React Getting Started
리액트를 위한 JS 문법 정리
개발 환경 체크
React Concept
React 라이브러리
Lead Software Engineer @ProtoPie
Microsoft MVP
TypeScript Korea User Group Organizer
Marktube (Youtube)
Mark Lee
이 웅재
리액트를 위한 JS 문법 정리
-
const let
-
template string
-
arrow function
-
.bind(this)
-
const {children} = this.props;
-
...props
-
Promise
-
async await
-
Generator
var 는 문제아
-
헷갈리는 함수 레벨 스코프
-
중복 선언이 가능
-
생략도 가능
-
호이스팅
// var.js
// 1. 헷갈리는 함수 레벨 스코프
(function() {
if (true) {
var variable = 'function scope';
}
console.log(variable);
})();// var.js
// 2. 중복 선언이 가능
(function() {
var variable = 'function scope';
var variable = 'duplicated';
console.log(variable);
})();// var.js
// 3. 생략도 가능
(function() {
variable = 'no var';
console.log(variable);
})();
console.log(variable);// var.js
// 4. 호이스팅
(function() {
console.log(variable);
var variable = 'hoisted';
})();
(function() {
var variable;
console.log(variable);
variable = 'hoisted';
})();let 은 해결사
-
블록 레벨 스코프
-
중복 선언 => SyntaxError
-
호이스팅 => ReferenceError
// let.js
// 1. 블록 레벨 스코프
{
let variable = 'block scope';
console.log(variable);
}
// 2. 중복 선언 => SyntaxError
{
let variable = 'block scope';
let variable = 'duplicated';
console.log(variable);
}
// 3. 호이스팅 => ReferenceError
{
console.log(variable);
let variable = 'hoisted';
}
let 은 변경 가능, const 는 불가능
-
Primitive
-
Reference
// const.js
// Primitive
let a = 'a';
a = 'b';
a;
const c = 'c';
c = 'd'; // TypeError
c;// const.js
// Reference
let e = {
foo: 'foo',
};
e = {
bar: 'bar',
};
e;
const f = {
foo: 'foo',
};
// f = {
// foo: 'bar',
// }; TypeError
f.foo = 'bar';
f;template string
-
`문자열`
-
`${자바스크립트 표현식}`
// string.js
const name = 'Mark';
console.log('안녕하세요.\n제 이름은 ' + name + ' 입니다.');
console.log(`안녕하세요.
제 이름은 ${name} 입니다.`);
arrow function
-
자신의 this 를 만들지 않는다.
-
생성자로 사용할 수 없다.
-
항상 익명 함수
-
리턴만 있으면, {} 생략
-
인자가 하나면, () 생략
// arrow.js
function Foo() {
this.name = 'Mark';
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(this.name);
}, 1000);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.name);
}, 1000);
}
const foo = new Foo();// arrow.js
// 익명 함수를 변수에 대입해서 사용
const a = () => {
return '리턴';
};
console.log(a());
// 리턴이 바로 표현 가능하면, { return } 생략
const b = () => '리턴';
console.log(b());
// 매개변수가 한개면 () 생략
const c = props => `리턴 ${props}`;
console.log(c('프롭스'));
함수.bind(디스)
함수의 this 로 인자로 넣은 "디스" 를 사용하는 함수를 만들어 리턴
// bind.js
function hello() {
console.log(`안녕하세요 ${this.name}`);
}
const mark = {
name: 'Mark',
};
const helloMark = hello.bind(mark);
helloMark();
const anna = {
name: 'Anna',
};
const helloAnna = hello.bind(anna);
helloAnna();
Destructuring assignment
-
구조 분해 할당
-
배열, 객체
// destructuring.js
const foo = {
a: '에이',
b: '비이',
};
const { a, b } = foo;
console.log(a, b);
const bar = ['씨이', '디이'];
const [c, d] = bar;
console.log(c, d);
const { a: newA, b: newB } = foo;
console.log(newA, newB);
Spread 와 Rest
-
...
-
배열, 객체
-
1 레벨 깊이 복사
// spread.js
function sum(a, b, c) {
return a + b + c;
}
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3));
const numbers = [2, 3, 4];
console.log(sum(...numbers));// spread.js
// 1 레벨 깊이
const obj = { a: 3, b: 4, c: 5 };
const cloned = { ...obj, a: 6 };
cloned.c = 10;
console.log(obj, cloned);
// spread.js
// 2 레벨 깊이
const obj1 = { a: { b: 100 } };
const obj1Cloned = { ...obj1 };
obj1Cloned.a.b = 200;
console.log(obj1, obj1Cloned);
const obj2 = { a: { b: 100 } };
const obj2Cloned = { ...obj2, a: { ...obj2.a } };
obj2Cloned.a.b = 200;
console.log(obj2, obj2Cloned);// rest.js
function rest1(...args) {
console.log(args);
}
rest1('mark', 37, 'korea');
function rest2(name, ...args) {
console.log(name, args);
}
rest2('mark', 37, 'korea');callback
과거 비동기 처리를 위한 선택
// callback.js
function foo(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 로직
callback();
}, 1000);
}
foo(() => {
console.log('end');
});
console.log('이것이 먼저 실행');
Promise 객체
-
Promise 객체를 만들고, 로직 처리 후 성공과 실패를 알려준다.
-
then 과 catch 를 통해 메인 로직에 전달한다.
// promise.js
function foo() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 로직
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
}
foo().then(() => {
console.log('end');
});
console.log('이것이 먼저 실행');
async - await
-
기본적으로 Promise 를 사용한다.
-
then 과 catch 를 통해 메인 로직에 전달한다.
-
async 키워드가 붙은 함수 안에서만 await 키워드를 사용할 수 있다.
// async.js
function foo() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 로직
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
}
(async () => {
await foo();
console.log('end');
console.log('이것이 먼저 실행');
})();
Generator 객체
-
function* 으로 만들어진 함수를 호출하면 반환되는 객체이다.
-
function* 에서 yield 를 호출하여, 다시 제어권을 넘겨준다.
-
제너레이터 객체에 next() 함수를 호출하면, 다음 yield 지점까지 간다.
// generator.js
function* foo() {
console.log(0.5);
yield 1;
console.log(1.5);
yield 2;
console.log(2.5);
yield 3;
console.log(3.5);
}
const g = foo();
console.log(g.next().value);
console.log(g.next().value);
console.log(g.next().value);
console.log(g.next().value);
console.log(g.next().value);
// generator.js
// 핸들
let handle = null;
// 비동기 함수
function bar() {
setTimeout(() => {
handle.next('hello');
}, 1000);
}
// 핸들을 통해 컨트롤을 넘기는 제너레이터 함수
function* baz() {
const text = yield bar();
console.log(text);
}
handle = baz();
handle.next();Git Repository
개발 환경 체크
-
Node.js
- Installer
- nvm
-
Browser (Chrome)
-
Git
-
VSCode
nvm install 14.15.1
nvm use 14.15.1
nvm alias default 14.15.1React Concept
Keyword
-
Angular vs React vs Vue
-
View 를 다루는 라이브러리
-
Only Rendering & Update
-
NOT included another functionality (ex. http client, ...)
-
-
Component Based Development
-
독립적인 코드 블럭 (HTML + CSS + JavaScript)
-
작업의 단위
-
-
Virtual DOM
-
이제는 DOM 을 직접 다루지 않음.
-
-
JSX
-
NOT Templates
-
transpile to JS (Babel, TypeScript)
-
-
CSR & SSR
Component ??
<!-- HTMLElement -->
<img src="이미지 주소"/>
<button class="클래스 이름">버튼</button>
<!-- 내가 만든 컴포넌트 -->
<내가지은이름1 name="Mark" />
<내가지은이름 prop={false}>내용</내가지은이름>
<!--
- src, class, name, props 밖에서 넣어주는 데이터
- 문서(HTML), 스타일(CSS), 동작(JS) 를 합쳐서 내가 만든 일종의 태그
-->Component Based Development - Version
Component Based Development - Links

Component Based Development - Title
Component Based Development - Content

Component Based Development - Card
Component Based Development - Card
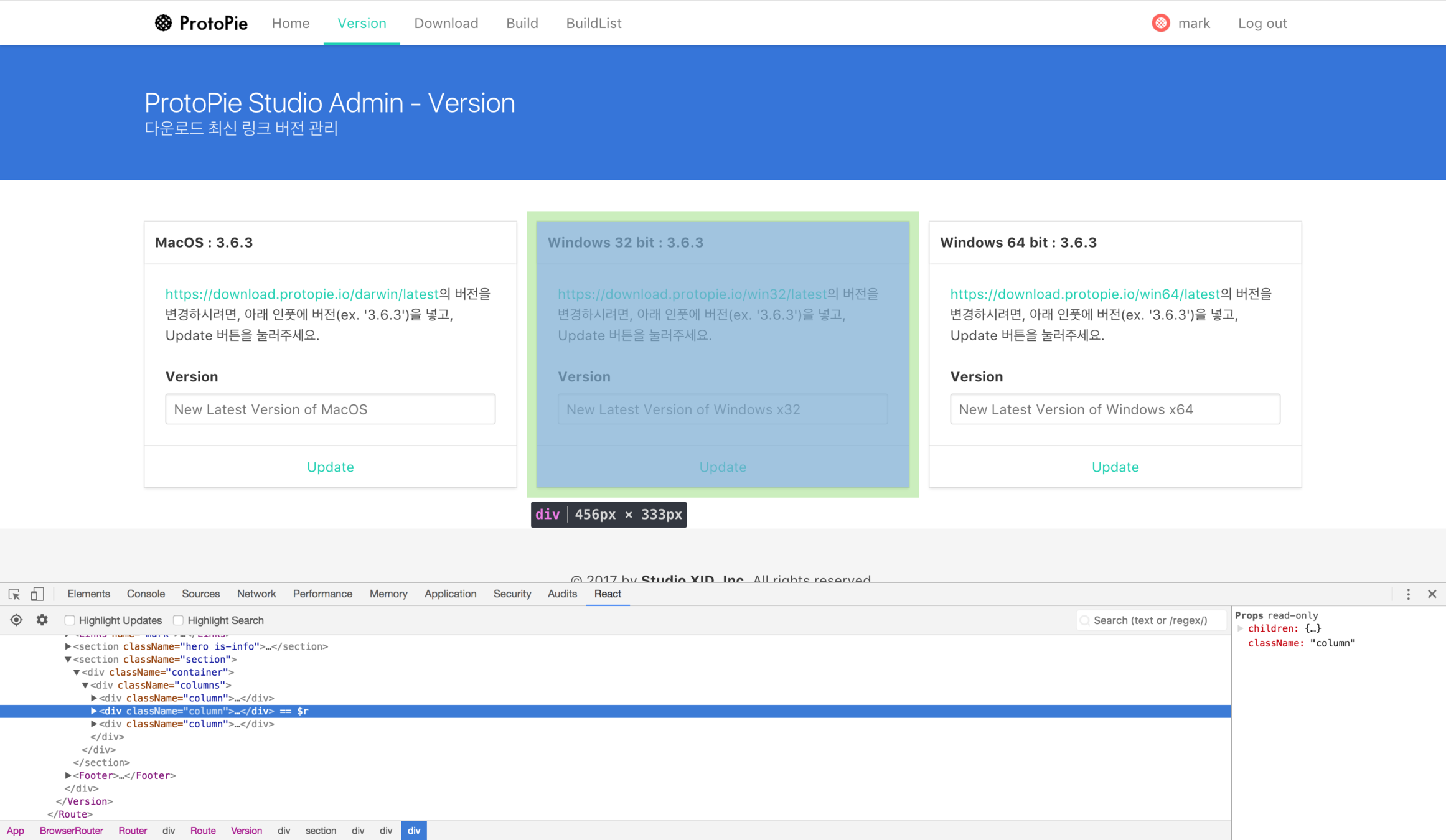

Component Based Development - Card
Component Tree => DOM Tree
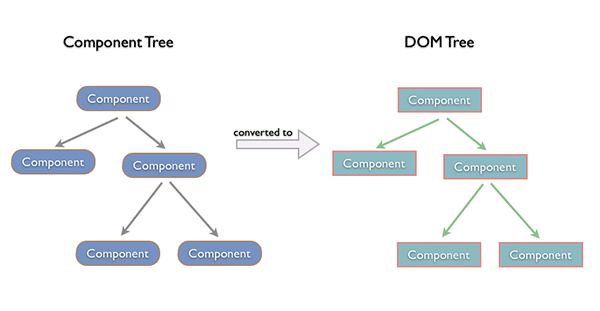
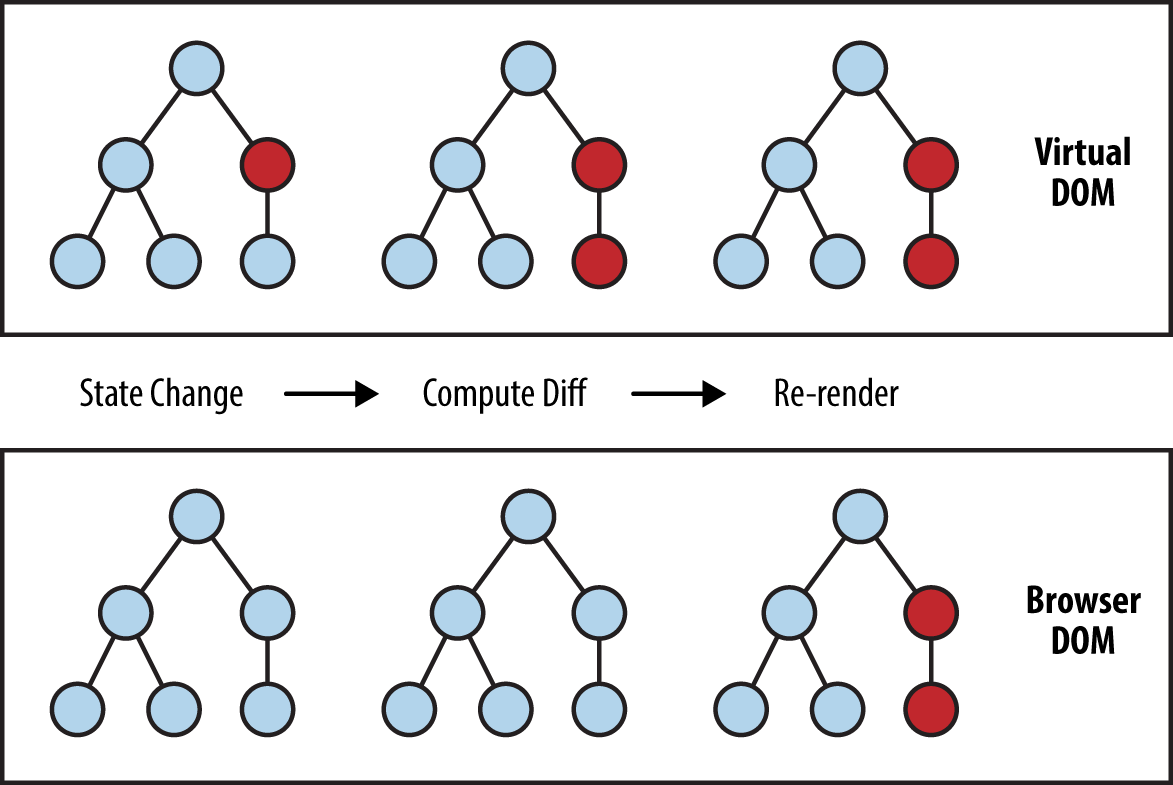
Why Virtual DOM ?
-
DOM 을 직접 제어하는 경우
-
바뀐 부분만 정확히 바꿔야 한다.
-
-
DOM 을 직접 제어하지 않는 경우
-
가상의 돔 트리를 사용해서,
-
이전 상태와 이후 상태를 비교하여,
-
바뀐 부분을 찾아내서 자동으로 바꾼다.
-
Virtual DOM - diff 로 변경
CSR vs SSR
-
CSR
-
JS 가 전부 다운로드 되어 리액트 애플리케이션이 정상 실행되기 전까지는
화면이 보이지 않음. -
JS 가 전부 다운로드 되어 리액트 애플리케이션이 정상 실행된 후,
화면이 보이면서 유저가 인터렉션 가능
-
-
SSR
-
JS 가 전부 다운로드 되지 않아도,
일단 화면은 보이지만 유저가 사용 할 수 없음. -
JS 가 전부 다운로드 되어 리액트 애플리케이션이 정상 실행된 후,
유저가 사용 가능
-
React Client Side Rendering

React Server Side Rendering

React 라이브러리
리액트가 하는 일
리액트의 핵심 모듈 2개로 리액트가 하는 일 알아보기
// 1. 리액트 컴포넌트 => HTMLElement 연결하기
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
// 2. 리액트 컴포넌트 만들기
import React from 'react';< HTMLElement >
{ React 컴포넌트 } - JS, JSX
ReactDOM.render(
<HelloMessage name="Taylor" />,
document.getElementById('hello-example'),
);class HelloMessage extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
Hello {this.props.name}
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<HelloMessage name="Taylor" />,
document.getElementById('hello-example')
);< HTMLElement >
{ React 컴포넌트 } - JS, JSX
"만들어진 리액트 컴포넌트" 를
실제 HTMLElement 에 연결할 때
ReactDOM 라이브러리를
이용합니다.

{ React 컴포넌트 } 만들기

리액트 컴포넌트를 만들 때 사용하는 API 모음
Use React, ReactDOM Library with CDN
CDN 을 통한 리액트 라이브러리 사용

<!-- ex1.html : CDN 을 통해 React, ReactDOM 가져오기 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script
crossorigin
src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js"
></script>
<script
crossorigin
src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js"
></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// Global 에 React 와 ReactDOM 객체가 생성
console.log(React);
console.log(ReactDOM);
</script>
</body>
</html>
고전 프론트엔드
HTML 로 문서 구조를 잡고,
CSS 로 스타일을 입히고,
JavaScript 로 DOM 을 조작합니다.

<!-- ex2.html : 고전 프론트엔드 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {margin: 0;padding: 0;border: 0;}
#root p {color: white;font-size: 20px;background-color: green;text-align: center;width: 200px;}
#btn_plus {background-color: red;border: 2px solid #000000;font-size: 15px;width: 200px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<button id="btn_plus">+</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
const root = document.querySelector("#root");
const btn_plus = document.querySelector("#btn_plus");
let i = 0;
root.innerHTML = `<p>init : 0</p>`;
btn_plus.addEventListener("click", () => {
root.innerHTML = `<p>init : ${++i}</p>`;
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
컴포넌트를 활용한 프론트엔드
컴포넌트를 정의하고,
실제 DOM 에 컴포넌트를 그려준다.

<!-- ex3.html : 컴포넌트를 만들고, 실제 DOM 에 그린다. -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>...</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<button id="btn_plus">+</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
// react 라이브러리가 하는 일
const component = {
message: "init",
count: 0,
render() {
return `<p>${this.message} : ${this.count}</p>`;
}
};
// react-dom 라이브러리가 하는 일
function render(dom, component) {
// 컴포넌트를 render 하고, DOM 에 그려준다.
root.innerHTML = component.render();
}
render(document.querySelector("#root"), component);
document.querySelector("#btn_plus").addEventListener("click", () => {
// 외부에서 컴포넌트의 값을 변경하는 행위
component.message = "update";
component.count = component.count + 1;
render(document.querySelector("#root"), component);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>React 프론트엔드
컴포넌트를 정의하고,
실제 DOM 에 컴포넌트를 그려준다.

브라우저 지원

<!-- ex4.html : React 로 컴포넌트를 만들고, 실제 DOM 에 그린다. -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>...</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<button id="btn_plus">+</button>
<script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
const Component = props => {
return React.createElement(
"p",
null,
`${props.message} ${props.count}`
);
};
let i = 0;
ReactDOM.render(
React.createElement(Component, { message: "init", count: i }, null),
document.querySelector("#root")
);
document.querySelector("#btn_plus").addEventListener("click", () => {
i++;
ReactDOM.render(
React.createElement(Component, { message: "update", count: i }, null),
document.querySelector("#root")
);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>React.createElement
순수 JavaScript (그렇다면 순수하지 않은 것은??)
<!-- ex5.html : React.createElement 로 컴포넌트를 만들기 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>...</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// React.createElement(
// type, // 태그 이름 문자열 | React 컴포넌트 | React.Fragment
// [props], // 리액트 컴포넌트에 넣어주는 데이터 객체
// [...children] // 자식으로 넣어주는 요소들
// );
// 1. 태그 이름 문자열 type
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement('h1', null, `type 이 "태그 이름 문자열" 입니다.`),
// document.querySelector('#root'),
// );
// 2. React 컴포넌트 type
// const Component = props => {
// return React.createElement('p', null, `type 이 "React 컴포넌트" 입니다.`);
// };
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement(
// Component,
// null,
// null
// ),
// document.querySelector("#root")
// );
// 3. React Fragment type
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement(
// React.Fragment,
// null,
// `type 이 "React Fragment" 입니다.`
// ),
// document.querySelector("#root")
// );
// 4. props 를 통해 데이터를 주입
// const Component = props => {
// return React.createElement(
// 'p',
// null,
// `message 는 "${props.message}" 입니다.`,
// );
// };
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement(
// Component,
// { message: '이것은 메세지 입니다.' },
// null,
// ),
// document.querySelector('#root'),
// );
// 5. props 에 들어가는 children
// const Component = props => {
// return React.createElement(
// 'p',
// null,
// `message 는 "${props.message}" 입니다.`,
// `props.children 은 "${props.children}" 입니다.`,
// );
// };
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement(
// Component,
// { message: '이것은 메세지 입니다.' },
// '이것은 children 입니다.',
// ),
// document.querySelector('#root'),
// );
// 6. 리액트 엘리먼트에 style 추가
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement(
// 'h1',
// { style: { color: 'red' } },
// `type 이 "태그 이름 문자열" 입니다.`,
// ),
// document.querySelector('#root'),
// );
// 7. 복잡한 컴포넌트
// ReactDOM.render(
// React.createElement(
// 'div',
// { style: { backgroundColor: 'red', width: 100, height: 100 } },
// React.createElement(
// 'div',
// { style: { backgroundColor: 'green', width: 50, height: 50 } },
// null,
// ),
// React.createElement(
// 'div',
// { style: { backgroundColor: 'yellow', width: 50, height: 50 } },
// null,
// ),
// ),
// document.querySelector('#root'),
// );
</script>
</body>
</html>