Lead Software Engineer @ProtoPie
Microsoft MVP
TypeScript Korea User Group Organizer
Marktube (Youtube)
Mark Lee
이 웅재
-
Dependency Injection
-
Inversion of control
-
inversify
-
React
Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection

dependency injection is a technique in which
an object receives other objects that it depends on.
의존성 주입은 개체가 의존하는 다른 개체들을 받는 기술입니다.
함수 hello 가 함수 person 을 사용한다.
function person(name) {
return name;
}
function hello() {
const p = person("Mark");
return `안녕하세요. 저는 ${p} 입니다.`
}
console.log(hello()); // '안녕하세요. 저는 Mark 입니다.'
// "The price of the crop" depends on "many factors".
// 그 작물의 가격은 여러 가지 요인에 달려있다.
// "Mark" depends on "his wife".
// 마크는 그의 아내에게 달려있다.
// "hello" 는 "person" 에 따라 달라진다.
// "hello" depend on "person".
// "hello"는 "person" 에 의존한다. = "hello" 는 "person" 을 의존하는 중
// 함수 person 은 함수 hello 의 의존성이다. (Dependency)person 이 바뀌면 ?
function person(name, gender) {
return `${name} (${gender})`;
}
function hello() {
const p = person("Mark", "male");
return `안녕하세요. 저는 ${p} 입니다.`
}
console.log(hello()); // '안녕하세요. 저는 Mark (male) 입니다.'
// person 의 결과가 달라지고,
// person 에 따라 hello 도 달라진다.
// hello 는 자신의 로직과 관계 없이 hello 를 테스트 하는 코드에 문제가 발생한다.개체를 만들어서 주입
function person(name, gender) {
return `${name} (${gender})`;
}
function hello(p) {
return `안녕하세요. 저는 ${p} 입니다.`
}
console.log(hello(person("Mark", "male"))); // '안녕하세요. 저는 Mark (male) 입니다.'Car
Engine
Depend on

Injecting Dependencies
Car
Engine
Dependency
자동차가 엔진을 사용하는 경우
-
자동차에서 엔진을 만들어 사용하면,
-
자동차를 테스트 할때, 엔진을 바꿀 수 없다.
-
엔진이 변경되면, 자동차의 테스트에도 영향을 준다.
-
-
엔진을 만들어서 자동차에 넣는다.
-
엔진의 인터페이스를 정의한다.
-
엔진의 인터페이스를 만족하는 실제 엔진을 만들어 엔진을 테스트 한다.
-
엔진의 인터페이스를 만족하는 테스트용 엔진을 탑재하여 자동차를 테스트한다.
-
tight coupling
interface Plan {
state: 'active' | 'none';
}
class BillingApi {
async getPlan(): Promise<Plan> {
const res = await fetch('');
return await res.json();
}
}
class BillingService {
private _billingApi = new BillingApiMock();
async getHasSubscription() {
const plan = await this._billingApi.getPlan();
return plan.state === 'active';
}
}
const hasSubscription = await new BillingService().getHasSubscription();
expect(hasSubscription).toBe(true);BillingApiMock
interface Plan {
state: 'active' | 'none';
}
interface IBillingApi {
getPlan(): Promise<Plan>;
}
class BillingApiMock implements IBillingApi {
async getPlan(): Promise<Plan> {
return {
state: 'active'
};
}
}BillingService Test - solution (1)
class BillingService {
constructor(private _billingApi: IBillingApi) {}
async getHasSubscription() {
const plan = await this.billingApi.getPlan();
return plan.state === 'active';
}
}
const hasSubscription = await new BillingService(new BillingApiMock()).getHasSubscription();
expect(hasSubscription).toBe(true);BillingService Test - solution (2)
class BillingService {
private _billingApi!: IBillingApi;
public setBillingApi(billingApi: IBillingApi) {
this._billingApi = billingApi;
}
async getHasSubscription() {
const plan = await this.billingApi.getPlan();
return plan.state === 'active';
}
}
const billingApi = new BillingApiMock();
const billinService = new BillingService();
billingService.setBillingApi(billingApi);
const hasSubscription = await billinService.getHasSubscription();
expect(hasSubscription).toBe(true);Inversion of control
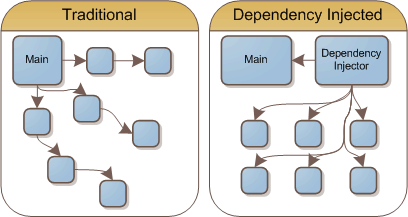
Dependency Injector
= 프로그래머 대신 디펜던시를 주입해 주는 프로그램 (라이브러리, 프레임워크)
IOC 컨테이너
// 프로그램 시작할 때
const container = new Container();
container 에 billingAPI 등록
container 에 billingService 등록
// 런타임 중에 사용하는 곳
const billingService = container 로부터 billingService 획득하기
const hasSubscription = await billingService.getHasSubscription();new 를 직접하지 않고, 컨테이너가 하는 것이 핵심
inversify
Install
mkdir inversify-test
cd inversify-test
npm init -y
npm i typescript inversify reflect-metadata ts-node
npx tsc --inittsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5" /* Specify ECMAScript target version: 'ES3' (default), 'ES5', 'ES2015', 'ES2016', 'ES2017', 'ES2018', 'ES2019', 'ES2020', or 'ESNEXT'. */,
"module": "commonjs" /* Specify module code generation: 'none', 'commonjs', 'amd', 'system', 'umd', 'es2015', 'es2020', or 'ESNext'. */,
"lib": [
"ES2015",
"DOM"
] /* Specify library files to be included in the compilation. */,
"strict": true /* Enable all strict type-checking options. */,
"esModuleInterop": true /* Enables emit interoperability between CommonJS and ES Modules via creation of namespace objects for all imports. Implies 'allowSyntheticDefaultImports'. */,
/* Experimental Options */
"experimentalDecorators": true /* Enables experimental support for ES7 decorators. */,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true /* Enables experimental support for emitting type metadata for decorators. */,
/* Advanced Options */
"skipLibCheck": true /* Skip type checking of declaration files. */,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true /* Disallow inconsistently-cased references to the same file. */
}
}
types.ts
export interface Plan {
state: "active" | "none";
}
export interface IBillingApi {
getPlan(): Promise<Plan>;
}
export interface IBillingService {
getHasSubscription(): Promise<boolean>;
}
export const TYPES = {
BillingApi: Symbol("BillingApi"),
BillingService: Symbol("BillingService"),
};
inversify.config.ts
import { Container } from "inversify";
import BillingApi from "./BillingApi";
import BillingService from "./BillingService";
import { IBillingApi, IBillingService, TYPES } from "./types";
const container = new Container();
container.bind<IBillingApi>(TYPES.BillingApi).to(BillingApi);
container.bind<IBillingService>(TYPES.BillingService).to(BillingService);
export default container;
main.ts
import container from "./inversify.config";
import { IBillingService, TYPES } from "./types";
(async () => {
const billingService = container.get<IBillingService>(TYPES.BillingService);
console.log(billingService);
const hasSubscription = await billingService.getHasSubscription();
console.log(hasSubscription);
})();
BillingApi.ts
import { injectable } from "inversify";
import "reflect-metadata";
import { IBillingApi, Plan } from "./types";
@injectable()
export default class BillingApi implements IBillingApi {
public async getPlan(): Promise<Plan> {
return {
state: "active",
};
}
}
BillingService.ts
import { injectable, inject } from "inversify";
import "reflect-metadata";
import { IBillingApi, IBillingService, TYPES } from "./types";
@injectable()
export default class BillingService implements IBillingService {
constructor(@inject(TYPES.BillingApi) private _billingApi: IBillingApi) {}
public async getHasSubscription(): Promise<boolean> {
const plan = await this._billingApi.getPlan();
return plan.state === "active";
}
}

다 있어요 공부합시다.
-
개체의 개수
-
싱글 / 멀티
-
-
여러가지 주입 방식
-
순환 참조
-
LazyServiceIdentifer
-
@lazyInject
-
React
이미 DI
// props
const Person = ({ name }) => (
<span>{ name }</span>
);
const Hello = ({ children }) => (
<div>
<p>안녕하세요. 저는 { children } 입니다.</p>
</div>
);
const App = () => (
<Hello><Person name="Mark" /></Hello>
);이미 DI
// context
const Hello = () => {
const context = useContext(PersonContext);
return (<p>안녕하세요. { context.name } 입니다.</p>);
}
const App = () => (
<PersonContext.Provider value={{ name: "Mark" }}>
<Hello />
</PersonContext.Provider>
);어디에 쓰면 좋을까요?
-
토의해보아요