DIVERSITY,
INCLUSIVITY,
& LEARNING
Two Case Studies
Ambrose, Chapter 6: Why do student development and course climate matter for student learning?
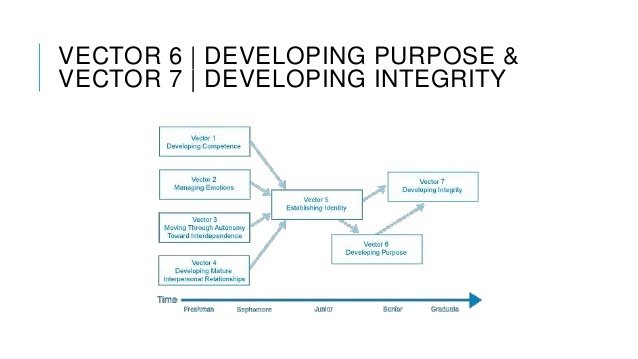
The Chickering Model of Student Development: Seven Vectors
1. developing competence
2. managing emotions
3. moving through autonomy to interdependence
4. developing mature relationships
7. developing integrity
5. establishing identity
6. developing purpose
Perry's Stages of Intellectual Development
-
Duality: find the truth!
-
Multiplicity: establish opinions!
-
Relativism: all the theories!
-
Commitment: synthesize, evaluate, and choose!
Why might this model be useful?
Hardiman & Jackson's Social Identity Model
Premise: Social identity is not given, but achieved & continually negotiated through interactions with others & environment
- Naivete
- Acceptance
- Resistance
- Immersion
- Disintegration
- Redefinition
- Internatlization
Dominant vs. minority group members?
Is this model useful?
What is "course climate"?
- Types of interactions?
- Marginalizing vs. centralizing
- Explicit vs. implicit
- Mitigating factors?
- Individual complexity?
Stereotype Threat (per Steele & Aronson)
- Hypothesis: stereotyping --> distracting emotions (cognitive effect) --> low performance --> dis-identification from discipline (motivational effects)
- Tone: from syllabus & documentation to interactions
- Faculty availability is major factor in STEM student retention
- Impacts participation, risk-taking, persistence
Reconsider case studies
Where did the professors go wrong? What could they have done better?
Strategies: which apply to you? How best to implement?
- Make uncertainty and ambiguity safe
- Resist leading quickly to a single right answer
- Use evidence-based grading
- Examine your own assumptions about your students
- Avoid low-ability cues
- Avoid asking an individual to speak for a group
- Reduce anonymity
- Provide multiple, diverse examples
- Establish and reinforce ground rules for interaction
- Consider course content
- Establish climate early; solicit feedback often
- Model and facilitate inclusion and active listening