Reliability
FYS 100, Module 2
In its broadest sense, test reliability indicates the extent to which individual differences in test scores are attributable to "true" differences in the characteristics under consideration and the extent to which they are attributable to chance errors.
-Anne Anastasi, Psychological Testing
What is reliability?
In its broadest sense, test reliability indicates the extent to which individual differences in test scores are attributable to "true" differences in the characteristics under consideration and the extent to which they are attributable to chance errors.
-Anne Anastasi, Psychological Testing
What is reliability?
observed score = true score + measurement error
What is reliability?
- Observed score is the score you actually got.
- True score is the score you should get if the test measures the trait in question perfectly.
- Measurement error is anything unrelated to the trait that causes a deviation between your oberved and true scores.
Measurement error
True score
Measurement error
True score
Observed score
Measurement error
True score
Observed score
Measurement error
What causes measurement error?
- Literally anything which is unrelated to the trait of interest, but which affects people's scores, is a source of measurement error.
- Transient states of test-takers
- Stable attributes of test-takers
- Characteristics of the measure
Let's think through a few sources of measurement error in tests we've taken...
What is reliability?
- A test being reliable in a certain way, for our purposes, means that it is robust to some corresponding type of measurement error.
- Test-retest reliability = robustness to measurement error due to time
- Interrater reliability = robustness to measurement error due to raters
- Interitem reliability = robustness to measurement error due to item choice
How do we calculate reliability?
- We use a number of measures (which we will discuss) that are based on correlations.
-
Correlations
- Range from -1.0 to 1.0
- Sometimes abbreviated r
- Positive r(x, y) means that as x increases, y increases
- Negative r(x, y) means that as x increases, y decreases
- N.B.: we aren't calculating any of these in this class. We may be looking at them though!
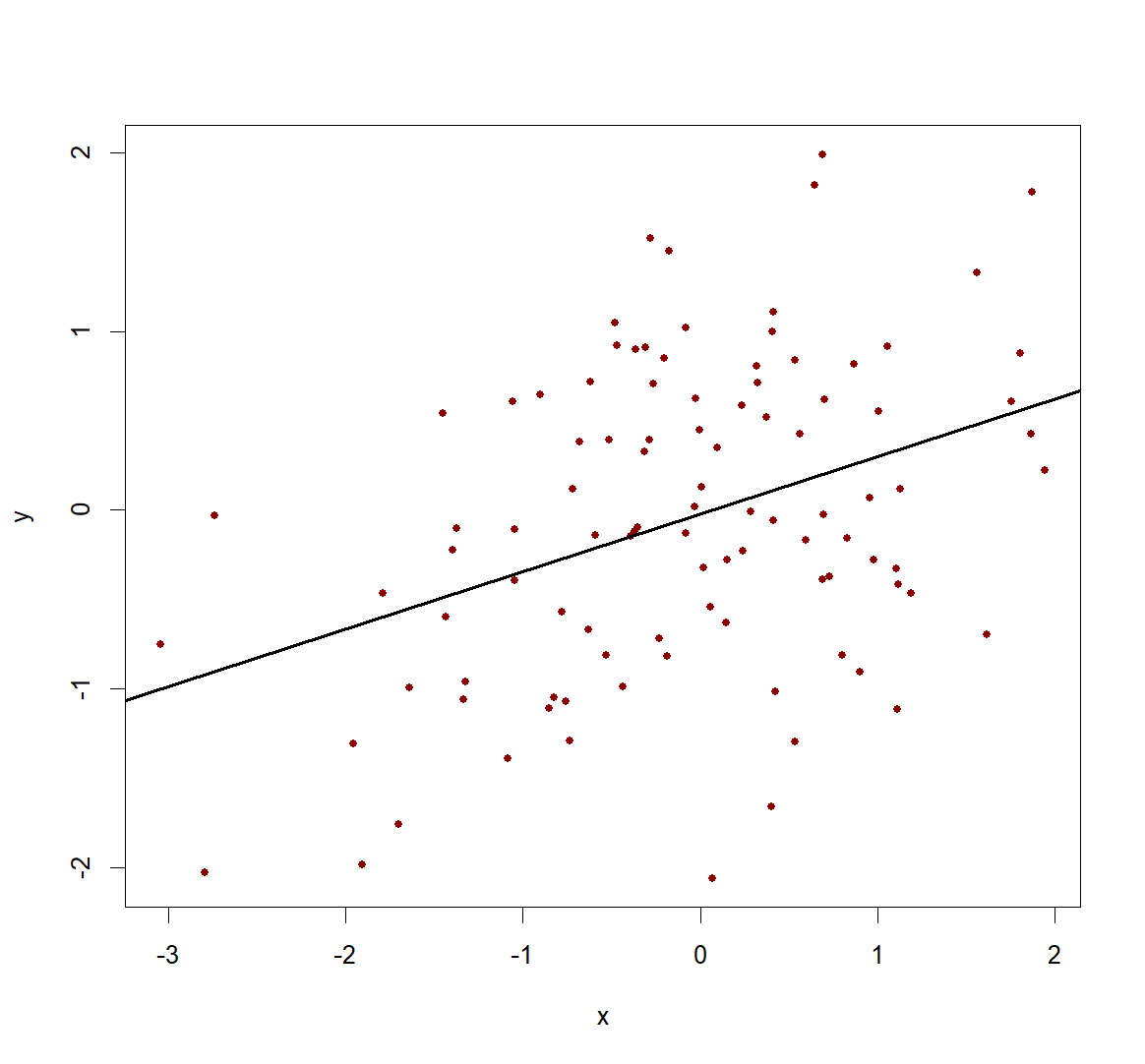
r(x, y) = .5
Test-retest reliability
- Measure: the correlation between your scores on the test now and your scores on the test later
- Meaning: how consistent are people's scores across time?
-
Caveats
- Only relevant to things that shouldn't change over a certain period of time!
Interrater reliability
-
Measure: the correlation between scores given by one rater and those given by another rater
- Sometimes referred to as \( \kappa\)
- Meaning: how consistent are your scores across raters?
-
Caveats
- Only relevant to things with multiple raters, which excludes most tests!
Interitem reliability
- Sometimes this will be referred to as internal consistency.
-
Measure: the average of the correlations between scores on one item and scores on another
- i.e., r(Item 1, Item 2), r(Item 1, Item 3), r(Item 1, Item 4)...
- Referred to as Cronbach's \( \alpha\)
-
Meaning: How consistently are these items measuring the same thing?
- Note: Not necessarily the right thing!
Interitem reliability
Imagine that we are asking someone to rate the following statements on a scale of 1-5:
- Item 1. I have been feeling happy lately.
- Item 2. I have been overwhelmed by joy lately.
- Item 3. I haven't been feeling particularly great these past few weeks.
- Item 4. I have been doing pretty well, all things considered.
Note that we would reverse any negative correlations - so a high negative correlation is still good!
Interitem reliability
Imagine that we are asking someone to rate the following statements on a scale of 1-5:
- Item 1. I enjoy peanut butter sandwiches.
- Item 2. I keep up with the Kardashians.
- Item 3. I think it's too warm outside.
- Item 4. I was personally affected by smoke from the Canadian wildfires.
Measurement error
True score
Observed score
Measurement error