What is a DDD Aggregate?
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
And how has its meaning evolved over time?
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Why do we need Aggregates?

Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Why do we need Aggregates?
It is difficult to guarantee the consistency of changes to objects in a model with complex associations. Invariants need to be maintained that apply to closely related groups of objects, not just discrete objects. Yet cautious locking schemes cause multiple users to interfere pointlessly with each other and make a system unusable.
Eric Evans; Domain-Driven Design: Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software

Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Aggregate, you have a few jobs!
Guarantee invariants
(Business rules)
Guarantee
internal consistency
Relaxed external consistency
Managing Concurrent Access
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Eric's definition of an Aggregate
An Aggregate is a cluster of associated objects that we treat as a unit for the purpose of data changes. Each Aggregate has a root and a boundary. The boundary defines what is inside the Aggregate. The root is a single, specific Entity contained in the Aggregate.
Eric Evans; Domain-Driven Design: Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software

Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Boundaries are artificial! Roots are real!
-
Aggregate boundaries are artificial and partition larger models into smaller ones to enforce the consistency, concurrency & invariant guarantees mentioned before.
- Aggregate roots are actual "things" (objects, entities) that manage the guarantees for other parts of the model outside the boundary, and that other "things" can hold a reference to, while the internal associations are hidden from the outside world.
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Invariants are driven by the domain!
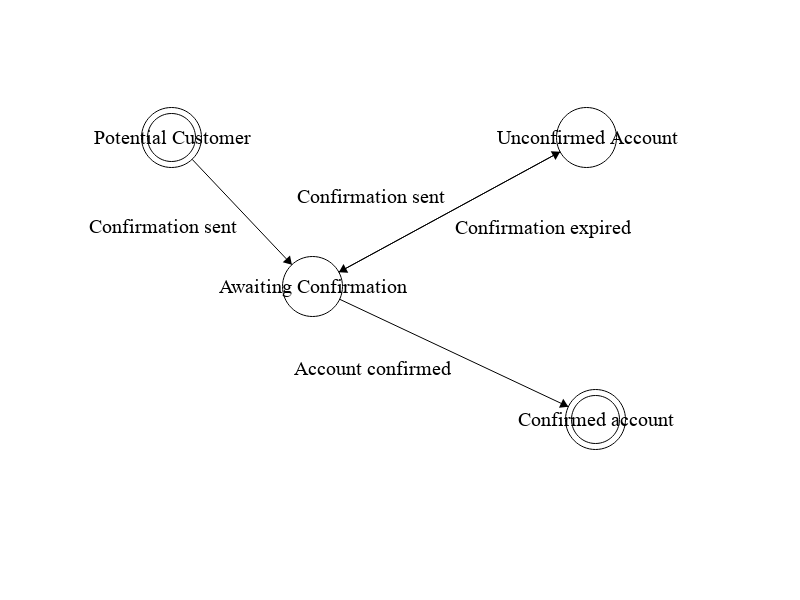
Client: We want potential customers to be able to register an account in our system.
Developer: OK, how do you imagine that to work out?
Client: The customer should only provide his email at this point of time. Later he can fill out his profile.
Developer: Understood. Best practice in this case is that we send a confirmation to the provided email address so that we are sure the person using that email address really has access to that email.
Client: That makes total sense! But what if the customer does not confirm his account?
Developer: Then at some point the confirmation token will expire and he has to request a new one.
Client: OK, let's do it that way!
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Customer Registration Aggregate
Account
ENTITY
ROOT
Status
VO
Token
ENTITY
Email
VO
Outer
World
Other parts of the model are allowed to hold references to the ROOT
References to Aggregate internals from the outer world are strictly forbidden!
Within the Aggregate Boundary Entities and Value Objects are allowed have references to each other, but they are only unique within the boundary.
All changes within the Aggregate Boundary must be consistent, i.e. by having all changes persisted in an all-or-nothing ACID transaction (there are other methods to ensure consistency).
All invariants are guarded by the ROOT, i.e. confirming an account only when the token is not expired.
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Success! Growth! Scale!


Database Shard A
Database Shard B
Account
ENTITY
Token
ENTITY
The Aggregate can only be reconstituted by querying all shards!
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Microservices!
Account Microservice
Token Microservice
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Success! Growth! Scale! Take II!


Database Shard A
Database Shard B
An Aggregate is also a unit of distribution!
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
How to make the following consistent?
Account
ENTITY
ROOT
Status
VO
Token
ENTITY
Email
VO
Account
ENTITY
ROOT
Contact
VO
Email
VO
User Registration Context
CRM Context
Whenever a customer has opened an account, an entry in our CRM module should be created.
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Eric on rules across Aggregates!
Any rule that spans Aggregates will not be expected to be up-to-date at all times. Through event processing, batch processing, or other update mechanisms, other dependencies can be resolved within some specified time.
Eric Evans; Domain-Driven Design: Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software

Communication between Aggregates is eventually consistent!
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Static models are missing something...
Time
A notion of
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
A little bit of systems theory...
Why are techniques like
#EventStorming
#DomainStoryTelling
#StoryMapping
so successful?
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Complex systems and events
The human organization lacks structure in this anatomical sense; its land and buildings are trappings; its members come and go. Yet it has structure; membership is not accidental and the behaviour of members is not random. We have argued that the resolution of this paradox lies in the patterns of the events of organizational life themselves. The events are structured, and the forms they assume have dynamic properties. Social organizations as contrived systems are sets of such patterned behavioural events
Katz, D., & Kahn, R. L. 1978.The social psychology of organizations (2nd ed.)
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Events, because Events!
#EventStorming
#DomainStoryTelling
#StoryMapping
Event-driven, temporal models are much closer to the actual behaviour of complex systems! Not only because they create a compatible mental model or include the dimension of time, but because they give a glimpse of how the systems actually work!
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
From static to process model
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Finite-State-Transducers
A mathematical model
Virtual Domain-Driven Design meetup | Nov. 6th 2019
Twitter: @tPl0ch
Conclusion
a unit of consistency
a boundary around a closely related part of the model
enforce all invariants
have root entities that isolate the inner workings from the outer world
a unit of concurrency
a unit of distribution
either implicitly or explicitly depict a part of the system's processes