Introduction to GraphQL
Web / Mobile / VR / AR / IoT / AI / Blockchain
Software architect, consultant, author

What is GraphQL
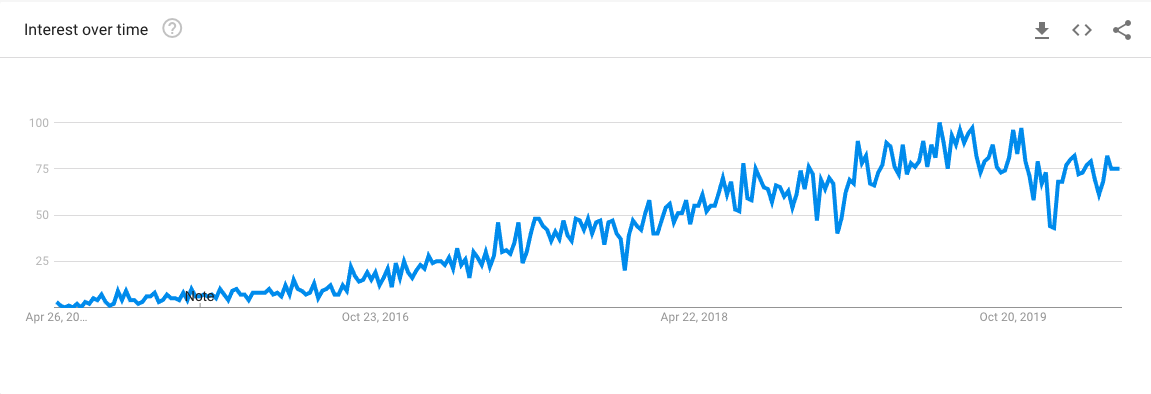
GraphQL
A query language for your API

What's wrong with REST

Restful API
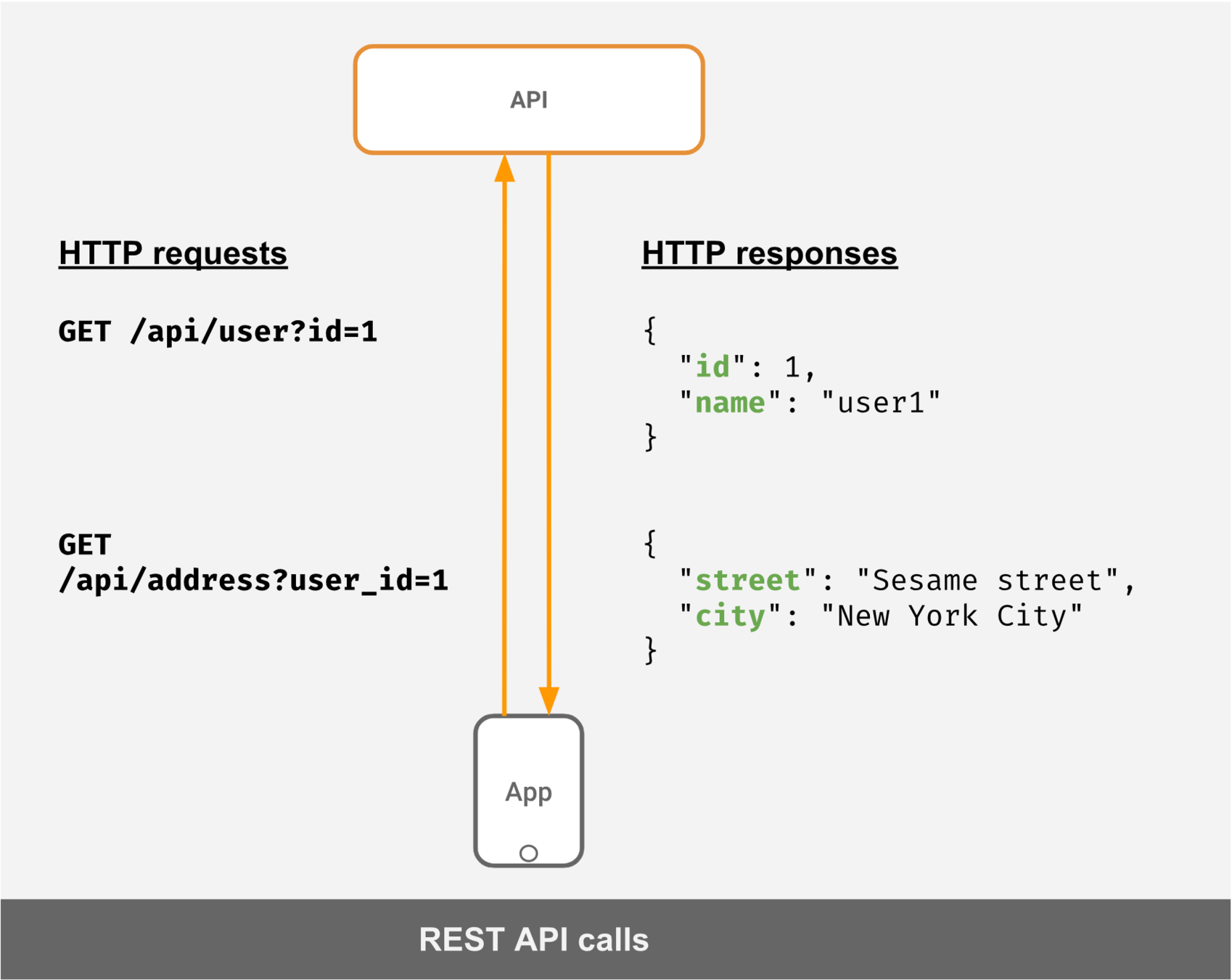
The core idea in REST is to have a URL for every resource
RESTfull API problems
Description of resource is coupled to implementation
Overfetching
Underfetching
chaining requests to server to get needed data
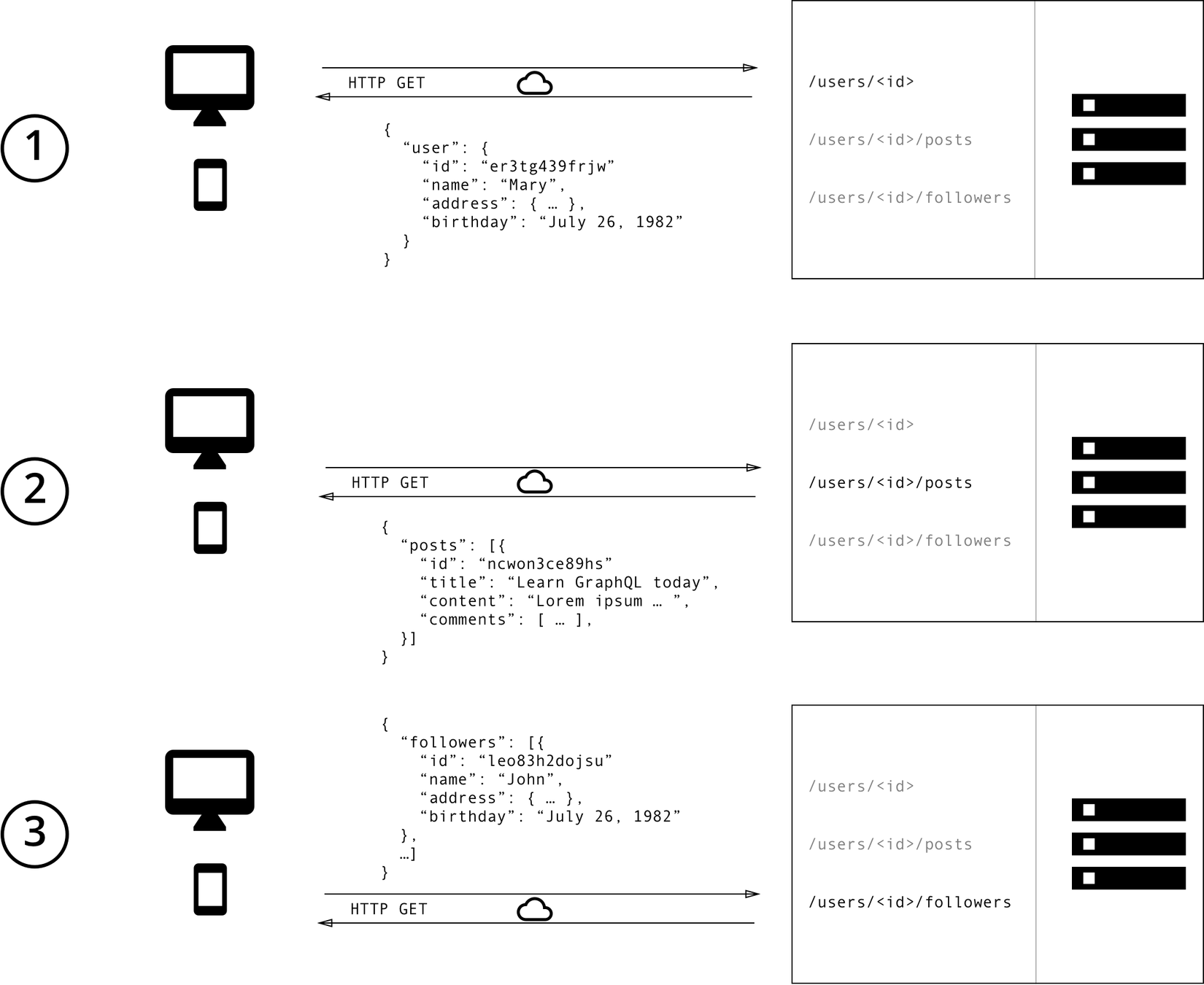
So how does GraphQL solve it
Avoid over-fetching
Prevent multipe API calls
Lesser communication with API developers
Self-documenting
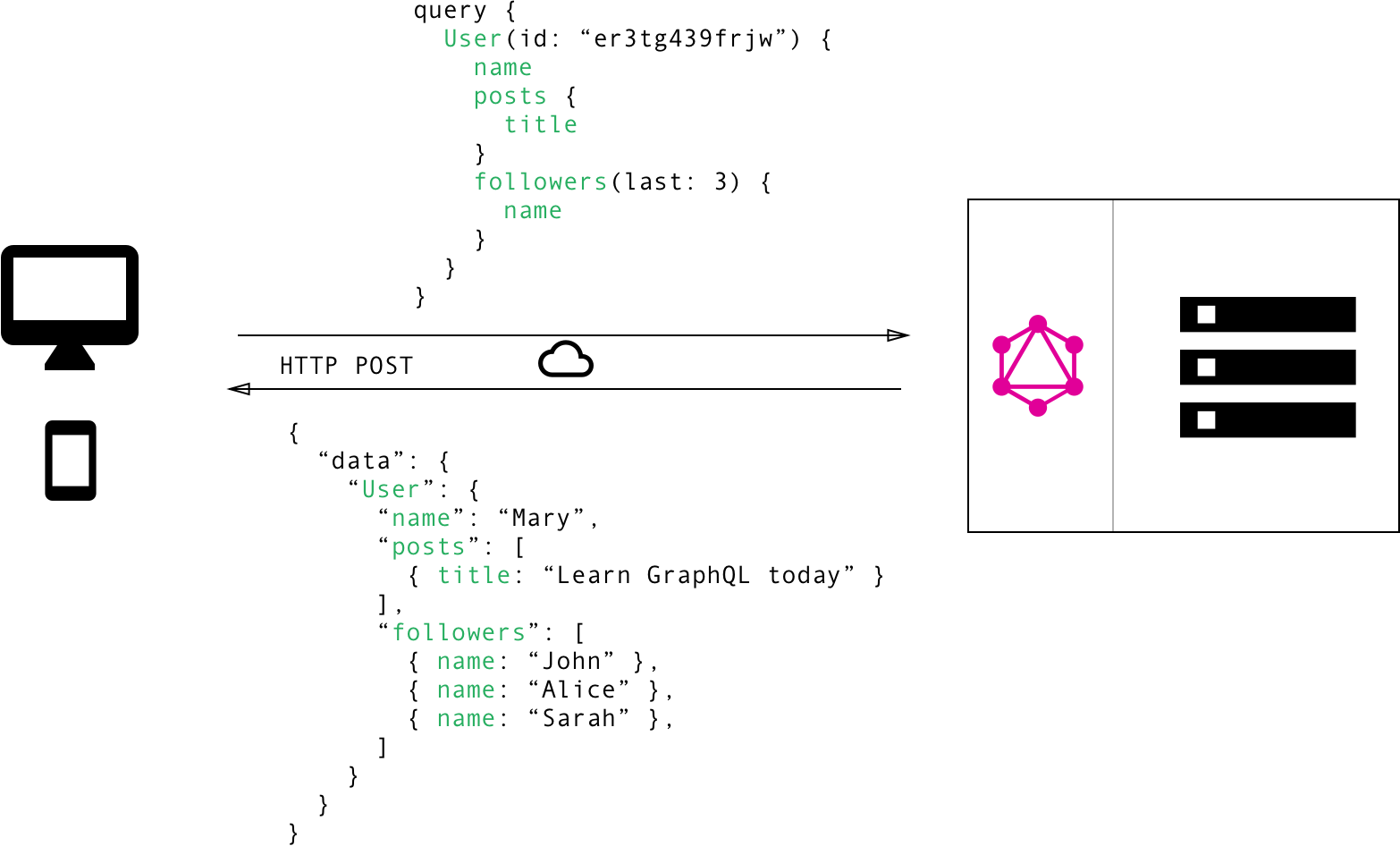
How does it look like
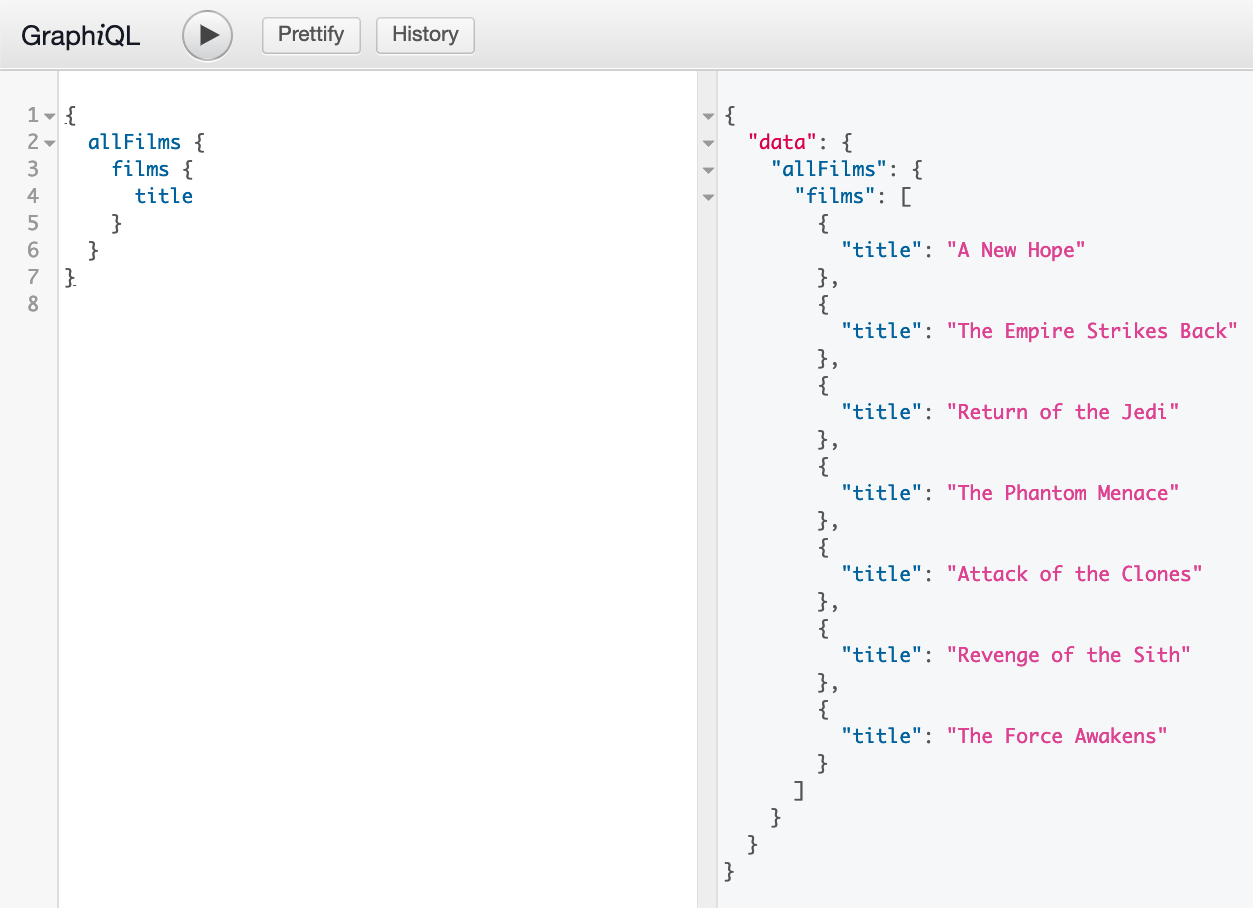
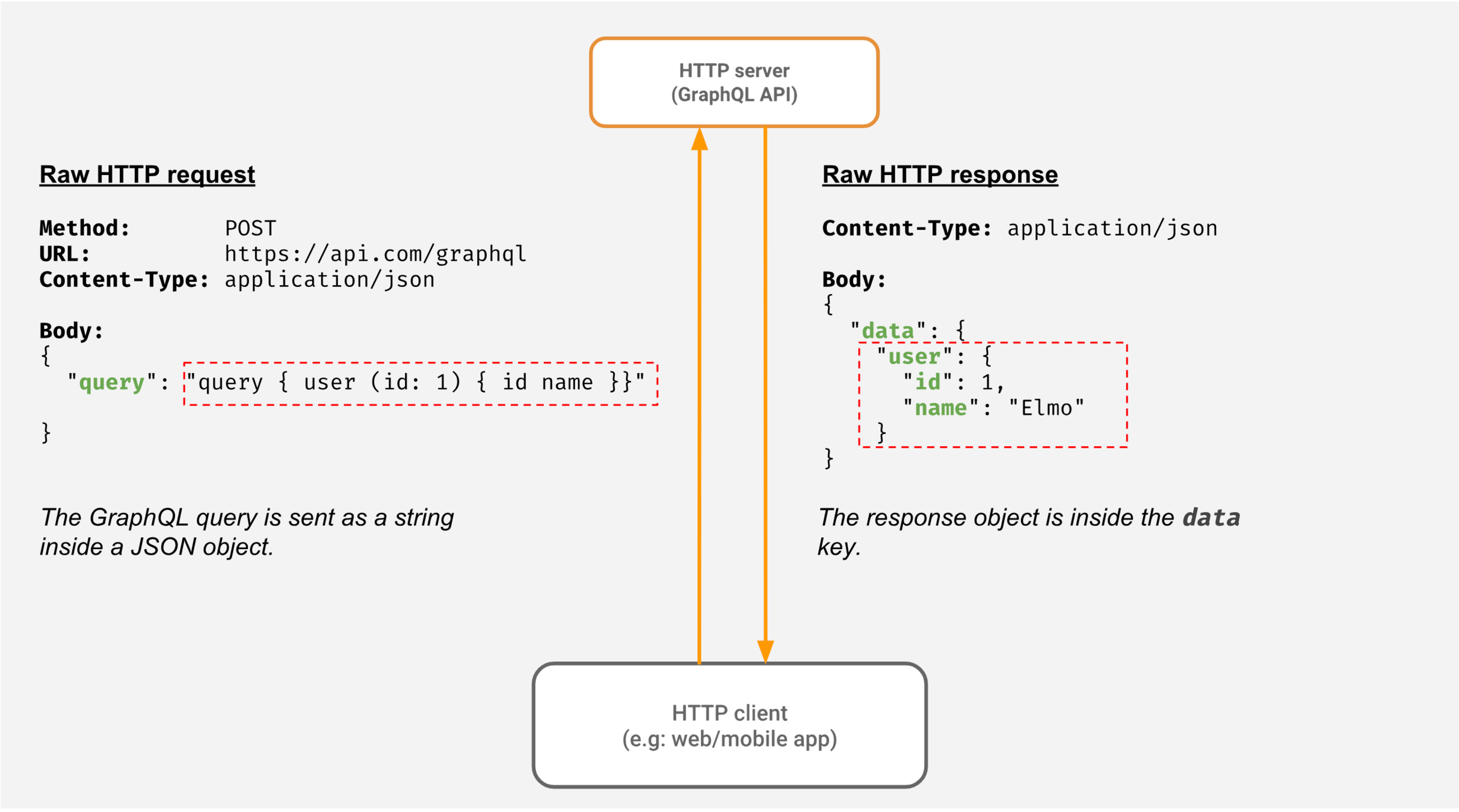
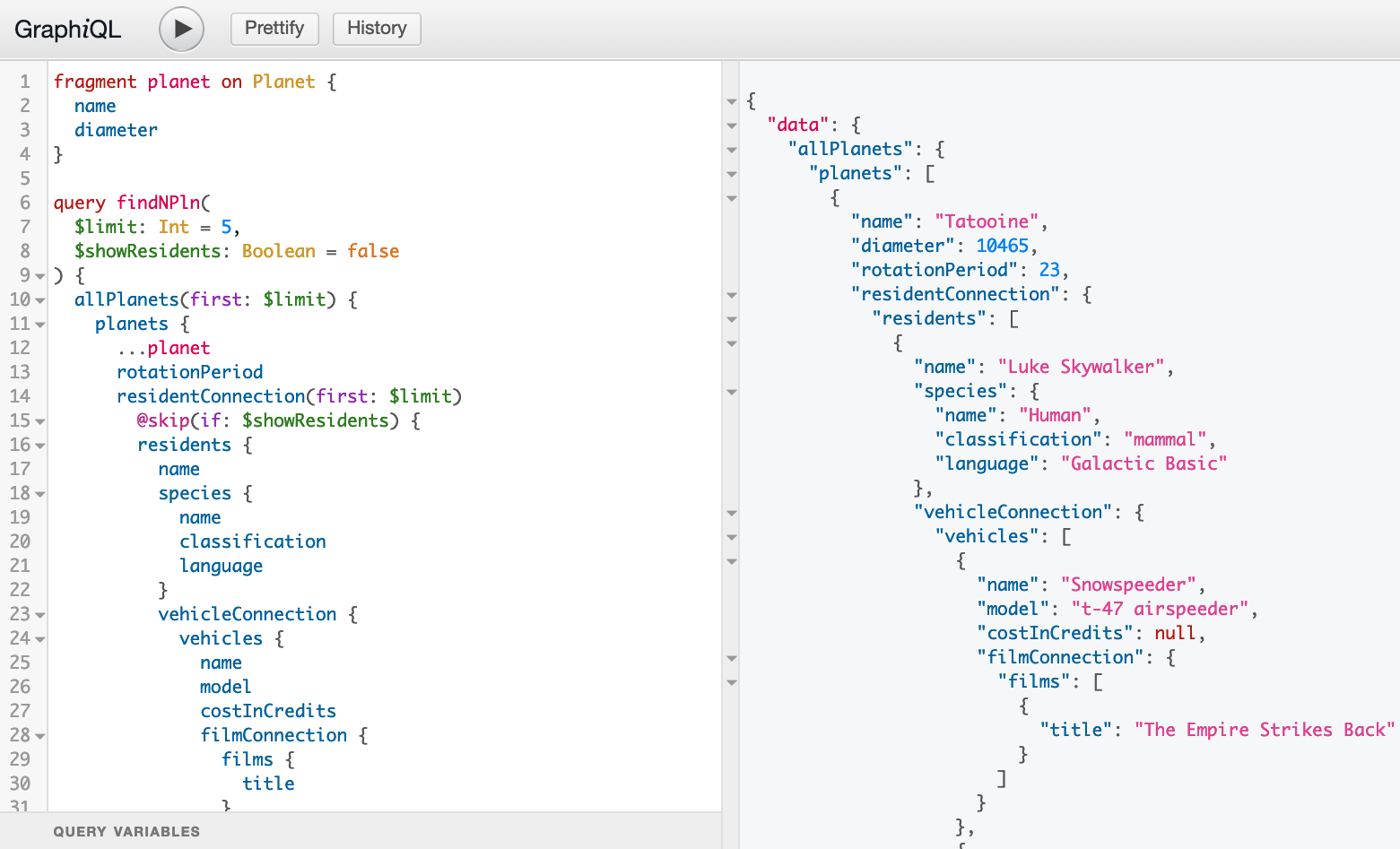
Operations
Queries - fetching data from graphql endpoint
Mutations- modifying the data or running a side effect
Subscriptions - subscribe to real-time updates through web sockets
query getPlanets {
allPlanets(first: 1) {
planets {
planet: {
name
}
}
}
}argument
query getPosts {
first_post: posts(order_by: [{ timestamp:asc}], limit: 1) {
subject
}
last_post: posts(order_by: [{ timestamp:asc}], limit: 1) {
subject
}
}
aliases
mutation deletePost($postId: uuid!) {
delete_posts(where:{id: {_eq: $postId}}) {
affected_rows
returning {
id
}
}
}variables
Queries - fetching data from graphql endpoint
mutation {
insert_posts(objects: [{
subject: "First blog post"
content: "Hello there"
user: {
data: {
firstName:"John"
lastName:"Smith"
profile: {
data:{ avatarUrl:"some url" bio:"Lorem ipsum"}
}
}
}
}]) {
returning {
id
subject
content
user {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}
}Mutations- modifying the data or running a side effect
subscription subscribeToMostLikedPosts {
posts(order_by:{ likes:asc} limit: 3) {
subject
content
}
}Subscriptions - subscribe to real-time updates through web sockets
Demo
GraphQL SDL
type Post {
title: String!
content: String!
user: User!
}
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
address: String
posts: [Post!]!
}
GraphQL Object Type,
fields
Built-in scalar type
Non Nullable
Array type
- Int: A signed 32‐bit integer.
- Float: A signed double-precision floating-point value.
- String: A UTF‐8 character sequence.
- Boolean: true or false.
- ID
GraphQL SDL
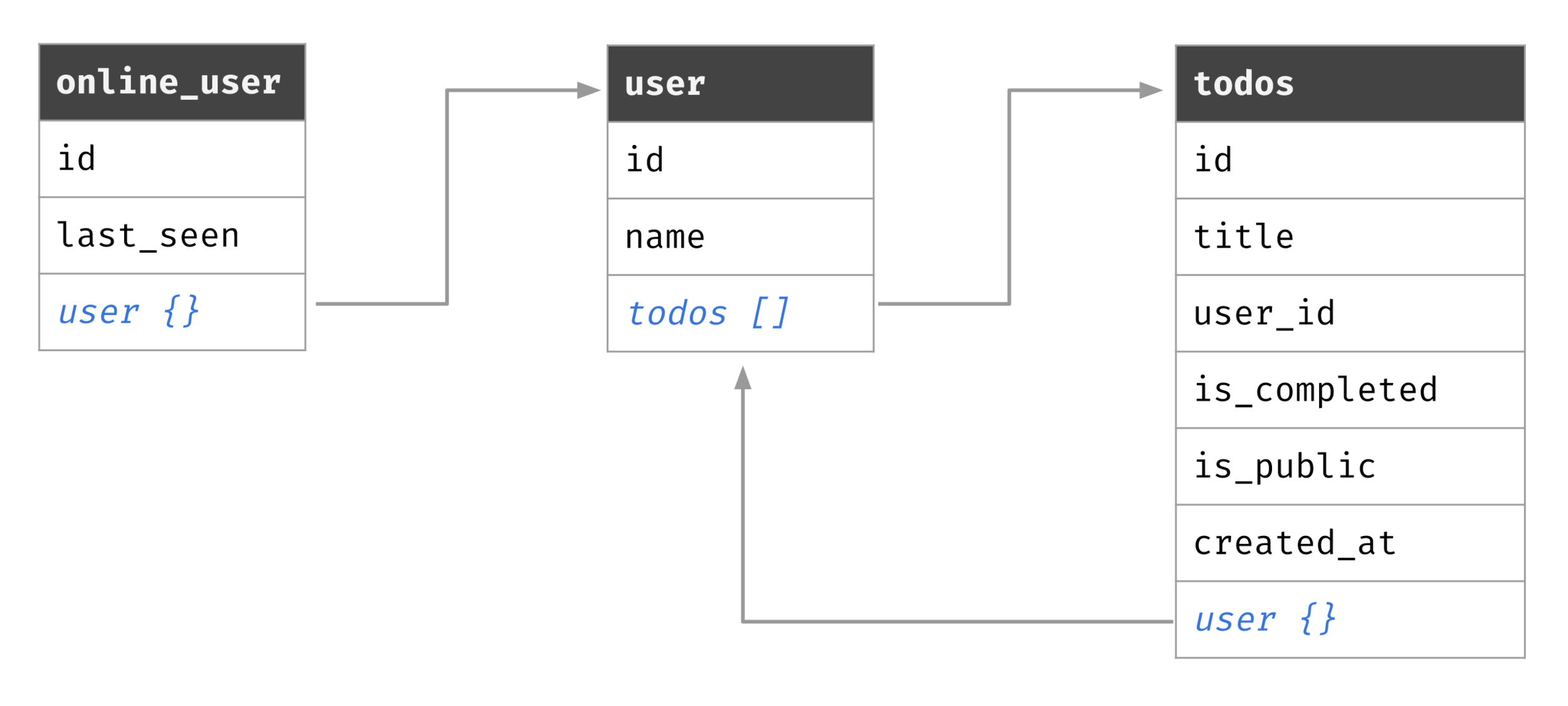
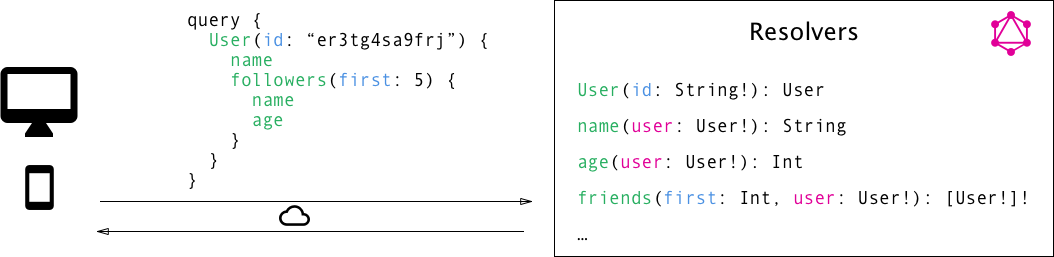
GraphQL Resolvers
Query: {
human(obj, args, context, info) {
return context.db.loadHumanByID(args.id).then(
userData => new Human(userData)
)
}
}Resolver is a function that resolves data for GraphQL type with compliance to schema
GraphQL Resolvers
Query: {
human(obj, args, context, info) {
return context.db.loadHumanByID(args.id).then(
userData => new Human(userData)
)
}
}- obj The previous object, which for a field on the root Query type is often not used.
- args The arguments provided to the field in the GraphQL query.
- context A value which is provided to every resolver and holds important contextual information like the currently logged in user, or access to a database.
- info A value which holds field-specific information relevant to the current query as well as the schema details
Server implementation
Writing your own server
yarn add apollo-server graphqlconst { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server')
const posts = [{
id: 1,
title: "Some title",
description: "Description",
userId: 1
}]
const users = [{
id: 1,
name: "Vladimir Novick",
email: "12312@asdfa.com"
}]
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
description: String!
user: User
}
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String
}
type Query {
posts: [Post]
users: [User]
}
type Mutation {
addPost(post: PostInputType): Post
}
input PostInputType {
userId: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
}
`
const resolvers = {
Query: {
posts: () => posts.map(post => {
const user = users.find(user => user.id === post.userId)
return {
id: post.id,
title: post.title,
description: post.description,
user
}
}),
users: () => users
},
Mutation: {
addPost: (_, { post: {userId, title, content}}) => {
const user = users.filter(user => user.id === userId).reduce((acc, u) => u, {})
const postToPublish = {
id: posts.reverse()[0].id + 1,
title,
description: content,
userId: user.id
}
posts.push(postToPublish)
return postToPublish
}
}
}
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers
})
server.listen().then(({ url }) => console.log(url));What about the client?
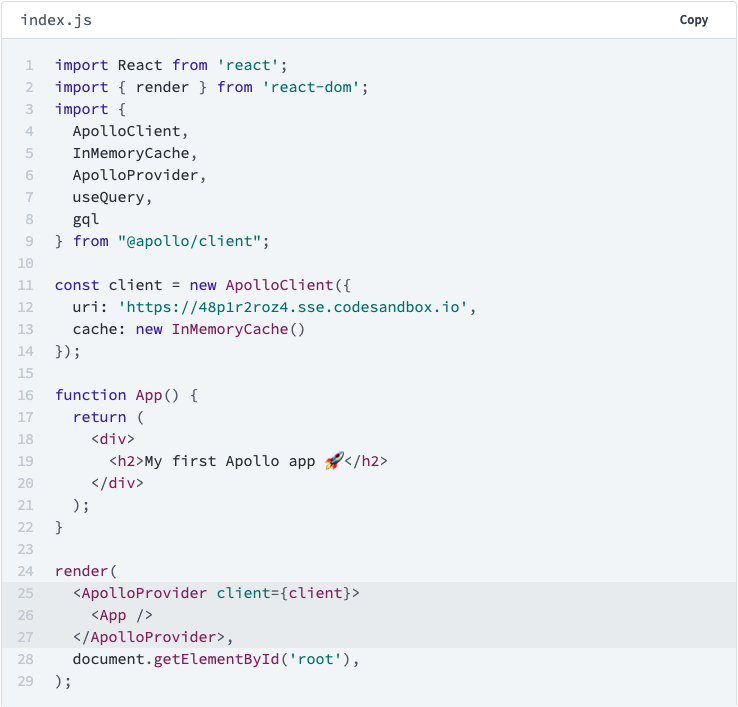
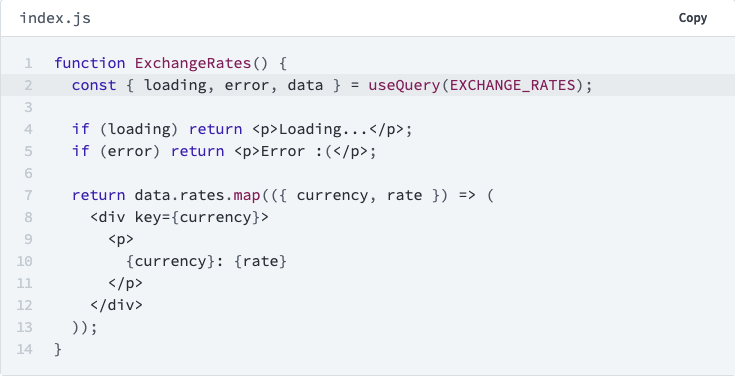
What about Architecture
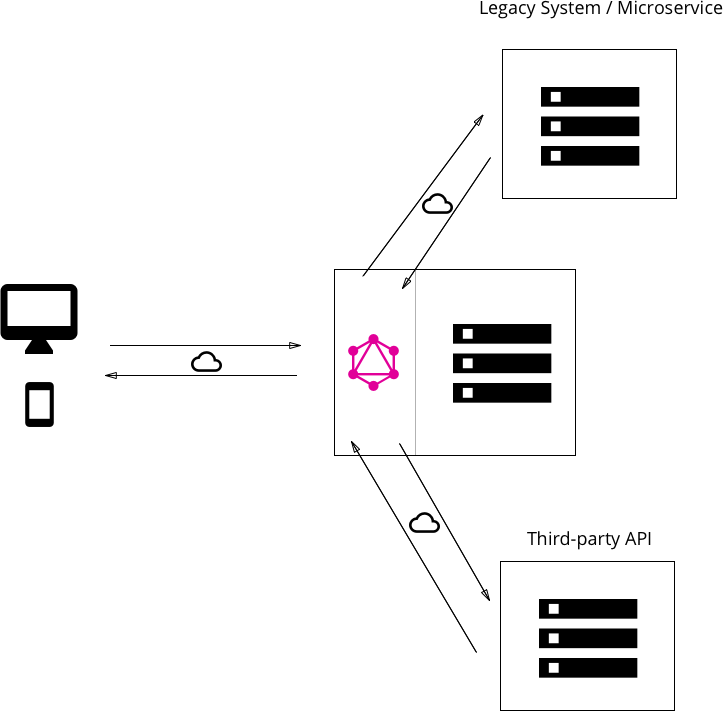
Microservices architecture
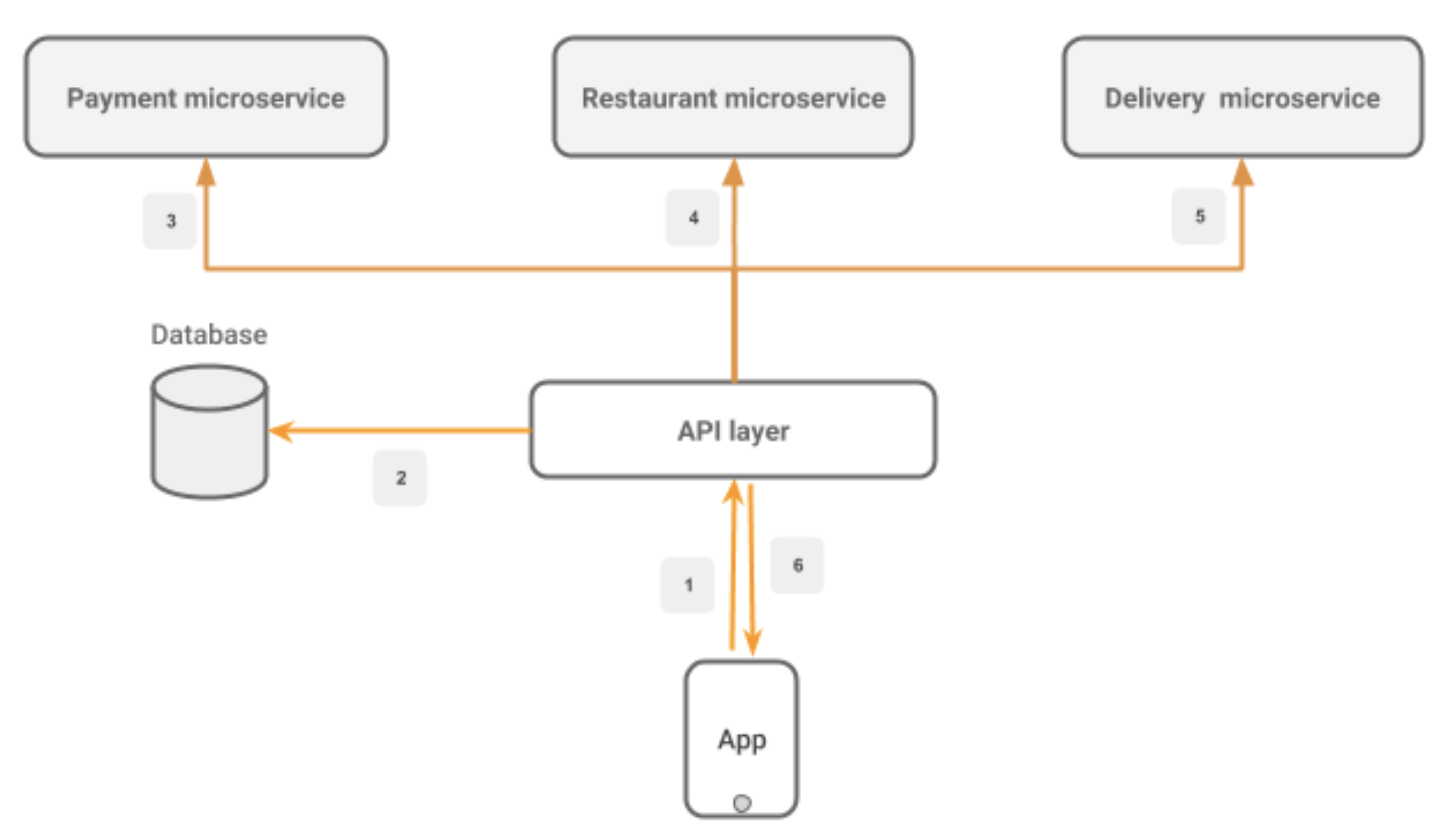
3factor.app Architecture

Thank You
@VladimirNovick