Stack
Stack & Queue
- Two Different Data Structure
- Stack: LIFO (Last in first out)
- Queue: FIFO (First in first out)
When to use Queue?
- BFS (Breadth-first Search)
- Priority Queue (Heap)
- Multi Task Queue
When to use Stack?
- Invoke a function
- Recursion (This is a special case of the first)
- DFS (Depth-first Search)
Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();Java
C++
stack <string> cards;Basic Opertaion
- size
- pop
- push
- peek
- size
- pop
- push
- top
Java
C++
Practice 1
Decode String
Given an encoded string, return its decoded string.
The encoding rule is: k[encoded_string], where the encoded_string inside the square brackets is being repeated exactly k times. Note that k is guaranteed to be a positive integer.
You may assume that the input string is always valid; there are no extra white spaces, square brackets are well-formed, etc. Furthermore, you may assume that the original data does not contain any digits and that digits are only for those repeat numbers, k. For example, there will not be input like 3a or 2[4].
The test cases are generated so that the length of the output will never exceed 10^5.
Example 1:
Input: s = "3[a]2[bc]"
Output: "aaabcbc"
Example 2:
Input: s = "3[a2[c]]"
Output: "accaccacc"
Example 3:
Input: s = "2[abc]3[cd]ef"
Output: "abcabccdcdcdef"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 30
s consists of lowercase English letters, digits, and square brackets '[]'.
s is guaranteed to be a valid input.
All the integers in s are in the range [1, 300].
Decode String
We need to use the stack to store the information:
Integer, String
Integer stack can help to store the numbers;
String stack can help to store the letters;
Notice the '[' and ']' as conditions
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
Stack<String> strStack = new Stack<>(); // Stores previous strings
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack<>(); // Stores repeat counts
StringBuilder currentStr = new StringBuilder(); // Current decoded string
int num = 0; // Current repeat count
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
num = num * 10 + (ch - '0'); // Handle multi-digit numbers
} else if (ch == '[') {
numStack.push(num); // Save repeat count
strStack.push(currentStr.toString()); // Save current string state
currentStr = new StringBuilder(); // Reset for the new substring
num = 0; // Reset count
} else if (ch == ']') {
int repeatCount = numStack.pop(); // Get repeat count
StringBuilder prevStr = new StringBuilder(strStack.pop()); // Restore previous string
for (int i = 0; i < repeatCount; i++) {
prevStr.append(currentStr); // Append repeated substring
}
currentStr = prevStr; // Update current string
} else {
currentStr.append(ch); // Append normal characters
}
}
return currentStr.toString();
}
}class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
if not s:
return ""
sInt = [] # 使用列表模拟整数堆栈
sStr = [] # 使用列表模拟字符串堆栈
currentNum = 0
currentStr = ""
for char in s:
if char.isdigit():
currentNum = currentNum * 10 + int(char)
elif char == '[':
sInt.append(currentNum)
currentNum = 0
sStr.append(currentStr)
currentStr = ""
elif char == ']':
repeatTimes = sInt.pop()
lastStr = sStr.pop()
currentStr = lastStr + currentStr * repeatTimes
else:
currentStr += char
return currentStr
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
s = "3[a]2[bc]"
print(solution.decodeString(s)) # 输出:"aaabcbc"Practice 2
Simplify Path
Given a string path, which is an absolute path (starting with a slash '/') to a file or directory in a Unix-style file system, convert it to the simplified canonical path.
In a Unix-style file system, a period '.' refers to the current directory, a double period '..' refers to the directory up a level, and any multiple consecutive slashes (i.e. '//') are treated as a single slash '/'. For this problem, any other format of periods such as '...' are treated as file/directory names.
The canonical path should have the following format:
The path starts with a single slash '/'.
Any two directories are separated by a single slash '/'.
The path does not end with a trailing '/'.
The path only contains the directories on the path from the root directory to the target file or directory (i.e., no period '.' or double period '..')
Return the simplified canonical path.
Example 1:
Input: path = "/home/" Output: "/home" Explanation: Note that there is no trailing slash after the last directory name.
Example 2:
Input: path = "/../" Output: "/" Explanation: Going one level up from the root directory is a no-op, as the root level is the highest level you can go.
Example 3:
Input: path = "/home//foo/" Output: "/home/foo" Explanation: In the canonical path, multiple consecutive slashes are replaced by a single one.
Consider an example
Input: path = "/a/./b/../../c/"
Output: "/c"
class Solution {
public String simplifyPath(String path) {
Stack<String> s = new Stack();
String[] splitPath = path.split("/");
for (int i = 0; i < splitPath.length; i++) {
if (!s.isEmpty() && splitPath[i].equals("..")) {
s.pop();
} else if (!splitPath[i].equals("") && !splitPath[i].equals(".") && !splitPath[i].equals("..")) {
s.push(splitPath[i]);
}
}
if (s.isEmpty()) {
return "/";
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
res.insert(0, s.pop()).insert(0, "/");
}
return res.toString();
}
}class Solution:
def simplifyPath(self, path: str) -> str:
stack = []
split_path = path.split("/")
for split in split_path:
if stack and split == "..":
stack.pop()
elif split and split != "." and split != "..":
stack.append(split)
if not stack:
return "/"
res = ""
while stack:
res = "/" + stack.pop() + res
return res
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
path = "/home//foo/"
print(solution.simplifyPath(path)) # 输出:"/home/foo"Practice 3
Basic Calculator
Given a string s representing a valid expression, implement a basic calculator to evaluate it, and return the result of the evaluation.
Basic Calculator
Example 1:
Input: s = "1 + 1" Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: s = " 2-1 + 2 " Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)" Output: 23
Example 4:
Input: s = "+48 + -48" Output: 0 Explanation: Numbers can have multiple digits and start with +/-.
Basic Calculator
Three things to notice:
- How to keep the priority of () and +/-
Use Stack - How to deal with the bad format
Remove space before processing the expression - How to keep track of the sign?
Use an integer to track it
public int calculate(String s) {
int result = 0;
String expression = s.replace(" ", "");
int sign = expression.charAt(0) == '-' ? -1 : 1;
int cur = expression.charAt(0) == '-' ? 1 : 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (cur < expression.length()) {
int i = cur;
if (Character.isDigit(expression.charAt(i))) {
for (i = cur; i < expression.length(); i ++) {
if (!Character.isDigit(expression.charAt(i))) break;
}
int value = Integer.parseInt(expression.substring(cur, i));
result = result + sign * value;
cur = i;
} else if (expression.charAt(i) == '+') {
sign = 1;
cur ++;
} else if (expression.charAt(i) == '-') {
sign = -1;
cur ++;
} else if (expression.charAt(i) == '(') {
stack.push(result);
stack.push(sign);
result = 0;
sign = 1;
cur ++;
} else if (expression.charAt(i) == ')') {
result = result * stack.pop() + stack.pop();
cur ++;
}
}
return result;
}class Solution:
def calculate(self, s: str) -> int:
result = 0
expression = s.replace(" ", "")
sign = -1 if expression[0] == '-' else 1
cur = 1 if expression[0] == '-' else 0
stack = []
while cur < len(expression):
i = cur
if expression[i].isdigit():
while i < len(expression) and expression[i].isdigit():
i += 1
value = int(expression[cur:i])
result += sign * value
cur = i
elif expression[i] == '+':
sign = 1
cur += 1
elif expression[i] == '-':
sign = -1
cur += 1
elif expression[i] == '(':
stack.append(result)
stack.append(sign)
result = 0
sign = 1
cur += 1
elif expression[i] == ')':
result = result * stack.pop() + stack.pop()
cur += 1
return result
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)"
print(solution.calculate(s)) # 输出:23Practice 4
Remove Duplicate Letters
Remove Duplicate Letters
Given a string which contains only lowercase letters, remove duplicate letters so that every letter appear once and only once. You must make sure your result is the smallest in lexicographical order among all possible results.
Example:
Given "bcabc"
Return "abc"
Given "cbacdcbc"
Return "acdb"
Remove Duplicate Letters
Consider a Stack:
What stack can help us?
Record the current shown letter
Pop element from the stack if:
1. this one is larger than the one just comes
2. this one still has some remaining can be used later
Remove Duplicate Letters
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
int[] freqs = new int[256];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
freqs[s.charAt(i)]++;
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[256];
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
freqs[c]--;
if (visited[c]) continue;
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > c && freqs[stack.peek()] > 0) {
visited[stack.pop()] = false;
}
stack.push(c);
visited[c] = true;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(stack.pop());
}
return sb.reverse().toString();
}Remove Duplicate Letters
class Solution:
def removeDuplicateLetters(self, s: str) -> str:
freqs = [0] * 256
for char in s:
freqs[ord(char)] += 1
visited = [False] * 256
stack = []
for char in s:
freqs[ord(char)] -= 1
if visited[ord(char)]:
continue
while stack and stack[-1] > char and freqs[ord(stack[-1])] > 0:
visited[ord(stack.pop())] = False
stack.append(char)
visited[ord(char)] = True
return ''.join(stack)
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
s = "bcabc"
print(solution.removeDuplicateLetters(s)) # 输出:"abc"Practice 5
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
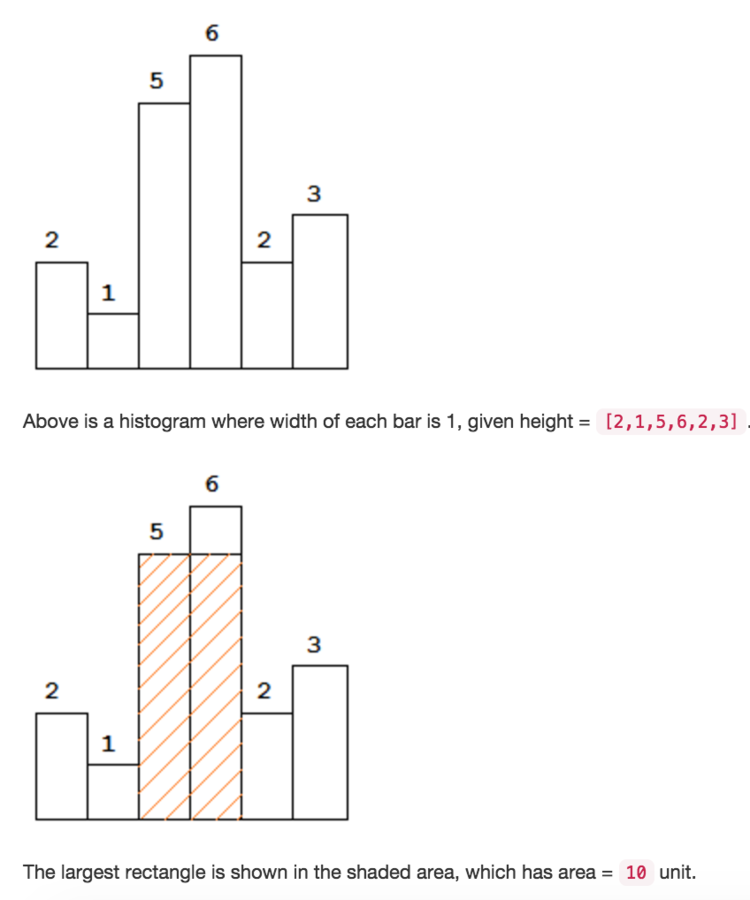
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Similar thought: How to use stack to find the right border?
Example: 2 1 5 6 2 3
Only put rectangle higher than peek into stack
The element before it is the left border
The element pushes it out is the right border
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Example: 2 1 5 6 2 3
Stack: 2
Stack: 1
Stack: 1 5
Stack: 1 5 6
Stack: 1 2
Stack: 1 2 3
Stack: 1 2
Stack: 1
Stack: Empty
Add 2
Pop 2 Add 1
Add 5
Add 6
Pop 6 5 Add 2
Add 3
Pop 3
Pop 2
Pop 1
2*1
6*1, 5*2
3*1
2*4
1*6
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Example: 2 1 5 6 2 3
How do we know the width?
Instead of directly putting height into stack, we put the index. Anyway height can be accessed by the index easily. And using index, we can know the width
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Example: 2 1 5 6 2 3
Stack: 0
Stack: 1
Stack: 1 2
Stack: 1 2 3
Stack: 1 4
Stack: 1 4 5
Stack: 1 4
Stack: 1
Stack: empty
Add 2
Pop 2 Add 1
Add 5
Add 6
Pop 6 5 Add 2
Add 3
Pop 3
Pop 2
Pop 1
2*1
6*1, 5*2
3*1
2*4
1*6
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
// this problem key is the width
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
int area = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[stack.peek()] > heights[i]) {
int start = stack.pop();
int width = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1;
area = Math.max(area, heights[start] * width);
}
stack.push(i);
}
int i = heights.length;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int start = stack.pop();
int width = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1;
area = Math.max(area, heights[start] * width);
}
return area;
}class Solution:
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
stack = []
area = 0
for i in range(len(heights)):
while stack and heights[stack[-1]] > heights[i]:
start = stack.pop()
width = i if not stack else i - stack[-1] - 1
area = max(area, heights[start] * width)
stack.append(i)
n = len(heights)
while stack:
start = stack.pop()
width = n if not stack else n - stack[-1] - 1
area = max(area, heights[start] * width)
return area
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
heights = [2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3]
print(solution.largestRectangleArea(heights)) # 输出:10