Medicaid and The Affordable Care Act

Original Medicaid program:
- State-federal partnership
- Entitlement (no cap on fed $)
- Closely linked to cash welfare (AFDC)
- Single mothers with very low incomes and their children
Medicaid Program
From 1965 to 1990, Medicaid and AFDC gradually decouple:
- 1972: Low-income disability program beneficiaries are included
- 1984: Children under age 5 in very low income households even if not headed by single mother
- 1986: Pregnant women in very low income families even if first time pregnancy or not headed by single mother
- 1988: Pregnant women up to poverty level
- 1990: Children under age 18 in households earning up to poverty rate
- 1997: State children's health insurance program
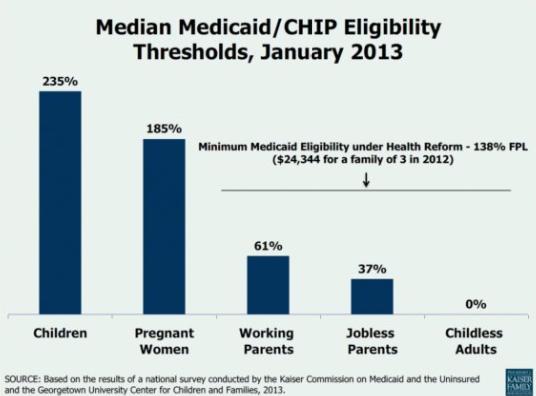
Still no way to get coverage if you are not 1) pregnant woman, 2) child, 3) (in some states) a parent with very low income
What was Coverage Like Before the ACA?
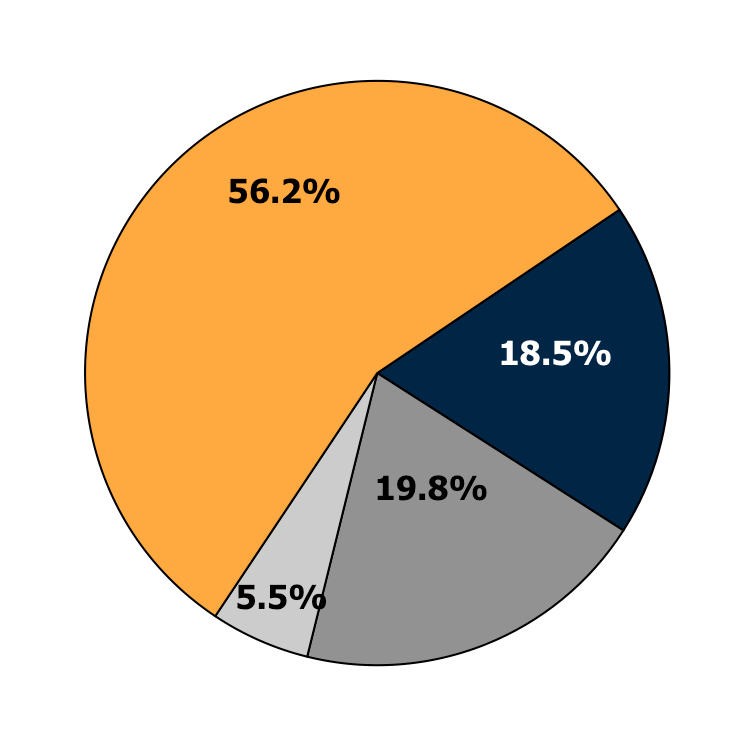
Employer-Sponsored
Health Insurance
Private Non-Group
Medicaid or other
public programs
Uninsured
Source: 2011 CPS ASEC, Non-Elderly Only
Health Insurance by Income Level
Affordable Care Act Goals
- Increase health insurance coverage
- Reduce health care costs
- Improve quality
ACA Expanded Coverage
1.Young adults allowed to stay on their parents’ private insurance until age 26 (effective September 2010)
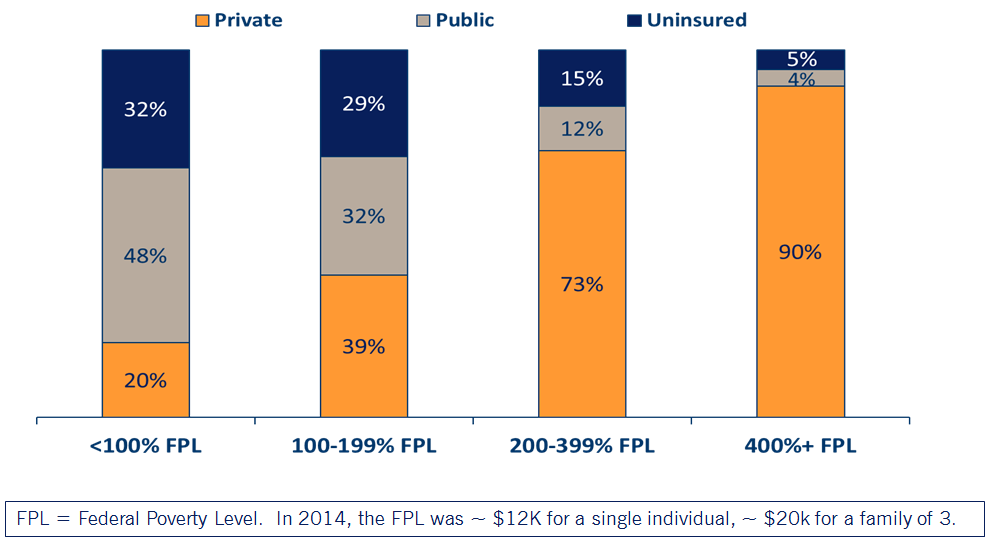
2.Eligibility for Medicaid extended to everyone with incomes below 138% of the Federal Poverty Level (effective Jan 2014*)
3.New tax credits for private insurance for families between 100 and 400% of the Federal Poverty Level (effective Jan 2014)
4. Individual mandate to purchase health insurance (now repealed)
* Several states elected to expand Medicaid at different times, or not at all!
Medicaid Expansion
NFIB v Sibelius 2012
High profile supreme court case challenging constitutionality of the ACA:
SCOTUS ruled the threat of losing all Medicaid funding was unconstitutionally coercive, a "gun to the head" as Roberts wrote in his majority opinion.
Because of this ruling, states could opt not to expand Medicaid without risking losing additional funding.
Status of State Expansions
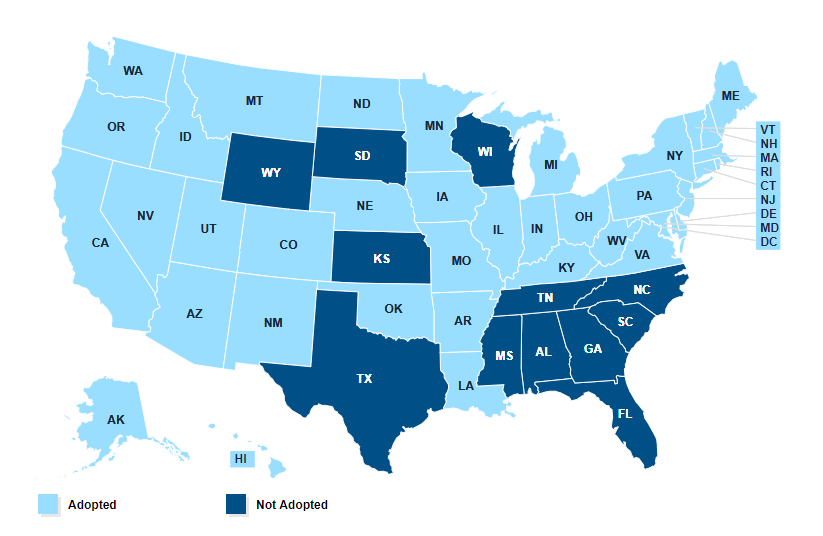
Source: KFF
Private Coverage Provisions
Underwriting reforms:
- "Guaranteed issue": no denials or exclusions for pre-existing conditions
•Adjusted community rating: premiums vary by age, smoking status, but nothing else
-Results in higher premiums for those who are younger, men; lower premiums for older, women
Health Insurance "Marketplaces"
The goal: make it easier to shop for health insurance if you don't have coverage through an employer
•Consumers choose from a menu of private plans
•All plans must offer 10 “essential health benefits” and conform to one of four actuarial value “metal levels.”
•Tax credits are based on consumer income and the premium for the 2nd lowest cost silver plan.
- 100-133 % of FPL: premiums are capped at 2% of income
- 300-400% of FPL: premiums are capped at 9.7% of income
•Low-income enrollees also qualify for cost-sharing reductions.
Other policies:
Employer mandate: large employers penalized if they don't offer coverage and their employees end up receiving a subsidy for health insurance
Experimenting with new ways of paying providers: "Accountable care organizations" trying to incentivize quality over quantity
Variety of other policies like requiring calorie posting, tanning bed tax etc
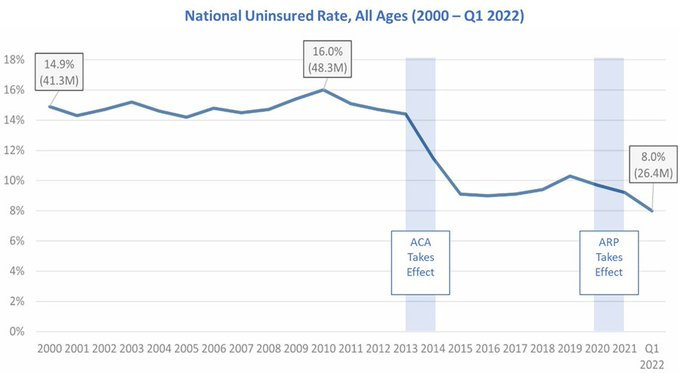
Overall Coverage Gains (Non-elderly adults)
The number of people with insurance increased by 20 million after ACA--but millions still uninsured
Coverage Gains Largest in states that expanded Medicaid
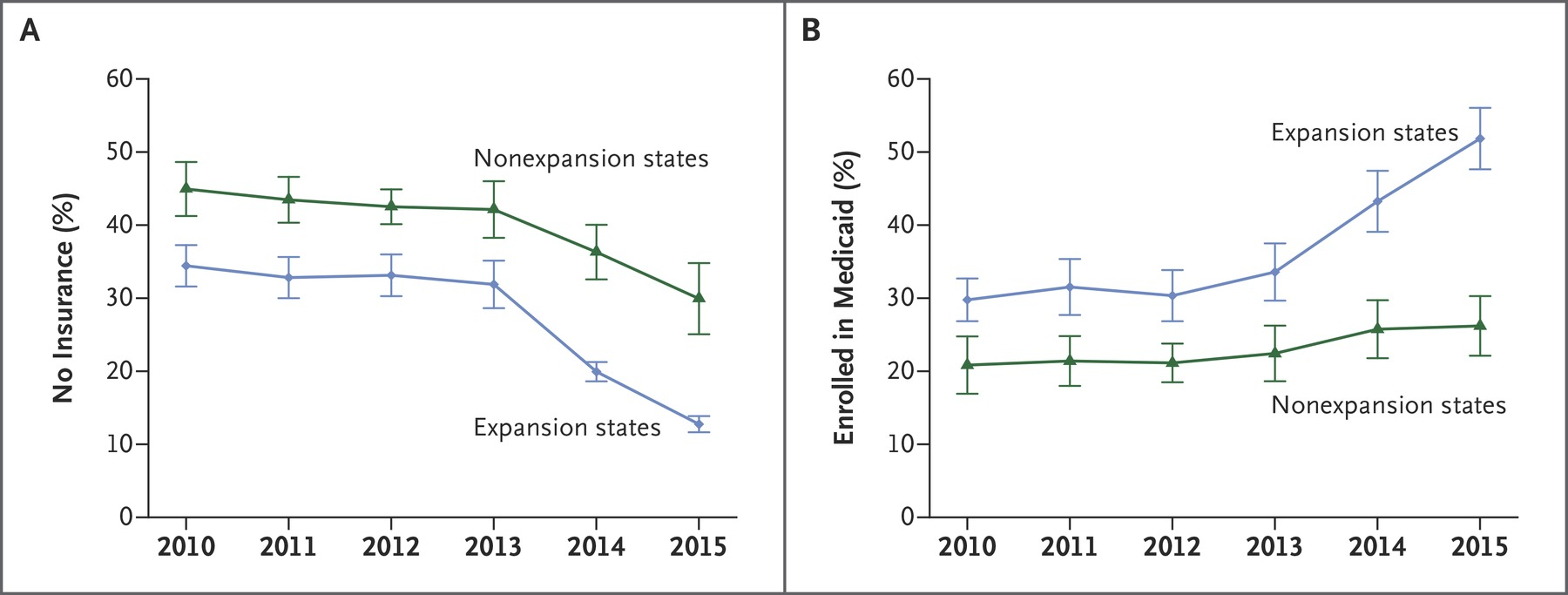
Sample among low income adults, Miller and Wherry 2016 New England Journal of Medicine
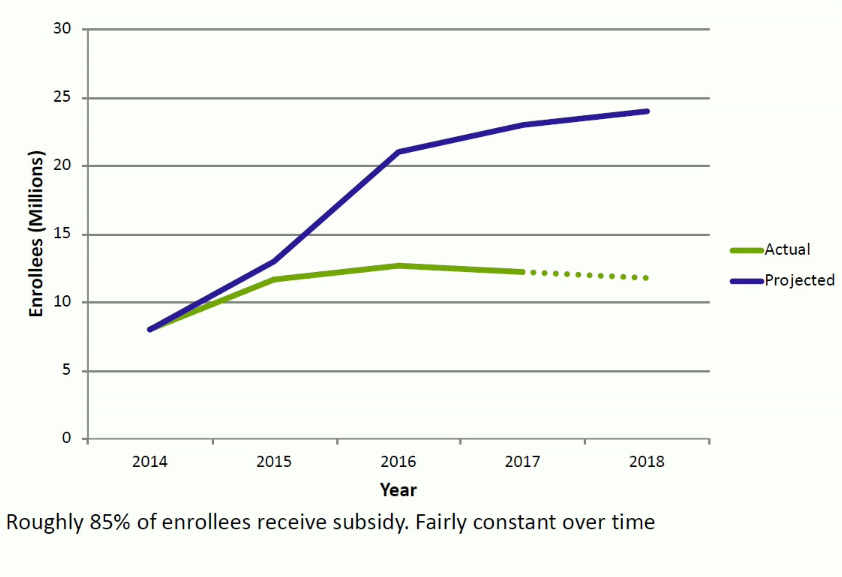
Marketplace Enrollments
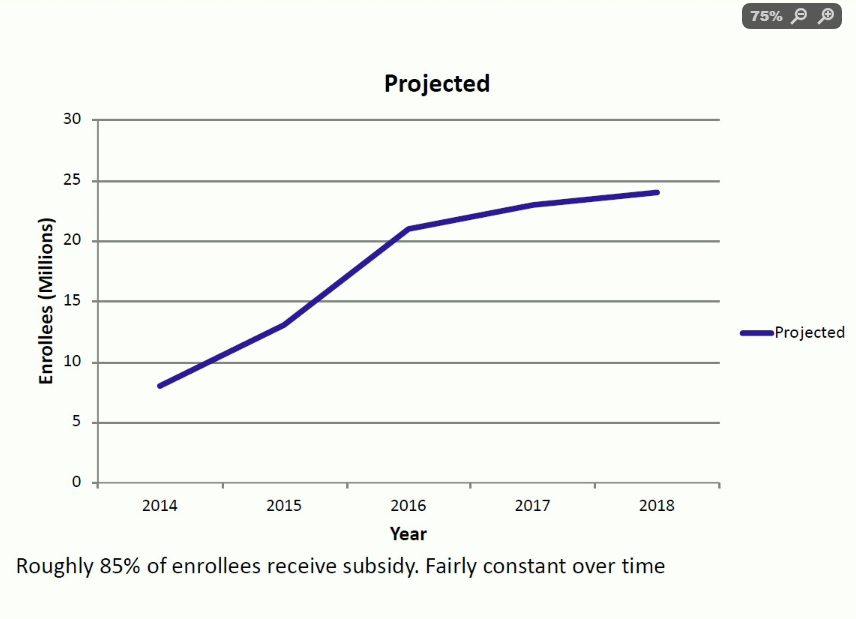
Marketplace Enrollments
Significant Premium Volatility
Competition on the Exchanges
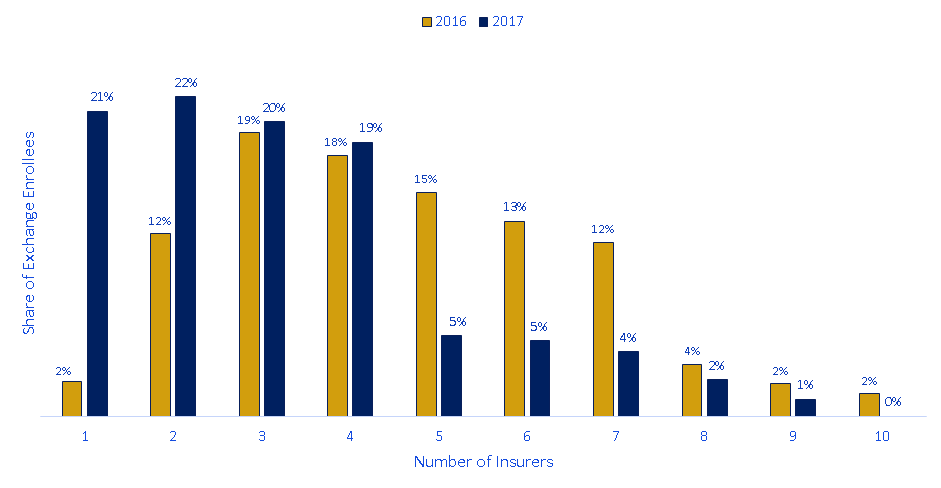
About 20% of enrollees have only one insurance company offering plans--far from the "perfect competition" ideal
Summary
- Clear evidence that a large number of people gained coverage.
- However, many people are still without! This is not "universal coverage"
- Dependent coverage mandate very popular, increased coverage
- Only benefits you if your parents can add you to their plan!
- Medicaid expansion a successful way to get low-income people covered--popular with strong evidence of improved health, access to care among the poorest.
- Exchanges seem to work okay if you are lower income and receiving a subsidy--in this case you are shielded from high premiums.
- Exchanges were not as popular as some analysts predicted.
Change to the ACA under the Trump Administration
Continued growth in Medicaid coverage
- During the Trump administration, 6 states (VA, ID, LA, NE, UT and ME) have elected to expand Medicaid.
- Federal government was also much more permissive in issuing waivers:
- Work requirements for Medicaid--but these have been struck down by the courts
- Allow "short term" health plans that don't follow ACA regulations
Mandate Repeal
To reduce adverse selection, the ACA included an individual mandate to purchase insurance with a penalty if you did not purchase it. This was repealed for tax year 2017.
Appears to not have had that big of an effect:
- Relatively few tax filers paid the penalty: about 12m were "exempted," 6.7 paid penalty
- Some confusion about whether mandate was repealed (about 40% did not know in latest Gallup poll)
- Many enrollees are subsidized, which is larger than the penalty
Inflation Reduction Act
Make exchange coverage subsidies more generous and allow everyone to use them, regardless of income
- Subsidies scale with income but do not "cut off" sharply at a certain income level.
State option to cover new mothers for 12 months post partum (vs 60 days).