Go beyond the software, automate hardware scenarios on
Android Emulators













@vrunoa
vrunoa
vruno@saucelabs.com

Usual case scenario

describe('Android Conference login tests', async () => {
before(async () => {
driver = await wd.promiseChainRemote(endpoint)
res = await driver.init(caps)
});
after(async () => {
await driver.quit()
});
it('Test login elements are disaplyed', async () => {
let el = await driver.elementById("textUsername");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
expect(await el.text()).to.equal('Username');
el = await driver.elementById("userEditText");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
el = await driver.elementById("textPassword");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
expect(await el.text()).to.equal('Password');
el = await driver.elementById("pwdEditText");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
el = await driver.elementById("enterBtt");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
});
...
But what if we want to go beyond the user interaction with our app UI?



Inconming SMS
Phone Call is accepted
Signal strength changes
Network drops
Battery is less than 5%
Charger is disconnected
Fingerprint is used
Device is rotated
Light sensor found is too dark
...and more

Android Emulator to the rescue


Wait a minute! I have to do all this manually?
- driver.fingerprint()
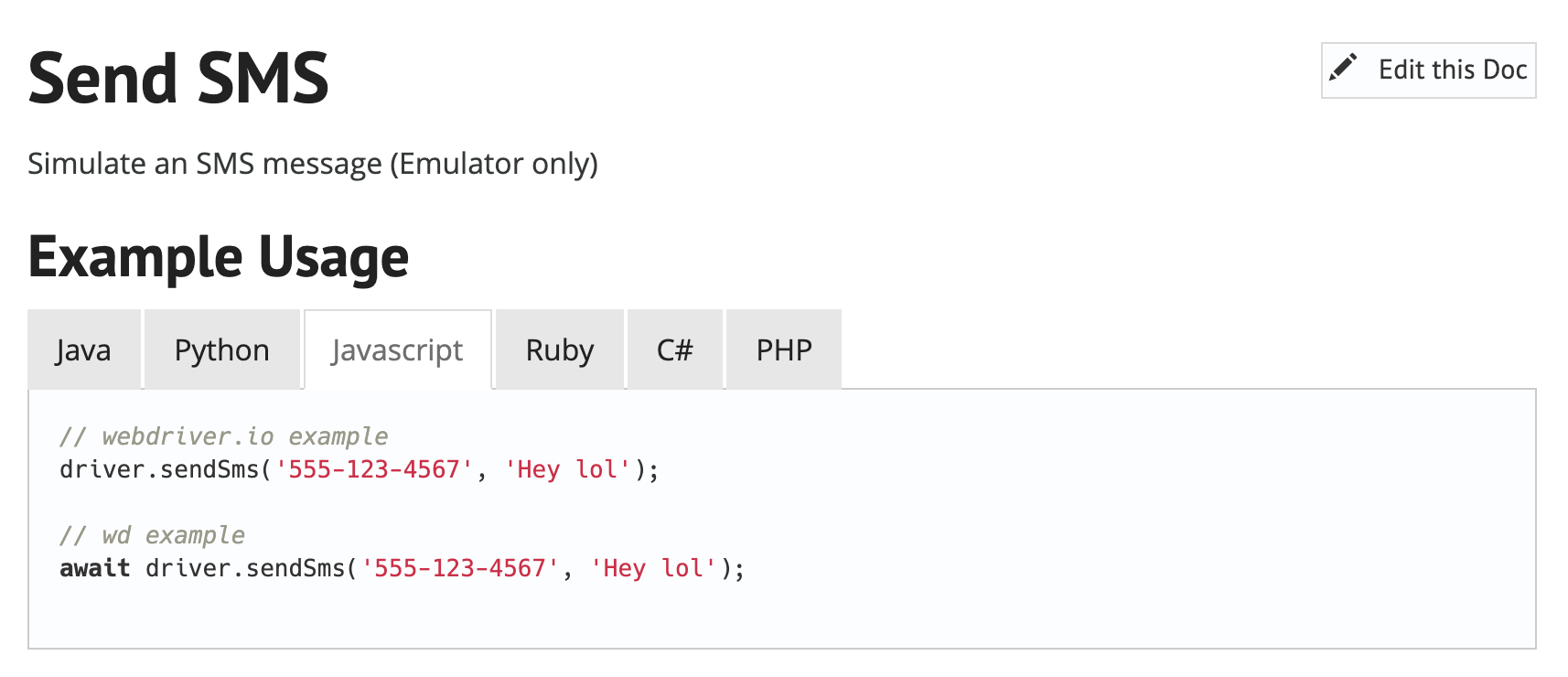
- driver.sendSms(phoneNumber, message)
- driver.gsmCall(phoneNumber, action)
- driver.gsmSignal(signalStrength)
- driver.gsmVoice(state)
- driver.powerCapacity(percent)
- driver.powerAC(state)
- driver.networkSpeed(netspeed)



Let's see some of this in action
sending and reading incoming sms

it('test code is set on SMS received', async () => {
let phoneContainer = await driver.elementById("enterPhoneContainer");
expect(await phoneContainer.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
let el = await driver.elementById("phoneEditText");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
await el.sendKeys("60512345678")
el = await driver.elementById("confirmBtt");
await el.click();
let codeContainer = await driver.elementById("validCodeContainer");
expect(await codeContainer.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
await driver.sendSms('2020', '1234');
await sleep(500);
el = await driver.elementById('smsCode1');
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("1");
el = await driver.elementById('smsCode2');
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("2");
el = await driver.elementById('smsCode3');
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("3");
el = await driver.elementById('smsCode4');
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("4");
});


handle login using the fingerprint
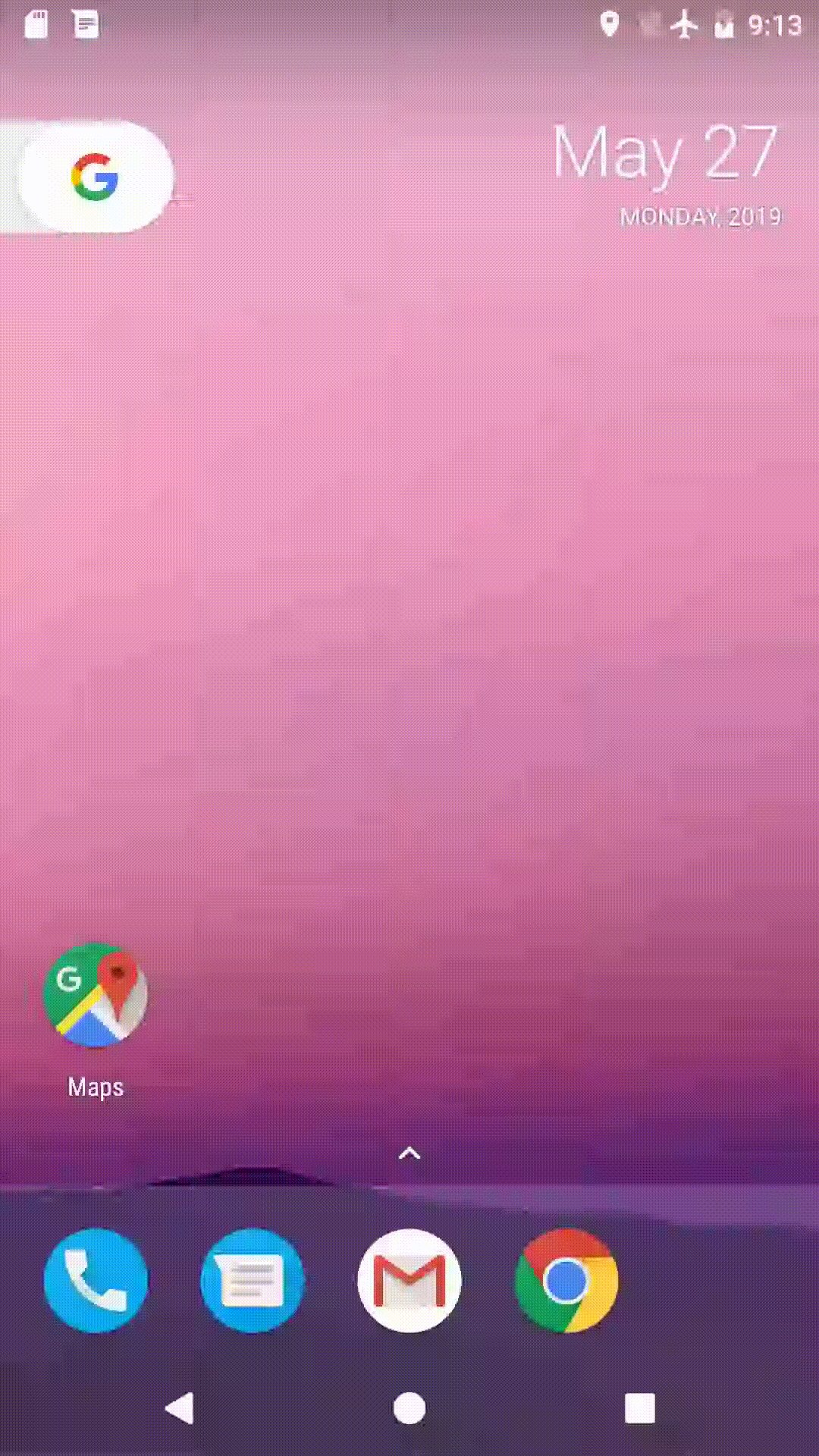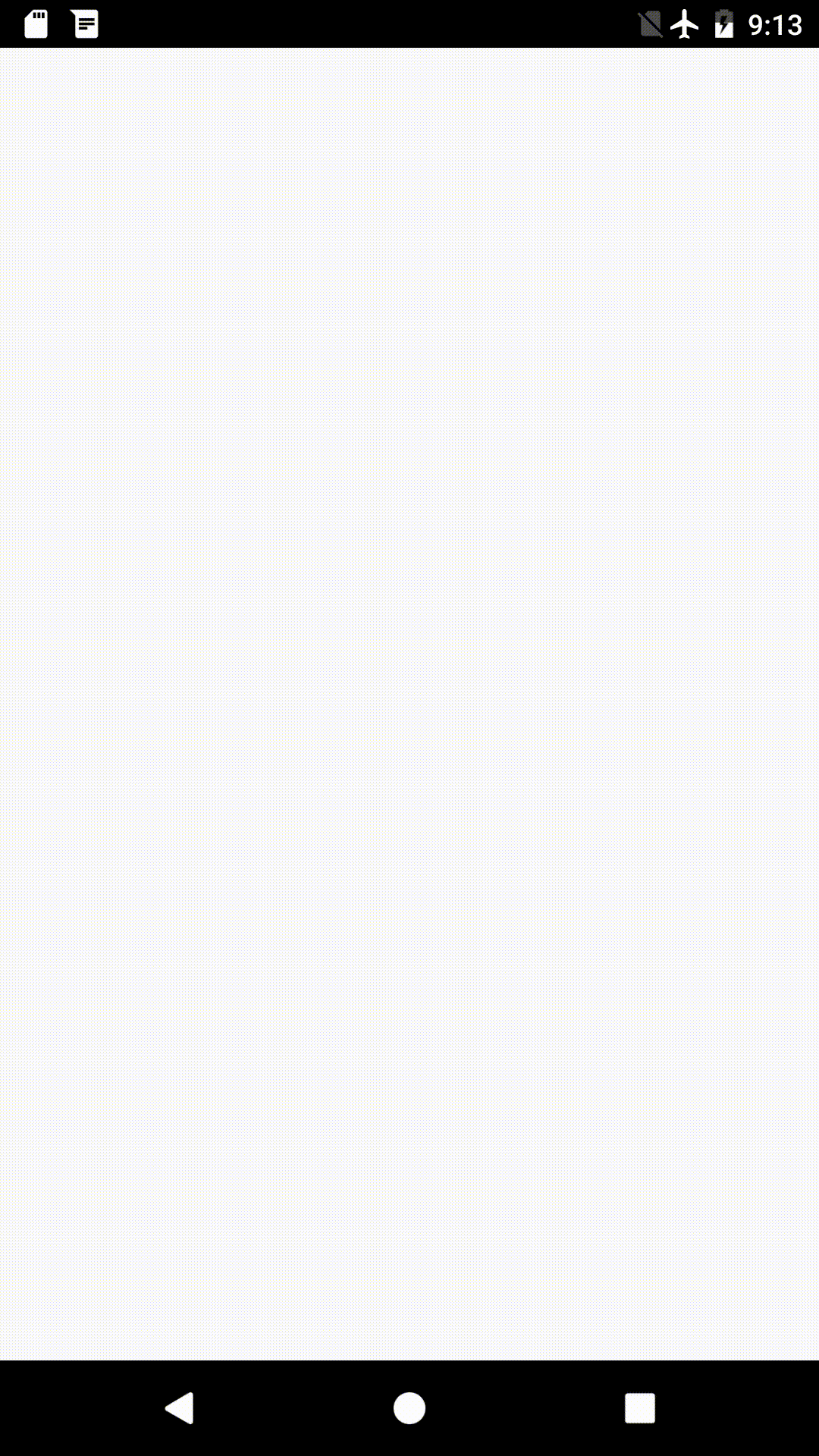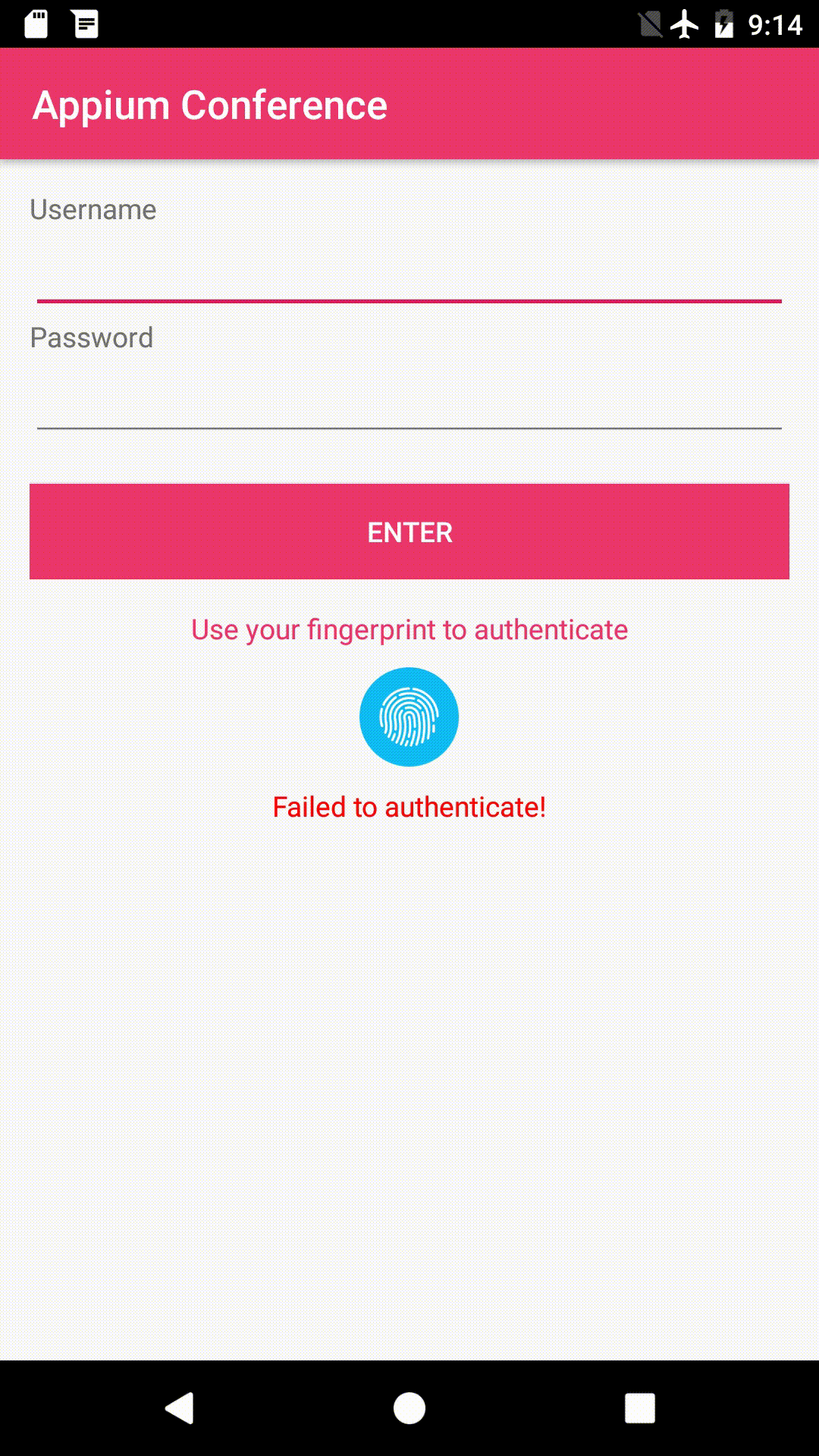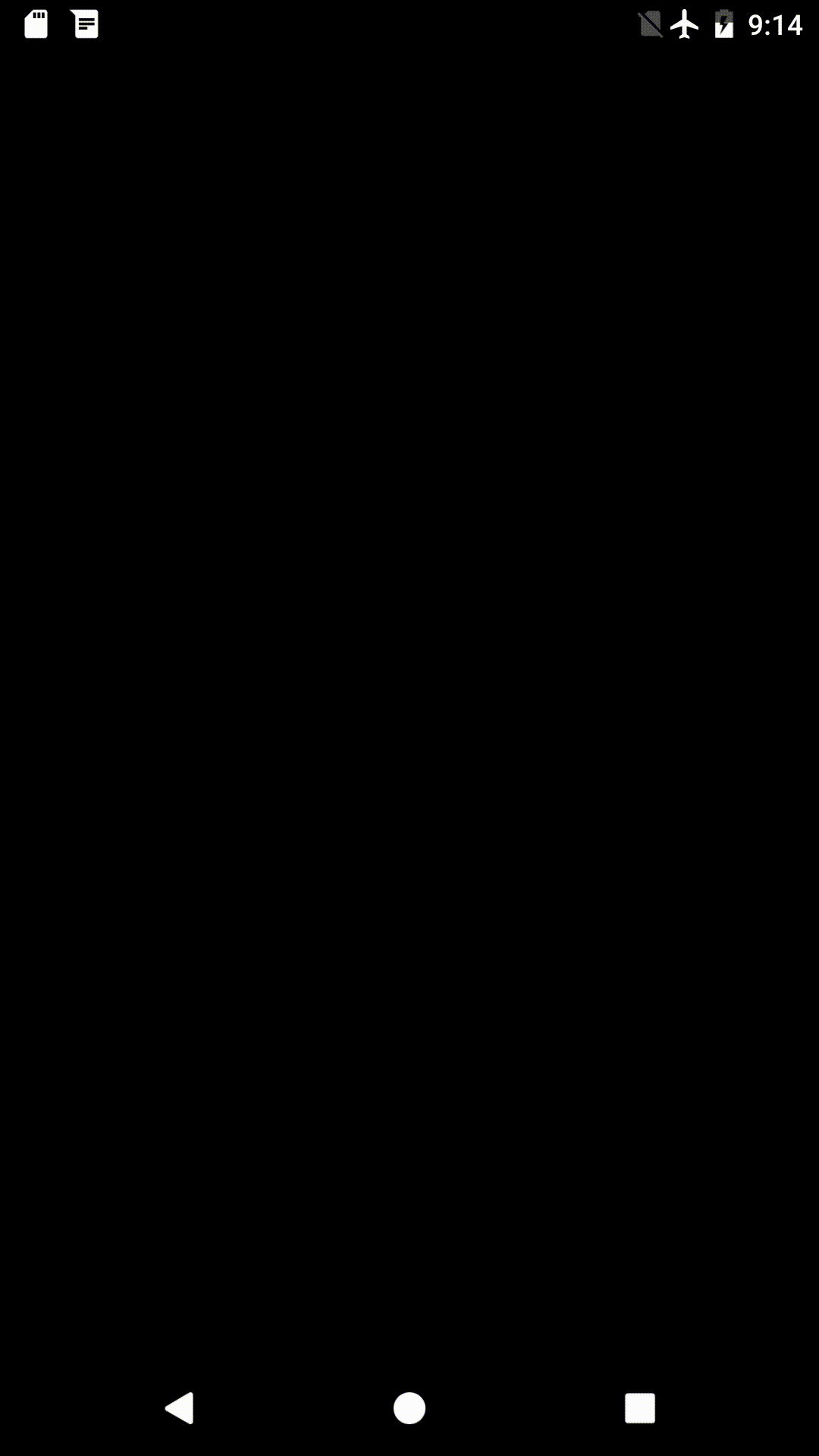
it('test shows correct message on failed fingerprint', async () => {
await driver.fingerprint(1112);
let el = await driver.elementById("fingerprintMessage");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("Failed to authenticate!");
await sleep(1500);
});
it('test shows correct message on success fingerprint', async () => {
await driver.fingerprint(1111);
let el = await driver.elementById("fingerprintMessage");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("Welcome you\'re authenticated");
await sleep(1500);
});

pause task on incoming phone call

it('test video is paused on incoming call', async () => {
await sleep(2500);
await driver.gsmCall('6505551212', 'call');
await sleep(8000);
let el = await driver.elementById('android:id/pause');
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
});
it('test video continues after call ended', async () => {
let el = await driver.elementById('android:id/pause');
await driver.gsmCall('6505551212', 'cancel');
await sleep(5000);
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(false);
await sleep(3000);
});


checking battery state

it('test battery level text is changed', async () => {
await driver.powerCapacity(52);
let el = await driver.elementById("batteryPercent");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("52%");
await sleep(1000);
});
it('test alarm starts on battery charged', async () => {
await driver.powerCapacity(100);
let el = await driver.elementById("batteryPercent");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
expect(await el.text()).to.equal("100%");
el = await driver.elementById("batteryAlarmText");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
el = await driver.elementById("stopBtt");
expect(await el.isDisplayed()).to.equal(true);
await sleep(2500);
});

How all this magic works?
adb emu sms send '6505551212' 'Hello from adb'
...become a new appium feature
adb emu sms send '6505551212' 'Hello from adb'appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium






Inconming SMS
Phone Call is accepted
Signal strength changes
Network drops
Battery is less than 5%
Charger is disconnected
Fingerprint is used
Device is rotated
Light sensor found is too dark
...and more
not supported in Appium

...until now
let's add light sensor support to Appium, right now

Light sensor found is too dark

Our light sensor application


Road to an Appium feature
adb emu ...appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium






adb emu ... ?
# inside telnet
sensor set light 6000
adb emu sensor set light X
# using adb
adb emu sensor set light 6000
Road to an Appium feature
adb emu sensor set light 6000appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium






Calling the new command from appium-adb
/**
* Emulate light sensor on the connected emulator.
*
* @param {float} light
*/
emuMethods.lightSensor = async function lightSensor (light = 0) {
// light sensor <light> allows you to set the ligth sensor values on the emulator.
await this.adbExecEmu(['sensor', 'set', 'light', light]);
};Our first step is to implement our know adb emu command in the appium-adb package. All commands for the emulator are in /lib/tools/adb-emu-commands.js
To quickly test this new appium-adb command we're going to use appium-adb-repl, a simple REPL package for appium-adb
npm linkOn the appium-adb folder we run
and in the appium-adb-repl folder we link the package
npm link appium-adb
adb.lightSensor(0);Now that we're set, let's watch it working

Road to an Appium feature
adb emu sensor set light 6000appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium







updating the driver
commands.lightSensor = async function lightSensor (light) {
if (!this.isEmulator()) {
log.errorAndThrow('lightSensor method is only available for emulators');
}
await this.adb.lightSensor(light);
};
With the method implement in appium-adb we can now call this from the driver. In the appium-android-driver we'll add a method in /lib/command/actions.js calling the lightSensor
and npm link it so it can be used in appium

Road to an Appium feature
adb emu sensor set light 6000appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium








'/wd/hub/session/:sessionId/appium/device/light_sensor': {
POST: {command: 'lightSensor', payloadParams: {required: ['light']}}
},On the appium-base-driver we are going to add the new endpoint for this new feature. All endpoints in the base driver are defined in /lib/protocol/routes.js; using finger_print method as example;
adding a new endpoint
'/wd/hub/session/:sessionId/appium/device/finger_print': {
POST: {command: 'fingerprint', payloadParams: {required: ['fingerprintId']}}
},we'll add a new light_sensor endpoint with light as a required parameter
and npm link it so it can be used in appium

Road to an Appium feature
adb emu sensor set light 6000appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium









Baking it all together into Appium
With all the changes applied to the appium dependencies, our text step is to put all this together in the appium server. In order to do this, we're going to link all the edited packages from the appium project
npm link appium-adb
npm link appium-android-driver
npm link appium-base-driverOnce appium is using all the new dependencies, let's start the appium server from the source code
node .
[Appium] Welcome to Appium v1.13.0-beta.3-light-sensor (REV 783252b09c5f932bd094b78c773da0865995f370)
[Appium] Appium REST http interface listener started on 0.0.0.0:4723
Road to an Appium feature
adb emu sensor set light 6000appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium










Updating the appium client
In our case we're going to update the Appium nodeJS client by adding a new method in lib/commands.js script.
/**
* lightSensor(light, cb) -> cb(err)
*
* @jsonWire POST /session/:sessionId/appium/device/light_sensor
*/
commands.lightSensor = function() {
var fargs = utils.varargs(arguments);
var cb = fargs.callback,
light = fargs.all[0];
var data = {light: light};
this._jsonWireCall({
method: 'POST'
, relPath: '/appium/device/light_sensor'
, data: data
, cb: simpleCallback(cb)
});
};and npm link it so it can be used in the tests we're about to create

Road to an Appium feature
adb emu sensor set light 6000appium-adbappium-android-driverappium-base-driverappiumappium clientsimplement adb emu command in
appium-adb package
add a call to appium-adb if the device in test is an emulator
add a new endpoint to call the new method
implemented in the android driver
integrate all the new dependencies
containing the emulator methods


add a new method calling the new endpoint implemented in appium











Building our light sensor test
Appium is running, the nodeJS client has been updated adding the new lightSensor method, so the only thing left is to create tests using this new feature. Let's do it. Let's create to handle this 3 case scenarios for our application:
const wd = require('wd');
...
describe('Test light sensor', async () => {
...
it('uses light mode on high luminance', async () => {
await driver.lightSensor(40000);
let container = await driver.elementById("sensorContainer");
expect(await container.getAttribute('content-desc')).to.equal("#FFFFFF");
let textEl = await driver.elementById("sensorText");
expect(await textEl.getAttribute('content-desc')).to.equal("#000000");
});
it ('uses dark mode on Zero luminance', async () => {
await driver.lightSensor(0);
await sleep(500);
let container = await driver.elementById("sensorContainer");
expect(await container.getAttribute('content-desc')).to.equal("#000000");
let textEl = await driver.elementById("sensorText");
expect(await textEl.getAttribute('content-desc')).to.equal("#FFFFFF");
});
...
});- high luminance uses light mode
- no luminance uses dark mode
- minimal luminance uses light mode

...
it('uses light mode when luminance is above the minimum', async () => {
await driver.lightSensor(5001);
await sleep(500);
let container = await driver.elementById("sensorContainer");
expect(await container.getAttribute('content-desc')).to.equal("#FFFFFF");
let textEl = await driver.elementById("sensorText");
expect(await textEl.getAttribute('content-desc')).to.equal("#000000");
});
});

Thank you!



@vrunoa
vrunoa