Recursion



什么是递归(recursion)
递归是计算机科学中一种通过重复将问题分解为同类的子问题而解决问题的方法(和迭代相对应).



如何解决问题
- 把问题分解为较小的问题.
- 解决较小的问题.
- 用较小的问题的结果去解决原问题.
- 如果较小的问题与原问题只有问题规模不一样, 其余部分完全一样, 这种情况被称为递归.



把问题分解为较小的问题
- 斐波那契数列: Fibonacci number
- 倒置链表: Reverse LinkedList
- 删除链表中的节点: Remove Node in LinkedList
- 把链表中所有的节点值等于给定值的节点全部删除.
- 归并排序: Merge Sort
- etc.



递归属性
- 基本情形(Base case)
- 简单的情况, 不需要再进行递归就可以得到结果.
- 递归(Recursion)
- 一系列将其他情形缩减到基本情形的规则.



数学归纳
- 为了证明一个命题
- 基本情形, 证明给定命题满足第一个自然数.
- 归纳过程, 证明当给定命题满足任意一个自然数时, 可以得到给定命题满足下一个自然数.



- 斐波那契数列(Fibonacci Number)
基本情形: F(0) = 0;
F(1) = 1;
递归规则: F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2)



// Fibonacci calculation
int Fibonacci (int n) {
//Base Case
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) return 1;
//recursion rule
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2);
}
f(5)
= f(4) + f(3)
= f(3) + f(2) f(2) + {f(1) = 1}
= f(2) + {f(1) = 1} {f(1)=1} + {f(0)=0} {f(1)=1} + {f(0)=0}
={f(1)=1} + {f(0)=0} 


更多递归问题



最大公约数(Greatest Common Divisor)
- 如何计算gcd(111, 259)
- gcd(111, 259) = gcd(111, 259%111) = gcd(111, 37) = gcd(37, 0) = 37
- gcd(x, y), x > y
- y = 0, x
- y != 0, gcd(y, x%y)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
- 有3根可以放置直径不同的盘子的柱子, 直径较大的盘子不能放在直径较小的盘子的上面. 假设开始时所有盘子都在一根柱子上, 每次只能移动一个盘子, 如何能把所有盘子移动到另外一根柱子上?




汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
-
如何把n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把第一个盘子从A移动到B
- 把其余n-1个盘子从A移动到C
- 把一盘子从B移动到C
1
2
3
4



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
-
如何把n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把前(n-1)个盘子从A移动到B
- 把第n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把其余的(n-1)个盘子从B移动到C
1
2
3
4






什么是递归?
一种特殊的解决问题的策略



Code problem with recursion
- 基本情形
- 递归规则
- 用代码中的函数去表示问题.



如何解决问题
- 将问题分解为较小的问题.
- 解决较小的问题.
- 用较小的问题的结果去解决原问题.
- 如果较小的问题与原问题只有问题规模不一样, 其余部分完全一样, 这种情况被称为递归.
function solveProblem() {
divide into small problems;
...
...
solveProblem();
}
大多数编程语言通过允许函数调用自身来支持递归.



Code problem with recursion
- 基本情形
- 递归规则
-
用代码中的函数去表示问题.
-
定义基本的参数
- 被用来定义问题的参数.
- 定义返回值
-
定义基本的参数



function tellStory() {
mountain();
temple();
oldMonk();
tellStory();
}
从前有个山,
山里有个庙,
庙里有个老和尚,
老和尚在给小和尚讲故事,
从前有个山...
讲故事
Old Monk Tells Story



function factorial(int n) {
int m = factorial(n-1);
return m*n;
}
n的阶乘
- 计算(n-1)的阶乘,将结果记为m.
- n的阶乘就是m*n
n的阶乘(Factorial of n)



function factorial(int n) {
if (n==1) return 1;
int m = factorial(n-1);
return m*n;
}
n的阶乘
- 如果n为1, 1的阶乘就是1.
- 计算(n-1)的阶乘,将结果记为m.
- n的阶乘就是m*n
n的阶乘(Factorial of n)
function factorial(int n) {
if (n==1) return 1;
return n * factorial(n-1);
}



function fibo(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 1;
return fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2);
}
第n个斐波那契数
- 如果n为1, 则结果是1.
- 如果n为2, 则结果是1.
第n个斐波那契数
The nth Fibonacci Number
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ...



爬楼梯(Climb Building)
一栋楼有n个楼梯, 一个人一次可以爬1或者2登楼梯, 那么这个人有多少种不同的方式可以爬到顶层.



Climb Building
- 1 stair left, one way.
- 2 stairs left, two ways.
- n stairs left,
- climb one stair first, climb the (n-1) later.
- climb two stairs first, climb the (n-2) later.
There is a building with n stairs, one person can climb 1 or 2 stairs at one time, then how many different ways there are for this person to climb to the top.
public static int climb(int n) {
if (n <= 2) return n;
return climb(n-1) + climb(n-2);
}



Code problem with recursion
- 基本情形
- 递归规则
- 用代码中的函数去表示问题.
- 定义基本参数
- 被用来定义问题的参数.
- 被用来存储临时结果或状态的变量.
- 定义返回值
- 定义基本参数



爬楼梯(Climb Building)
一栋楼有n个楼梯, 一个人一次可以爬1或者2登楼梯, 那么这个人有多少种不同的方式可以爬到顶层..
public static void climb(int n, String preWay) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println(preWay + " 1");
return;
}
if (n == 2) {
System.out.println(preWay + " 2");
System.out.println(preWay + " 1 1");
return;
}
String preWay1 = preWay + " 1";
climb(n-1, preWay1);
String preWay2 = preWay + " 2";
climb(n-2, preWay2);
}



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
- 把前(n-1)个盘子从A移动到B
- 把第n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把其余的(n-1)个盘子从B移动到C
把所有盘子从A移动到C一共需要多少步.
public static int hanoi(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
return hanoi(n-1) + 1 + hanoi(n-1);
}



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
- 把前(n-1)个盘子从A移动到B
- 把第n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把其余的(n-1)个盘子从B移动到C
把所有盘子从A移动到C一共需要多少步.
public static int hanoi(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
return 2 * hanoi(n-1) + 1;
}



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
- 把前(n-1)个盘子从A移动到B
- 把第n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把其余的(n-1)个盘子从B移动到C
请输出把所有盘子从A移动到C的所有步骤.
public static void hanoi(int n, char source, char spare, char target) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move " + source + " to " + target);
return;
}
hanoi(n-1, source, target, spare);
System.out.println("Move " + source + " to " + target);
hanoi(n-1, spare, source, target);
}



汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
- 把前(n-1)个盘子从A移动到B
- 把第n个盘子从A移动到C
- 把其余的(n-1)个盘子从B移动到C
请输出把所有盘子从A移动到C的所有步骤.
public static void hanoi(int n, char source, char spare, char target) {
if (n > 0) {
hanoi(n-1, source, target, spare);
System.out.println("Move " + source + " to " + target);
hanoi(n-1, spare, source, target);
}
}



链表之和(Sum of Linked List)
- 如果链表为空, 和为0.
- 计算从头节点的下一个节点开始的链表的和.
- 最终的结果是头结点的值加上之前计算出来的部分和.
计算链表中所有节点之和.



链表之和(Sum of Linked List)
- 如果链表为空, 和为0.
- 计算从头节点的下一个节点开始的链表的和.
- 最终的结果是头结点的值加上之前计算出来的部分和.
计算链表中所有节点之和.
public static int sum(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return 0;
return head.val + sum(head.next);
}



Remove Linked List Elements
- 如果链表为空, 不需要执行任何操作.
- 对以head.next为头结点的链表执行删除操作, 将其存储为newHead.
- 如果头结点的值为val, 则删除头结点.
- 并将newHead作为新的head.
把链表中所有的节点值等于给定值val的节点全部删除.
public static ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode newHead = removeElements(head.next, val);
if (head.val == val) {
return newHead;
} else {
head.next = newHead;
return head;
}
}



- 倒置以head.next为头结点的链表, 将其记为newHead
- newTail.next = head
- 返回newHead;
倒置链表(Reverse Linked List)



1
2
3
4
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
Reverse Linked List



1
2
3
4
1
4
3
2
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
Reverse Linked List



1
2
3
4
1
4
3
2
1
4
3
2
- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
Reverse Linked List



public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}- Reverse head.next, mark as newHead
- newTail.next = head
- return newHead;
Reverse Linked List



0-1背包(0-1 Knapsack)
给定一个可以装s磅物品的背包, 以及一组重量为 w1, w2, ... wn 的物品. 返回我们是否可以挑选特定物品, 以便它们的总重量为s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;



0-1背包(0-1 Knapsack)
给定一个可以装s磅物品的背包, 以及一组重量为 w1, w2, ... wn 的物品. 返回我们是否可以挑选特定物品, 以便它们的总重量为s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
14



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
14, 8



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
14, 8, 7



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
14, 7, 5



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
14, 5, 3



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
14, 5, 3, 8



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
8, 7



0-1 Knapsack
Given a knapsack which can hold s pounds of items, and a set of items with weight w1, w2, ... wn. Return whether we can pick specific items so that their total weight s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
8, 7, 5



0-1背包(0-1 Knapsack)
给定一个可以装s磅物品的背包, 以及一组重量为 w1, w2, ... wn 的物品. 返回我们是否可以挑选特定物品, 以便它们的总重量为s.
Example Input:
s = 20;
w = [14, 8, 7, 5, 3];
Example Output:
True;
给定一个物品, 只有两种选择:
- 选择这个物品, 则问题变为(s-w[i], w - w[i])
- 不选择这个物品, 则问题变为(s, w - w[i])



0-1 Knapsack
给定一个可以装s磅物品的背包, 以及一组重量为 w1, w2, ... wn 的物品. 返回我们是否可以挑选特定物品, 以便它们的总重量为s.
public static boolean knapsack(int s, int[] weights, int index) {
if (s == 0) {
return true;
}
if (s < 0 || index >= weights.length) {
return false;
}
return knapsack(s - weights[index], weights, index+1) ||
knapsack(s, weights, index+1);
}





迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.
示例输入:
起点: (0, 0); 终点:(5, 5);
Maze: char[][] = {
{'.', 'X', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'X', 'X', '.', 'X', '.', '.'},
{'.', 'X', 'X', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'}
}
示例输出: True



迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.
示例输入:
起点: (0, 0); 终点:(5, 5);
Maze: char[][] = {
{'.', 'X', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'X', 'X', '.', 'X', '.', '.'},
{'.', 'X', 'X', 'X', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', 'X'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'}
}
示例输出: True



迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.



- 越界
- 墙
迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.



- 越界
- 墙
-
已访问
- (1, 2) -> (2, 2) -> (1, 2) -> (2, 2) -> ...
迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.



迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.



public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
boolean[][] visited) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X' || visited[startX][startY]) {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
visited[startX][startY] = true;
if (solveMaze(maze, startX + 1, startY, targetX, targetY, visited) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY + 1, targetX, targetY, visited) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX - 1, startY, targetX, targetY, visited) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY - 1, targetX, targetY, visited)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 判断是否可以到达目标.



public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
if (solveMaze(maze, startX + 1, startY, targetX, targetY) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY + 1, targetX, targetY) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX - 1, startY, targetX, targetY) ||
solveMaze(maze, startX, startY - 1, targetX, targetY)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.



public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (solveMaze(maze, startX + dx[i], startY + dy[i], targetX, targetY)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.



public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = startX + dx[i], newY = startY + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= maze.length || newY < 0 || newY >= maze.length ||
maze[newX][newY] == 'X') {
continue;
}
if (solveMaze(maze, newX, newY, targetX, targetY)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return whether the target can be reached.



Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem



Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem



Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem



Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem



Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem



Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem



Problem
sub-problem-1
sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-sub-problem
base-problem
Problem
sub-problem-1
base-problem
sub-problem-2
sub-problem-3
sub-sub-problem-2
sub-sub-sub-problem
sub-sub-problem-1
...
...
...
回溯(Backtracking)



public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
String path) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
System.out.println(path);
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char[] direction = {'D', 'R', 'U', 'L'};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
String newPath = path + direction[i] + " ";
if (solveMaze(maze, startX+dx[i], startY+dy[i], targetX, targetY, newPath)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}迷宫(Maze)
给定一个迷宫以及一个起点和一个终点, 输出到达终点的路径.



public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
ArrayList<Character> path) {
if (startX < 0 || startX >= maze.length ||
startY < 0 || startY >= maze[0].length ||
maze[startX][startY] == 'X') {
return false;
}
if (startX == targetX && startY == targetY) {
return true;
}
maze[startX][startY] = 'X';
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char[] direction = {'D', 'R', 'U', 'L'};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
path.add(direction[i]);
if (solveMaze(maze, startX+dx[i], startY+dy[i], targetX, targetY, path)) {
return true;
}
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
return false;
}Maze
Given a maze and a start point and a target point, return the path to reach the target.



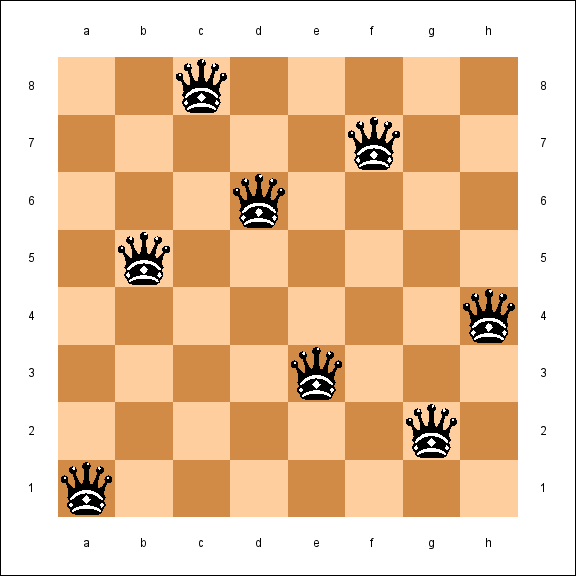
八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
..Q.....
.....Q..
...Q....
.Q......
.......Q
....Q...
......Q.
Q.......



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | Q | X |
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X | X | ||||||
| X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | ||||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X | X | |||||
| X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X | X | |||
| X | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| X | X | X | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| X | X | X | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | Q | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
| X | Q | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | X | Q | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | Q | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Q |
| X | X | Q | X | X | X | X | X |
| Q | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| X | X | X | X | X | X | Q | X |
| X | X | X | X | Q | X | X | X |



八皇后(Eight Queens)
八皇后难题: 将8个国际象棋皇后放在一个8×8的棋盘上, 使得任意两个皇后之间不会相互威胁.
void putQueens(char[][] board, int row,
List<List<String>> results) {
if (row == board.length) {
saveResult(board, results);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board[0].length; col++) {
if (isLegal(board, row, col)) {
board[row][col] = 'Q';
putQueens(board, row+1, results);
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
return;
}


Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
void saveResult(char[][] board,
List<List<String>> results) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
result.add(new String(board[i]));
}
results.add(result);
}


Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
boolean isLegal(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
for (int i = row-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
return false;
int tempCol = col - row + i;
if (tempCol >= 0 &&
tempCol < board.length &&
board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
tempCol = col + row - i;
if (tempCol >= 0 &&
tempCol < board.length &&
board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
}
return true;
}


Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
putQueens(board, 0, results);
return results;
}


Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
putQueens(board, 0, results);
return results;
}
void putQueens(char[][] board, int row, List<List<String>> results) {
if (row == board.length) {
saveResult(board, results);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board[0].length; col++) {
if (isLegal(board, row, col)) {
board[row][col] = 'Q';
putQueens(board, row+1, results);
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
return;
}
void saveResult(char[][] board, List<List<String>> results) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
result.add(new String(board[i]));
}
results.add(result);
}
boolean isLegal(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
for (int i = row-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
return false;
int tempCol = col - row + i;
if (tempCol >= 0 && tempCol < board.length && board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
tempCol = col + row - i;
if (tempCol >= 0 && tempCol < board.length && board[i][tempCol] == 'Q')
return false;
}
return true;
}


Eight Queens
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
-
We don't need a char[][] to store the board
- int[] will be enough



Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
int[] board = new int[n];
putQueens(board, 0, results);
return results;
}
void putQueens(int[] board, int row, List<List<String>> results) {
if (row == board.length) {
saveResult(board, results);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board.length; col++) {
if (isLegal(board, row, col)) {
board[row] = col;
putQueens(board, row+1, results);
}
}
return;
}
boolean isLegal(int[] board, int row, int col) {
for (int i = row-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i] == col || Math.abs(board[i] - col) == Math.abs(row - i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void saveResult(int[] board, List<List<String>> results) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
StringBuilder oneLine = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
if (j == board[i]) {
oneLine.append('Q');
} else {
oneLine.append('.');
}
}
result.add(oneLine.toString());
}
results.add(result);
}


回溯总结(Backtracking Summary)
- 回溯(Backtrack) = 尝试(try), 迭代(iterate), 遍历(traverse), etc.
- 在搜索空间不停尝试, 直到
- 问题被解决
- 没有更多的方法可以尝试
- Level-N problem -> M * Level-(N-1) subproblem
- 进入子问题时, 除了参数以为, 其他状态要保持相同.



排列(Permutation)
给定一组不相同的数字, 返回所有可能的排列.
例如,
[1,2,3]有如下排列:
[1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], and [3,2,1].
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
// Implement this method.
}



Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Arrays.sort(num);
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++)
numList.add(num[i]);
return permute(new ArrayList<Integer>(), numList);
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(List<Integer> cur,
List<Integer> num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (num.size() == 0) {
results.add(cur);
return results;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.size(); i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> newCur = new ArrayList<Integer>(cur);
newCur.add(num.get(i));
ArrayList<Integer> newNum = new ArrayList<Integer>(num);
newNum.remove(i);
results.addAll(permute(newCur, newNum));
}
return results;
}Permutation



Permutation
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
Arrays.sort(num);
return permute(new ArrayList<Integer>(), num);
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(ArrayList<Integer> cur, int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (cur.size() == num.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return results;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (cur.contains(num[i])) {
continue;
}
cur.add(num[i]);
results.addAll(permute(cur, num));
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
return results;
}


Permutation
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible permutations.
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(num);
permute(results, new ArrayList<Integer>(), num);
return results;
}
public void permute(List<List<Integer>> results,
ArrayList<Integer> cur, int[] num) {
if (cur.size() == num.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (cur.contains(num[i])) {
continue;
}
cur.add(num[i]);
permute(results, cur, num);
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
}


组合(Combination)
给定一组不相同的数字, 返回所有可能的组合.
例如,
[2, 6, 8]有如下的所有组合:
[], [2], [6], [8], [2, 6], [2, 8], [6, 8], [2, 6, 8].
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
// Implement this method.
}



Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(items);
return;
}
ArrayList<Integer> newItems1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(items);
combination(results, nums, index+1, newItems1);
ArrayList<Integer> newItems2 = new ArrayList<Integer>(items);
newItems2.add(nums[index]);
combination(results, nums, index+1, newItems2);
}


Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
combination(results, nums, index+1, items);
items.add(nums[index]);
combination(results, nums, index+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}


Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
items.add(nums[i]);
combination(results, nums, i+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}
}Missing Empty Set



Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <= nums.length; i++) {
if (i == nums.length) {
combination(results, nums, i, items);
return;
}
items.add(nums[i]);
combination(results, nums, i+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}
}


Combination
Given a collection of distinct numbers, return all possible combinations.
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combination(results, nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
public void combination(List<List<Integer>> results,
int[] nums, int index,
ArrayList<Integer> items) {
if (index == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(items));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
items.add(nums[i]);
combination(results, nums, i+1, items);
items.remove(items.size()-1);
}
combination(results, nums, nums.length, items);
}


总结
Recursion
subproblem
-> problem
subproblem-1 ||
subproblem-2 ||
subproblem-N
-> problem
subproblem-1 &&
subproblem-2 &&
subproblem-N
-> problem
Factorial,
Sum of LinkedList,
Remove Linked List Element, etc.
Maze,
Sudoku,
Most DFS problems, etc.
Knapsack
Permutations,
Combinations,
Eight Queen,
kSum, etc.



总结
- 递归是一种策略.
- 总是尝试将问题分解为子问题, 并先解决子问题.
- 如果两个子问题的解相同, 可以调用同一个方法.



总结
Level N
Level N-1
Level N-1
Level N-1
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY, String path) {
...
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
String newPath = path + direction[i] + " ";
if (solveMaze(maze, startX+dx[i], startY+dy[i],
targetX, targetY, newPath)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}parameters
parameters
parameters
这些参数(parameters)互不影响.



总结
Level N
Level N-1
Level N-1
Level N-1
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
ArrayList<Character> path) {
...
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
path.add(direction[i]);
if (solveMaze(maze, startX+dx[i], startY+dy[i],
targetX, targetY, path)) {
return true;
}
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
return false;
}- 对于作为标记的变量, 要确保它们被更新.
- 对于不同的解决方案, 在进入N-1级问题时共享参数需要相同.
Shared Parameters



Homework (Optional)


