcomePage(props) {
return (
<div className="card bg-light">
<div className="container card-body">
<h2>Welcome to React Chat!</h2>
<p>The latest and greatest messaging app</p>
<p><a href="app/signin">Sign in to get started!</a></p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
...
updated to include 'app'
Nesting Routes (Header Bar)
import React from 'react';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';
export function HeaderBar(props) {
const currentUser = props.currentUser;
return (
<header className="text-light bg-primary px-1 d-flex justify-content-between">
<h1>React Chat</h1>
<ul className="nav nav-pills">
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/app/chat">Chat</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/app/about">About</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/app/signin">
<img src={currentUser.userImg} alt={currentUser.userName + " avatar"} />
</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</header>
)
}updated to include 'app'
Protected Routes
A common use of nested routes is to make some routes protected, only showing content if e.g., the user is logged in.
function RequireAuth(props) {
//...determine if user is logged in
if(!userIsLoggedIn) { //if no user, say so
return <p>Forbidden!</p>
}
else { //otherwise, show the child route content
return <Outlet />
}
}
function App(props) {
return (
<Routes>
{/* protected routes */}
<Route element={<RequireAuth />}>
<Route path="profile" element={<ProfilePage />} />
<Route path="secret" element={<SecretPage />} />
</Route>
{/* public routes */}
<Route path="signin" element={<SignInPage />} />
</Routes>
)
}protected path parent
if user isn't logged in show 'forbidden', else show outlet (subroute)
Protected Routes Nexted (App changes)
...
export default function App(props) {
... return (
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<HeaderBar currentUser={currentUser} />
<Routes>
<Route index element={<Static.WelcomePage />} />
<Route path="about" element={<Static.AboutPage />} />
<Route path="*" element={<Static.ErrorPage />} />
<Route path="signin" element={<SignInPage
currentUser={currentUser} loginCallback={loginUser} />} />
<Route element={<RequireAuth currentUser={currentUser} />}>
<Route path="chat" element={<ChatPage currentUser={currentUser} />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
</div>
);
}
function RequireAuth(props){
if(props.currentUser.userId === null) { //if no user, say so
return <p>Forbidden!</p>
}
else { //otherwise, show the child route content
return <Outlet />
}
}Top 4 Route's don't need RequiredAuth
<Chat> does do the RequiredAuth check
Is current user null?
Protected Routes Nested (Header)
export function HeaderBar(props) {
const currentUser = props.currentUser;
return (
<header className="text-light bg-primary px-1 d-flex justify-content-between">
<h1>React Chat</h1>
<ul className="nav nav-pills">
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/chat">Chat</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/about">About</Link>
</li>
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to="/signin">
<img src={currentUser.userImg} alt={currentUser.userName + " avatar"} />
</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</header>
)
}Go back to the old path with no /app
Protected Routes Nested (static)
// Slide 29
import React from 'react';
export function WelcomePage(props) {
return (
<div className="card bg-light">
<div className="container card-body">
<h2>Welcome to React Chat!</h2>
<p>The latest and greatest messaging app</p>
<p><a href="/signin">Sign in to get started!</a></p>
</div>
</div>
);
}fix the path here too
protocol
domain
resource

"Hi Wikipedia, I'd like you to send me the Informatics page!"
two
t
(how to handle info)
(who has info)
(what info you want)
Web Server
Response
Using the Internet
Request

Uniform Resource Indicator
http://www.domain.com/users => a list of users
-
The address is the identifier, the list is the resource
HTTP requests are sent to a particular resource on the web, identified by its URI (think: web address).
URI Format
Like postal addresses, URIs follow a particular format.
-
scheme (protocol)how to access the information -
domainwhich web service has the resource -
pathwhat resource to access -
queryextra parameters (arguments) to the request
format:
?key=value&key=value&key=value

Many web services allow you to access their data through their web API.
E.g., GitHub! (https://docs.github.com/en/rest)
https://api.github.com/users/your-github-name/repos
# command-line downloading
curl https://api.github.com/users/info201/repos
# authenticate (to see private repos)
curl -u username https://api.github.com/repos/info201/repos
# include headers
curl -i https://api.github.com/users/info201/repos
Example URIs (API)
Example URIs (API)
A web service's URI has two parts:
-
The Base URI
- The EndPoint (e.g., path)
https://api.github.com
/users/{username}/repos
/repos/:owner/:repo
/emojis
A variable (also
:username)

URL Params
Use :param syntax in the path to specify URL parameters. The useParams() hook lets you access the value of those parameters in the rendered element.
function App(props) {
return (
<Routes>
{/* if currentUrl == "posts/______" */}
{/* the string in the "blank" portion will be the
* `postId` param */}
<Route path="posts/:postId" element={<BlogPost />} />
</Routes>
);
}import { useParams } from 'react-router-dom';
function BlogPost(props) {
const urlParams = useParams(); //access the URL params as an object
const postId = urlParams.postId; //can use destructuring instead
return (
{/* postId was the URL parameter from above! */}
<h1>You are looking at blog post {urlParams.postId}</h1>
)
}URL Params App Page
export default function App(props) {
const [currentUser, setCurrentUser] = useState(DEFAULT_USERS[1])
const loginUser = (userObj) => {
setCurrentUser(userObj);
}
return (
<div className="container-fluid d-flex flex-column">
<HeaderBar currentUser={currentUser} />
<Routes>
<Route index element={<Static.WelcomePage />} />
<Route path="about" element={<Static.AboutPage />} />
<Route path="*" element={<Static.ErrorPage />} />
<Route path="signin" element={<SignInPage
currentUser={currentUser} loginCallback={loginUser} />} />
<Route element={<RequireAuth currentUser={currentUser} />}>
<Route path="chat/:channelName" element={<ChatPage currentUser={currentUser} />} />
<Route path="chat" element={<ChatPage currentUser={currentUser} />} />
</Route>
</Routes>
</div>
);
}
use the syntax to specify the url param
Note we added a 2nd 'chat' path for the case where there is no url param
URL Params Chat Page
...
import { useParams } from 'react-router-dom';
...
export default function ChatPage(props) {
...
const urlParamsObj = useParams(); //get me the url parameters
console.log(urlParamsObj);
...
const currentChannel = urlParamsObj.channelName;
const addMessage = (messageText) => {
const userObj = currentUser;
const newMessage = {
...
"channel": currentChannel
}
...
return (
<div className="row flex-grow-1">
<div className="col-3">
<ChannelList channels={channelList} currentChannel={currentChannel} />
</div>
...
</div>
)
}set the channel from the url param
get the param object
import useParams hook
URL Params Chat Pane
...
import {useParams} from 'react-router-dom';
export function ChatPane(props) {
const paramResult = useParams();
console.log("paramResult in ChatPane :", paramResult);
const currentChannel = paramResult.channelName || "general";
// const currentChannel = "general" //hard code for the moment
...
return (
<> {/* fake div */}
<div className="scrollable-pane pt-2 my-2">
{ messageArray.length === 0 &&
<p>No messages found</p>
}
{messageElemArray}
</div>
<ComposeForm
currentUser={currentUser}
currentChannel={currentChannel}
addMessageFunction={addMessageFunction} />
</>
)
}
set the channel from the url param
get the param object
import useParams hook
URL Params ChannelNav Page
import React from 'react';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';
export function ChannelList(props) {
const channels = props.channels;
const currentChannel = props.currentChannel;
const linkElemArray = channels.map((channelNameString) => {
let classList = "btn btn-sm btn-outline-light my-1";
if(channelNameString === currentChannel) {
classList = "btn btn-sm btn-warning"
}
const element = (
<div key={channelNameString}>
<Link className={classList} to={"/chat/" +channelNameString}>
{channelNameString}</Link>
</div>
)
return element;
})
return (
<nav className="text-light bg-secondary h-100 py-3 channel-nav px-2">
{linkElemArray}
</nav>
)
}Fix the nav links to include the url param
Hosting on Firebase
GitHub pages is not able to cleanly handle client-side routing, so we'll use Firebase to host your projects instead!
Firebase is a web backend solution; it provides multiple features which you can access without need to "code" them yourselves.
- Web Hosting
- Databases
- User Authentication

next weeks
React Deployment to Firebase
Use a combination of firebase command line tools and create-react-app scripts to build and deploy your React application to Firebase hosting!
Action Items!
-
Project Draft 2 due Friday!!
-
Review Ch 17: React Router
-
Read Ch 18: AJAX Requests
-
(we'll apply to React in lecture)
-
-
Problem Set 08 due Friday 5/24 (it's small)
-
Problem Set 09 due Friday 5/24 (it's small)
Next time: Working with Data: AJAX
Naming Routes
The web is based on the REST architecture. In this structure, each route (identifier, URI) should refer to a unique resource (set of information).
Think about what "information" should be found at each route. Come up with your routes first, and decide the components second!
function App(props) {
return (
<Routes>
{/* good routes */}
<Route path="/products" element={<AllProductsPage />} />
<Route path="/products/hat" element={<HatPage />} />
<Route path="/products/shoes" element={<ShoesPage />} />
<Route path="/account" element={<AccountPage />} />
{/* less good route -- an action, not a resource! */}
{/* (bad component definition as well) */}
<Route path="/purchase" element={<ProcessPurchase />} />
</Routes>
)
}"Variable" Routes
Sometimes you have a multiple routes that show the same component, just for different data--where that data is specified by one of the segments!
function App(props) {
return (
<Routes>
<Route path="/products" element={<AllProductsPage />} />
{/* routes go to same "view", just different content based on url */}
<Route path="/products/hat" element={<ProductDetails item={"hat"} />} />
<Route path="/products/shoes" element={<ProductDetails item={"shoes"} />} />
</Routes>
)
}