React with TypeScript 1st
2woongjae@gmail.com





Mark Lee (이웅재)
- Studio XID inc. ProtoPie Engineer
- Seoul.JS 오거나이저
- 타입스크립트 한국 유저 그룹 오거나이저
- 일렉트론 한국 유저 그룹 운영진
- Seoul.js 오거나이저
- Microsoft MVP - Visual Studio and Development Technologies
- Code Busking with Jimmy
- https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCrKE8ihOKHxYHBzI0Ys-Oow
React 프로젝트 만들기
webpack with babel-loader
React with webpack, babel-loader [ jsx ]
- module bundler
- webpack, webpack-dev-server
- html-webpack-plugin
-
loader
-
babel-loader
- babel-core
- babel-preset-react-app
- style-loader, css-loader
-
babel-loader
- react
- react
- react-dom
React with webpack, babel-loader [ jsx ]
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i webpack webpack-dev-server html-webpack-plugin -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i babel-loader babel-core babel-preset-react-app -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i react react-dom -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i style-loader css-loader -D{
"name": "webpack-react-js",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "NODE_ENV=development webpack-dev-server",
"build": "NODE_ENV=production webpack"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"babel-core": "^6.26.0",
"babel-loader": "^7.1.2",
"babel-preset-react-app": "^3.1.0",
"css-loader": "^0.28.8",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^2.30.1",
"react": "^16.2.0",
"react-dom": "^16.2.0",
"style-loader": "^0.19.1",
"webpack": "^3.10.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "^2.10.1"
}
}
React with webpack, babel-loader [ jsx ]
{
"_from": "babel-preset-react-app@^3.1.0",
"_id": "babel-preset-react-app@3.1.0",
"_inBundle": false,
"_integrity": "sha512-jEAeVozxLzftLl0iDZ0d5jrmfbo3yogON/eI4AsEDIs8p6WW+t9mDRUsj5l12bqPOLSiVOElCQ3QyGjMcyBiwA==",
"_location": "/babel-preset-react-app",
"_phantomChildren": {},
"_requested": {
"type": "range",
"registry": true,
"raw": "babel-preset-react-app@^3.1.0",
"name": "babel-preset-react-app",
"escapedName": "babel-preset-react-app",
"rawSpec": "^3.1.0",
"saveSpec": null,
"fetchSpec": "^3.1.0"
},
"_requiredBy": [
"/react-scripts"
],
"_resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/babel-preset-react-app/-/babel-preset-react-app-3.1.0.tgz",
"_shasum": "d77f6061ab9d7bf4b3cdc86b7cde9ded0df03e48",
"_spec": "babel-preset-react-app@^3.1.0",
"_where": "/Users/mark/Project/cra-test/node_modules/react-scripts",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/facebookincubator/create-react-app/issues"
},
"bundleDependencies": false,
"dependencies": {
"babel-plugin-dynamic-import-node": "1.1.0",
"babel-plugin-syntax-dynamic-import": "6.18.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-class-properties": "6.24.1",
"babel-plugin-transform-object-rest-spread": "6.26.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-react-constant-elements": "6.23.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-react-jsx": "6.24.1",
"babel-plugin-transform-react-jsx-self": "6.22.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-react-jsx-source": "6.22.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-regenerator": "6.26.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-runtime": "6.23.0",
"babel-preset-env": "1.6.1",
"babel-preset-react": "6.24.1"
},
"deprecated": false,
"description": "Babel preset used by Create React App",
"files": [
"index.js"
],
"homepage": "https://github.com/facebookincubator/create-react-app#readme",
"license": "MIT",
"name": "babel-preset-react-app",
"peerDependencies": {
"babel-runtime": "^6.23.0"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/facebookincubator/create-react-app.git"
},
"version": "3.1.0"
}
babel-preset-react-app
const webpack = require('webpack');
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = env => {
const config = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
devServer: {
contentBase: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
compress: true,
historyApiFallback: true,
inline: true,
port: 4000
},
module: {
loaders: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
loader: 'style-loader!css-loader'
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
inject: true,
template: 'public/index.html'
})
]
};
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
config.plugins.push(new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin());
}
return config;
};
webpack.config.js
webpack-react-js
https://github.com/2woongjae/webpack-react-js
React 프로젝트 만들기
webpack with ts-loader
- module bundler
- webpack, webpack-dev-server
- html-webpack-plugin
-
loader
-
ts-loader
- typescript
-
tslint-loader
- tslint
- tslint-react
- source-map-loader
- style-loader, css-loader
-
ts-loader
- react
- react, @types/react
- react-dom, @types/react-dom
React with webpack, ts-loader [ tsx ]
React with webpack, ts-loader [ tsx ]
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i webpack webpack-dev-server html-webpack-plugin -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i ts-loader typescript -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i react react-dom @types/react @types/react-dom -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i tslint-loader tslint tslint-react -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i source-map-loader -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i style-loader css-loader -DReact with webpack, ts-loader [ tsx ]
{
"name": "webpack-react-ts",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "NODE_ENV=development webpack-dev-server",
"build": "NODE_ENV=production webpack"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/react": "^16.0.34",
"@types/react-dom": "^16.0.3",
"css-loader": "^0.28.8",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^2.30.1",
"react": "^16.2.0",
"react-dom": "^16.2.0",
"source-map-loader": "^0.2.3",
"style-loader": "^0.19.1",
"ts-loader": "^3.2.0",
"tslint": "^5.9.1",
"tslint-loader": "^3.5.3",
"tslint-react": "^3.4.0",
"typescript": "^2.6.2",
"webpack": "^3.10.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "^2.10.1"
}
}
const webpack = require('webpack');
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = env => {
const config = {
entry: './src/index.tsx',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
devServer: {
contentBase: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
compress: true,
historyApiFallback: true,
inline: true,
port: 4000
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(ts|tsx)$/,
loader: 'ts-loader'
},
{
enforce: 'pre',
test: /\.(ts|tsx)$/,
loader: 'tslint-loader'
},
{
enforce: 'pre',
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'source-map-loader'
},
{
oneOf: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
loader: 'style-loader!css-loader'
}
]
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
inject: true,
template: 'public/index.html'
})
]
};
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
config.plugins.push(new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin());
}
return config;
};
React with webpack, ts-loader [ tsx ]
tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5",
"module": "commonjs",
"jsx": "react",
"sourceMap": true,
"strict": true
}
}tslint.json
{
"defaultSeverity": "error",
"extends": [
"tslint-react"
],
"jsRules": {},
"rules": {
"no-console": [
true,
"log",
"error",
"debug",
"info",
"time",
"timeEnd",
"trace"
]
},
"rulesDirectory": []
}webpack-react-ts
https://github.com/2woongjae/webpack-react-ts
React 프로젝트 만들기
parcel with built-in babel transform
- module bundler
- parcel-bundler
-
babel config
- babel-preset-react-app
- react
- react
- react-dom
React with parcel, babel [ jsx ]
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i parcel-bundler -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i babel-preset-react-app -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i react react-dom -DReact with parcel, babel [ jsx ]
React with parcel, babel [ jsx ]
{
"name": "parcel-react-js",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "parcel src/index.html",
"build": "parcel build src/index.html --public-url '/'",
"serve": "serve -s dist"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"babel-preset-react-app": "^3.1.0",
"parcel-bundler": "^1.4.1",
"react": "^16.2.0",
"react-dom": "^16.2.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"serve": "^6.4.4"
}
}
parcel-react-js
https://github.com/2woongjae/parcel-react-js
React 프로젝트 만들기
parcel with built-in ts transform
- module bundler
- parcel-bundler
-
ts config
- typescript
- react
- react, @types/react
- react-dom, @types/react-dom
React with parcel, ts [ tsx ]
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i parcel-bundler -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i typescript -D
~/Project/webpack-react-js is 📦 v1.0.0 via ⬢ v8.9.4
➜ npm i react react-dom -DReact with parcel, ts [ tsx ]
parcel-react-ts
https://github.com/2woongjae/parcel-react-ts
React with parcel, ts [ tsx ]
{
"name": "parcel-react-ts",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "parcel src/index.html",
"build": "parcel build src/index.html --public-url '/'",
"serve": "serve -s dist"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/react": "^16.0.34",
"@types/react-dom": "^16.0.3",
"parcel-bundler": "^1.4.1",
"react": "^16.2.0",
"react-dom": "^16.2.0",
"typescript": "^2.6.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"serve": "^6.4.4"
}
}
React 프로젝트 만들기
create-react-app
Creact React App by Dan Abramov
Create React App
- 리액트 프로그래밍 이외의 설정은 이제 그만
- 프로젝트 생성
- create-react-app <프로젝트명>
- 개발용 서버 실행
- npm run start
- 프로덕션 빌드
- npm run build
- 유닛 테스트
- npm run test
- 프로젝트 cra 에서 꺼내기 (?)
- npm run eject
- 프로젝트 생성
- pwa 적용
npx create-react-app cra-ts --scripts-version=react-scripts-ts
npm start
npm test
npm run build
npm run eject
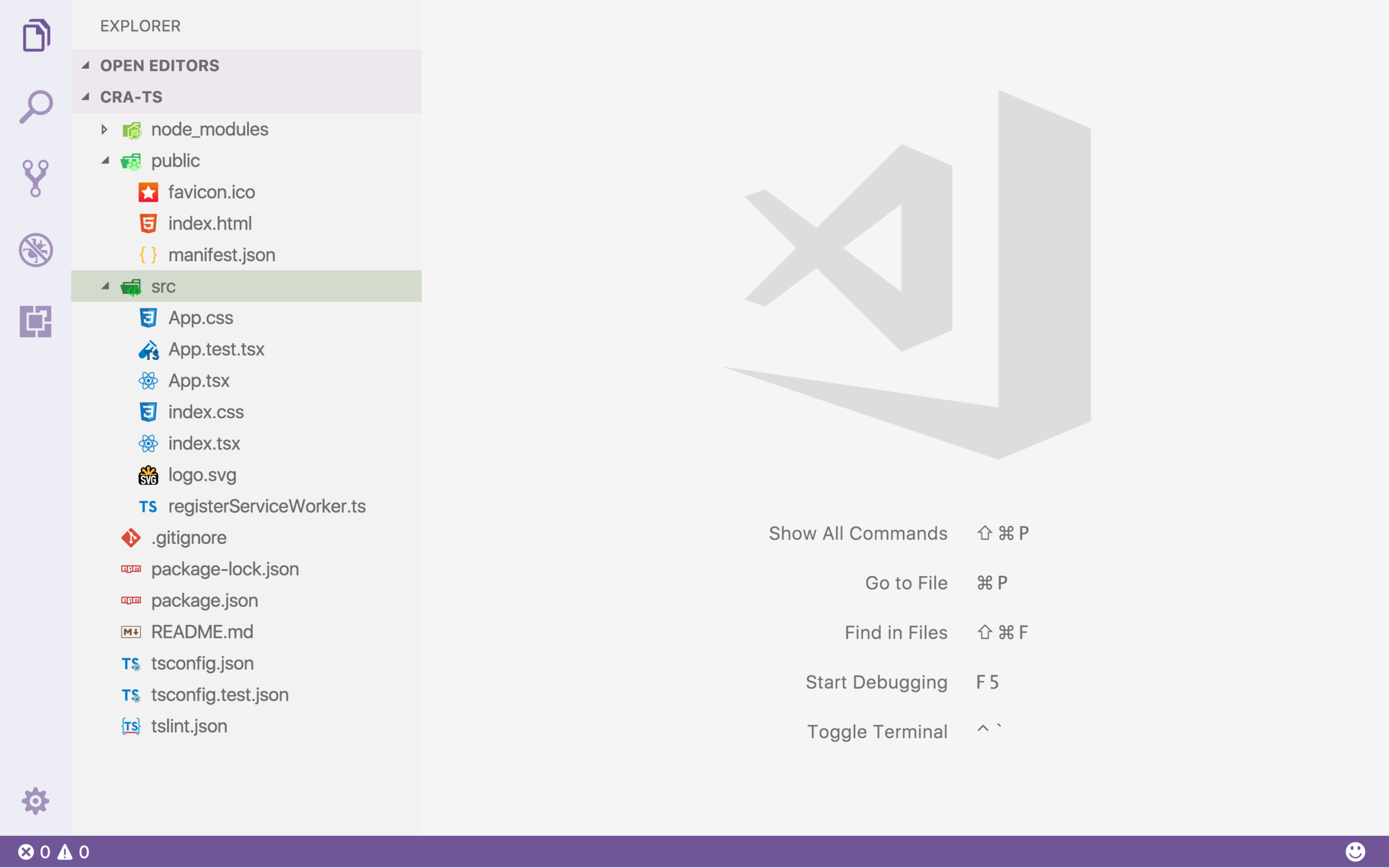
디렉토리 구조
package.json
{
"name": "cra-ts",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"react": "^16.2.0",
"react-dom": "^16.2.0",
"react-scripts-ts": "2.8.0"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts-ts start",
"build": "react-scripts-ts build",
"test": "react-scripts-ts test --env=jsdom",
"eject": "react-scripts-ts eject"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/jest": "^22.0.1",
"@types/node": "^9.3.0",
"@types/react": "^16.0.34",
"@types/react-dom": "^16.0.3"
}
}
ts-loader => tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "build/dist", // 빌드 결과물 폴더
"module": "esnext", // 빌드 결과의 모듈 방식은 esnext
"target": "es5", // 빌드 결과물은 es5 방식으로
"lib": ["es6", "dom"], // 라이브러리는 es6 와 dom
"sourceMap": true, // .map.js 파일도 함께 생성
"allowJs": true, // JS 파일도 컴파일 대상
"jsx": "react", // jsx 구문 사용 가능
"moduleResolution": "node", // 모듈 해석 방식은 node 처럼
"rootDir": "src", // 컴파일할 대상들이 들어있는 폴더 (루트 폴더)
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, // https://github.com/TypeStrong/ts-loader/issues/89
"noImplicitReturns": true, // 제대로 리턴 다 안되면 에러
"noImplicitThis": true, // this 표현식에 암시적으로 any 로 추론되면
"noImplicitAny": true, // 암시적으로 선언되었는데 any 로 추론되면
"strictNullChecks": true, // null 이나 undefined 을 서브 타입으로 사용하지 못하게 함
"suppressImplicitAnyIndexErrors": true, // 인덱싱 시그니처가 없는 경우, 인덱스를 사용했을때 noImplicitAny 에 의해 에러가 뜨는 것을 방지
"noUnusedLocals": true // 사용 안하는 로컬 변수가 있으면 에러
},
"exclude": [
"node_modules",
"build",
"scripts",
"acceptance-tests",
"webpack",
"jest",
"src/setupTests.ts"
]
}
tslint-loader => tslint.json
{
"extends": ["tslint-react"],
"rules": {
"align": [
true,
"parameters",
"arguments",
"statements"
],
"ban": false,
"class-name": true,
"comment-format": [
true,
"check-space"
],
"curly": true,
"eofline": false,
"forin": true,
"indent": [ true, "spaces" ],
"interface-name": [true, "never-prefix"],
"jsdoc-format": true,
"jsx-no-lambda": false,
"jsx-no-multiline-js": false,
"label-position": true,
"max-line-length": [ true, 120 ],
"member-ordering": [
true,
"public-before-private",
"static-before-instance",
"variables-before-functions"
],
"no-any": true,
"no-arg": true,
"no-bitwise": true,
"no-console": [
true,
"log",
"error",
"debug",
"info",
"time",
"timeEnd",
"trace"
],
"no-consecutive-blank-lines": true,
"no-construct": true,
"no-debugger": true,
"no-duplicate-variable": true,
"no-empty": true,
"no-eval": true,
"no-shadowed-variable": true,
"no-string-literal": true,
"no-switch-case-fall-through": true,
"no-trailing-whitespace": false,
"no-unused-expression": true,
"no-use-before-declare": true,
"one-line": [
true,
"check-catch",
"check-else",
"check-open-brace",
"check-whitespace"
],
"quotemark": [true, "single", "jsx-double"],
"radix": true,
"semicolon": [true, "always"],
"switch-default": true,
"trailing-comma": [false],
"triple-equals": [ true, "allow-null-check" ],
"typedef": [
true,
"parameter",
"property-declaration"
],
"typedef-whitespace": [
true,
{
"call-signature": "nospace",
"index-signature": "nospace",
"parameter": "nospace",
"property-declaration": "nospace",
"variable-declaration": "nospace"
}
],
"variable-name": [true, "ban-keywords", "check-format", "allow-leading-underscore", "allow-pascal-case"],
"whitespace": [
true,
"check-branch",
"check-decl",
"check-module",
"check-operator",
"check-separator",
"check-type",
"check-typecast"
]
}
}
src 디렉토리에서 코딩을 시작

src 디렉토리
-
index.tsx
- 메인 엔트리 파일
- 꼭대기에서 ReactDom.render 를 수행
- pwa 를 위한 서비스 워커 등록 작업
-
index.css
- 글로벌 스타일 작성 => 프로그래밍 적으로 제한되지 않는다.
-
App.tsx
- App 컴포넌트 (샘플 컴포넌트)
- 클래스 이름과 파일 이름을 맞추는 것이 관례
-
App.css
- App 컴포넌트에서 쓰이는 스타일 => 일종의 암묵적 합의
-
App.test.tsx
- App 컴포넌트에 대한 테스트 작성 파일
-
registerServiceWorker.ts
- pwa 서비스 워커 사용 등록 => 나중에 pwa 공부하면서...
index.tsx
import * as React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
import registerServiceWorker from './registerServiceWorker';
import './index.css';
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root') as HTMLElement
);
registerServiceWorker();App.tsx
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
const logo = require('./logo.svg');
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h2>Welcome to React</h2>
</div>
<p className="App-intro">
To get started, edit <code>src/App.tsx</code> and save to reload.
</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
Prettier
- 프리티어는 개발자가 작성한 코드를 파싱하여, 어떤 정해진 룰에 의해 재작성하는 프로그램입니다.
- A 라는 코드 ==(어떤 룰에 의해 작동하는 프리티어 프로그램)==> B 라는 코드
- 룰 작성 (.prettierrc)
- http://json.schemastore.org/prettierrc
Prettier for VS Code Extension
- 단축키로 실행
- 전체
- 영역
- 저장할때 실행
- 커밋할때 실행
React Concept
- React Keyword
- View 라이브러리
- Only Rendering & Update
- NOT included another functionality
- Component Based Development
- 작업의 단위
- Virtual DOM
- 이제는 DOM 을 직접 다루지 않음.
- JSX
- NOT Templates
- transpile to JS
- CSR & SSR
- IE9 with React v15
- View 라이브러리
Declarative 디클레러티브
Design simple views for each state in your application, and React will efficiently update and render just the right components when your data changes.
함께 사용하는 대표적인 라이브러리들
Component Based Development - Version
Component Based Development - Links

Component Based - Title
Component Based - Content

Component Based Development - Card
Component Based Development - Card
Component Based Development - Card

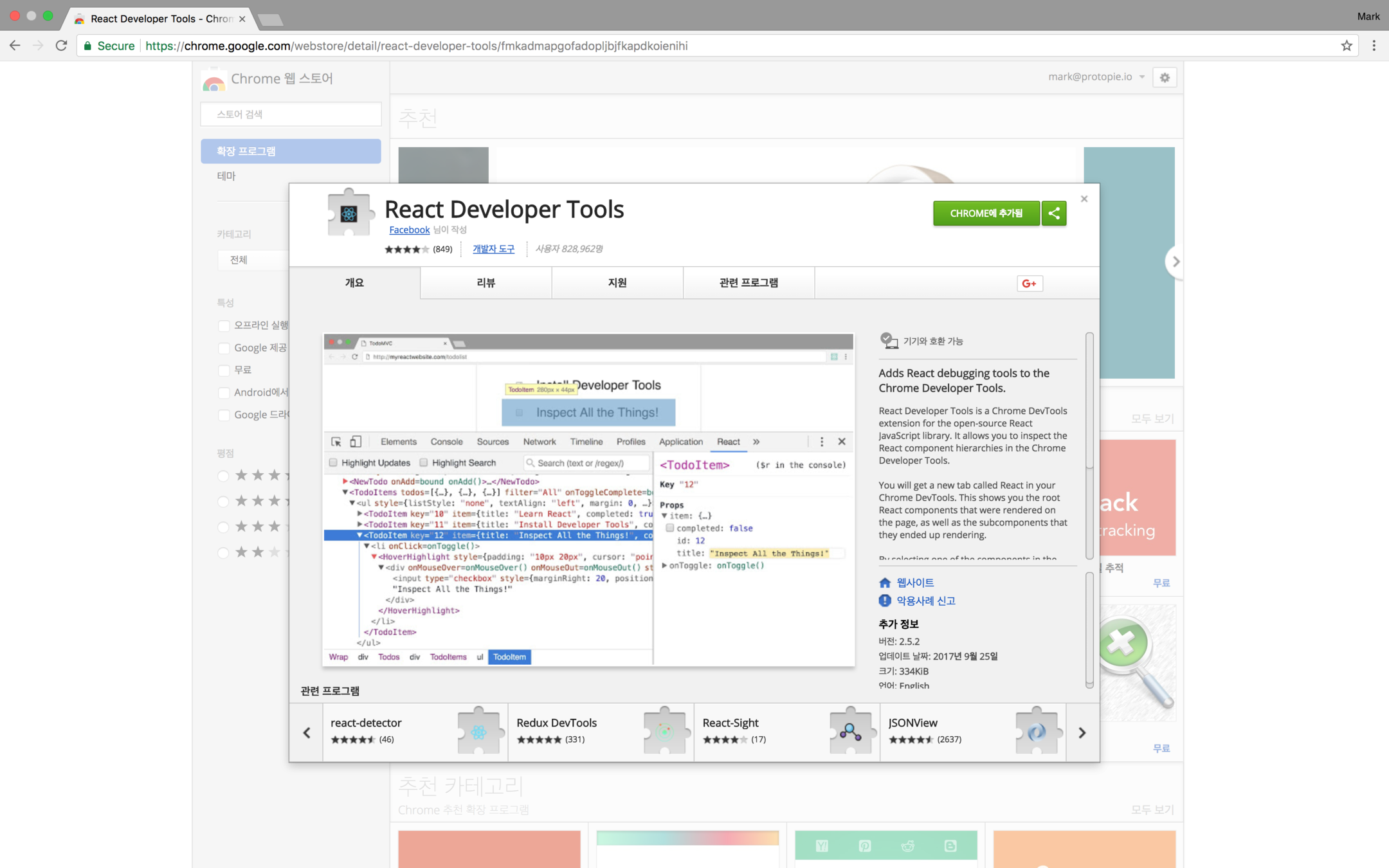
React Developer Tools
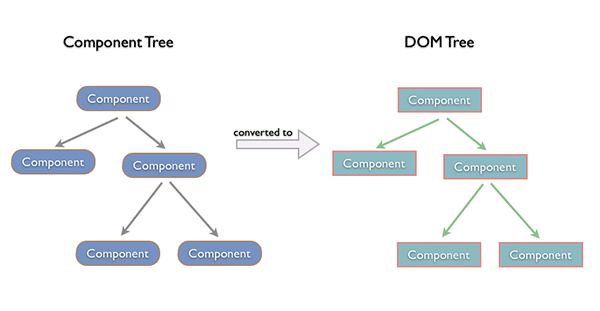
Component Tree => DOM Tree
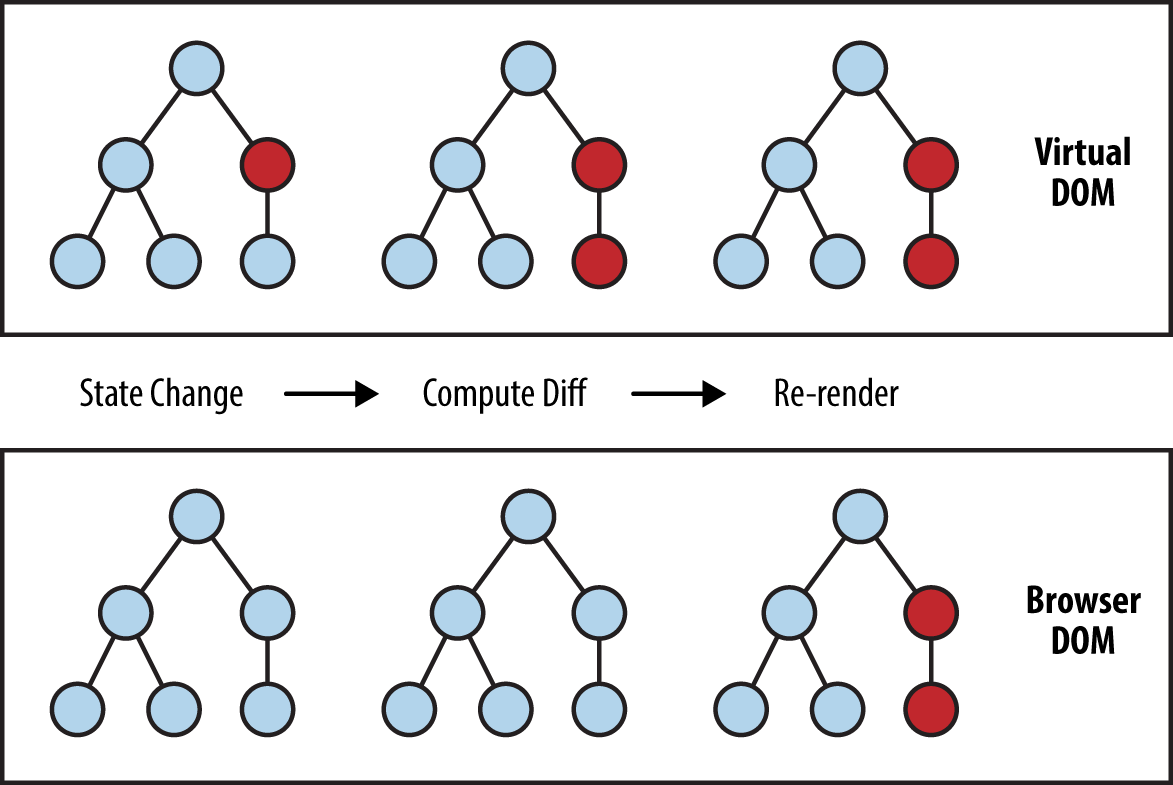
Virtual DOM - diff 로 변경
JSX
- Templates 스타일이 아님.
- 옵션이지만, 다들 사용
- JavaScript XML - JSX 자체는 문법
- 리액트에서는 JSX.Element 로 그려질 컴포넌트를 표현합니다.
- React.createElement 함수를 통해서도 JSX.Element 를 만들수 있습니다.
class HelloMessage extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>Hello {this.props.name}</div>;
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<HelloMessage name="Jane" />, mountNode);class HelloMessage extends React.Component {
render() {
return React.createElement(
"div",
null,
"Hello ",
this.props.name
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(React.createElement(HelloMessage, { name: "Jane" }), mountNode);CSR & SSR
- React 는 CSR 이 기본
-
ReactDOM.render(element, container[, callback]);
-
- React 에서 SSR 지원을 위한 API 존재
-
ReactDOMServer.renderToString(element);
-
리액트 컴포넌트를 서버에서 랜더해서 문자열로 만들어줌
-
import * as React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
const App = () => <h1>Hello, React!</h1>;
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.querySelector('#root'));app.get('*', (req, res) => {
const html = path.join(__dirname, '../build/index.html');
const htmlData = fs.readFileSync(html).toString();
const ReactApp = ReactDOMServer.renderToString(React.createElement(App));
const renderedHtml = htmlData.replace('{{SSR}}', ReactApp);
res.status(200).send(renderedHtml);
});React Client Side Rendering

React Server Side Rendering

React 컴포넌트 만들기
props, stateful, stateless
React.Component<P, S> - Generic
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<h2>Hello World</h2>
);
}
}
interface Component<P = {}, S = {}> extends ComponentLifecycle<P, S> { }
class Component<P, S> {
constructor(props: P, context?: any);
// We MUST keep setState() as a unified signature because it allows proper checking of the method return type.
// See: https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/issues/18365#issuecomment-351013257
// Also, the ` | S` allows intellisense to not be dumbisense
setState<K extends keyof S>(
state: ((prevState: Readonly<S>, props: P) => (Pick<S, K> | S)) | (Pick<S, K> | S),
callback?: () => void
): void;
forceUpdate(callBack?: () => void): void;
render(): ReactNode;
// React.Props<T> is now deprecated, which means that the `children`
// property is not available on `P` by default, even though you can
// always pass children as variadic arguments to `createElement`.
// In the future, if we can define its call signature conditionally
// on the existence of `children` in `P`, then we should remove this.
props: Readonly<{ children?: ReactNode }> & Readonly<P>;
state: Readonly<S>;
context: any;
refs: {
[key: string]: ReactInstance
};
}props, state
props, state
- props
- 컴포넌트 외부에서 컴포넌트로 넣어주는 데이터 (함수도 가능)
- 컴포넌트 내부에서는 자신의 props 를 변경할수 없다.
- 물론 돌아가면 가능은 하다.
- 컴포넌트 외부에서 props 데이터를 변경하면, render 가 다시 호출된다.
- state
- 컴포넌트 내부의 데이터
- 클래스의 프로퍼티와는 다르다.
- 프로퍼티는 변경한다고 render 가 호출되지 않는다는 점
- 생성자 혹은 프로퍼티 초기 할당으로 state 를 초기 할당 해줘야 한다.
- 내부에서 변경을 하더라도 setState 함수를 이용해야 render 가 호출된다.
props
class App extends React.Component<{ name: string }> {
render() {
return (
<h2>Hello {this.props.name}</h2>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App name="Mark" />,
document.getElementById('root') as HTMLElement
);
interface Component<P = {}, S = {}> extends ComponentLifecycle<P, S> { }
class Component<P, S> {
constructor(props: P, context?: any);
// We MUST keep setState() as a unified signature because it allows proper checking of the method return type.
// See: https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/issues/18365#issuecomment-351013257
// Also, the ` | S` allows intellisense to not be dumbisense
setState<K extends keyof S>(
state: ((prevState: Readonly<S>, props: P) => (Pick<S, K> | S)) | (Pick<S, K> | S),
callback?: () => void
): void;
forceUpdate(callBack?: () => void): void;
render(): ReactNode;
// React.Props<T> is now deprecated, which means that the `children`
// property is not available on `P` by default, even though you can
// always pass children as variadic arguments to `createElement`.
// In the future, if we can define its call signature conditionally
// on the existence of `children` in `P`, then we should remove this.
props: Readonly<{ children?: ReactNode }> & Readonly<P>;
state: Readonly<S>;
context: any;
refs: {
[key: string]: ReactInstance
};
}state 초기 할당 (X) - 사용을 안하면 문제 없다.
class App extends React.Component<{ name: string; }, { age: number; }> {
render() {
return (
// <h2>{this.props.name}</h2>
<h2>{this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
);
}
}
state 초기 할당
class App extends React.Component<{ name: string; }, { age: number; }> {
public state = {
age: 35
};
render() {
return (
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component<{ name: string; }, { age: number; }> {
constructor(props: { name: string; }) {
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35
};
}
render() {
return (
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
);
}
}
interface Component<P = {}, S = {}> extends ComponentLifecycle<P, S> { }
class Component<P, S> {
constructor(props: P, context?: any);
// We MUST keep setState() as a unified signature because it allows proper checking of the method return type.
// See: https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/issues/18365#issuecomment-351013257
// Also, the ` | S` allows intellisense to not be dumbisense
setState<K extends keyof S>(
state: ((prevState: Readonly<S>, props: P) => (Pick<S, K> | S)) | (Pick<S, K> | S),
callback?: () => void
): void;
forceUpdate(callBack?: () => void): void;
render(): ReactNode;
// React.Props<T> is now deprecated, which means that the `children`
// property is not available on `P` by default, even though you can
// always pass children as variadic arguments to `createElement`.
// In the future, if we can define its call signature conditionally
// on the existence of `children` in `P`, then we should remove this.
props: Readonly<{ children?: ReactNode }> & Readonly<P>;
state: Readonly<S>;
context: any;
refs: {
[key: string]: ReactInstance
};
}setState
class App extends React.Component<{ name: string; }, { age: number; }> {
constructor(props: { name: string; }) {
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35
};
setInterval(() => {
// this.state.age = this.state.age + 1;
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1
});
}, 1000);
}
render() {
return (
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
);
}
}
interface Component<P = {}, S = {}> extends ComponentLifecycle<P, S> { }
class Component<P, S> {
constructor(props: P, context?: any);
// We MUST keep setState() as a unified signature because it allows proper checking of the method return type.
// See: https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/issues/18365#issuecomment-351013257
// Also, the ` | S` allows intellisense to not be dumbisense
setState<K extends keyof S>(
state: ((prevState: Readonly<S>, props: P) => (Pick<S, K> | S)) | (Pick<S, K> | S),
callback?: () => void
): void;
forceUpdate(callBack?: () => void): void;
render(): ReactNode;
// React.Props<T> is now deprecated, which means that the `children`
// property is not available on `P` by default, even though you can
// always pass children as variadic arguments to `createElement`.
// In the future, if we can define its call signature conditionally
// on the existence of `children` in `P`, then we should remove this.
props: Readonly<{ children?: ReactNode }> & Readonly<P>;
state: Readonly<S>;
context: any;
refs: {
[key: string]: ReactInstance
};
}interface
export interface AppProps {
name: string;
}
interface AppState {
age: number;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
constructor(props: AppProps) {
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35
};
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1
});
}, 1000);
}
render() {
return (
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
);
}
}Stateless Component
const StatelessComponent = (props: AppProps) => {
return (
<h2>{props.name}</h2>
);
}
const StatelessComponent: React.SFC<AppProps> = (props) => {
return (
<h2>{props.name}</h2>
);
}
type SFC<P = {}> = StatelessComponent<P>;
interface StatelessComponent<P = {}> {
(props: P & { children?: ReactNode }, context?: any): ReactElement<any> | null;
propTypes?: ValidationMap<P>;
contextTypes?: ValidationMap<any>;
defaultProps?: Partial<P>;
displayName?: string;
}P & {children?: ReactNode}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
<StatelessComponent name="Anna" />
<StatelessComponent name="Anna">여기는 칠드런입니다. 있을수도 있고 없을 수도 있고</StatelessComponent>
</div>
);
}
const StatelessComponent: React.SFC<AppProps> = (props) => {
return (
<h2>{props.name}, {props.children}</h2>
);
}
type SFC<P = {}> = StatelessComponent<P>;
interface StatelessComponent<P = {}> {
(props: P & { children?: ReactNode }, context?: any): ReactElement<any> | null;
propTypes?: ValidationMap<P>;
contextTypes?: ValidationMap<any>;
defaultProps?: Partial<P>;
displayName?: string;
}
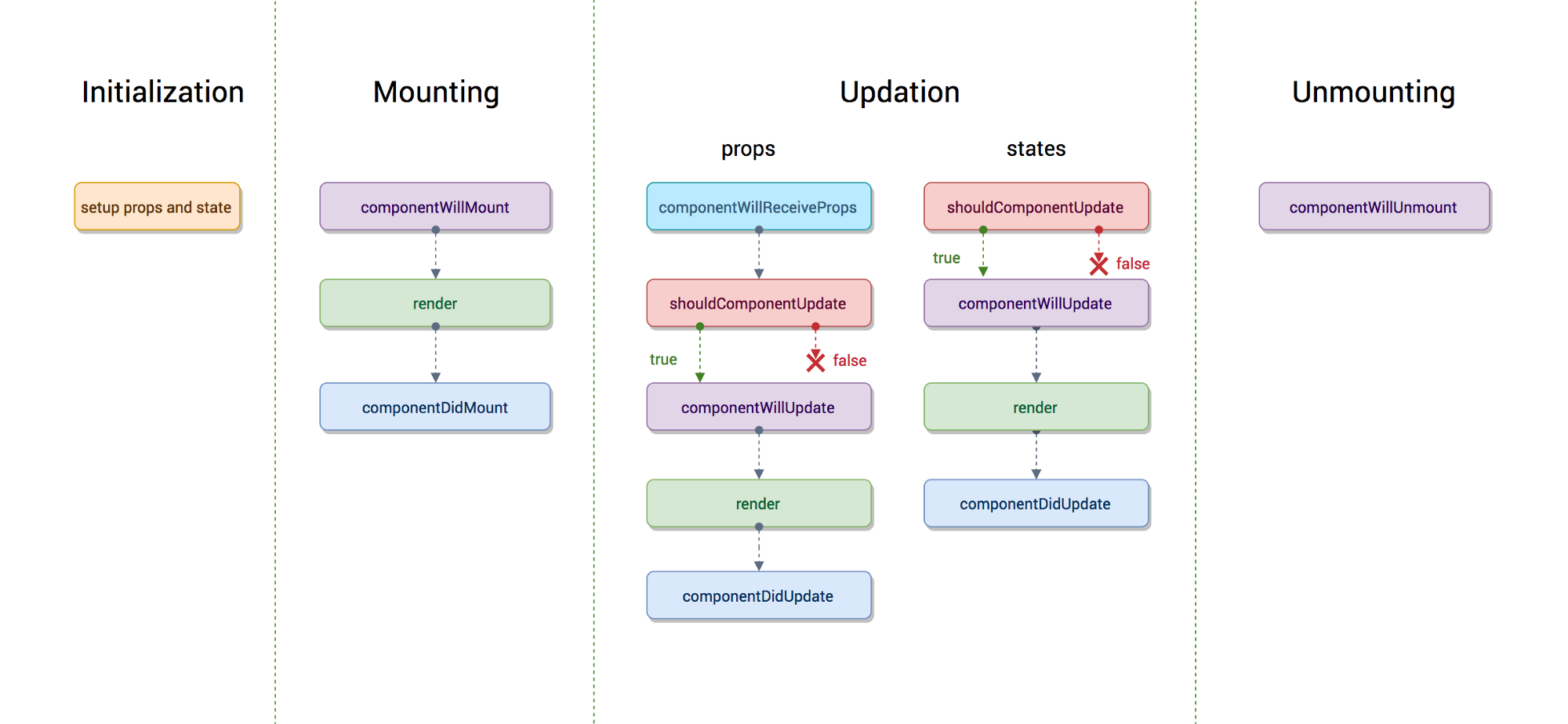
Lifecycle
Component 생성 및 마운트
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
export interface AppProps {
name: string;
}
export interface AppState {
age: number;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
private _interval: number;
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35
};
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
this._interval = window.setInterval(
() => {
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1
});
},
1000
);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
clearInterval(this._interval);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
Component 생성 및 마운트
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
export interface AppProps {
name: string;
}
export interface AppState {
age: number;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
private _interval: number;
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35
};
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
this._interval = window.setInterval(
() => {
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1
});
},
1000
);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
clearInterval(this._interval);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;

constructor
componentWillMount
render
componentDidMount
Component props, state 변경
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}componentWillReceiveProps
shouldComponentUpdate
componentWillUpdate
render
componentDidUpdate

componentWillReceiveProps
- props 를 새로 지정했을 때 바로 호출됩니다.
- 여기는 state 의 변경에 반응하지 않습니다.
- 여기서 props 의 값에 따라 state 를 변경해야 한다면,
- setState 를 이용해 state 를 변경합니다.
- 그러면 다음 이벤트로 각각 가는것이 아니라 한번에 변경됩니다.
- 여기서 props 의 값에 따라 state 를 변경해야 한다면,
shouldComponentUpdate
- props 만 변경되어도
- state 만 변경되어도
- props & state 둘다 변경되어도
- newProps 와 new State 를 인자로 해서 호출
- return type 이 boolean 입니다.
- true 면 render
- false 면 render 가 호출되지 않습니다.
- 이 함수를 구현하지 않으면, 디폴트는 true
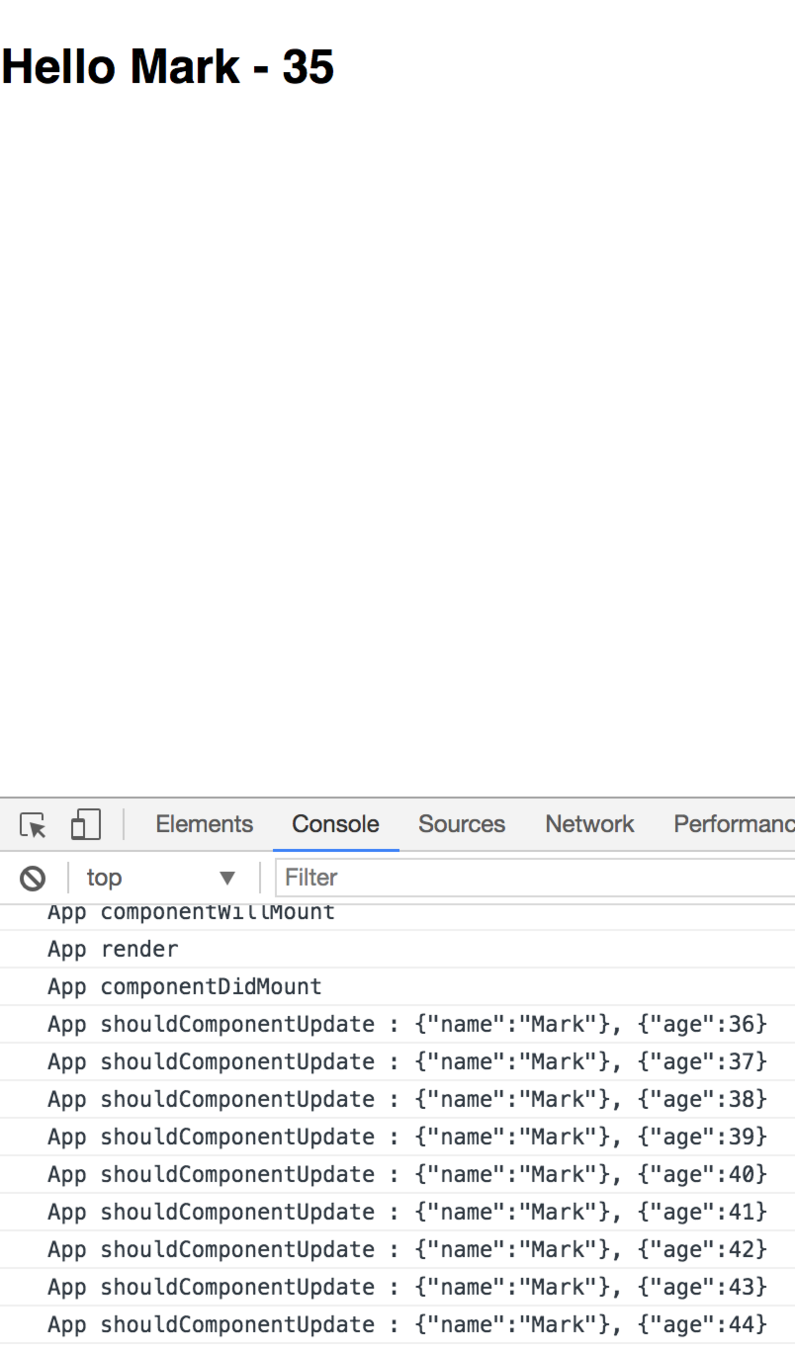
componentWillUpdate
- 컴포넌트가 재 랜더링 되기 직전에 불립니다.
- 여기선 setState 같은 것을 쓰면 아니됩니다.
componentDidUpdate
- 컴포넌트가 재 랜더링을 마치면 불립니다.

Event
DOM onclick => JSX onClick
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35
};
this._reset = this._reset.bind(this);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
<button onClick={this._reset}>리셋</button>
</div>
);
}
private _reset(): void {
this.setState({
age: 35
});
}DOM onchange => JSX onChang
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
export interface AppProps {
name: string;
}
export interface AppState {
age: number;
company: string;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
private _interval: number;
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
age: 35,
company: 'Studio XID'
};
this._reset = this._reset.bind(this);
this._change = this._change.bind(this);
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
this._interval = window.setInterval(
() => {
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1
});
},
1000
);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
clearInterval(this._interval);
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello {this.props.name} - {this.state.age}</h2>
<button onClick={this._reset}>리셋</button>
<input type="text" onChange={this._change} value={this.state.company} />
</div>
);
}
private _reset(): void {
this.setState({
age: 35
});
}
private _change(e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>): void {
this.setState({
company: e.target.value
});
}
}
export default App;
autobind-decorator
Bye PropTypes & Flow
PropTypes
- React.PropTypes 를 더이상 함께 제공해 주지 않습니다.
- 별도의 라이브러리로 분리하였습니다.
- 사용자에게 선택의 폭을 준것이라 생각합니다.
- 선택
- 라이브러리로 제공되는 PropTypes
- https://www.npmjs.com/package/prop-types
- Facebook 에서 제공하는 Flow
- https://flow.org/
-
TypeScript 만세
- https://www.typescriptlang.org
- 라이브러리로 제공되는 PropTypes
- Flow 와 TypeScript 의 실사용 비교를 해보세요
- 전 그냥 타입스크립트 쓸게용
defaultProps
defaultProps 사용법 - class
// 사용시에 name props 를 쓰지 않으면,
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root') as HTMLElement
);
// 이렇게 name 을 물음표를 이용해 옵셔널하게 처리
export interface AppProps {
name?: string;
}
// 클래스 안에 static 메서드를 이용해서 디폴트 값을 작성한다.
public static defaultProps = {
name: 'Default'
};
// type definition 에 따르면 Props 의 부분집합이다.
defaultProps?: Partial<P>;defaultProps 사용법 - function
export interface AppProps {
name?: string;
}
const StatelessComponent: React.SFC<AppProps> = (props) => {
return (
<h2>{props.name}</h2>
);
}
StatelessComponent.defaultProps = {
name: 'Default'
};defaultProps 사용법 - function 2
export interface AppProps {
name?: string;
}
const StatelessComponent: React.SFC<AppProps> = ({name = 'Default'}) => {
return (
<h2>{props.name}</h2>
);
}Why use TypeScript with React
- Autocomplete
- Type Checking
- Refactoring
- Understanding Code
Refs
ref 를 props 로 끌어올리기
interface CustomTextInputProps {
inputRef(element: HTMLInputElement): void;
}
function CustomTextInput(props: CustomTextInputProps) {
return (
<div>
<input ref={props.inputRef} />
</div>
);
}
function Parent(props: ParentProps) {
return (
<div>
My input: <CustomTextInput inputRef={props.inputRef} />
</div>
);
}
interface ParentProps {
inputRef(element: HTMLInputElement): void;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
inputElement: HTMLInputElement | null;
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<Parent inputRef={element => this.inputElement = element} />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;자식의 무언가를 변경하려면, props ?
- props 를 다루지 않고 자식의 어떤 요소를 건들고 싶다면 ?
- ref 를 이용해서 랜더를 다시 하지 않고 하위 요소를 다룰 수 있다.
PureComponent
Component props, state 변경
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}componentWillReceiveProps
shouldComponentUpdate
componentWillUpdate
render
componentDidUpdate

shouldComponentUpdate
- 일반 컴포넌트는
- 따로 구현하지 않으면 props, state 가 바뀌면 무조건 render
- Pure 컴포넌트는
- shouldComponentUpdate 가 다른 방식으로 구현되어 있는 것이다.
- shallow compare
- nested object 값의 변경을 감지하지 못한다.
- immutable.js 를 사용하는 이유
- 모든 컴포넌트를 Pure 로 하는 것이 성능상 이점이 있는건 아니다.
PureComponent
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
export interface AppProps {
}
export interface AppState {
todo: string[];
}
class App extends React.PureComponent<AppProps, AppState> {
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
todo: ['First']
};
this._addSecond = this._addSecond.bind(this);
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
/*
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
*/
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<p>{this.state.todo.join(', ')}</p>
<button onClick={this._addSecond}>Second 추가</button>
</div>
);
}
private _addSecond(): void {
const todo: string[] = this.state.todo;
todo.push('Second');
this.setState({
todo: todo
});
}
}
export default App;Copy 를 하거나, Immutable.js
Composition
"Facebook 은 수천개의 컴포넌트에서 React 를 사용하며, 컴포넌트 상속 계층을 사용하는 것이 권장되는 use case 를 찾지 못했습니다."
"컴포넌트에서 UI 이외의 기능을 재사용 하고 싶으면,
상속을 이용하지 말고 자바스크립트 모듈로 분리해서 사용하는것이 좋다"
컴포지션의 기본은
children 혹은 props 의 활용
props 를 이용한 명시적이고 안전한 재사용
function SplitPane(props) {
return (
<div className="SplitPane">
<div className="SplitPane-left">
{props.left}
</div>
<div className="SplitPane-right">
{props.right}
</div>
</div>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<SplitPane
left={
<Contacts />
}
right={
<Chat />
} />
);
}Higher-Order Component
- 함수
- 컴포넌트를 입력받아
- 컴포넌트를 리턴하는 함수
- React 의 API 가 아님, 이거슨 자바스크립트
- Redux 의 connect 함수가 HOC
logProps
function logProps(WrappedComponent) {
return class extends React.Component {
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
console.log('Current props: ', this.props);
console.log('Next props: ', nextProps);
}
render() {
// Wraps the input component in a container, without mutating it. Good!
return <WrappedComponent {...this.props} />;
}
}
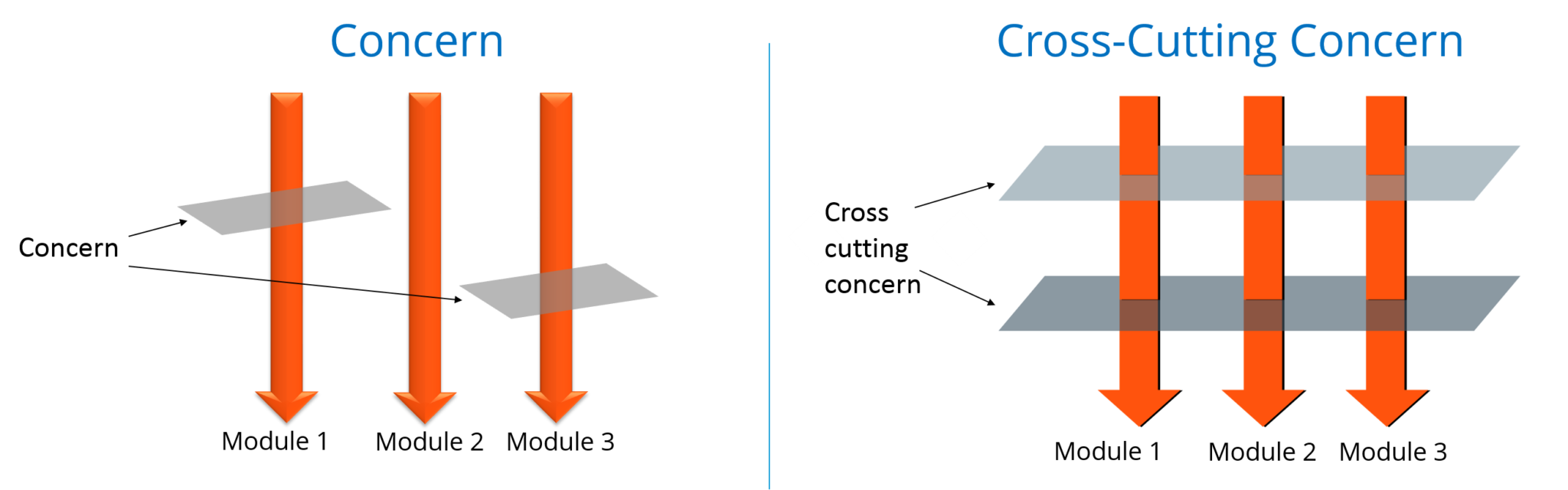
}Cross-Cutting Concern
Communication Between Components
하위 컴포넌트를 변경하기
button 를 클릭하여 Grand Child 를 변경하려면
- Grand Parent
- Parent
- Me
- Child
- Grand Chid
- Child
- Me
- <button></button>
- Parent
- 1. Grand Parent 컴포넌트에서 button 에 onClick 이벤트를 만들고,
- 2. 클릭하면, Grand Parent 의 state 를 변경하여, Parent1 로 내려주는 Props 를 변경
- 3. Parent1 의 Props 가 변경되면, Me 의 props 에 전달
- 4. Me 의 Props 가 변경되면, Child 의 props 로 전달
- 5. Child 의 Props 가 변경되면 Grand Child 의 props 로 전달
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
export interface AppProps {
}
export interface AppState {
toGrandChild: string;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
toGrandChild: '아직 안바뀜'
};
this._clickToGrandChild = this._clickToGrandChild.bind(this);
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<Parent {...this.state} />
<button onClick={this._clickToGrandChild}>GrandChild 의 값을 바꾸기</button>
</div>
);
}
private _clickToGrandChild(): void {
this.setState({
toGrandChild: '그랜드 차일드의 값을 변경'
});
}
}
interface ParentProp {
toGrandChild: string;
}
const Parent: React.SFC<ParentProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 Parent</p>
<Me {...props} />
</div>
);
};
interface MeProp {
toGrandChild: string;
}
const Me: React.SFC<MeProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 Me</p>
<Child {...props} />
</div>
);
};
interface ChildProp {
toGrandChild: string;
}
const Child: React.SFC<ChildProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 Child</p>
<GrandChild {...props} />
</div>
);
};
interface GrandChildProp {
toGrandChild: string;
}
const GrandChild: React.SFC<GrandChildProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 GrandChild</p>
<h3>{props.toGrandChild}</h3>
</div>
);
};
export default App;button 를 클릭하여 Grand Child 를 변경하려면
상위 컴포넌트를 변경하기
Grand Child 를 클릭하여 p 의 내용을 변경하려면
- Grand Parent
- Parent
- Me
- Child
- Grand Chid
- Child
- Me
- <p></p>
- Parent
- 1. Grand Parent 에서 함수를 만들고, 그 함수 안에 state 를 변경하도록 구현, 그 변경으로 인해 p 안의 내용을 변경.
- 2. 만들어진 함수를 props 에 넣어서, parent1 로 전달
- 3. Parent1 의 props 의 함수를 Me 의 props 로 전달
- 4. Me 의 Props 의 함수를 Child 의 props 로 전달
- 5. Child 의 Props 의 함수를 Grand Child 의 props 로 전달
import * as React from 'react';
import './App.css';
export interface AppProps {
}
export interface AppState {
fromGrandChild: string;
}
class App extends React.Component<AppProps, AppState> {
constructor(props: AppProps) {
console.log('App constructor');
super(props);
this.state = {
fromGrandChild: '아직 안바뀜'
};
this._clickFromGrandChild = this._clickFromGrandChild.bind(this);
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('App componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('App componentDidMount');
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('App componentWillUnmount');
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: AppProps) {
console.log(`App componentWillReceiveProps : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}`);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState): boolean {
console.log(`App shouldComponentUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps: AppProps, nextState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentWillUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(nextProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(nextState)}`);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: AppProps, prevState: AppState) {
console.log(`App componentDidUpdate : ${JSON.stringify(prevProps)}, ${JSON.stringify(prevState)}`);
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
return (
<div>
<Parent clickFromGrandChild={this._clickFromGrandChild} />
<p>{this.state.fromGrandChild}</p>
</div>
);
}
private _clickFromGrandChild(): void {
this.setState({
fromGrandChild: '그랜드 차일드로 부터 값이 변경되었음.'
});
}
}
interface ParentProp {
clickFromGrandChild(): void;
}
const Parent: React.SFC<ParentProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 Parent</p>
<Me {...props} />
</div>
);
};
interface MeProp {
clickFromGrandChild(): void;
}
const Me: React.SFC<MeProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 Me</p>
<Child {...props} />
</div>
);
};
interface ChildProp {
clickFromGrandChild(): void;
}
const Child: React.SFC<ChildProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 Child</p>
<GrandChild {...props} />
</div>
);
};
interface GrandChildProp {
clickFromGrandChild(): void;
}
const GrandChild: React.SFC<GrandChildProp> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>여긴 GrandChild</p>
<button onClick={props.clickFromGrandChild}>GrandChild 버튼</button>
</div>
);
};
export default App;