BFS
BFS
- Breadth First Search
- One starts at the root (selecting some arbitrary node as the root in the case of a graph) and explores the neighbor nodes first, before moving to the next level neighbors.
- Find minimum path/distance/...
- Minimum Tree Depth
- Word Edit Distance
- etc...
- No Recursion, QUEUE
Queue
- Used for BFS
- FIFO
- VS Stack?
- Multitask Queue / System queue -> Design
Queue in Java
- Queue<> queue = new LinkedList<>();
- boolean offer(Element e); (add)
- offer can return false while add can only cause exception when the element cannot be added due to capacity restriction.
- Element poll(); (remove)
- poll returns null when empty while remove will throw exception.
- Element peek(); (element)
- peek returns null when empty while element will throw exception.
- boolean offer(Element e); (add)
Queue in Python
from collections import deque
# Creating a queue
queue = deque()
# Adding elements to the queue
queue.append('element1') # Similar to offer in Java
queue.append('element2')
# Removing elements from the queue
element = queue.popleft() # Similar to poll in Java; use pop() for a stack
if not queue:
print("Queue is empty")
# Peeking at the front of the queue
if queue:
front = queue[0] # Similar to peek in Java
print("Front element:", front)
else:
print("Queue is empty, nothing to peek")
BFS for Binary Trees
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
A
/ \
B C
/ \ / \
D E F G
/ \
H I
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
// visit top.
if (top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
}
}
Given a binary tree, return its level order traversal.
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
A
/ \
B C
/ \ / \
D E F G
/ \
H I
Given a binary tree, return its level order traversal.
def level_order_traversal(root):
queue = deque([root]) # Initialize the queue with the root
while queue:
top = queue.popleft() # Pop from the front of the queue
# visit top (can be replaced with any operation)
print(top.val) # Example visit operation
if top.left:
queue.append(top.left) # Add left child to queue if exists
if top.right:
queue.append(top.right) # Add right child to queue if existsBinary Tree Level Order Traversal
A
/ \
B C
/ \ / \
D E F G
/ \
H I
Given a binary tree, return its level order traversal.
The output is A B C D E F G H I
What if we want to separate each level?
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given a binary tree, return its level order traversal.
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
[ [3], [9,20], [15,7] ]
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given a binary tree, return its level order traversal.
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top.left != null) {
queue2.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue2.offer(top.right);
}
oneResult.add(top.val);
}
results.add(oneResult);
queue = queue2;
}
return results;
}Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given a binary tree, return its level order traversal.
def levelOrder(root):
results = []
queue = []
if root is not None:
queue.append(root)
while len(queue) > 0:
oneResult = []
queue2 = []
while len(queue) > 0:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top.left is not None:
queue2.append(top.left)
if top.right is not None:
queue2.append(top.right)
oneResult.append(top.val)
results.append(oneResult)
queue = queue2
return resultsBinary Tree Level Order Traversal
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
queue.offer(null);
List<Integer> oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top == null) {
results.add(oneResult);
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
queue.offer(null);
}
oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
} else {
if (top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
}
oneResult.add(top.val);
}
}
return results;
}Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
def levelOrder(root):
if not root:
return []
results = []
queue = []
queue.append(root)
queue.append(None)
oneResult = []
while len(queue) > 0:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top is None:
results.append(oneResult)
if len(queue) > 0:
queue.append(None)
oneResult = []
else:
if top.left is not None:
queue.append(top.left)
if top.right is not None:
queue.append(top.right)
oneResult.append(top.val)
return results
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size = 1;
int nextSize = 0;
if (root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
}
List<Integer> oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
nextSize ++;
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
nextSize ++;
}
oneResult.add(top.val);
size --;
if (size == 0) {
results.add(oneResult);
oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
size = nextSize;
nextSize = 0;
}
}
return results;
}Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
def levelOrder(root):
results = []
queue = []
size = 1
nextSize = 0
if root is not None:
queue.append(root)
oneResult = []
while queue:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top.left is not None:
queue.append(top.left)
nextSize += 1
if top.right is not None:
queue.append(top.right)
nextSize += 1
oneResult.append(top.val)
size -= 1
if size == 0:
results.append(oneResult)
oneResult = []
size = nextSize
nextSize = 0
return results
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
Given a binary tree, return its zigzag level order traversal.
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
}
boolean isOdd = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top.left != null) {
queue2.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue2.offer(top.right);
}
oneResult.add(top.val);
}
if (!isOdd) {
Collections.reverse(oneResult);
}
results.add(oneResult);
isOdd = !isOdd;
queue = queue2;
}
return results;
}Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
def zigzagLevelOrder(root):
results = []
queue = []
if root is not None:
queue.append(root)
isOdd = True
while len(queue) > 0:
oneResult = []
queue2 = []
while len(queue) > 0:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top.left is not None:
queue2.append(top.left)
if top.right is not None:
queue2.append(top.right)
oneResult.append(top.val)
if not isOdd:
oneResult.reverse()
results.append(oneResult)
isOdd = not isOdd
queue = queue2
return results
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
- Reversing an ArrayList for every loop is time-consuming. It is really time consuming?
- What is the run time?
- Visit order is opposite from level to level
- LIFO
- Stack
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return results;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
boolean isOdd = true;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> oneResult = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
if (!isOdd) {
if (top.right != null)
stack2.push(top.right);
if (top.left != null)
stack2.push(top.left);
} else {
if (top.left != null)
stack2.push(top.left);
if (top.right != null)
stack2.push(top.right);
}
oneResult.add(top.val);
}
results.add(oneResult);
stack = stack2;
isOdd = !isOdd;
}
return results;
} 3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
def zigzagLevelOrder(root):
results = []
if root is None:
return results
stack = []
stack.append(root)
isOdd = True
while len(stack) > 0:
oneResult = []
stack2 = []
while len(stack) > 0:
top = stack.pop()
if not isOdd:
if top.right is not None:
stack2.append(top.right)
if top.left is not None:
stack2.append(top.left)
else:
if top.left is not None:
stack2.append(top.left)
if top.right is not None:
stack2.append(top.right)
oneResult.append(top.val)
results.append(oneResult)
stack = stack2
isOdd = not isOdd
return results
Find Bottom Left Tree Value
BFS
- Same as level traversal, but need to know which one is the first one of this level
Given a binary tree, find the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
1 / \ 2 0 \ / \ 4 7 9
Result: 4
Find Bottom Left Tree Value
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int leftValue = 0;
boolean isFirst = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
isFirst = true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (isFirst) {
leftValue = top.val;
isFirst = false;
}
if (top.left != null) {
queue2.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue2.offer(top.right);
}
}
queue = queue2;
}
return leftValue;
}Find Bottom Left Tree Value
def findBottomLeftValue(root):
queue = []
queue.append(root)
leftValue = 0
isFirst = False
while queue:
isFirst = True
queue2 = []
while queue:
top = queue.pop(0)
if isFirst:
leftValue = top.val
isFirst = False
if top.left:
queue2.append(top.left)
if top.right:
queue2.append(top.right)
queue = queue2
return leftValue
How to level order traverse
- If level is important, most cases
- Two queues.
- Dummy node, different from all other nodes to be a flag.
- Maintain size of current level.
- If level is unimportant
- One queue.
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
1 / \ 2 2 / \ / \ 3 4 4 3
1 / \ 2 2 / \ 3 4
1 / \ 2 2 / \ 3 3
3
2
3
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
DFS
- Minimum depth of Root
- if root is leaf, 1.
- if root.left is null, return right.
- if root.right is null, return left.
- return the minimum of (left, right).
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
BFS
- Level Traverse the tree, return the depth of the first leaf node.
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
queue.offer(null);
int minDepth = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top == null) {
minDepth++;
queue.offer(null);
continue;
}
if (top.left == null && top.right == null) {
return minDepth;
}
if (top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
}
}
return minDepth;
}Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
def minDepth(root):
if root is None:
return 0
queue = []
queue.append(root)
queue.append(None)
minDepth = 1
while len(queue) > 0:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top is None:
minDepth += 1
queue.append(None)
continue
if top.left is None and top.right is None:
return minDepth
if top.left is not None:
queue.append(top.left)
if top.right is not None:
queue.append(top.right)
return minDepth
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int minDepth = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top.left == null && top.right == null) {
return minDepth;
}
if (top.left != null) {
queue2.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue2.offer(top.right);
}
}
minDepth++;
queue = queue2;
}
return minDepth;
}BFS vs DFS, which is better?
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
def minDepth(root):
if root is None:
return 0
queue = []
queue.append(root)
minDepth = 1
while len(queue) > 0:
queue2 = []
while len(queue) > 0:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top.left is None and top.right is None:
return minDepth
if top.left is not None:
queue2.append(top.left)
if top.right is not None:
queue2.append(top.right)
minDepth += 1
queue = queue2
return minDepth- Level is important, most cases
- Two queues.
- Dummy node, different from all other nodes to be a flag.
- Maintain size of current level.
- Level is unimportant
- One queue.
- Don't add null (except dummy) into queues.
- Left/Right null pointer check.
BFS for Binary Trees
General BFS
Simple Maze
We can solve using DFS
We can also do it in BFS
Simple Maze
public static boolean solveMaze(char[][] maze,
int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY,
boolean[][] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int xLen = maze.length, yLen = maze[0].length;
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
queue.offer(startX * yLen + startY);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int temp = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = temp / yLen + dx[i], ny = temp % yLen + dy[i];
if (nx == targetX && ny == targetY) {
return true;
}
if (nx >= 0 && nx < xLen && ny >= 0 && ny < yLen
&& maze[nx][ny] == 'O' && !visited[nx][ny]) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
queue.offer(nx * yLen + ny);
}
}
}
return false;
}Queue setup:
2 dimension ->
1 dimension
Simple Maze
from collections import deque
def solveMaze(maze, startX, startY, targetX, targetY, visited):
queue = deque()
xLen, yLen = len(maze), len(maze[0])
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
dy = [0, 1, 0, -1]
queue.append(startX * yLen + startY)
while queue:
temp = queue.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = temp // yLen + dx[i]
ny = temp % yLen + dy[i]
if nx == targetX and ny == targetY:
return True
if 0 <= nx < xLen and 0 <= ny < yLen and maze[nx][ny] == 'O' and not visited[nx][ny]:
visited[nx][ny] = True
queue.append(nx * yLen + ny)
return False
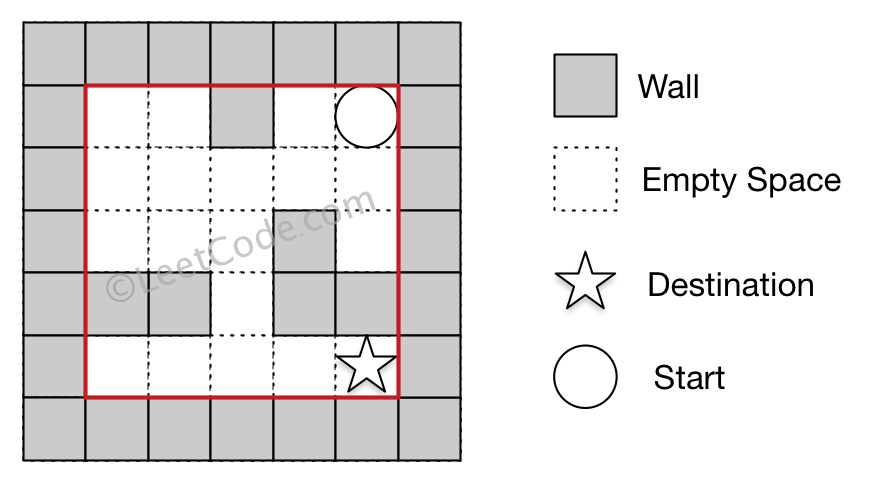
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, find the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included). If the ball cannot stop at the destination, return -1.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
The Maze II
the biggest difference: This time the ball not always goes only 1 step.
Example 1
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)
Output: 12
The Maze II
Explanation: One shortest way is :
left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right. The total distance is
1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
We need to use BFS to solve the problem since it wants to get the shortest way. And BFS could simulate the behavior well.
The most important thing is to let the queue mock the action that the ball will continue rolling till it hits the edge or a block.
As long as we can mock this operation, it will be much easier for us to solve the problem.
How do we simulate this operation?
For each step we pop from queue, we need to use a while loop to keep rolling the ball till the end
The Maze II

class Pair {
int x;
int y;
public Pair(int a, int b) {
x = a;
y = b;
}
}
public int findShortestWay(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] dest) {
int row = maze.length;
int col = maze[0].length;
int[][] distance = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j ++) {
distance[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
int[] dx = new int[] {1, 0, 0, -1};
int[] dy = new int[] {0, -1, 1, 0};
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<Pair>();
queue.offer(new Pair(start[0],start[1]));
distance[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
The Maze II
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair current = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) {
int x = current.x;
int y = current.y;
int dist = distance[x][y];
while (x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 & y < col && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += dx[i];
y += dy[i];
dist ++;
}
x -= dx[i];
y -= dy[i];
--dist;
if (distance[x][y] > dist) {
distance[x][y] = dist;
if (x != dest[0] || y != dest[1]) {
queue.offer(new Pair(x, y));
}
}
}
}
int res = distance[dest[0]][dest[1]];
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
}The Maze II
The Maze II
def shortestDistance(self, maze, start, dest):
row = len(maze)
col = len(maze[0])
distance = [[float('inf') for _ in range(col)] for _ in range(row)]
dx = [1, 0, 0, -1]
dy = [0, -1, 1, 0]
queue = []
queue.append(Pair(start[0], start[1]))
distance[start[0]][start[1]] = 0
while queue:
current = queue.pop(0)
for i in range(4):
x = current.x
y = current.y
dist = distance[x][y]
while x >= 0 and x < row and y >= 0 and y < col and maze[x][y] == 0:
x += dx[i]
y += dy[i]
dist += 1
x -= dx[i]
y -= dy[i]
dist -= 1
if distance[x][y] > dist:
distance[x][y] = dist
if x != dest[0] or y != dest[1]:
queue.append(Pair(x, y))
res = distance[dest[0]][dest[1]]
return -1 if res == float('inf') else res
The Maze II
class Pair:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
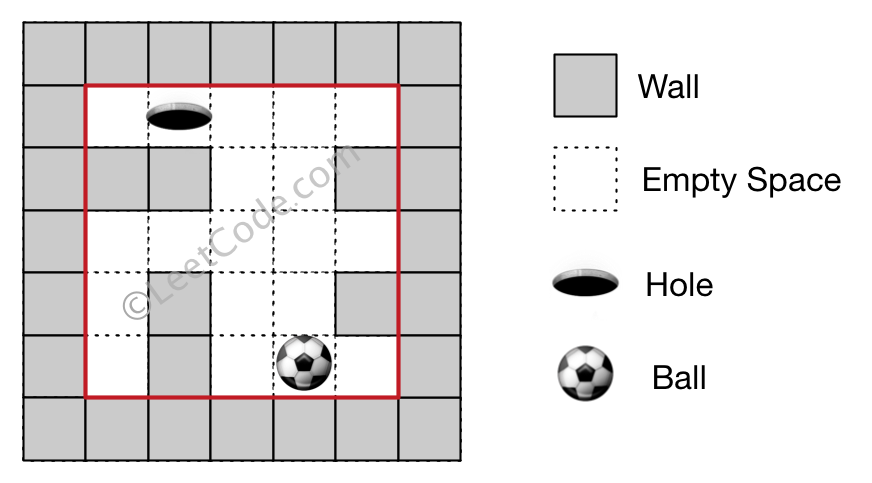
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up (u), down (d), left (l) or right (r), but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction. There is also a hole in this maze. The ball will drop into the hole if it rolls on to the hole.
Given the ball position, the hole position and the maze, your job is to find out how the ball could drop into the hole by moving shortest distance in the maze. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces the ball go through from the start position (exclude) to the hole (include). Output the moving directions by using 'u', 'd', 'l' and 'r'. Since there may have several different shortest ways, you should output the lexicographically smallest way. If the ball cannot reach the hole, output "impossible".
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The ball and hole coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
The Maze III
Example:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0
Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (0, 1)
Output: "lul"
Explanation: There are two shortest ways for the ball to drop into the hole.
The first way is left -> up -> left, represented by "lul".
The second way is up -> left, represented by 'ul'.
Both ways have shortest distance 6, but the first way is lexicographically smaller because 'l' < 'u'. So the output is "lul".
The Maze III
We still need to use BFS to solve the problem.
We need to use a Path to keep the result since even within the same shortest way, we want to output the smallest one in lexicographical order.
The other part is very similar to The Maze II. But one thing to keep in mind:
If you hit the destination, since it is a trap, you can stop immediately instead of keeping rolling foward.
The Maze III
The Maze III
public String findShortestWay(int[][] maze, int[] ball, int[] hole) {
int row = maze.length;
int col = maze[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[] {1, 0, 0, -1};
int[] dy = new int[] {0, -1, 1, 0};
String[] dir = new String[] {"d", "l", "r", "u"};
int[][] distance = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j ++) {
distance[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
distance[ball[0]][ball[1]] = 0;
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<Pair>();
queue.offer(new Pair(ball[0], ball[1]));
String[][] path = new String[row][col];
path[ball[0]][ball[1]] = "";
The Maze III
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair cur = queue.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = cur.x, y = cur.y;
int dist = distance[x][y];
String currentPath = path[x][y];
while(x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col && maze[x][y] == 0
&& (x != hole[0] || y != hole[1])) {
x += dx[i];
y += dy[i];
dist ++;
}
if (x != hole[0] || y != hole[1]) {
x -= dx[i];
y -= dy[i];
dist --;
}
String newPath = currentPath.concat(dir[i]);
if (distance[x][y] > dist || (distance[x][y] == dist
&& path[x][y].compareTo(newPath) > 0)) {
distance[x][y] = dist;
path[x][y] = newPath;
if (x != hole[0] || y != hole[1]) queue.offer(new Pair(x, y));
}
}
}
String result = path[hole[0]][hole[1]];
return distance[hole[0]][hole[1]] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "impossible" : result;
}The Maze III
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
row = len(maze)
col = len(maze[0])
dx = [1, 0, 0, -1]
dy = [0, -1, 1, 0]
dir = ["d", "l", "r", "u"]
distance = [[float('inf')] * col for _ in range(row)]
distance[ball[0]][ball[1]] = 0
queue = [(ball[0], ball[1])]
path = [[""] * col for _ in range(row)]
path[ball[0]][ball[1]] = ""
while queue:
cur = queue.pop(0)
for i in range(4):
x, y = cur[0], cur[1]
dist = distance[x][y]
currentPath = path[x][y]
while x >= 0 and x < row and y >= 0 and y < col and maze[x][y] == 0 and (x != hole[0] or y != hole[1]):
x += dx[i]
y += dy[i]
dist += 1
if x != hole[0] or y != hole[1]:
x -= dx[i]
y -= dy[i]
dist -= 1
newPath = currentPath + dir[i]
if distance[x][y] > dist or (distance[x][y] == dist and path[x][y] > newPath):
distance[x][y] = dist
path[x][y] = newPath
if x != hole[0] or y != hole[1]:
queue.append((x, y))
result = path[hole[0]][hole[1]]
return "impossible" if distance[hole[0]][hole[1]] == float('inf') else result
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find the length of shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, such that:
- Only one letter can be changed at a time
- Each intermediate word must exist in the word list
For example,
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
Note:
- Return 0 if there is no such transformation sequence.
- All words have the same length.
- All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
Word Ladder
DFS
- begin: hot, end: hip, list: [hog, hig, dig, dip, hip, hit]
- hot -> hog -> hig -> dig -> dip -> hip
- Much deeper than needed, time consuming.
BFS
- Keep a set of all words that can be transformed to.
- Put all words with 1 edit distance into the set every time.
- When the end word is met, then the minimum distance is found.
Word Ladder
- BFS
- Keep a set of all words that can be transformed to.
- Put all words with 1 edit distance into the set every time.
- When the end word is met, then the minimum distance is found.
Word Ladder
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
- BFS
- Keep a set of all words that can be transformed to.
- Put all words with 1 edit distance into the set every time.
- When the end word is added, then the minimum distance is found.
Word Ladder
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
- BFS
- Keep a set of all words that can be transformed to.
- Put all words with 1 edit distance into the set every time.
- When the end word is added, then the minimum distance is found.
Word Ladder
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
- BFS
- Keep a set of all words that can be transformed to.
- Put all words with 1 edit distance into the set every time.
- When the end word is added, then the minimum distance is found.
Word Ladder
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
dog
log
- BFS
- Keep a set of all words that can be transformed to.
- Put all words with 1 edit distance into the set every time.
- When the end word is added, then the minimum distance is found.
Word Ladder
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
dog
log
cog
Word Ladder
transformed_words <- beginWord
while (transformed_words is not empty) {
for (word_b in transformed_words) {
if (endWord is within 1 distance) {
return distance
}
if (some word in dict is within 1 distance
&& it is not in transformed_words) {
transformed_words.add(word)
}
}
update distance
}
return 0
How to check?
Word Ladder
transformed_words <- beginWord
while (transformed_words is not empty) {
for (word_b in transformed_words) {
if (endWord is within 1 distance) {
return distance
}
if (some word in dict is within 1 distance
&& it is not in transformed_words) {
transformed_words.add(word)
}
}
update distance
}
return 0
How to check?
Word Ladder
transformed_words <- beginWord
while (transformed_words is not empty) {
for (word_b in transformed_words) {
if (endWord is within 1 distance) {
return distance
}
if (some word in dict is within 1 distance
&& it is not in transformed_words) {
transformed_words.add(word)
}
}
update distance
}
return 0
How to check?
Word Ladder
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>();
for(String aWord: wordList) {
wordSet.add(aWord);
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(beginWord);
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.add(beginWord);
int distance = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Queue<String> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
distance++;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String top = queue.poll();
List<String> wordsWithinDistance =
getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, top);
for (String word : wordsWithinDistance) {
if (word.equals(endWord)) {
return distance;
}
if (!visited.contains(word)) {
queue2.add(word);
visited.add(word);
}
}
}
queue = queue2;
}
return 0;
}Word Ladder
public ArrayList<String> getWordsWithinDistance(Set<String> wordSet, String word) {
ArrayList<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
char[] wordCharArr = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char oriChar = wordCharArr[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (c == oriChar) {
continue;
}
wordCharArr[i] = c;
String newStr = new String(wordCharArr);
if (wordSet.contains(newStr)) {
results.add(newStr);
}
}
wordCharArr[i] = oriChar;
}
return results;
} Word Ladder
def ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList):
wordSet = set(wordList)
queue = []
queue.append(beginWord)
visited = set()
visited.add(beginWord)
distance = 1
while queue:
queue2 = []
distance += 1
while queue:
top = queue.pop(0)
wordsWithinDistance = getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, top)
for word in wordsWithinDistance:
if word == endWord:
return distance
if word not in visited:
queue2.append(word)
visited.add(word)
queue = queue2
return 0 Word Ladder
def getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, word):
results = []
wordCharArr = list(word)
for i in range(len(word)):
oriChar = wordCharArr[i]
for c in range(ord('a'), ord('z')+1):
if c == ord(oriChar):
continue
wordCharArr[i] = chr(c)
newStr = ''.join(wordCharArr)
if newStr in wordSet:
results.append(newStr)
wordCharArr[i] = oriChar
return resultsWord Ladder
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord,
List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>();
for(String aWord: wordList) {
wordSet.add(aWord);
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(beginWord);
int distance = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && !wordSet.isEmpty()) {
Queue<String> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
distance++;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String top = queue.poll();
ArrayList<String> wordsWithinDistance =
getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, top);
if (wordsWithinDistance.contains(endWord)) {
return distance;
}
queue2.addAll(wordsWithinDistance);
}
queue = queue2;
}
return 0;
}Word Ladder
public ArrayList<String> getWordsWithinDistance(Set<String> wordSet,
String word) {
ArrayList<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
char[] wordCharArr = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char oriChar = wordCharArr[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (c == oriChar) {
continue;
}
wordCharArr[i] = c;
String newStr = new String(wordCharArr);
if (wordSet.contains(newStr)) {
results.add(newStr);
wordSet.remove(newStr);
}
}
wordCharArr[i] = oriChar;
}
return results;
}访问过的可以在wordSet删掉, 已经在results保存, 下次也不需要再check
Word Ladder
def ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList):
wordSet = set(wordList)
queue = [beginWord]
distance = 1
while queue and wordSet:
queue2 = []
distance += 1
while queue:
top = queue.pop(0)
wordsWithinDistance = getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, top)
if endWord in wordsWithinDistance:
return distance
queue2.extend(wordsWithinDistance)
queue = queue2
return 0
Word Ladder
def getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, word):
results = []
wordCharArr = list(word)
for i in range(len(word)):
oriChar = wordCharArr[i]
for c in 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz':
if c == oriChar:
continue
wordCharArr[i] = c
newStr = ''.join(wordCharArr)
if newStr in wordSet:
results.append(newStr)
wordSet.remove(newStr)
wordCharArr[i] = oriChar
return resultsWord Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Return
[
["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],
["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]
]
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
dog
log
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
dog
log
cog
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
dog
log
cog
- Visited needs to be updated after one level.
- wordList need to be updated after one level.
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
Example:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
hit
hot
dot
lot
dog
log
cog
- Path needs to be recorded backwards.
- HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>>
Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
- BFS to get shortest transformation
-
Record the path information during transformation so that the sequence can get regenerated later.
- with visited set, all nodes on the path can guarantee the shortest distance.
-
DFS to get all the transformation sequences
- backward from endWord instead of forward from startWord
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String beginWord, String endWord,
List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>();
for(String aWord: wordList) {
wordSet.add(aWord);
}
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> preList = new HashMap<>();
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(beginWord);
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.add(beginWord);Word Ladder II
while (!queue.isEmpty() && !wordList.isEmpty()) {
Set<String> queue2 = new HashSet<>();
boolean isFinished = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String top = queue.poll();
Set<String> wordsWithinDistance =
getWordsWithinDistance(wordList, top);
for (String word : wordsWithinDistance) {
if (word.equals(endWord)) {
isFinished = true;
}
if (!visited.contains(word)) {
updatePreList(preList, word, top);
queue2.add(word);
}
}
}
visited.addAll(queue2);
if (isFinished) {
getPaths(results, preList, new ArrayList<String>(), endWord);
break;
}
queue.addAll(queue2);
}
return results;
}Word Ladder II
public void updatePreList(HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> preList,
String cur, String pre) {
if (!preList.containsKey(cur)) {
preList.put(cur, new ArrayList<String>());
}
preList.get(cur).add(pre);
}
public Set<String> getWordsWithinDistance(Set<String> wordSet, String word) {
Set<String> results = new HashSet<>();
char[] wordCharArr = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char oriChar = wordCharArr[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (c == oriChar) {
continue;
}
wordCharArr[i] = c;
String newStr = new String(wordCharArr);
if (wordSet.contains(newStr)) {
results.add(newStr);
}
}
wordCharArr[i] = oriChar;
}
return results;
}Word Ladder II
Word Ladder II
def findLadders(beginWord, endWord, wordList):
wordSet = set(wordList)
results = []
preList = {}
queue = [beginWord]
visited = set()
visited.add(beginWord)
while queue and wordList:
queue2 = set()
isFinished = False
while queue:
top = queue.pop(0)
wordsWithinDistance = getWordsWithinDistance(wordList, top)
for word in wordsWithinDistance:
if word == endWord:
isFinished = True
if word not in visited:
updatePreList(preList, word, top)
queue2.add(word)
visited.update(queue2)
if isFinished:
getPaths(results, preList, [], endWord)
break
queue.extend(queue2)
return results
Word Ladder II
def updatePreList(preList, cur, pre):
if cur not in preList:
preList[cur] = []
preList[cur].append(pre)
def getWordsWithinDistance(wordSet, word):
results = set()
wordCharArr = list(word)
for i in range(len(word)):
oriChar = wordCharArr[i]
for c in 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz':
if c == oriChar:
continue
wordCharArr[i] = c
newStr = ''.join(wordCharArr)
if newStr in wordSet:
results.add(newStr)
wordCharArr[i] = oriChar
return results
Word Ladder II
- How to get paths backward from endWord?
- DFS (recursion)
- Base Case: endWord.pre == null
- Recursion rule: path from endWord = path from endWord.pre + endWord
- DFS (recursion)
public void getPaths(List<List<String>> paths,
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> preList,
List<String> curPath,
String end) {
if (!preList.containsKey(end)) {
curPath.add(end);
Collections.reverse(curPath);
paths.add(curPath);
return;
}
for (String pre : preList.get(end)) {
List<String> newPath = new ArrayList<String>(curPath);
newPath.add(end);
getPaths(paths, preList, newPath, pre);
}
}Word Ladder II
def getPaths(paths, preList, curPath, end):
if end not in preList:
curPath.append(end)
curPath.reverse()
paths.append(curPath)
return
for pre in preList[end]:
newPath = curPath.copy()
newPath.append(end)
getPaths(paths, preList, newPath, pre)Word Ladder II
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord
- BFS to get shortest transformation
- Record the paths from beginning while BFSing
- Add only the valid paths into results.
- Distance means level important
- Two queues
- Pruning for duplicate word
- HashSet for visited words
- Remove from dict.
BFS for Word Distance
- Both complete search
- DFS is recursion
- stack
- better at checking connection, etc.
- BFS is iteration
- queue
- better at minimum distance, etc.
- Many problems are both solvable by DFS/BFS
- Surrounded Region
- Number of Islands
- etc.
DFS v.s. BFS
Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if (board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0)
return;
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
search(board, 0, j);
search(board, board.length-1, j);
}
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
search(board, i, 0);
search(board, i, board[0].length-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
board[i][j] = board[i][j] == 'F' ? 'O' : 'X';
}
}
}Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
// BFS
public void search(char[][] board, int x, int y) {
if (board[x][y] == 'X') {
return;
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int xLen = board.length, yLen = board[0].length;
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
queue.offer(x * yLen + y);
board[x][y] = 'F';
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int temp = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = temp / yLen + dx[i], ny = temp % yLen + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < xLen && ny >= 0 && ny < yLen
&& board[nx][ny] == 'O') {
board[nx][ny] = 'F';
queue.offer(nx * yLen + ny);
}
}
}
}Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
// DFS
public void search(char[][] board, int i, int j) {
if (board[i][j] != 'O')
return;
board[i][j] = 'F';
if (i > 1)
search(board, i-1, j);
if (i < board.length - 2)
search(board, i+1, j);
if (j > 1)
search(board, i, j-1);
if (j < board[i].length - 2)
search(board, i, j+1);
}Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
def solve(board):
if len(board) == 0 or len(board[0]) == 0:
return
for j in range(len(board[0])):
search(board, 0, j)
search(board, len(board)-1, j)
for i in range(len(board)):
search(board, i, 0)
search(board, i, len(board[0])-1)
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
board[i][j] = 'O' if board[i][j] == 'F' else 'X'
Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
# BFS
def search(board, x, y):
if board[x][y] == 'X':
return
queue = []
xLen = len(board)
yLen = len(board[0])
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
dy = [0, 1, 0, -1]
queue.append(x * yLen + y)
board[x][y] = 'F'
while queue:
temp = queue.pop(0)
for i in range(4):
nx = temp // yLen + dx[i]
ny = temp % yLen + dy[i]
if nx >= 0 and nx < xLen and ny >= 0 and ny < yLen and board[nx][ny] == 'O':
board[nx][ny] = 'F'
queue.append(nx * yLen + ny)
Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Surrounded Region
# DFS
def search(board, i, j):
if board[i][j] != 'O':
return
board[i][j] = 'F'
if i > 1:
search(board, i-1, j)
if i < len(board) - 2:
search(board, i+1, j)
if j > 1:
search(board, i, j-1)
if j < len(board[i]) - 2:
search(board, i, j+1)