TypeScript 시작하기
TypeScript 컴파일러 이해하기
Lead Software Engineer @ProtoPie
Microsoft MVP
TypeScript Korea User Group Organizer
Marktube (Youtube)
Mark Lee
이 웅재
1. What is TypeScript
2. Compiler 사용하기
3. Compiler Options
4. Basic Types, Primitive Types, Literal Types
5. var, let, const 와 type
6. Type System
1. What is TypeScript
Typed JavaScript at any Scale
-
TypeScript extends JavaScript by adding types.
-
By understanding JavaScript,
TypeScript saves you time catching errors and providing fixes
before you run code. -
Any browser, any OS, anywhere JavaScript runs.
Entirely Open Source.
TypeScript
= Language
= Typed Superset of JavaScript
= compiles to plain JavaScript


Editor
Browser, Node.js
TypeScript
Compiler
-
타입스크립트는 ' Programming Language 언어 ' 입니다.
-
타입스크립트는 ' Compiled Language ' 입니다.
-
전통적인 Compiled Language 와는 다른 점이 많습니다.
-
그래서 ' Transpile ' 이라는 용어를 사용하기도 합니다.
-
-
자바스크립트는 ' Interpreted Language ' 입니다.
Compiled
-
컴파일이 필요 O
-
컴파일러가 필요 O
-
컴파일하는 시점 O
-
=> 컴파일 타임
-
-
컴파일된 결과물을 실행
-
컴파일된 결과물을 실행하는 시점
Interpreted
-
컴파일이 필요 X
-
컴파일러가 필요 X
-
컴파일하는 시점 X
-
코드 자체를 실행
-
코드를 실행하는 시점 o
-
= 런타임
-
2. Compiler 사용하기


Editor
Browser, Node.js
TypeScript
Compiler
A. 자바스크립트 실행 환경 설치
node.js
Chrome's
V8 JavaScript Engine
을 사용하여,
자바스크립트를 해석하고
OS 레벨에서의 API를 제공하는
서버사이드 용
자바스크립트 런타임 환경
browser
HTML 을 동적으로 만들기 위해
브라우저에서
자바스크립트를 해석하고,
DOM 을 제어할 수 있도록 하는
자바스크립트 런타임 환경
node.js 설치
-
https://nodejs.org
-
v14.15.1 LTS
-
v15.2.1 Current
-
-
node.js version manager
browser 설치
-
있는거 쓰시면 됩니다.
-
그래도 크롬이 좀... 낫겠죠 ?
B. 타입스크립트 컴파일러 설치
npm / Visual Studio plugin
-
npm
-
npm i typescript -g
-
node_modules/.bin/tsc
-
tsc source.ts
-
-
Visual Studio plugin 설치
-
Visual Studio 2017 / 2015 Update 3 에서는 디폴트로 설치되어 있음
-
아니면 설치
-
C. 에디터 설치
Visual Studio Code
- Compiler
- VS Code 에 컴파일러가 내장되어 있습니다.
- 내장된 컴파일러 버전은 VS Code 가 업데이트 되면서 올라갑니다.
- 그래서 컴파일러 버전과 VS Code 의 버전은 상관 관계가 있습니다.
- 내장된 컴파일러를 선택할수 있고, 직접 설치한 컴파일러를 선택할 수도 있습니다.
Visual Studio Code

IDE : 통합 개발 환경
Integrated Development Environment
-
코딩, 디버그, 컴파일, 배포 등 프로그램 개발에 관련된 모든 작업을
하나의 프로그램 안에서 처리하는 환경을 제공하는 소프트웨어 -
Visual Studio
-
Visual Studio Code
-
타입스크립트로 만들어졌기 때문에 타입스크립트에 대한 지원이 강력
-
IntelliJ IDEA / WebStorm
-
특별한 플러그인 설치가 필요 없습니다.
ItelliJ IDEA
-
Node interpreter 를 지정해야합니다.
-
타입스크립트 컴파일러를 지정해야합니다.
-
내장된 타입스크립트 컴파일러도 있습니다.
-
설치된 타입스크립트 컴파일러를 지정할 수 있습니다.
-
-
Use TypeScript Service
-
컴파일이 아니라 컴파일 오류 체크를 해줍니다.
-
헬퍼도 해줍니다.
-
코드 완성 옵션도 있습니다.
-
-
Enable TypeScript Compiler 를 설정해서 컴파일을 할 수 있습니다.
-
gulp 같은걸 쓰지 않아도 됩니다.
-
IntelliJ IDEA - TypeScript Compiler
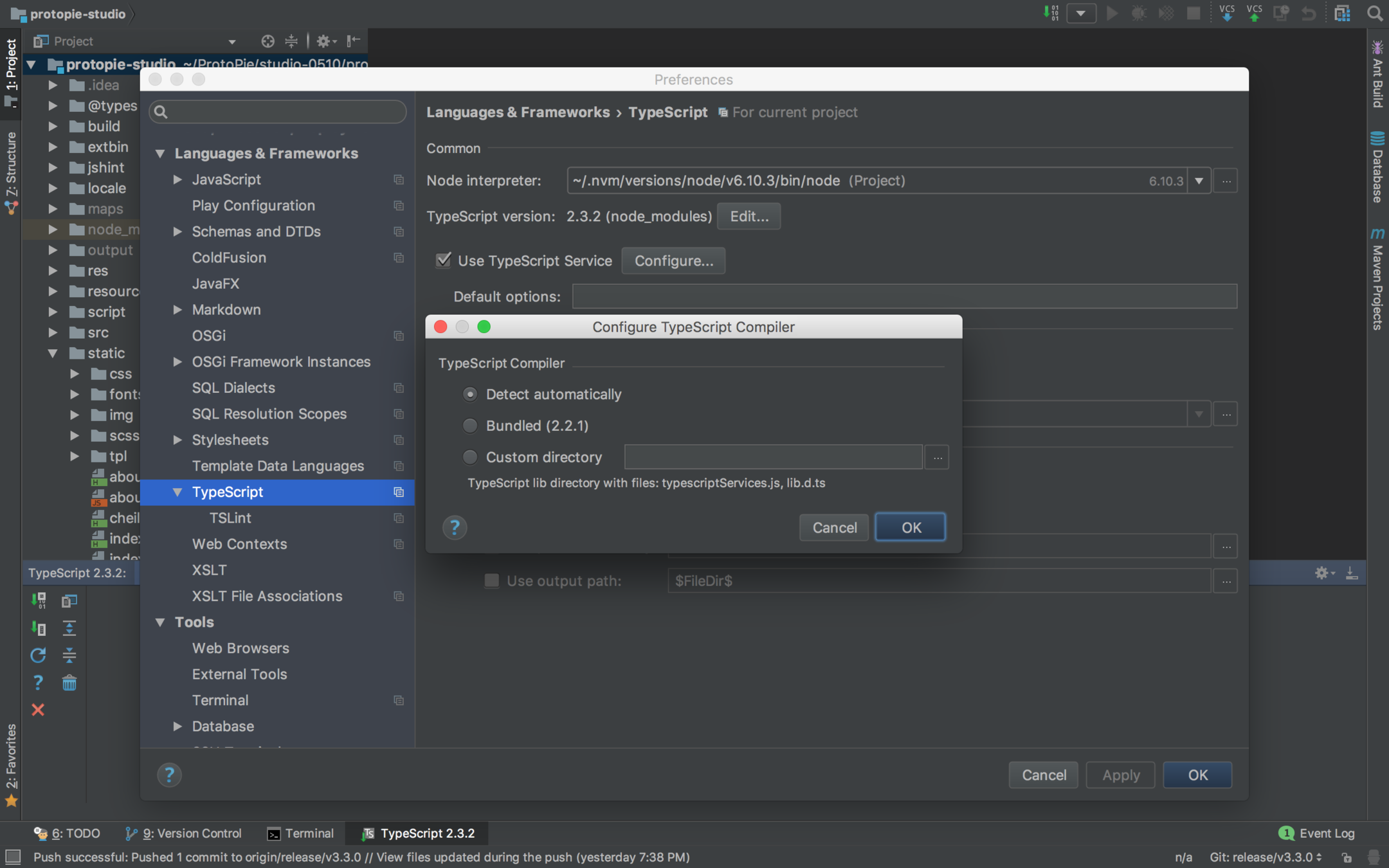
간단한 컴파일러 사용 예제
-
타입스크립트 컴파일러를 글로벌로 설치 후,
-
cli 명령어로 파일 컴파일
-
특정 프로젝트 폴더에서 타입스크립트 컴파일러 설정에 맞춰 컴파일
-
특정 프로젝트 폴더에서 타입스크립트 컴파일러 설정에 맞춰 컴파일 (watch 모드)
-
-
프로젝트에 타입스크립트 컴파일러를 설치 후,
-
.bin 안의 명령어로 파일 컴파일
-
npm 스크립트로 파일 컴파일
-
프로젝트에 있는 타입스크립트 설정에 맞춰, npm 스크립트로 컴파일
-
프로젝트에 있는 타입스크립트 설정에 맞춰, npm 스크립트로 컴파일 (watch 모드)
-
3. Compiler Options
최상위 프로퍼티
-
compileOnSave
-
extends
-
compileOptions
-
files
-
include
-
exclude
-
references
-
typeAcquisition
compileOnSave
-
true / false (default false)
-
최상단에 설정해야 한다 ?
-
누가 ??
-
Visual Studio 2015 with TypeScript 1.8.4 이상
-
atom-typescript 플러그인
-
extends
-
파일 (상대) 경로명: string
-
TypeScript 2.1 New Spec
// in config/base.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"noImplicitAny": true,
"strictNullChecks": true
}
}
// in tsconfig.json
{
"extends": "./configs/base",
"files": [
"main.ts",
"supplemental.ts"
]
}npm install --save-dev @tsconfig/deno
{
"extends": "@tsconfig/deno/tsconfig.json",
...
}files, include, exclude
-
셋다 설정이 없으면, 전부다 컴파일
-
files
-
상대 혹은 절대 경로의 리스트 배열입니다.
-
exclude 보다 쎕니다.
-
-
include, exclude
-
glob 패턴 (마치 .gitignore)
-
include
-
exclude 보다 약합니다.
-
* 같은걸 사용하면, .ts / .tsx / .d.ts 만 include (allowJS)
-
-
exclude
-
설정 안하면 4가지(node_modules, bower_components, jspm_packages, <outDir>)를 default 로 제외합니다. (아하!)
-
<outDir> 은 항상 제외합니다. (include 에 있어도)
-
-
compileOptions
{
"type": "object",
"description": "Instructs the TypeScript compiler how to compile .ts files.",
"properties": {
"charset": {
"description": "The character set of the input files.",
"type": "string"
},
"declaration": {
"description": "Generates corresponding d.ts files.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"declarationDir": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Specify output directory for generated declaration files. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later."
},
"diagnostics": {
"description": "Show diagnostic information.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"emitBOM": {
"description": "Emit a UTF-8 Byte Order Mark (BOM) in the beginning of output files.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"inlineSourceMap": {
"description": "Emit a single file with source maps instead of having a separate file.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"inlineSources": {
"description": "Emit the source alongside the sourcemaps within a single file; requires --inlineSourceMap to be set.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"jsx": {
"description": "Specify JSX code generation: 'preserve', 'react', or 'react-native'.",
"enum": [ "preserve", "react", "react-native" ]
},
"reactNamespace": {
"description": "Specifies the object invoked for createElement and __spread when targeting 'react' JSX emit.",
"type": "string"
},
"listFiles": {
"description": "Print names of files part of the compilation.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"locale": {
"description": "The locale to use to show error messages, e.g. en-us.",
"type": "string"
},
"mapRoot": {
"description": "Specifies the location where debugger should locate map files instead of generated locations",
"type": "string"
},
"module": {
"description": "Specify module code generation: 'none', 'CommonJS', 'Amd', 'System', 'UMD', or 'es2015'.",
"enum": [ "commonjs", "amd", "umd", "system", "es6", "es2015", "none" ]
},
"newLine": {
"description": "Specifies the end of line sequence to be used when emitting files: 'CRLF' (dos) or 'LF' (unix).",
"enum": [ "CRLF", "LF" ]
},
"noEmit": {
"description": "Do not emit output.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noEmitHelpers": {
"description": "Do not generate custom helper functions like __extends in compiled output.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noEmitOnError": {
"description": "Do not emit outputs if any type checking errors were reported.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noImplicitAny": {
"description": "Warn on expressions and declarations with an implied 'any' type.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noImplicitThis": {
"description": "Raise error on 'this' expressions with an implied any type.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noUnusedLocals": {
"description": "Report errors on unused locals. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noUnusedParameters": {
"description": "Report errors on unused parameters. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noLib": {
"description": "Do not include the default library file (lib.d.ts).",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noResolve": {
"description": "Do not add triple-slash references or module import targets to the list of compiled files.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"skipDefaultLibCheck": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"skipLibCheck": {
"description": "Skip type checking of declaration files. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"outFile": {
"description": "Concatenate and emit output to single file.",
"type": "string"
},
"outDir": {
"description": "Redirect output structure to the directory.",
"type": "string"
},
"preserveConstEnums": {
"description": "Do not erase const enum declarations in generated code.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"pretty": {
"description": "Stylize errors and messages using color and context (experimental).",
"type": "boolean"
},
"removeComments": {
"description": "Do not emit comments to output.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"rootDir": {
"description": "Specifies the root directory of input files. Use to control the output directory structure with --outDir.",
"type": "string"
},
"isolatedModules": {
"description": "Unconditionally emit imports for unresolved files.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"sourceMap": {
"description": "Generates corresponding '.map' file.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"sourceRoot": {
"description": "Specifies the location where debugger should locate TypeScript files instead of source locations.",
"type": "string"
},
"suppressExcessPropertyErrors": {
"description": "Suppress excess property checks for object literals.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"suppressImplicitAnyIndexErrors": {
"description": "Suppress noImplicitAny errors for indexing objects lacking index signatures.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"stripInternal": {
"description": "Do not emit declarations for code that has an '@internal' annotation.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"target": {
"description": "Specify ECMAScript target version. Permitted values are 'es3', 'es5', 'es2015', 'es2016', 'es2017' or 'esnext'.",
"type": "string",
"default": "es3",
"anyOf": [
{
"enum": [
"es3",
"es5",
"es2015",
"es2016",
"es2017",
"esnext"
]
}, {
"pattern": "^([eE][sS]([356]|(201[567])|[nN][eE][xX][tT]))$"
}
]
},
"watch": {
"description": "Watch input files.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"experimentalDecorators": {
"description": "Enables experimental support for ES7 decorators.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"emitDecoratorMetadata": {
"description": "Emit design-type metadata for decorated declarations in source.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"moduleResolution": {
"description": "Specifies module resolution strategy: 'node' (Node) or 'classic' (TypeScript pre 1.6) .",
"type": "string",
"pattern": "^(([Nn]ode)|([Cc]lassic))$",
"default": "classic"
},
"allowUnusedLabels": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Do not report errors on unused labels."
},
"noImplicitReturns": {
"description": "Report error when not all code paths in function return a value.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": {
"description": "Report errors for fallthrough cases in switch statement.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"allowUnreachableCode": {
"description": "Do not report errors on unreachable code.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": {
"description": "Disallow inconsistently-cased references to the same file.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"baseUrl": {
"description": "Base directory to resolve non-relative module names.",
"type": "string"
},
"paths": {
"description": "Specify path mapping to be computed relative to baseUrl option.",
"type": "object"
},
"rootDirs": {
"description": "Specify list of root directories to be used when resolving modules.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"typeRoots": {
"description": "Specify list of directories for type definition files to be included. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"types": {
"description": "Type declaration files to be included in compilation. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"traceResolution": {
"description": "Enable tracing of the name resolution process.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"allowJs": {
"description": "Allow javascript files to be compiled.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": {
"description": "Allow default imports from modules with no default export. This does not affect code emit, just typechecking.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"noImplicitUseStrict": {
"description": "Do not emit 'use strict' directives in module output.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"listEmittedFiles": {
"description": "Enable to list all emitted files. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"lib": {
"description": "Specify library file to be included in the compilation. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [ "es5", "es6", "es2015", "es7", "es2016", "es2017", "esnext", "dom", "dom.iterable", "webworker", "scripthost", "es2015.core", "es2015.collection", "es2015.generator", "es2015.iterable", "es2015.promise", "es2015.proxy", "es2015.reflect", "es2015.symbol", "es2015.symbol.wellknown", "es2016.array.include", "es2017.object", "es2017.sharedmemory", "esnext.asynciterable"
]
}
},
"strictNullChecks": {
"description": "Enable strict null checks. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"maxNodeModuleJsDepth": {
"description": "The maximum dependency depth to search under node_modules and load JavaScript files. Only applicable with --allowJs.",
"type": "number",
"default": 0
},
"importHelpers": {
"description": "Import emit helpers (e.g. '__extends', '__rest', etc..) from tslib. Requires TypeScript version 2.1 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"jsxFactory": {
"description": "Specify the JSX factory function to use when targeting react JSX emit, e.g. 'React.createElement' or 'h'. Requires TypeScript version 2.1 or later.",
"type": "string",
"default": "React.createElement"
},
"alwaysStrict": {
"description": "Parse in strict mode and emit 'use strict' for each source file. Requires TypeScript version 2.1 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"strict": {
"description": "Enable all strict type checking options. Requires TypeScript version 2.3 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"downlevelIteration": {
"description": "Provide full support for iterables in 'for-of', spread, and destructuring when targeting 'ES5' or 'ES3'. Requires TypeScript version 2.3 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
},
"checkJs": {
"description": "Report errors in .js files. Requires TypeScript version 2.3 or later.",
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}compileOptions : type
{
"type": "object",
"description": "Instructs the TypeScript compiler how to compile .ts files.",
"properties": {
"typeRoots": {
"description": "Specify list of directories for type definition files to be included. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"types": {
"description": "Type declaration files to be included in compilation. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}@types
-
TypeScript 2.0 부터 사용 가능해진 내장 type definition 시스템
-
아무 설정을 안하면 ?
-
node_modules/@types 라는 모든 경로를 찾아서 사용
-
-
typeRoots 를 사용하면 ?
-
배열 안에 들어있는 경로들 아래서만 가져옵니다.
-
-
types 를 사용하면 ?
-
배열 안의 모듈 혹은 ./node_modules/@types/ 안의 모듈 이름에서 찾아옵니다.
-
[] 빈 배열을 넣는다는건 이 시스템을 이용하지 않겠다는 것입니다.
-
-
typeRoots 와 types 를 같이 사용하지 않습니다.
compileOptions : target 과 lib
{
"type": "object",
"description": "Instructs the TypeScript compiler how to compile .ts files.",
"properties": {
"target": {
"description": "Specify ECMAScript target version. Permitted values are 'es3', 'es5', 'es2015', 'es2016', 'es2017' or 'esnext'.",
"type": "string",
"default": "es3",
"anyOf": [
{
"enum": [
"es3",
"es5",
"es2015",
"es2016",
"es2017",
"esnext"
]
}, {
"pattern": "^([eE][sS]([356]|(201[567])|[nN][eE][xX][tT]))$"
}
]
},
"lib": {
"description": "Specify library file to be included in the compilation. Requires TypeScript version 2.0 or later.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [ "es5", "es6", "es2015", "es7", "es2016", "es2017", "esnext", "dom", "dom.iterable", "webworker", "scripthost", "es2015.core", "es2015.collection", "es2015.generator", "es2015.iterable", "es2015.promise", "es2015.proxy", "es2015.reflect", "es2015.symbol", "es2015.symbol.wellknown", "es2016.array.include", "es2017.object", "es2017.sharedmemory", "esnext.asynciterable"
]
}
},
"noLib": {
"description": "Do not include the default library file (lib.d.ts).",
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}target 과 lib
-
target
-
빌드의 결과물을 어떤 버전으로 할 것이냐
-
지정을 안하면 es3 입니다.
-
-
lib
-
기본 type definition 라이브러리를 어떤 것을 사용할 것이냐
-
lib 를 지정하지 않을 때,
-
target 이 'es3' 이고, 디폴트로 lib.d.ts 를 사용합니다.
-
target 이 'es5' 이면, 디폴트로 dom, es5, scripthost 를 사용합니다.
-
target 이 'es6' 이면, 디폴트로 dom, es6, dom.iterable, scripthost 를 사용합니다.
-
-
lib 를 지정하면 그 lib 배열로만 라이브러리를 사용하니다.
-
빈 [] => 'no definition found 어쩌구'
-
-
compileOptions : outDir, outFile
{
"type": "object",
"description": "Instructs the TypeScript compiler how to compile .ts files.",
"properties": {
"outFile": {
"description": "Concatenate and emit output to single file.",
"type": "string"
},
"outDir": {
"description": "Redirect output structure to the directory.",
"type": "string"
},
"rootDir": {
"description": "Specifies the root directory of input files. Use to control the output directory structure with --outDir.",
"type": "string"
}
}
}compileOptions : module
{
"type": "object",
"description": "Instructs the TypeScript compiler how to compile .ts files.",
"properties": {
"module": {
"description": "Specify module code generation: 'none', 'CommonJS', 'Amd', 'System', 'UMD', or 'es2015'.",
"enum": [ "commonjs", "amd", "umd", "system", "es6", "es2015", "none" ]
},
"moduleResolution": {
"description": "Specifies module resolution strategy: 'node' (Node) or 'classic' (TypeScript pre 1.6) .",
"type": "string",
"pattern": "^(([Nn]ode)|([Cc]lassic))$",
"default": "classic"
},
"baseUrl": {
"description": "Base directory to resolve non-relative module names.",
"type": "string"
},
"paths": {
"description": "Specify path mapping to be computed relative to baseUrl option.",
"type": "object"
},
"rootDirs": {
"description": "Specify list of root directories to be used when resolving modules.",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}module
-
module
-
컴파일 된 모듈의 결과물을 어떤 모듈 시스템으로 할지를 결정
-
target 이 'es6' 이면 es6 가 디폴트이고,
-
target 이 'es6' 가 아니면 commonjs 가 디폴트 입니다.
-
AMD 나 System 와 사용하려면, outFile 이 지정되어야 합니다.
-
ES6 나 ES2015 를 사용하려면, target 이 es5 이하여야 합니다.
-
-
moduleResolution
-
ts 소스에서 모듈을 사용하는 방식을 지정해야 합니다.
-
Classic 아니면 Node 입니다.
-
CommonJS 일때만 Node 라고 생각하시면 됩니다.
-
-
paths 와 baseUrl
-
상대경로 방식이 아닌 baseUrl 로 꼭지점과 paths 안의 키/밸류로 모듈을 가져가는 방식입니다.
-
-
rootDirs : 배열 안에서 상대 경로를 찾는 방식입니다.
references
-
작은 프로젝트로 나눠서 설정할 수 있는 방법
-
{path: "하위 프로젝트의 tsconfig 가 있는 폴더 혹은 tsconfig 파일"}
{
"type": "array",
"description": "Referenced projects. Requires TypeScript version 3.0 or later.",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Project reference.",
"properties": {
"path": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Path to referenced tsconfig or to folder containing tsconfig."
}
}
}
}4. Basic Types,
Primitive Types,
Literal Types
-
TypeScript 에서 프로그램 작성을 위해 기본 제공하는 데이터 타입
-
사용자가 만든 타입은 결국은 이 기본 자료형들로 쪼개집니다.
-
JavaScript 기본 자료형을 포함 (superset)
-
ECMAScript 표준에 따른 기본 자료형은 6가지
-
Boolean
-
Number
-
String
-
Null
-
Undefined
-
Symbol (ECMAScript 6 에 추가)
-
Array : object 형
-
-
-
프로그래밍을 도울 몇가지 타입이 더 제공된다.
-
Any, Void, Never, Unknown
-
Enum
-
Tuple : object 형
-
Primitive Type
-
오브젝트와 레퍼런스 형태가 아닌 실제 값을 저장하는 자료형입니다.
-
프리미티브 형의 내장 함수를 사용 가능한것은 자바스크립트 처리 방식 덕분
let name = 'mark';
name.toString();literal ?
-
값자체가 변하지 않는 값을 의미합니다.
-
상수와 다른 것은 상수는 가리키는 포인터가 고정이라는 것이고, 리터럴은 그 자체가 값이자 그릇입니다.
35; // number 리터럴
'mark' // string 리터럴
true // boolean 리터럴
// object 리터럴
{
name: 'mark',
age: 35
}literal ?
-
값자체가 변하지 않는 값을 의미합니다.
-
상수와 다른 것은 상수는 가리키는 포인터가 고정이라는 것이고, 리터럴은 그 자체가 값이자 그릇입니다.
-
"리터럴 상수는 5, 1.23 과 같은 숫자나, 과 같은 문자열 등을 말합니다. 'This is a string' 혹은 "It’s a string!"이것들이 리터럴 상수라고 불리우는 이유는 이것들이 프로그램 내에 직접 문자 형태로(literally)지정되는 값들이기 때문입니다. 이러한 값들은 한번 지정되면 변하지 않습니다. 예를 들면 숫자2 는 언제나 자기 자신이 2라는 숫자임을 나타내며 어떤 다른 의미도 갖지 않습니다. 이들은 한번 지정되면 그 값을 변경할 수 없기 때문에 _상수_입니다. 그 중에서도 특별히 이러한 값들을 리터럴 상수라고 부릅니다."
Boolean / boolean
-
가장 기본적인 데이터 타입
-
단순한 true 혹은 false 값 입니다.
-
JavaScript / TypeScript 에서 'boolean' 이라고 부른다.
let isDone: boolean = false;
typeof isDone === 'boolean' // true
// Type 'boolean' is assignable to type 'Boolean'.
let isOk: Boolean = true;
// Type 'Boolean' is not assignable to type 'boolean'.
// 'boolean' is a primitive, but 'Boolean' is a wrapper object.
// Prefer using 'boolean' when possible.
let isNotOk: boolean = new Boolean(true);Number / number
-
JavaScript 와 같이, TypeScript 의 모든 숫자는 부동 소수점 값 입니다.
-
TypeScript는 16진수 및 10진수 리터럴 외에도, ECMAScript 2015에 도입된 2진수 및 8진수를 지원합니다.
let decimal: number = 6; // 10진수 리터럴
let hex: number = 0xf00d; // 16진수 리터럴
let binary: number = 0b1010; // 2진수 리터럴
let octal: number = 0o744; // 8진수 리터럴String / string
-
다른 언어에서와 마찬가지로이 텍스트 형식을 참조하기 위해 `string` 형식을 사용합니다.
-
JavaScript 와 마찬가지로, TypeScript는 문자열 데이터를 둘러싸기 위해 큰 따옴표 ( " ) 나, 작은 따옴표 ( ' ) 를 사용합니다.
let name: string = "mark";
name = 'anna';Template String
-
행에 걸쳐 있거나, 표현식을 넣을 수 있는 문자열
-
이 문자열은 backtick (= backquote) 기호에 둘러쌓여 있습니다.
-
포함된 표현식은 `${ expr }` 와 같은 형태로 사용합니다.
let fullName: string = `Bob Bobbington`;
let age: number = 38;
let sentence: string = `Hello, my name is ${ fullName }.
I'll be ${ age + 1 } years old next month.`;
// template string 을 사용하지 않을 경우
let sentence: string = "Hello, my name is " + fullName + ".\n\n" +
"I'll be " + (age + 1) + " years old next month.";Undefined & Null
-
TypeScript 에서 'undefined' 와 'null' 은 실제로 각각 'undefined' 와 'null' 이라는 고유한 타입을가집니다.
-
'void' 와 마찬가지로, undefined 와 null 은 그 자체로는 쓸모가 없습니다.
-
둘다 소문자만 존재합니다.
// 이 변수들에 할당할 수 있는 것들은 거의 없다.
let u: undefined = undefined;
let n: null = null;undefined & null are subtypes
of all other types.
-
기본 설정이 그렇습니다.
-
number 에 null 또는 undefined 를 할당할 수 있다는 의미입니다.
-
하지만, 컴파일 옵션에서 `--strictNullChecks`사용하면, null 과 undefined 는 void 나 자기 자신들에게만 할당할 수 있습니다.
-
이 경우, null 과 undefined 를 할당할 수 있게 하려면, union type 을 이용해야 합니다.
-
let name: string = null;
let age: number = undefined;
// strictNullChecks => true
// Type 'null' is not assignable to type 'string'.
let name: string = null; (X)
// null => null || void, undefined => undefined || void
// Type 'null' is not assignable to type 'undefined'.
let u: undefined = null; // (X)
let v: void = undefined; // (O)
let union: string | null | undefined = 'str';null in JavaScript
-
null 이라는 값으로 할당된 것을 null 이라고 합니다.
-
무언가가 있는데, 사용할 준비가 덜 된 상태.
-
null 이라는 타입은 null 이라는 값만 가질 수 있습니다.
-
런타임에서 typeof 연산자를 이용해서 알아내면, object 입니다.
let n: null = null;
console.log(n); // null
console.log(typeof n); // objectundefined in JavaScript
-
값을 할당하지 않은 변수는 undefined 라는 값을 가집니다.
-
무언가가 아예 준비가 안된 상태
-
object 의 property 가 없을 때도 undefined 입니다.
-
런타임에서 typeof 연산자를 이용해서 알아내면, undefined 입니다.
let u: undefined = undefined;
console.log(u); // undefined
console.log(typeof u); // undefinedVoid
-
타입이 없는 상태입니다.
-
`any` 와 반대의 의미를 가집니다.
-
Void 는 없습니다. 소문자입니다.
-
주로 함수의 리턴이 없을 때 사용합니다. 그 외에는 사용할 일이 거의 없습니다.
function returnVoid(message): void {
console.log(message);
}
returnVoid('리턴이 없다');Any
-
어떤 타입이어도 상관없는 타입입니다.
-
이걸 최대한 쓰지 않는게 핵심입니다.
-
왜냐면 컴파일 타임에 타입 체크가 정상적으로 이뤄지지 않기 때문입니다.
-
그래서 컴파일 옵션 중에는 any 를 쓰면 오류를 뱉도록 하는 옵션도 있습니다.
-
noImplicitAny
-
function returnAny(message): any {
console.log(message);
}
returnVoid('리턴은 아무거나');Never
-
리턴에 주로 사용됩니다.
-
아래 3가지 정도의 경우가 대부분입니다.
// Function returning never must have unreachable end point
function error(message: string): never {
throw new Error(message);
}
// Inferred return type is never
function fail() {
return error("Something failed");
}
// Function returning never must have unreachable end point
function infiniteLoop(): never {
while (true) {
}
}Array
-
원래 자바스크립트에서 array 는 객체입니다.
-
사용방법
-
Array<타입>
-
타입[]
-
let list: number[] = [1, 2, 3];
let list: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3];Tuple
-
배열인데 타입이 한가지가 아닌 경우
-
마찬가지로 객체입니다.
-
꺼내 사용할때 주의가 필요합니다.
-
배열을 Destructuting 하면 타입이 제대로 얻어집니다.
-
// Declare a tuple type
let x: [string, number];
// Initialize it
x = ["hello", 10]; // OK
// Initialize it incorrectly
x = [10, "hello"]; // Error
x[3] = "world"; // OK, 'string' can be assigned to 'string | number'
console.log(x[5].toString()); // OK, 'string' and 'number' both have 'toString'
x[6] = true; // Error, 'boolean' isn't 'string | number'
const person: [string, number] = ['mark', 35];
const [name, age] = person;Enum
-
C 에서 보던것과 같습니다.
-
아래 예제만 이해하면 사용 준비 끝
enum Color {Red, Green, Blue}
let c: Color = Color.Green;
enum Color {Red = 1, Green, Blue}
let c: Color = Color.Green;
enum Color {Red = 1, Green = 2, Blue = 4}
let c: Color = Color.Green;
enum Color {Red = 1, Green, Blue}
let colorName: string = Color[2];Symbol
-
ECMAScript 2015 의 Symbol 입니다.
-
프리미티브 타입의 값을 담아서 사용합니다.
-
고유하고 수정불가능한 값으로 만들어줍니다.
-
그래서 주로 접근을 제어하는데 쓰는 경우가 많았습니다.
let sym = Symbol();
let obj = {
[sym]: "value"
};
console.log(obj[sym]); // "value"5. var, let, const 와 type
var 는 문제아
-
헷갈리는 함수 레벨 스코프
-
중복 선언이 가능
-
생략도 가능
-
호이스팅
// var.js
// 1. 헷갈리는 함수 레벨 스코프
(function() {
if (true) {
var variable = 'function scope';
}
console.log(variable);
})();// var.js
// 2. 중복 선언이 가능
(function() {
var variable = 'function scope';
var variable = 'duplicated';
console.log(variable);
})();// var.js
// 3. 생략도 가능
(function() {
variable = 'no var';
console.log(variable);
})();
console.log(variable);// var.js
// 4. 호이스팅
(function() {
console.log(variable);
var variable = 'hoisted';
})();
(function() {
var variable;
console.log(variable);
variable = 'hoisted';
})();let 은 해결사
-
블록 레벨 스코프
-
중복 선언 => syntax error
-
호이스팅 => syntax error
// let.js
// 1. 블록 레벨 스코프
{
let variable = 'block scope';
console.log(variable);
}
// 2. 중복 선언 => SyntaxError
{
let variable = 'block scope';
let variable = 'duplicated';
console.log(variable);
}
// 3. 호이스팅 => ReferenceError
{
console.log(variable);
let variable = 'hoisted';
}
let 은 변경 가능, const 는 불가능
-
Primitive
-
Reference
// const.js
// Primitive
let a = 'a';
a = 'b';
a;
const c = 'c';
c = 'd'; // TypeError
c;// const.js
// Reference
let e = {
foo: 'foo',
};
e = {
bar: 'bar',
};
e;
const f = {
foo: 'foo',
};
// f = {
// foo: 'bar',
// }; TypeError
f.foo = 'bar';
f;6. Type System
타입 시스템
-
컴파일러에게 사용하는 타입을 명시적으로 지정하는 시스템
-
컴파일러가 자동으로 타입을 추론하는 시스템
타입스크립트의 타입 시스템
-
타입을 명시적으로 지정할 수 있다.
-
타입을 명시적으로 지정하지 않으면, 타입스크립트 컴파일러가 자동으로 타입을 추론
형태를 정해둔 함수
자신의 코드에서 해당 함수를 사용하는 사용자
해당 함수를 구현하는 구현자
타입이란 해당 변수가 할 수 있는 일을 결정합니다.
// JavaScript
// f1 이라는 함수의 body 에서는 a 를 사용할 것 입니다.
// a 가 할 수 있는 일은 a 의 타입이 결정합니다.
function f1(a) {
return a;
}함수 사용법에 대한 오해를 야기하는 자바스크립트
// JavaScript
// (f2 실행의 결과가 NaN 을 의도한 것이 아니라면)
// 이 함수의 작성자는 매개변수 a 가 number 타입이라는 가정으로 함수를 작성했습니다.
function f2(a) {
return a * 38;
}
// 사용자는 사용법을 숙지하지 않은 채, 문자열을 사용하여 함수를 실행했습니다.
console.log(f2(10)); // 380
console.log(f2('Mark')); // NaN타입스크립트의 추론에 의지하는 경우
// 타입스크립트 코드지만,
// a 의 타입을 명시적으로 지정하지 않은 경우이가 때문에 a 는 any 로 추론됩니다.
// 함수의 리턴 타입은 number 로 추론됩니다. (NaN 도 number 의 하나입니다.)
function f3(a) {
return a * 38;
}
// 사용자는 a 가 any 이기 때문에, 사용법에 맞게 문자열을 사용하여 함수를 실행했습니다.
console.log(f3(10)); // 380
console.log(f3('Mark') + 5); // NaN
noImplicitAny 옵션을 켜면
타입을 명시적으로 지정하지 않은 경우,
타입스크립트가 추론 중 `any` 라고 판단하게 되면,
컴파일 에러를 발생시켜
명시적으로 지정하도록 유도한다.
noImplicitAny 에 의한 방어
// error TS7006: Parameter 'a' implicitly has an 'any' type.
function f3(a) {
return a * 38;
}
// 사용자의 코드를 실행할 수 없습니다. 컴파일이 정상적으로 마무리 될 수 있도록 수정해야 합니다.
console.log(f3(10));
console.log(f3('Mark') + 5);
number 타입으로 추론된 리턴 타입
// 매개변수의 타입은 명시적으로 지정했습니다.
// 명시적으로 지정하지 않은 함수의 리턴 타입은 number 로 추론됩니다.
function f4(a: number) {
if (a > 0) {
return a * 38;
}
}
// 사용자는 사용법에 맞게 숫자형을 사용하여 함수를 실행했습니다.
// 해당 함수의 리턴 타입은 number 이기 때문에, 타입에 따르면 이어진 연산을 바로 할 수 있습니다.
// 하지만 실제 undefined + 5 가 실행되어 NaN 이 출력됩니다.
console.log(f4(5)); // 190
console.log(f4(-5) + 5); // NaN
strictNullChecks 옵션을 켜면
모든 타입에 자동으로 포함되어 있는
`null` 과 `undefined` 를
제거해줍니다.
number | undefined 타입으로 추론된 리턴 타입
// 매개변수의 타입은 명시적으로 지정했습니다.
// 명시적으로 지정하지 않은 함수의 리턴 타입은 number | undefined 로 추론됩니다.
function f4(a: number) {
if (a > 0) {
return a * 38;
}
}
// 사용자는 사용법에 맞게 숫자형을 사용하여 함수를 실행했습니다.
// 해당 함수의 리턴 타입은 number | undefined 이기 때문에,
// 타입에 따르면 이어진 연산을 바로 할 수 없습니다.
// 컴파일 에러를 고쳐야하기 하기 때문에 사용자와 작성자가 의논을 해야합니다.
console.log(f4(5));
console.log(f4(-5) + 5); // error TS2532: Object is possibly 'undefined'.
명시적으로 리턴 타입을 지정해야할까?
// 매개변수의 타입과 함수의 리턴 타입을 명시적으로 지정했습니다.
// 실제 함수 구현부의 리턴 타입과 명시적으로 지정한 타입이 일치하지 않아 컴파일 에러가 발생합니다.
// error TS2366: Function lacks ending return statement and return type does not include 'undefined'.
function f5(a: number): number {
if (a > 0) {
return a * 38;
}
}
noImplicitReturns 옵션을 켜면
함수 내에서 모든 코드가 값을 리턴하지 않으면,
컴파일 에러를 발생시킨다.
모든 코드에서 리턴을 직접해야한다.
// if 가 아닌 경우 return 을 직접 하지 않고 코드가 종료된다.
// error TS7030: Not all code paths return a value.
function f5(a: number) {
if (a > 0) {
return a * 38;
}
}
매개변수에 object 가 들어오는 경우
// JavaScript
function f6(a) {
return `이름은 ${a.name} 이고, 연령대는 ${
Math.floor(a.age / 10) * 10
}대 입니다.`;
}
console.log(f6({ name: 'Mark', age: 38 })); // 이름은 Mark 이고, 연령대는 30대 입니다.
console.log(f6('Mark')); // 이름은 undefined 이고, 연령대는 NaN대 입니다.
object literal type
function f7(a: { name: string; age: number }): string {
return `이름은 ${a.name} 이고, 연령대는 ${
Math.floor(a.age / 10) * 10
}대 입니다.`;
}
console.log(f7({ name: 'Mark', age: 38 })); // 이름은 Mark 이고, 연령대는 30대 입니다.
console.log(f7('Mark')); // error TS2345: Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type '{ name: string; age: number; }'.
나만의 타입을 만드는 방법
interface PersonInterface {
name: string;
age: number;
}
type PersonTypeAlias = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
function f8(a: PersonInterface): string {
return `이름은 ${a.name} 이고, 연령대는 ${
Math.floor(a.age / 10) * 10
}대 입니다.`;
}
console.log(f8({ name: 'Mark', age: 38 })); // 이름은 Mark 이고, 연령대는 30대 입니다.
console.log(f8('Mark')); // error TS2345: Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type 'PersonInterface'.
서브 타입 (1)
// sub1 타입은 sup1 타입의 서브 타입이다.
let sub1: 1 = 1;
let sup1: number = sub1;
sub1 = sup1; // error! Type 'number' is not assignable to type '1'.
// sub2 타입은 sup2 타입의 서브 타입이다.
let sub2: number[] = [1];
let sup2: object = sub2;
sub2 = sup2; // error! Type '{}' is missing the following properties from type 'number[]': length, pop, push, concat, and 16 more.
// sub3 타입은 sup3 타입의 서브 타입이다.
let sub3: [number, number] = [1, 2];
let sup3: number[] = sub3;
sub3 = sup3; // error! Type 'number[]' is not assignable to type '[number, number]'. Target requires 2 element(s) but source may have fewer.
슈퍼 타입 (1)
// sub1 타입은 sup1 타입의 서브 타입이다.
// sup1 타입은 sub1 타입의 슈퍼 타입이다.
let sub1: 1 = 1;
let sup1: number = sub1;
sub1 = sup1; // error! Type 'number' is not assignable to type '1'.
// sub2 타입은 sup2 타입의 서브 타입이다.
// sup2 타입은 sub2 타입의 슈퍼 타입이다.
let sub2: number[] = [1];
let sup2: object = sub2;
sub2 = sup2; // error! Type '{}' is missing the following properties from type 'number[]': length, pop, push, concat, and 16 more.
// sub3 타입은 sup3 타입의 서브 타입이다.
// sup3 타입은 sub3 타입의 슈퍼 타입이다.
let sub3: [number, number] = [1, 2];
let sup3: number[] = sub3;
sub3 = sup3; // error! Type 'number[]' is not assignable to type '[number, number]'. Target requires 2 element(s) but source may have fewer.
서브 타입 (2)
// sub4 타입은 sup4 타입의 서브 타입이다.
let sub4: number = 1;
let sup4: any = sub4;
sub4 = sup4;
// sub5 타입은 sup5 타입의 서브 타입이다.
let sub5: never = 0 as never;
let sup5: number = sub5;
sub5 = sup5; // error! Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'never'.
class SubAnimal {}
class SubDog extends SubAnimal {
eat() {}
}
// sub6 타입은 sup6 타입의 서브 타입이다.
let sub6: SubDog = new SubDog();
let sup6: SubAnimal = sub6;
sub6 = sup6;
서브 타입 (2)
// sub4 타입은 sup4 타입의 서브 타입이다.
// sup4 타입은 sub4 타입의 슈퍼 타입이다.
let sub4: number = 1;
let sup4: any = sub4;
sub4 = sup4;
// sub5 타입은 sup5 타입의 서브 타입이다.
// sup5 타입은 sub5 타입의 슈퍼 타입이다.
let sub5: never = 0 as never;
let sup5: number = sub5;
sub5 = sup5; // error! Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'never'.
class SubAnimal {}
class SubDog extends SubAnimal {
eat() {}
}
// sub6 타입은 sup6 타입의 서브 타입이다.
// sup6 타입은 sub6 타입의 슈퍼 타입이다.
let sub6: SubDog = new SubDog();
let sup6: SubAnimal = sub6;
sub6 = sup6; // error! Property 'eat' is missing in type 'SubAnimal' but required in type 'SubDog'.
1. 같거나 서브 타입인 경우, 할당이 가능하다. => 공변
// primitive type
let sub7: string = '';
let sup7: string | number = sub7;
// object - 각각의 프로퍼티가 대응하는 프로퍼티와 같거나 서브타입이어야 한다.
let sub8: { a: string; b: number } = { a: '', b: 1 };
let sup8: { a: string | number; b: number } = sub8;
// array - object 와 마찬가지
let sub9: Array<{ a: string; b: number }> = [{ a: '', b: 1 }];
let sup9: Array<{ a: string | number; b: number }> = sub8;2. 함수의 매개변수 타입만 같거나 슈퍼타입인 경우, 할당이 가능하다. => 반병
class Person {}
class Developer extends Person {
coding() {}
}
class StartupDeveloper extends Developer {
burning() {}
}
function tellme(f: (d: Developer) => Developer) {}
// Developer => Developer 에다가 Developer => Developer 를 할당하는 경우
tellme(function dToD(d: Developer): Developer {
return new Developer();
});
// Developer => Developer 에다가 Person => Developer 를 할당하는 경우
tellme(function pToD(d: Person): Developer {
return new Developer();
});
// Developer => Developer 에다가 StartipDeveloper => Developer 를 할당하는 경우
tellme(function sToD(d: StartupDeveloper): Developer {
return new Developer();
});strictFunctionTypes 옵션을 켜면
함수를 할당할 시에 함수의 매개변수 타입이 같거나 슈퍼타입인 경우가 아닌 경우,
에러를 통해 경고한다.
any
// 입력은 마음대로,
// 함수 구현이 자유롭게 => 자유가 항상 좋은건 아니다.
function fany(a: any): number | string | void {
a.toString();
if (typeof a === 'number') {
return a * 38;
} else if (typeof a === 'string') {
return `Hello ${a}`;
}
}
console.log(fany(10)); // 380
console.log(fany('Mark')); // Hello Mark
console.log(fany(true)); // undefined
any 대신 unknown
// 입력은 마음대로,
// 함수 구현은 문제 없도록
function funknown(a: unknown): number | string | void {
a.toString(); // error! Object is of type 'unknown'.
if (typeof a === 'number') {
return a * 38;
} else if (typeof a === 'string') {
return `Hello ${a}`;
}
}
console.log(funknown(10)); // 380
console.log(funknown('Mark')); // Hello Mark
console.log(funknown(true)); // undefined