Data Repositories
Text
The Rockefeller University
Bioinformatics Resource Centre
Getting hold of HTS data
- From public repositories
- From collaborators
- By sequencing some of your own material!
Public Repositories
- Several public sources of HTS data exist.
- First concentrating on those acting as repositories.
- GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus)
- ENA (European Nucleotide Database)
- SRA (Short Read Archive)
- GEO holds different types of biological datasets.
- Very popular for submission of data accompanying publication.
- Captures metadata, processed files and raw data.
- GEO was not built for HTS data
GEO - Quick Tour
SRA (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra)
- NCBI's HTS specific repository.
- Sequencing specific metadata.
- Stores Raw data (in SRA format)
- SRA format - requires SRA Toolkit
- Lost then regained funding?
SRA - Quick Tour
ENA (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena)
- ENA acts as a european HTS repository.
- Mirrors much of SRA.
- Stores Raw data
- No SRA formats - fastq by default.
ENA - Quick Tour
Other Repositories
- Many repositories contain processed or unprocessed data.
- These typically are the result or a consortium's data release policies.
- Good example is Encode site. (https://www.encodeproject.org/)
- UCSC has many useful links to genomics data in various formats. (http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/downloads.html)
Other Repositories
- Other specialist repositories exist.
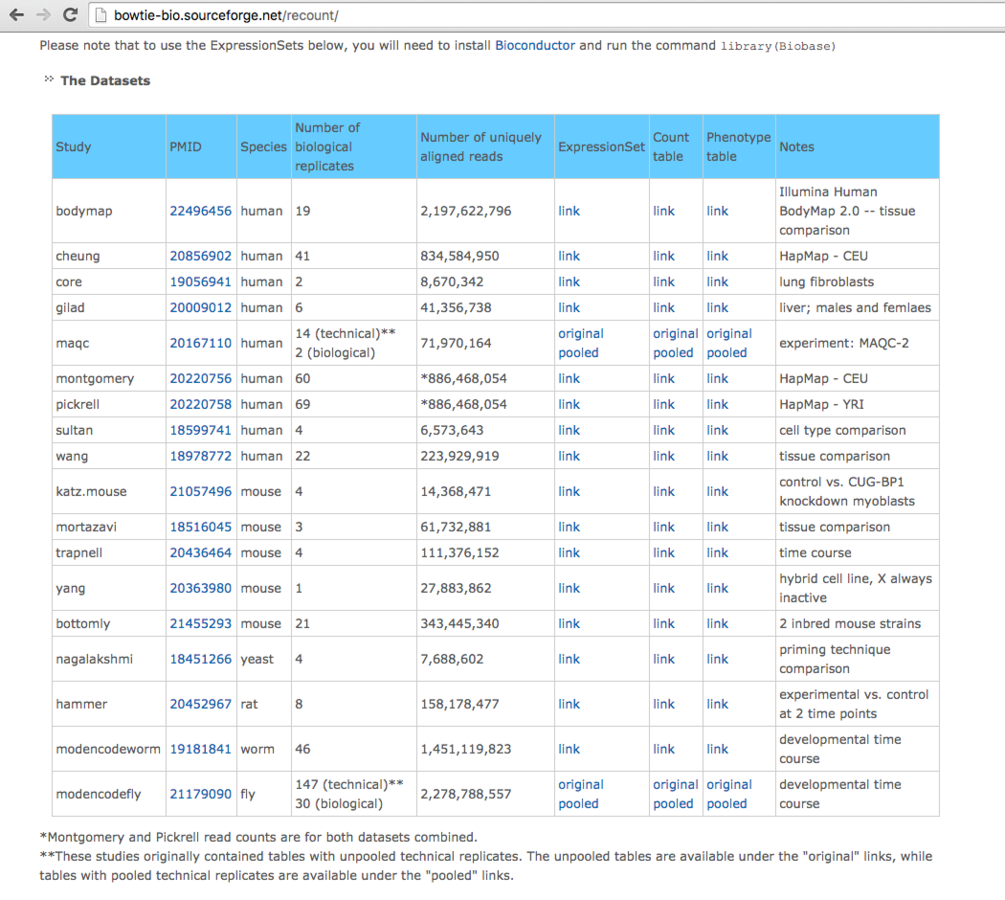
- ReCount database provides standardised counts for user analysis.
- Other databases like Immgen/Bodymap provide RNAseq for specific cells/tissues.
Reference data
- Reference Genome available from many locations.
- Different assemblies
- Major Revisisons - Change locations
- Minor Revisions - Update annotation
- Genome sequence stored as FASTA.
- Gene build as GFF3 or GTF.
- IGenomes contains full annotation files for many genomes.