the internet
& the world wide web
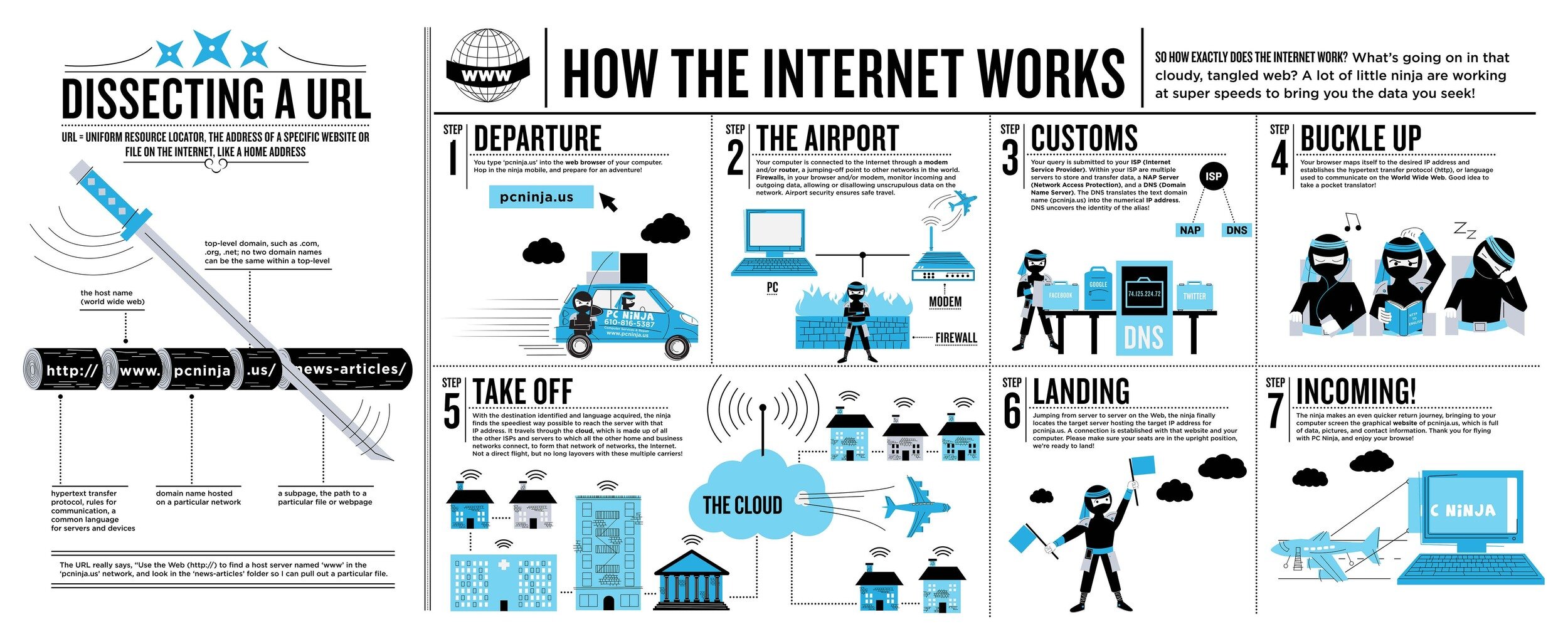
in other words
- You enter, say, http://website.com into your browser’s address bar.
- Your browser looks up the IP address for website.com.
- Your browser issues a request for the home page at website.com.
- The request crosses the Internet and arrives at the web server on which the files that make up website.com are stored.
- The web server, having received the request, looks for the requested page on its hard drive.
- If the server contains scripts that request (say) user data from a database, they go find the database and fetch the requested data.
- The server retrieves the web page and any requested data and returns it to the browser, which displays the web page.
front-end vs. back-end web development

front-end vs. back-end tasks
Back end
Organizing information on the server
Processing and managing user inputs
Database programming & content management
More advanced server-side web apps using (usually) scripting/programming languages like PHP to enable more sophisticated interactivity, dynamic content generation, secure exchanges and data storage, etc.
Front end
Design, usability
UI, UX, IxD
HTML & CSS
JavaScript or other scripting language for client-side interactions