Webpack

Warning
Webpack's documentation, although extensive, is only helpful if you speak webpack already.

or
What the cr*p is it?
It's a module bundler.

What's a module bundler?
add.js
index.js
subtract.js

bundle.js
import add from './add.js';
import subtract from './subtract.js';
console.log(`Add: ${add(4,5)}`);
console.log(`Subtract: ${subtract(9,5)}`);
const add = (a, b) => {
return a + b;
}
export default add;
const subtract = (a, b) => {
return a - b;
}
export default subtract;
index.js
add.js
subtract.js
const add = (a, b) => {
return a + b;
}
const subtract = (a, b) => {
return a - b;
}
console.log(`Add: ${add(4,5)}`);
console.log(`Subtract: ${subtract(9,5)}`);
bundle.js
Well, kinda
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { enumerable: true, get: getter });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // define __esModule on exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.r = function(exports) {
/******/ if(typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: 'Module' });
/******/ }
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true });
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // create a fake namespace object
/******/ // mode & 1: value is a module id, require it
/******/ // mode & 2: merge all properties of value into the ns
/******/ // mode & 4: return value when already ns object
/******/ // mode & 8|1: behave like require
/******/ __webpack_require__.t = function(value, mode) {
/******/ if(mode & 1) value = __webpack_require__(value);
/******/ if(mode & 8) return value;
/******/ if((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) return value;
/******/ var ns = Object.create(null);
/******/ __webpack_require__.r(ns);
/******/ Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', { enumerable: true, value: value });
/******/ if(mode & 2 && typeof value != 'string') for(var key in value) __webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function(key) { return value[key]; }.bind(null, key));
/******/ return ns;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./src/index.js");
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ({
/***/ "./src/add.js":
/*!********************!*\
!*** ./src/add.js ***!
\********************/
/*! exports provided: default */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
eval("__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\nconst add = (a, b) => {\n return a + b;\n}\n\n/* harmony default export */ __webpack_exports__[\"default\"] = (add);\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/add.js?");
/***/ }),
/***/ "./src/index.js":
/*!**********************!*\
!*** ./src/index.js ***!
\**********************/
/*! no exports provided */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
eval("__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\n/* harmony import */ var _add_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ./add.js */ \"./src/add.js\");\n/* harmony import */ var _subtract_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ./subtract.js */ \"./src/subtract.js\");\n\n\n\nconsole.log(`Add: ${Object(_add_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__[\"default\"])(4,5)}`);\nconsole.log(`Subtract: ${Object(_subtract_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__[\"default\"])(9,5)}`);\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?");
/***/ }),
/***/ "./src/subtract.js":
/*!*************************!*\
!*** ./src/subtract.js ***!
\*************************/
/*! exports provided: default */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
eval("__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\nconst subtract = (a, b) => {\n return a - b;\n}\n\n/* harmony default export */ __webpack_exports__[\"default\"] = (subtract);\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/subtract.js?");
/***/ })
/******/ });bundle.js
Try it out
1-basic

Basic Webpack Config
webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'bundle.js'
}
}
Entry file
Output
Module Types
ES Modules
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
export default add;add.js
import add from './add.js'
add(2,2); //5index.js
define((a,b) => {
return a + b;
});add.js
define(['./add'], (add) => {
add(2,2); //5
});index.js
module.exports = (a,b) => {
return a + b;
}add.js
const add = require('./add.js');
add(2,2); //5index.js
AMD
(dojo, require.js)
Common JS
(node)
Export
Import
UMD
Universal Module Definition
CJS?
(function (root, factory) {
if(typeof exports === 'object' && typeof module === 'object')
module.exports = factory();
else if(typeof define === 'function' && define.amd)
define([], factory);
else {
var a = factory();
for(var i in a) (typeof exports === 'object' ? exports : root)[i] = a[i];
}
})(window, function() {
// my code
});AMD?
K, fine global
Input
- AMD
- UMD (CommonJS)
- CommonJS
- SystemJS
- browserify
- requireJs
- ES Module
Webpack uses node (CommonJS) under the hood
import thing from 'thing.js'const thing = require('thing.js')export default thing;module.exports = thing;Output
- jsonp (default)
- CommonJS
- AMD
- UMD
- global (IIFE)
ES Module
Pull in node modules
import { sortBy } from 'lodash'; // automatically resolves to node_modules
const users = [
{ 'user': 'fred', 'age': 48 },
{ 'user': 'barney', 'age': 36 },
{ 'user': 'fred', 'age': 40 },
{ 'user': 'barney', 'age': 34 }
];
console.log(sortBy(users, ['user', 'age']));
$ npm i lodashES Module Syntax
Try it out
2-node-module

Webpack supports HTML
import personHTML from './person.html';
import './style.css';
let el = document.createElement('div');
el.innerHTML = personHTML;
document.body.appendChild(el);
index.js
<div class="person">
<img src="./tyler.jpg" class="photo">
<p class="name">Tyler Graf</p>
</div>
person.html
HTML is Easy
import personHTML from './person.html';
import styles from './style.css';
.person {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.photo {
height: 80px;
width: 80px;
}
.name {
margin-left: 10px;
font-size: 30px;
}
style.css
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
mode: 'development',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(html)$/,
use: {
loader: 'html-loader'
}
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
{ loader: "style-loader" },
{ loader: "css-loader" }
]
}
]
}
}
Loaders

Everything in webpack is a module
Loaders just transform things into javascript modules*
*kinda
html-loader
<div>
<span>Tyler Graf</span>
</div>module.exports = '<div><span>Tyler Graf</span></div>'
HTML
JavaScript
import html from './person.html';
let el = document.createElement('div');
el.innerHTML = html;import html as a string
module.exports = '<div><span>Tyler Graf</span></div>'person.html
html-loader

style-loader
.name {
font-size: 30px;
}module.exports = appendToHead('<style>.name {font-size: 30px;}</style>')
CSS
JavaScript
import 'style.css';Webpack will automatically append this to the <head>
style-loader
module.exports = appendToHead('<style>.name {font-size: 30px;}</style>')
style.css
Try it out
3-html
Loader Config
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(html)$/,
use: {
loader: 'html-loader'
}
}
]
}
}
Entry file
Output
Loaders
which files go through this loader
name of the loader
html-loader

<div class="person">
<img src="./tyler.jpg" class="photo">
<p class="name">Tyler Graf</p>
</div>
module.exports = `
<div class="person">
<img src="${require('./tyler.jpg')}" class="photo">
<p class="name">Tyler Graf</p>
</div>
`;
external file
external file
file-loader
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif)$/i,
use: [
{
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
name(file) {
return '../[path][name].[ext]';
}
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
Options
multiple filename endings

Try it out
3-html

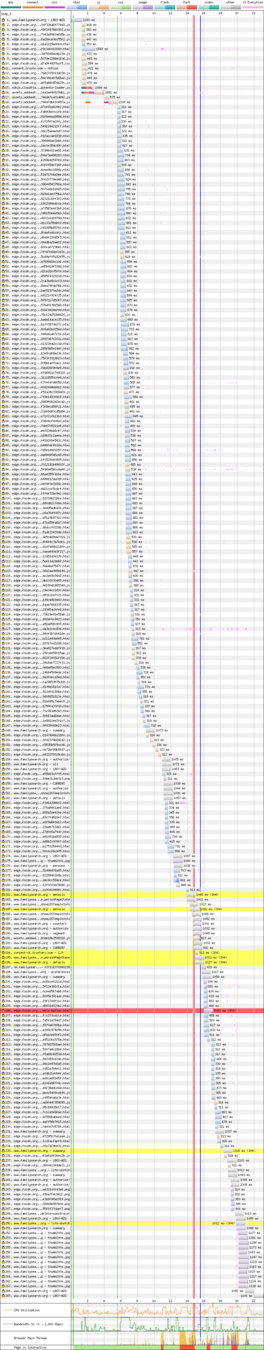
Why the cr*p?
Moto G4 3G (1.6Mbps/768Kbps)
Tree Landscape Pedigree
Wasatch Desktop Cable (5/1Mbps)
Tree Landscape Pedigree
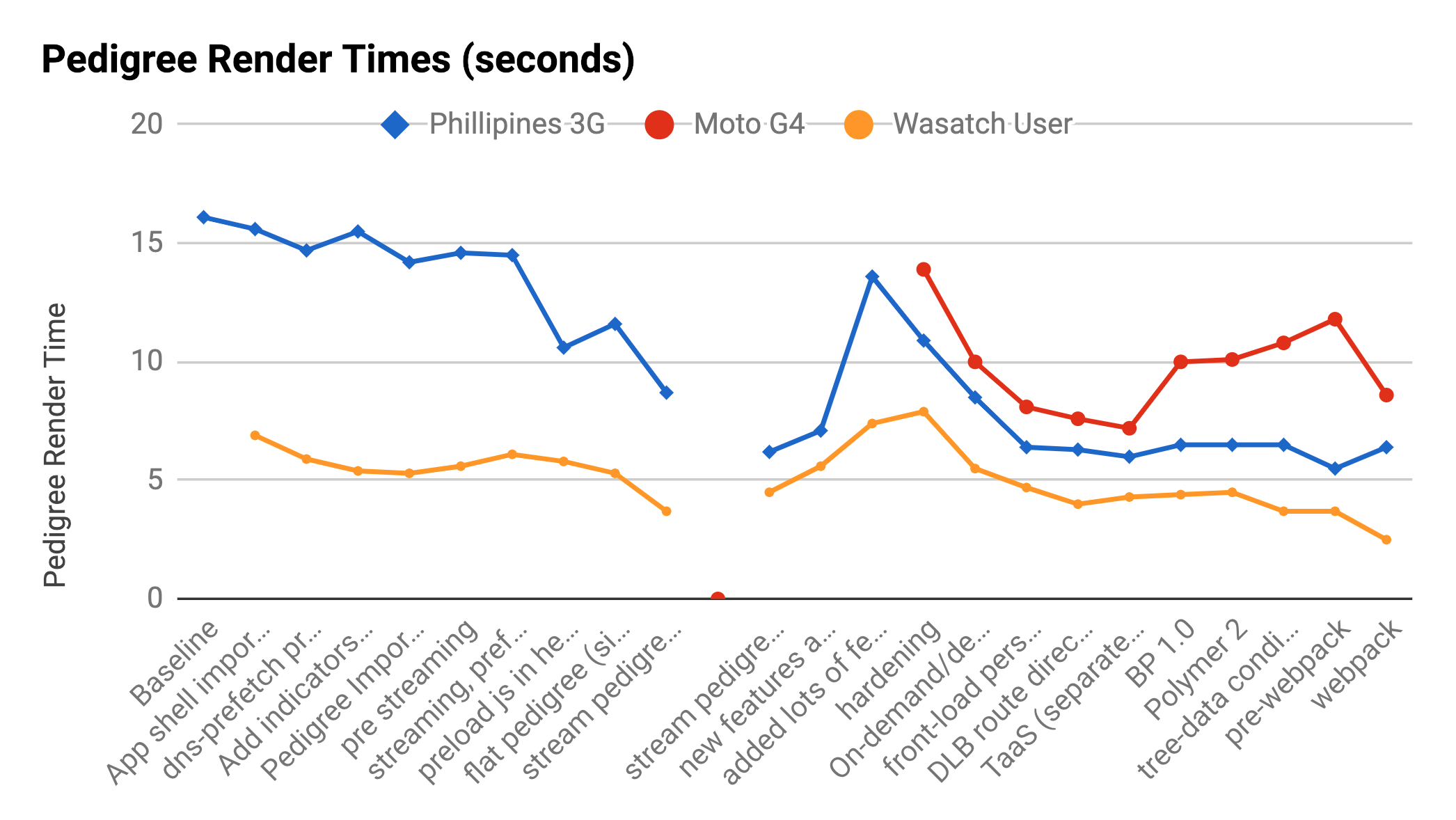
Tree Pedigree
429KB
375KB
12%
10.2s
8.5s
16%
Moto G4 from Virginia - 3G (1.6Kbps/768Kbps)
3.2s
2.5s
32%
Wasatch Front Desktop - Cable (5/1Mbps)
Tree Person Waterfalls
265 Reqs
87 Reqs
9.5s
17s
775KB
354KB
54%
67%
44%
Philippines Desktop - 3G (1.6Mbps/768Kbs)


Bundling is still necessary for top performance
Code Splitting
Only load the code you need, when you need it.
el.addEventListener('click', e => {
//dynamic import after a click
import('./add.js').then(({default:add})=>{
//I now have access to the new module
add(2,2);
});
});
renamed and destructured
add.js won't load until this import is called
Try it out
4-code-splitting

Polymer 2
polymer-webpack-loader
import './my-app.html';module.exports = {
...
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(html)$/,
use: {
loader: 'polymer-webpack-loader'
}
}
]
}
}
index.js
webpack.config.js
<my-app></my-app>
<script src="./dist/bundle.js"></script>index.html
Try it out
5-polymer-2

Loaders
more in depth
Loaders take a string and return a string
module.exports = (source) => {
source = source.replace('stuff','things');
return source;
};string
string
do a transformation
thing-replace-loader.js
items.map(item=>{
return item.replace('stuff','thing');
});Remind's me of a map function
add.js
index.js
subtract.js
bundle.js
replace-loader
once for each file
{
...
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.html$/,
use: [
{ loader: 'polymer-webpack-loader' },
{ loader: 'webpack-lazy-group-loader' }
]
}
]
}
}Loaders run in reverse order. Weird.
Hey webpack,
Whenever you find a filename that ends in .html, run it through these loaders.
Thanks.
First
Second
resolved to node_modules. Weird.
lazy-imports
(code splitting)
<link rel="lazy-import" group="profile" href="./my-profile.html">
...
loadProfile() {
this.importLazyGroup('profile').then();
}Don't load ./my-profile.html until loadProfile is called.
webpack-lazy-group-loader
module.exports = (source) => {
// if no `importLazyGroup` just return source.
if(!source.includes('importLazyGroup')) return source;
var doc = parse5.parseFragment(source);
var scriptEls = dom5.queryAll(doc, pred.hasTagName('script'));
// find all lazy-import groups
const lazyGroups = parseLazyGroups(doc);
scriptEls.forEach(scriptEl=>{
source = replaceLazyImports(doc, scriptEl, lazyGroups);
});
return source;
};<link rel="lazy-import" group="profile" href="./my-profile.html">
...
loadProfile() {
this.importLazyGroup('profile').then();
}loadProfile() {
import('./my-profile.html')
}webpack-lazy-group-loader

Plugins
add.js
index.js
subtract.js
bundle.js
replace-loader
once for each file
UglifyPlugin
Only one time
module.exports = {
...
plugins: [
new UglifyJsPlugin({
sourceMap: true,
uglifyOptions: {
mangle: {
safari10: true
}
}
})
]
}Plugin in config
Try it out
6-plugin

HMR
hot module replacement
Good luck with these docs
Try it out
7-hmr

On your touch device