cog sci 131 section
week 04/18/22
by yuan meng
agenda
- weber's w (piantadosi, 2016)
- implement metropolis-hastings
- hw9 prompt walkthrough
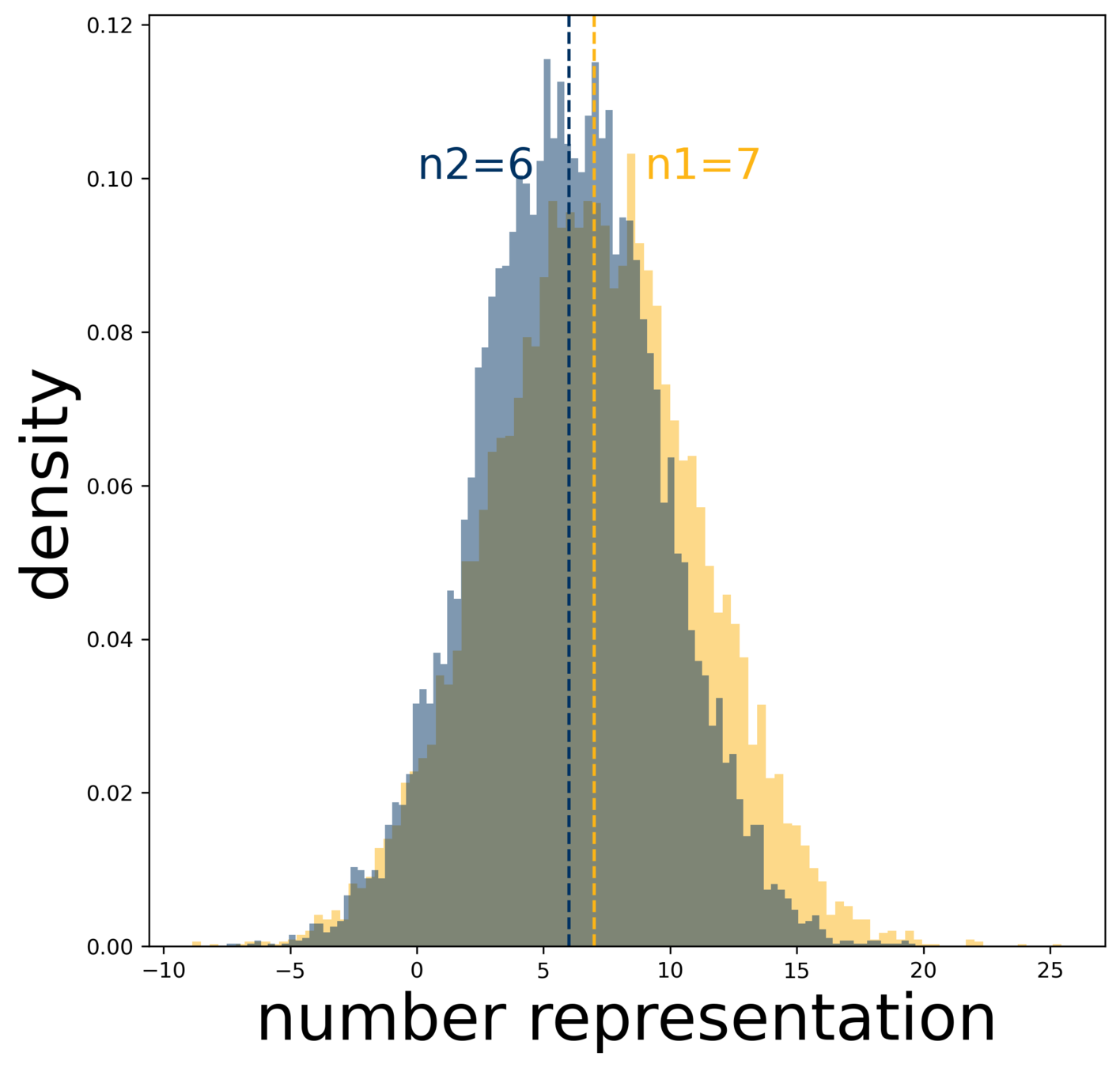
weber ratio W
measures the acuity of the approximate number system (ans)
- a large number n is represented as a normal distribution centered at n
- the probability that we say n1 ≥ n2 when it's indeed the case is a function of n1, n2, and W
two packs of extremely dangerous dogs 👉 which pack has more?
probability of getting it right 👉 this small area













weber ratio W
infer W from response data
- prior of W (prior is 0 if W < 0):
- likelihood given k data points:
- unstandardized posterior of W:
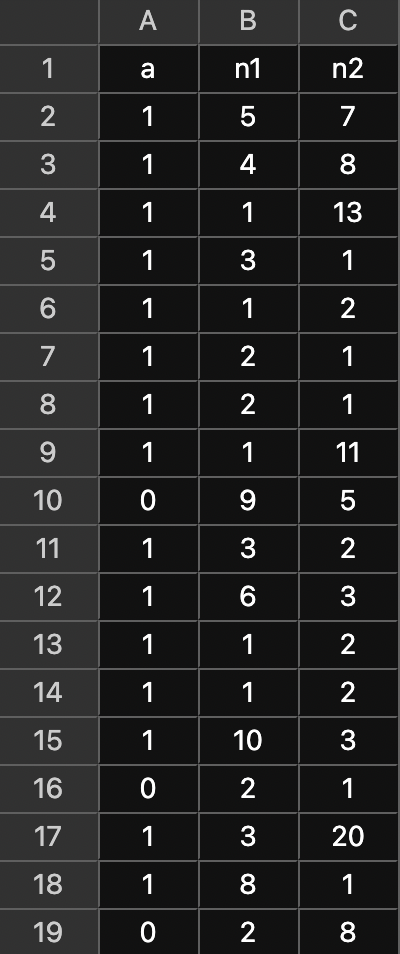
data:
- each trial is a judgment (do you think n1 > n2?);
- a = 1: answered correctly; a = 0: answered incorrectly
be sure to take log!
implement metropolis-hastings
- goal: collect representative samples from the posterior distribution of W
-
the sampling algorithm
- initialize: pick a random W
- propose: W' = W + noise
-
decide whether to accept W'
- if P(W'|D) > P(W|D), definitely accept
- even if P(W'|D) ≤ P(W|D), accept W' with a P(W'|D)/P(W|D) probability
- iterate over 1-3, each time starting with the last accepted W
- sampling vs. optimization: a sampler doesn't alter the value of W, but an optimizer (e.g., gradient descent) does
- burn-in: people usually discard the first bunch of samples which may not be good
def metropolis_hastings(n1, n2, a, n_iters):
# generate a random W
W = # sample a value from some distribution
# log posterior of initial W
log_p = log_posterior(n1, n2, a, W)
# arrays to collect samples and log posteriors
Ws, log_ps = np.zeros(n_iters), np.zeros(n_iters)
# collect samples from posterior
for iter in range(n_iters):
# propose a new W
W_new = # add a noise from Normal(0, 0.1)
# calculate new log posterior
log_p_new = log_posterior(n1, n2, a, W_new)
# log ratio of new and old log posteriors
log_ratio = # what should this be?
# decide whether to accept W_new
if # write your own condition:
W = W_new
log_post = log_post_new
# collect sample from this iteration
Ws[iter], log_ps[iter] = W, log_post
# return samples
return {"W": Ws, "log_posteriors": log_ps}most challenging bit
- need to adapt original criteria to log-transformation
- if cleverly written, can use one simple if-statement to catch both acceptance conditions
(ofc, critical parts commented out)
hw9 prompts
samples from posterior
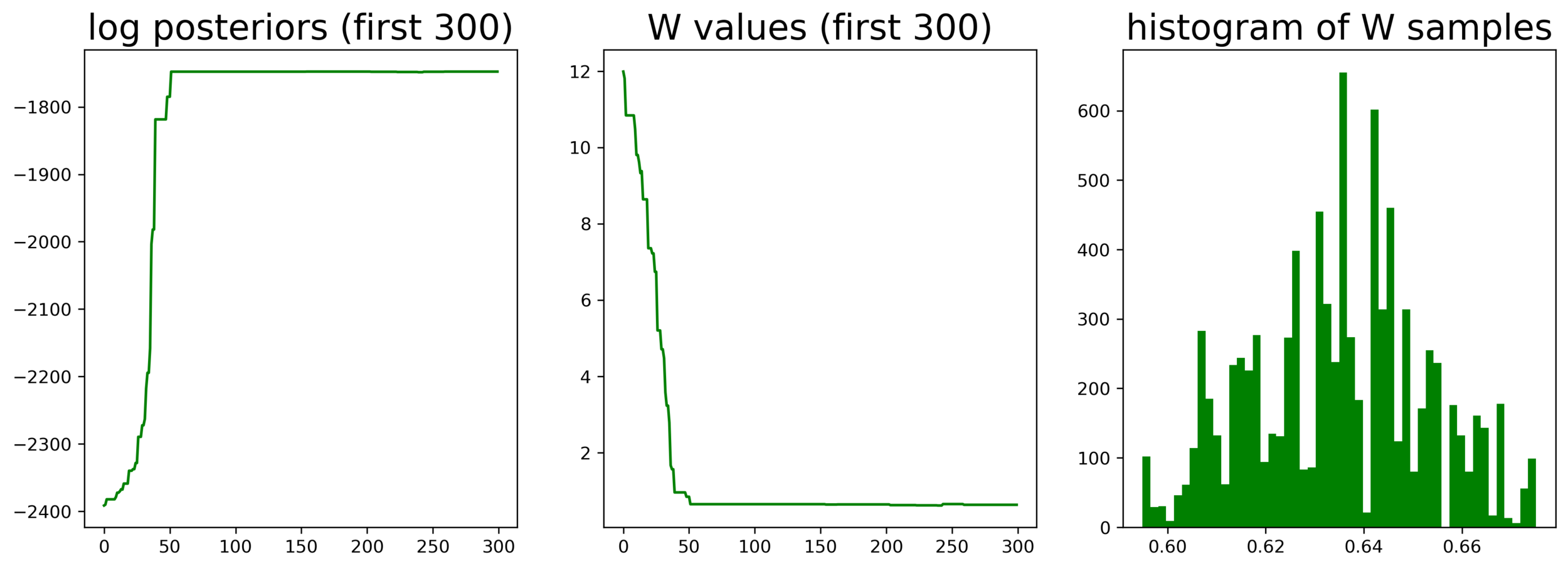
homework 9, q5
samples from prior
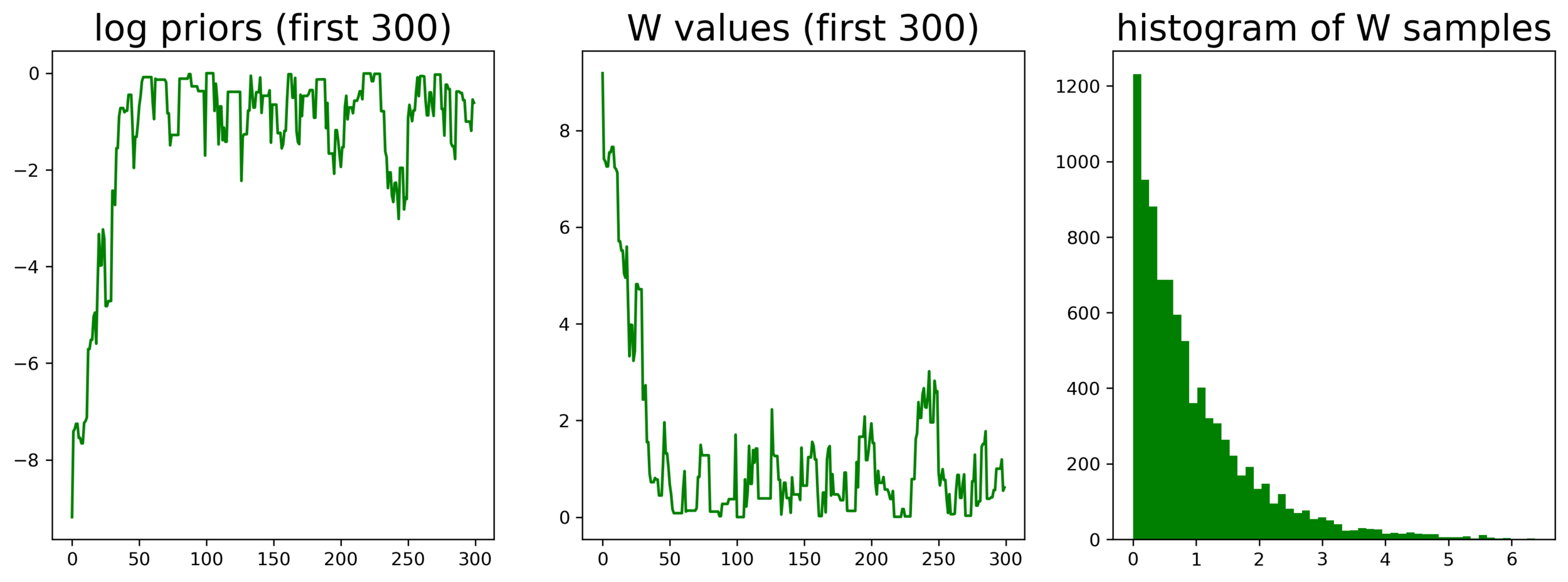
homework 9, q7
bayesian cognitive model
vs. bayesian data analysis
bayes as a model of cognition: a normative model that dictates what an ideal learner should do given data and prior
bayes as a data analysis tool: a descriptive model that captures what a real learner did do given data and prior
the same prior and data lead to the same inference 👉 if prior is optimal, then inference is optimal
e.g., seeing 100 heads in a row, the probability that the tosser is a psychic?
different people may discount observations differently 👉 can learn each person's "discount rate" from data