Nest.js Microservices

How
Why
What

Nest.js Microservices


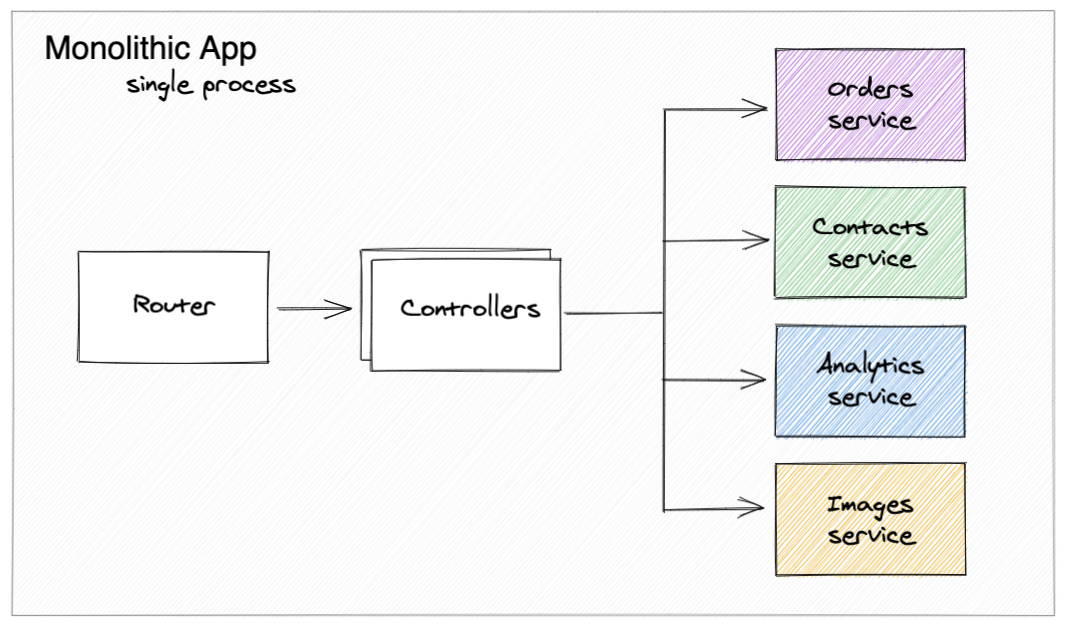

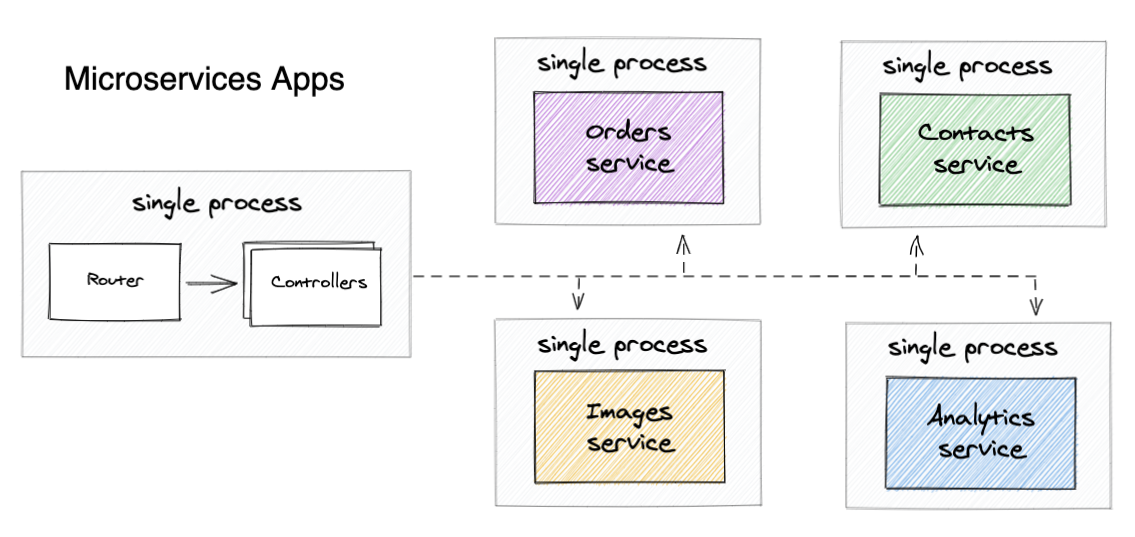
Motivation & advantages
Code reuse - Each service can serve many apps
Why

Scalable R&D - Each service can be managed by a separate team
Separate repositories, testing & deployment schedule
Resources - Easier for DevOps to manage the load separately
Scale each process individually
Some services are more popular than others
Challenges & tradeoffs
Testing - integration testing are more complex
Why

Memory allocation -
Monoliths are easier - using DI - same process - the same memory
Microservices run on separate processes - separate memory
They need a standard way to communicate with each other
Monoliths - DI
Injecting a reference to an instantiated object stored in the same memory process, then invoking methods on it...
import { PetsService } from './pets.service';
@Controller('pets')
export class PetsController {
constructor(private readonly petsService: PetsService) {}
@Get()
getAllPets() {
return this.petsService.getAllPets();
}
}
How
Microservices - DI
Injecting a microservice client proxy, who knows how to communicate with it and get results.
import { Inject, Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ClientProxy } from '@nestjs/microservices';
@Injectable()
export class AppService {
constructor(@Inject('SOME_SERVICE') private client: ClientProxy) {}
async getHello() {
return await this.client.send<string>('hello', {});
}
}
How
Supported
Transports

How
Basic TCP
direct
Redis
MQTT
NATS
RabbitMQ
Kafka
Message
Brokers
gRPC
Remote
Procedure call

How
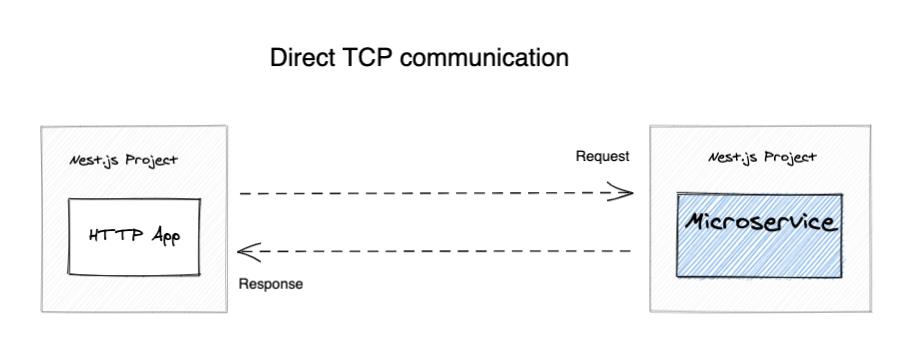
Tight coupling -
The client app needs to know about the microservice existence
and how to contact it. This info will be stored in config files...
When you have dozens or hundreds of microservices, it becomes a problem
as things move and change all the time...

How
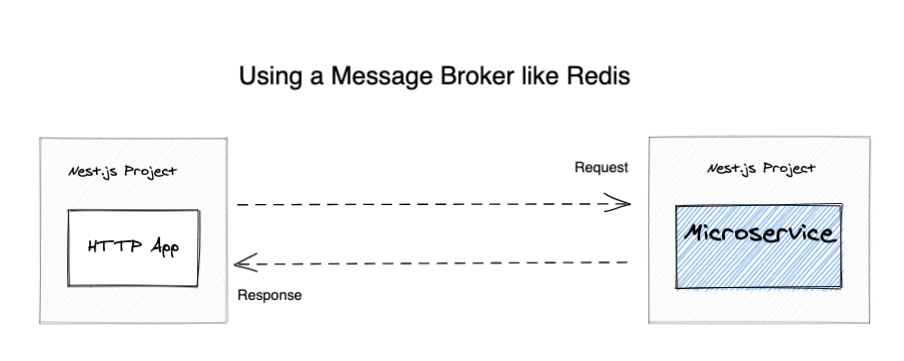

Loose coupling -
A message broker like Redis helps us decouple the different microservices from our apps. Managing many microservices becomes a lot easier when we route all of our communication through a single address. That goes for monitoring as well...
Demo time!


How