SRUG 2024.03 Meetup
Introductions
Brad G.
- Online: U007D ("Curly")
- Started tech back in the 1980's
- Hold a B.Sc. in Computer Science
- Started in BASIC
- Historically gravitated to low-level languages
- MOS 6502/6510 Assembly
- Motorola 68k Assembly
- K&R C, ANSI C, Pascal/Object Pascal, C++
You?
Upcoming Meetups
- April 11 Meetup * 2nd Thu*
-
May 16 Meetup
- * Bonus * April 16 Meetup (Tue)
Bonus Apr. Meetup (Apr. 16)
FutureWei/Linux Foundation Europe
giving OSSNA Talks on:
* Servo
* Robius
Offered to speak to our group
Pizza will be provided!
Text
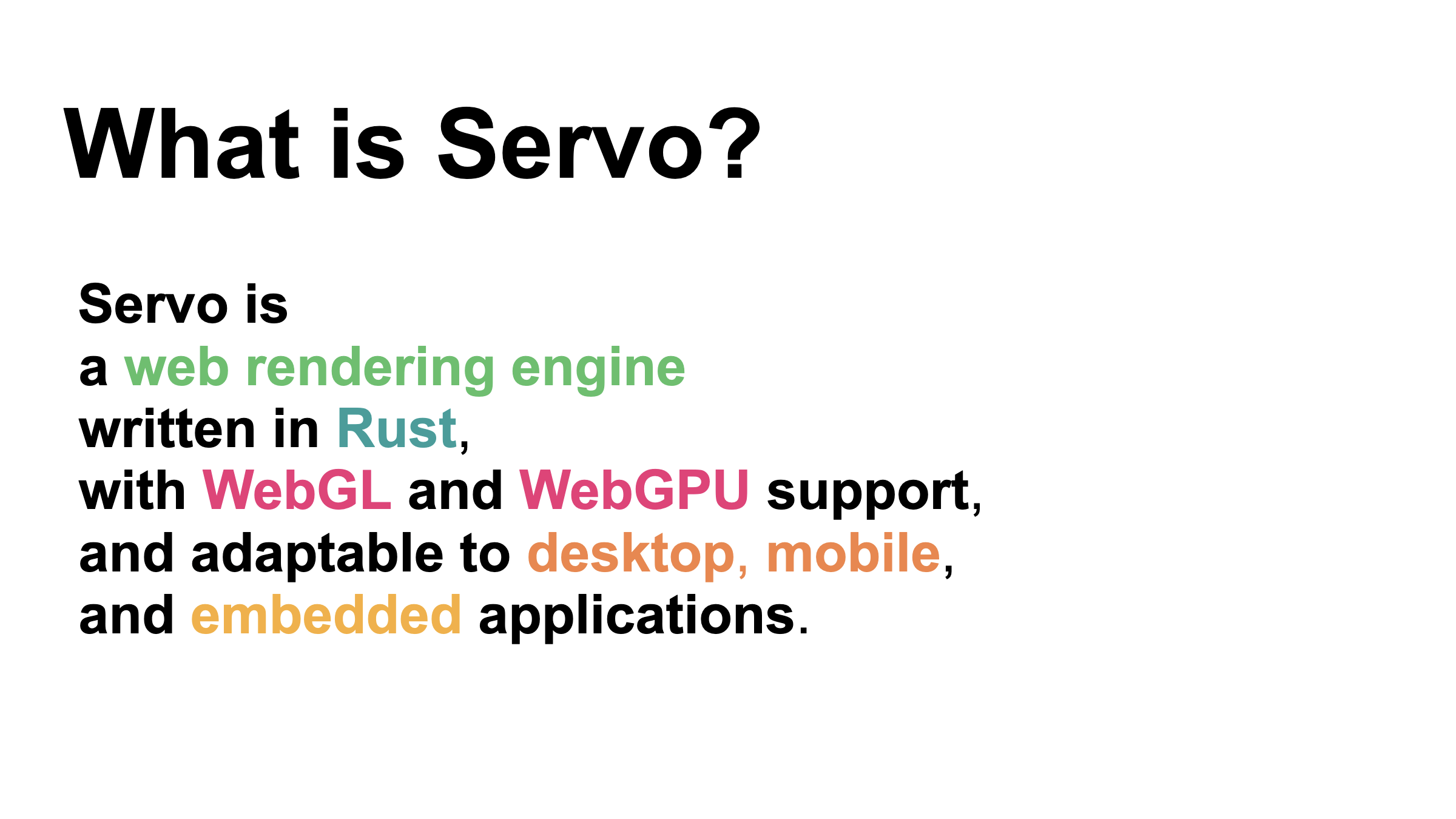
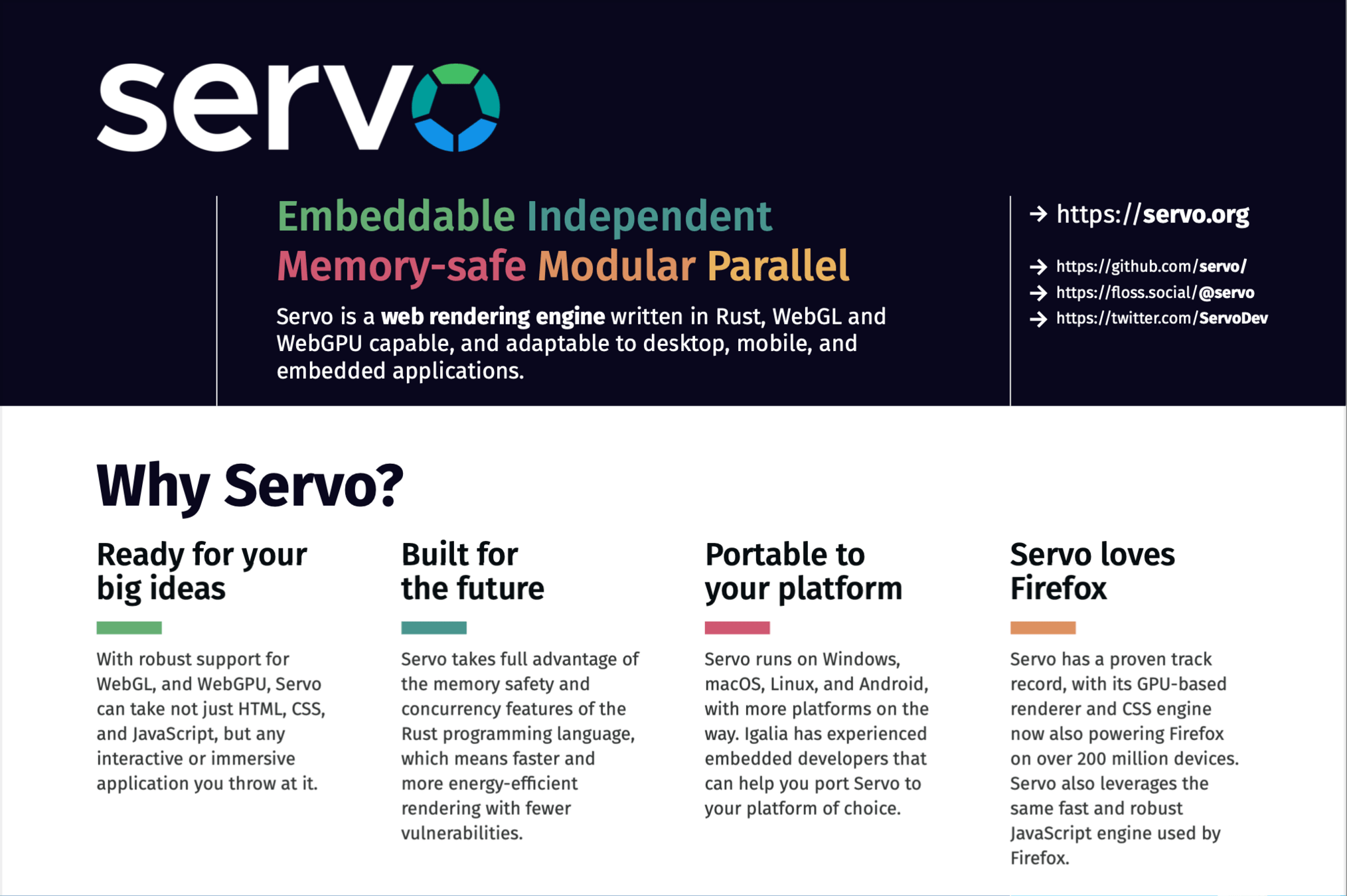
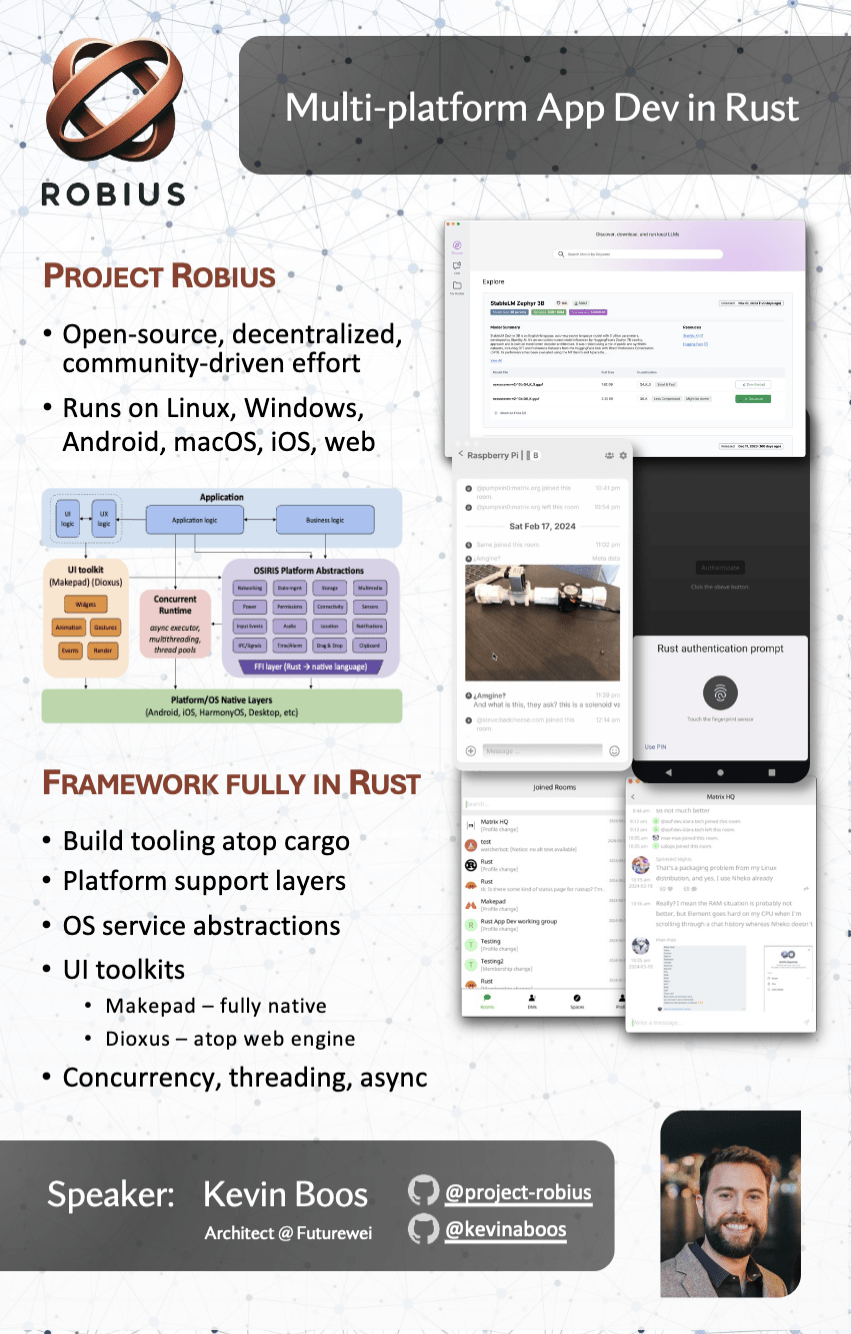
After-Meet Gathering
All are invited to join us tonight at Flatstick Pub
- (@ RTC)
Tonight's Talks
- Embedded Follow-Up (Brad G.)
- Little Helpers (Azi)
- Error Propagation in Rust (Sagaar)
An Introduction to Bare-Metal Embedded Systems Programming in Rust
On a Raspberry Pi Pico
- Brad G.
Prerequisites:
Install Rust
1. https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install
2. `rustup target add thumbv6m-none-eabi`
Install Tooling (git)
Mac: `brew install git` (see https://brew.sh/) or
https://github.com/git-guides/install-git
Ubuntu: `apt install git`
Windows: https://github.com/git-guides/install-git
Install Tooling (Other)
- `cargo install elf2uf2-rs svd2rust form`
- (Optional) Visual Studio Code Editor:
https://code.visualstudio.com
- (Optional) Mac: `brew install binutils`
Ubuntu: `apt install binutils`
Setting up the Board
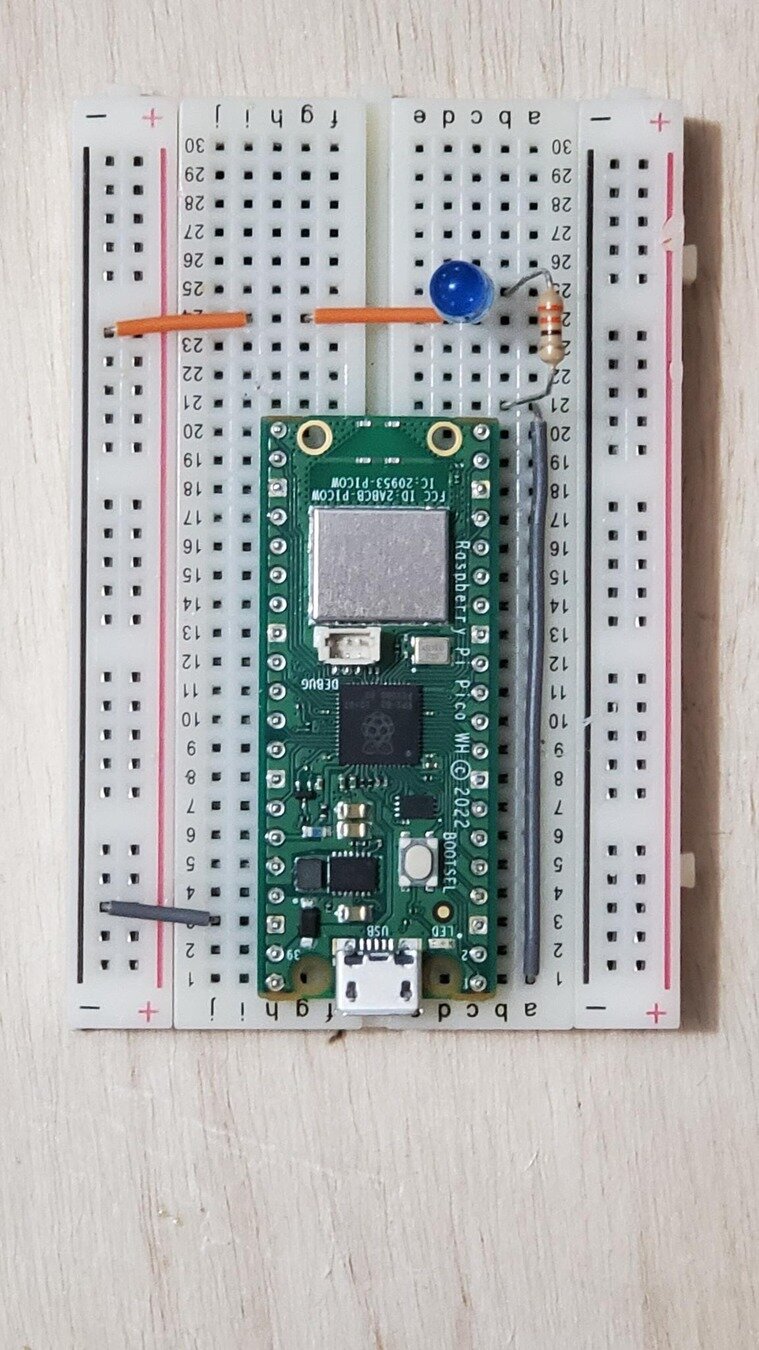
1. Wire pin 1 (GPIO 0) to an empty row
2. Add resistor from wire end row to new empty row
3. Add LED (long leg) from resistor end row to new empty row
4. Wire from LED (short leg) to - rail
5. Wire - rail to pin 38 (Ground)
Setting up the Board
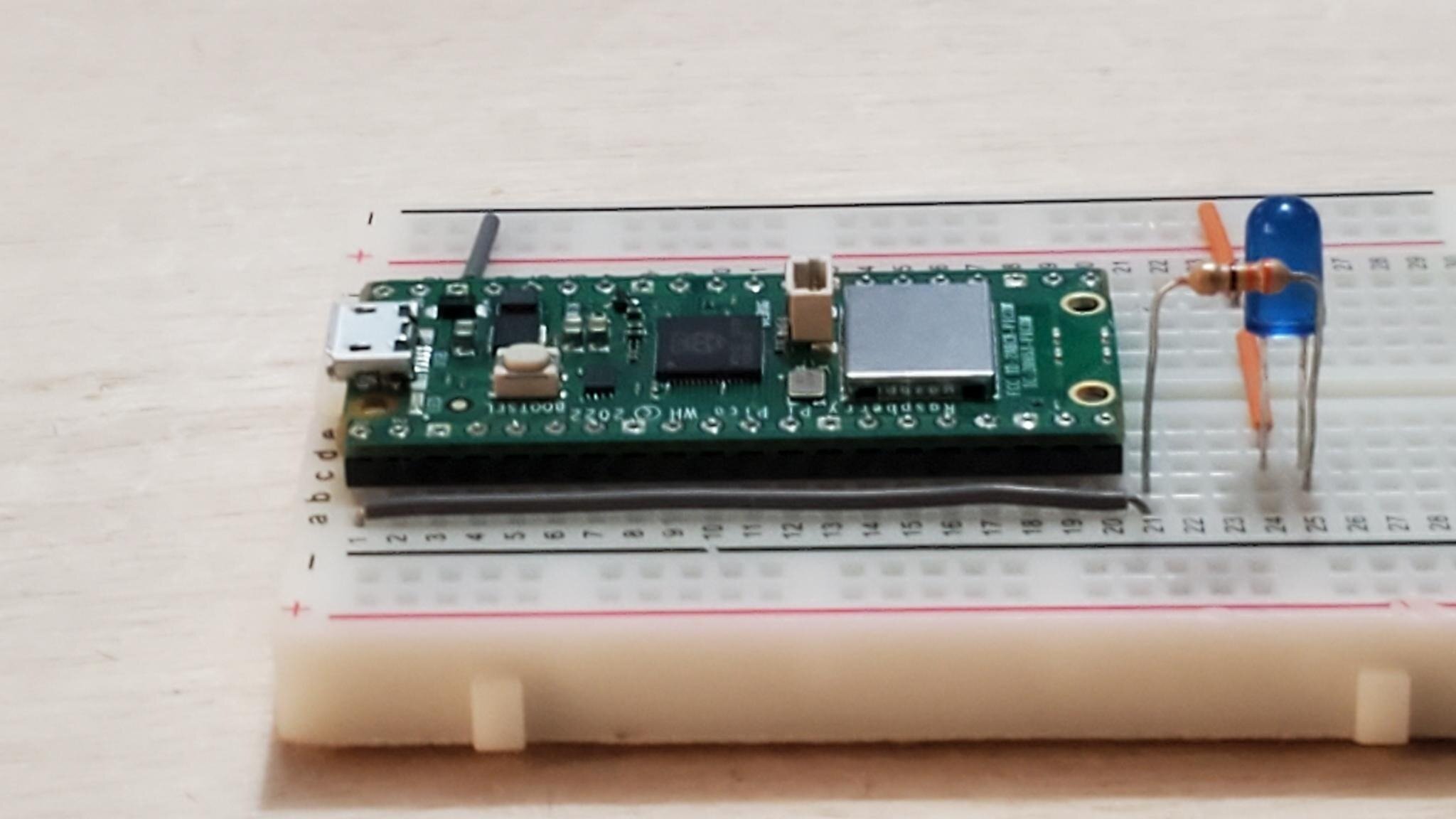
Setting up the Board
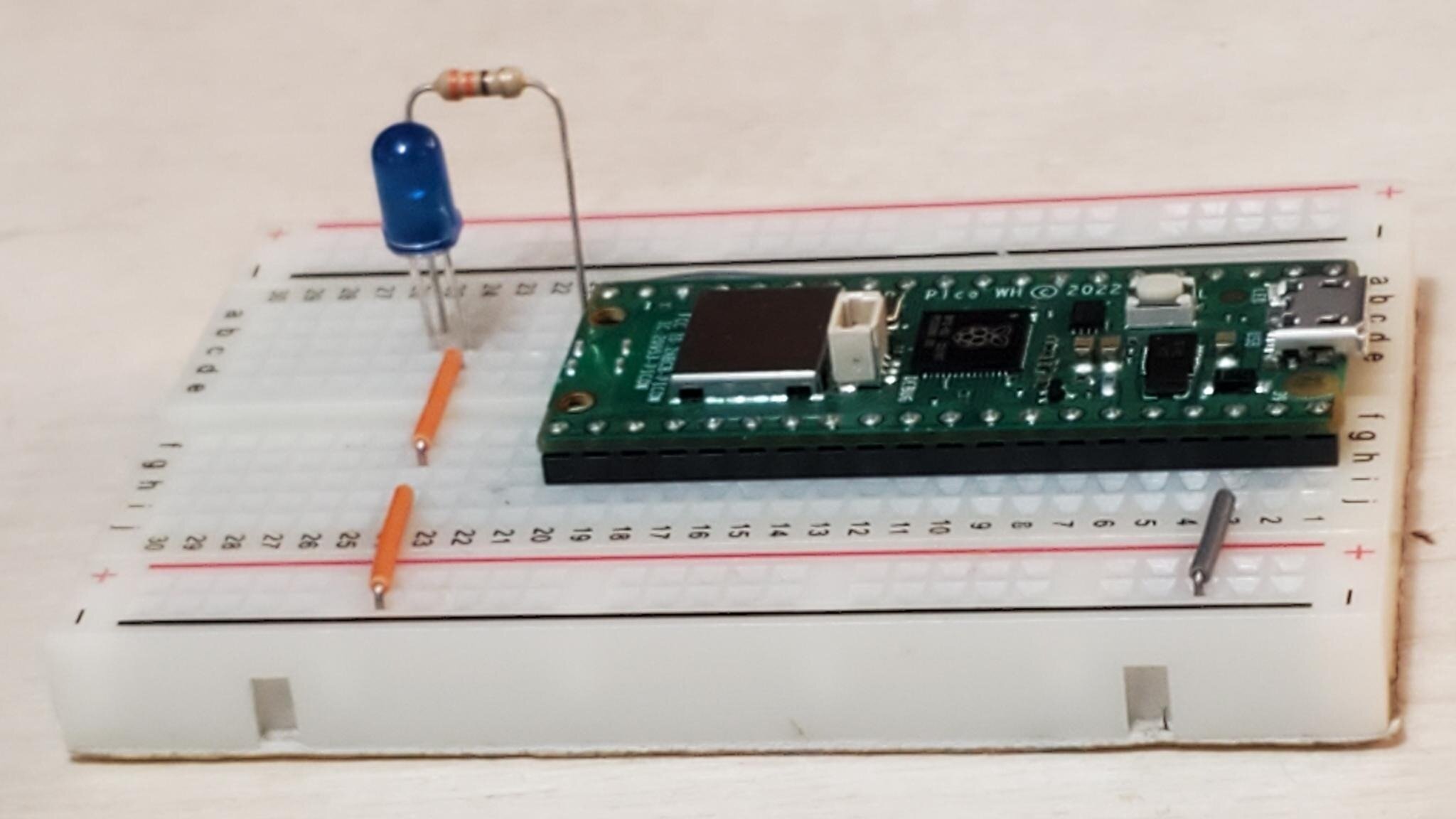
Running on the Pi
The Raspberry Pi Pico has a different CPU then your computer.
Your computer has to compile your source code to machine language for a processor it can't run. This is called cross-compiling.
Your cross-compiled program then needs to be transferred to the Pi and run there.
Running on the Pi (2)
To do this:
1. Unplug your RPi Pico USB cable (either end) if it is plugged in.
2. Hold down the white button on the RPi Pico.
3. Re-connect your RPi Pico with the white button held down.
(Your RPi Pico is now ready to receive your cross-compiled program.)
4. `cargo run`. (Your program is now running on your RPi Pico.)
5. Repeat the above procedure to send and run a new version of your code to your RPi Pico.
What is "Embedded Systems" Programming?
- Writing code for any device with limited human
interface capabilities
What is "Bare Metal" Programming?
- Wrting code that runs without an Operating System.
Base N Encoding
Decimal Binary Hexadecimal
(Base 10) (Base 2) (Base 16)
Value | Encoding | Encoding | Encoding
------+----------+----------+-------------
Zero | 0 | |
One | 1 | |
Two | 2 | |
Three | 3 | |
Four | 4 | |
Five | 5 | |
Six | 6 | |
Seven | 7 | |
Eight | 8 | |
Nine | 9 | |
--------+----------+----------+-------------
Ten | 10 | |
Eleven | 11 | |
Twelve | 12 | |
Thirteen | 13 | |
Fourteen | 14 | |
Fifteen | 15 | |
Sixteen | 16 | |
Seventeen | 17 | |
... | ... | ... | ...
Base N Encoding
Decimal Binary Hexadecimal
(Base 10) (Base 2) (Base 16)
Value | Encoding | Encoding | Encoding
------+----------+----------+-------------
Zero | 0 | 0 |
One | 1 | 1 |
--------+----------+----------+-------------
Two | 2 | 10 |
Three | 3 | 11 |
Four | 4 | 100 |
Five | 5 | 101 |
Six | 6 | 110 |
Seven | 7 | 111 |
Eight | 8 | 1000 |
Nine | 9 | 1001 |
Ten | 10 | 1010 |
Eleven | 11 | 1011 |
Twelve | 12 | 1100 |
Thirteen | 13 | 1101 |
Fourteen | 14 | 1110 |
Fifteen | 15 | 1111 |
Sixteen | 16 | 1 0000 |
Seventeen | 17 | 1 0001 |
... | ... | ... | ...
Base N Encoding
Decimal Binary Hexadecimal
(Base 10) (Base 2) (Base 16)
Value | Encoding | Encoding | Encoding
------+----------+----------+-------------
Zero | 0 | 0 | 0
One | 1 | 1 | 1
Two | 2 | 10 | 2
Three | 3 | 11 | 3
Four | 4 | 100 | 4
Five | 5 | 101 | 5
Six | 6 | 110 | 6
Seven | 7 | 111 | 7
Eight | 8 | 1000 | 8
Nine | 9 | 1001 | 9
Ten | 10 | 1010 | a
Eleven | 11 | 1011 | b
Twelve | 12 | 1100 | c
Thirteen | 13 | 1101 | d
Fourteen | 14 | 1110 | e
Fifteen | 15 | 1111 | f
--------+----------+----------+-------------
Sixteen | 16 | 1 0000 | 10
Seventeen | 17 | 1 0001 | 11
... | ... | ... | ...
Sample Values
# Sample Values
Decimal 42 = 0b0010_1010, 0x2a
Decimal 255 = 0bffff_ffff, 0xff
Decimal 53_280 = 0b1101_0000_0010_0000, 0xd020
Anatomy of a Microprocessor (CPU)/Microcontroller (MCU):
CPU vs. MCU
- What's the difference between a CPU and an MCU?
- How they work
- "Memory" vs. Registers (DRAM vs. SRAM)
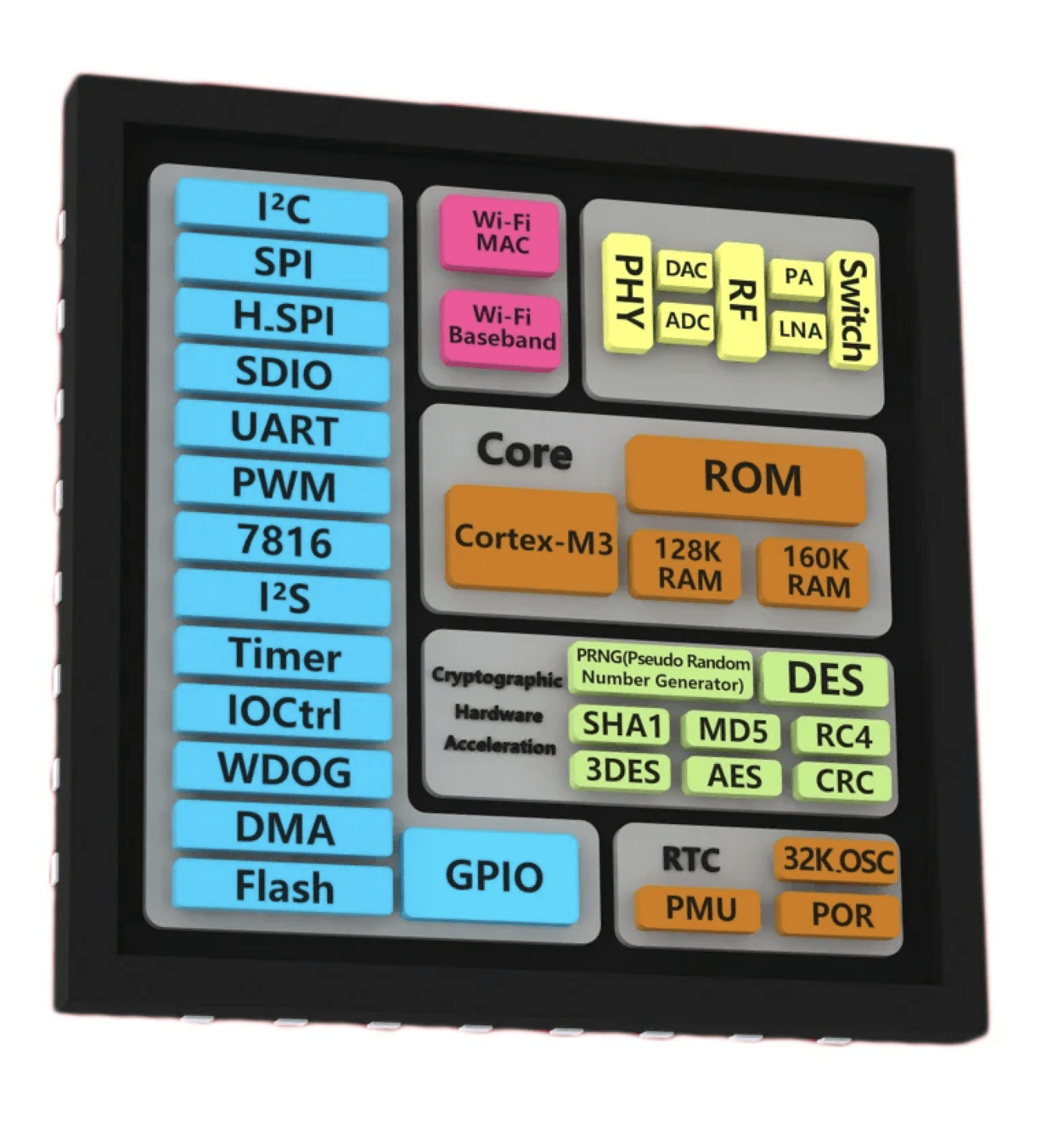
Tracking State
Status Register (Status)
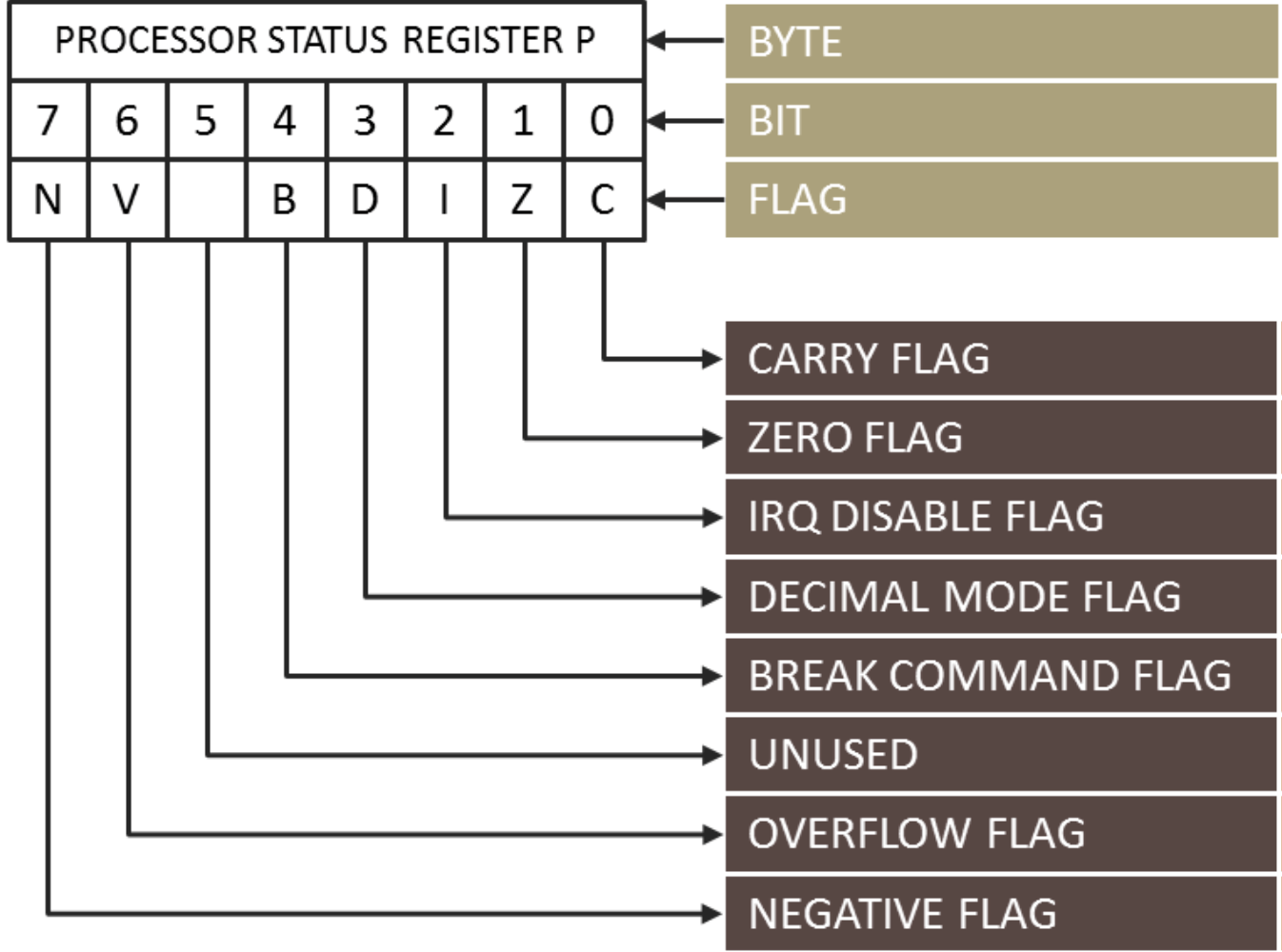
Instruction Set Architecture
- Machine Language
- Assembly Language
- AMD64 (Intel x86-64)
- Example: https://rust.godbolt.org/z/b5fEzdMET

Status Register Example
Status Register Example
```
mov r0, #2 ;r0 = 2, SR: 0
loop:
sub r0, r0, #1 ;r0 = 1, SR: Z=0; r0 = 0, SR: Z=1
bne loop ;if Z != 0 { goto loop }
```
- Supervisor vs User Mode
Low-Level Device Communication
Devices
- Memory Mapping
- Memory Maps
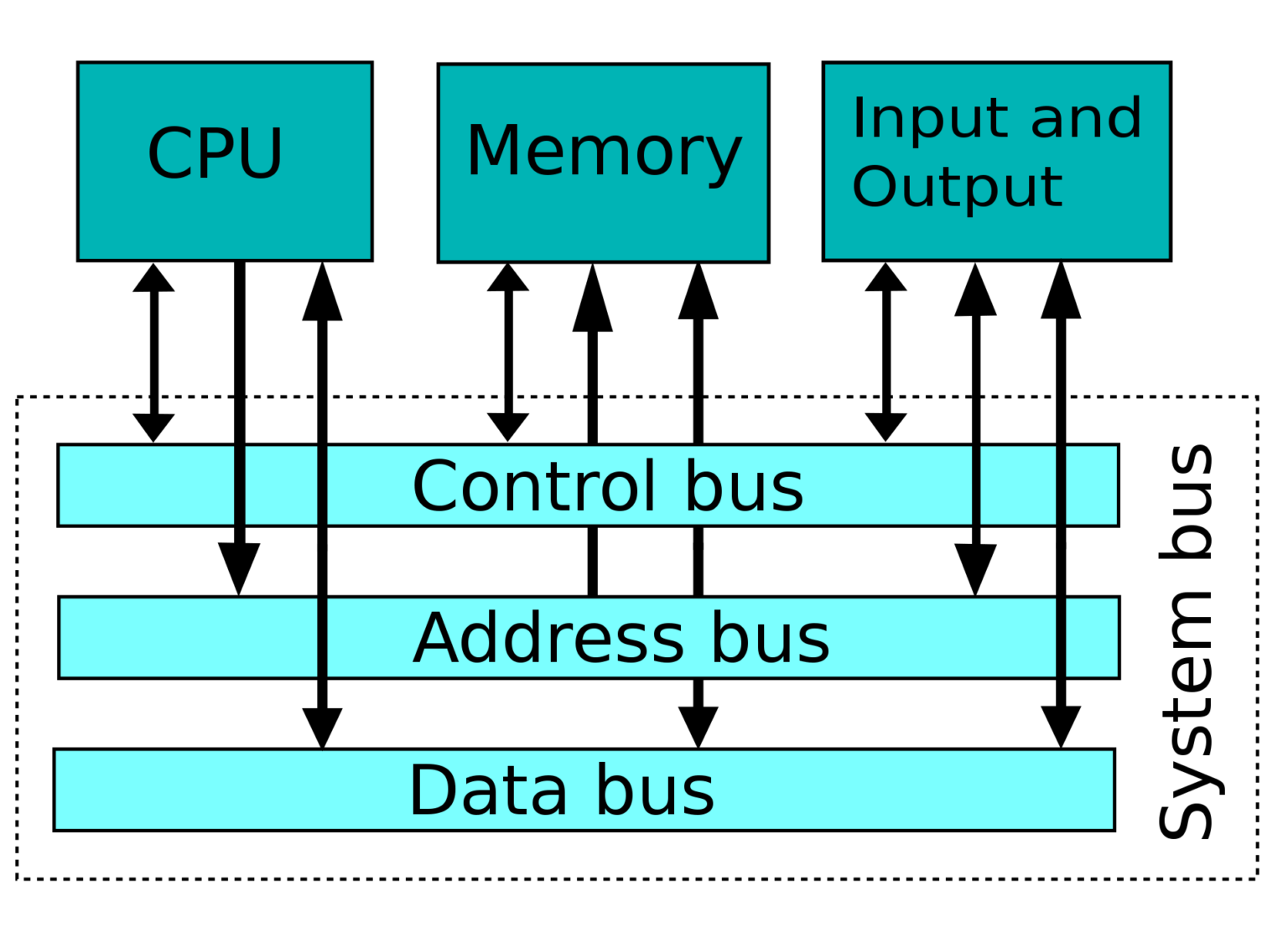
Low-Level Device Communication
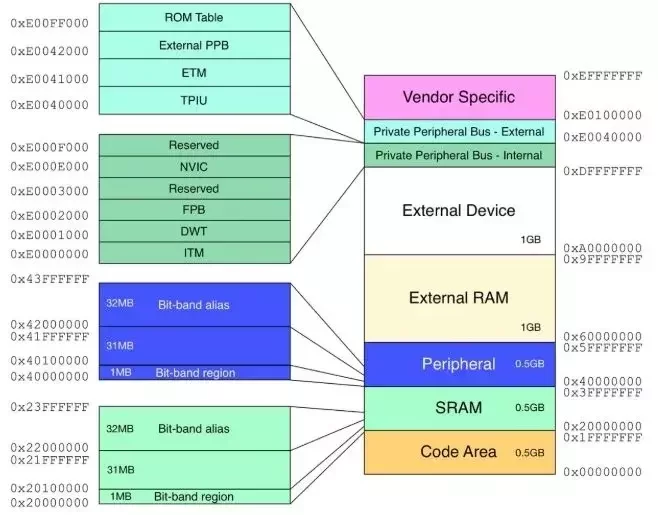
Bare-Metal Programming Like It's 1972
Bare-Metal Programming Like It's 2024
Let's Get Started
- git clone https://github.com/u007d/blinky
- cd blinky
- code . # or start your editor/IDE pointing here
Bonus: Making our own PAC
(We are in a new Golden Age for programming!)
- Silicon Vendor Description files
- https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk/blob/master/src/rp2040/hardware_regs/rp2040.svd
- `svd2rust -i rp2040.svd -o . --pascal-enum-values`
- `form -i rp2040/lib.rs -o src`
Thank you!
Presentation
Little Helpers
-Azi
Presentation
Error Propagation in Rust
-Sagaar