Graph & Topology Sort
Graph
- Definition
- Graph is very similar to trees
- Directed v.s. Undirected
- Interview Questions
- DFS, BFS
- DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
- Topological sort
Graph Representation
- Graph node
- Adjacent matrices
- |V| vertices, then |V|*|V| matrix of 0s and 1s for the graph.
- Adjacent lists
- |V| vertices, then |V| arraylist, each containing the adjacent vertices.
- 2|E| space for undirected, and |E| space for directed.
GraphNode {
int val;
List<GraphNode> neighbors;
}
Graph Representation
- Adjacent matrices
- Adjacent lists
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0
0 1 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1
0 1 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 1
1 2,3
2 1,5
3 1
4 5
5 2,4
1 3,5
2 1,5
3 1
4 5
5 1,3,4
Topological Sort
A topological sort (sometimes abbreviated toposort) or topological ordering of a directed graph is a linear ordering of its vertices such that for every directed edge uv from vertex u to vertex v, u comes before v in the ordering.
- Maintain a set of vertices with 0-incoming vertices.
- Keep selecting 0-incoming vertex, remove all its outcoming edges, add it into the set.
- If all vertices are merged into 0-incoming vertices set, then topological sort result is found.
Course Schedule
There are a total of n courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to n - 1.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example to take course 0 you have to first take course 1, which is expressed as a pair: [0,1]
Given the total number of courses and a list of prerequisite pairs, is it possible for you to finish all courses?
Example:
[1, 0], possible; [[1,0], [0,1]], impossible.
Course Schedule
How would we solve it in real life?
- Draw a directed graph, with prerequisite order.
- Select a course which has no prerequisite, and remove all its prerequisite relationships.
- Repeat the above operation until all courses are scheduled or 0-prerequisite course doesn't exist.
- If there are courses not selected, then the courses cannot be scheduled.
Course Schedule
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] degrees = new int[numCourses]; // how many courses need to finish if we want to take the course
List<List<Integer>> pre = new ArrayList<>(); // I am who's the prerequisites
// Initialize the pre list
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
pre.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// Populate degrees and pre lists
for (int[] pair : prerequisites) { // O(E)
int course = pair[0];
int preCourse = pair[1];
degrees[course]++;
pre.get(preCourse).add(course);
}
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) { // O(V)
if (degrees[i] == 0) { // the courses doesn't need prerequisites
cur.add(i);
}
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (!cur.isEmpty()) { // O(V + E)
List<Integer> next = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i : cur) {
for (int x : pre.get(i)) {
degrees[x]--;
if (degrees[x] == 0) {
next.add(x);
}
}
}
ans.addAll(cur);
cur = next;
}
return ans.size() == numCourses;
}Course Schedule
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
degrees = [0 for _ in range(numCourses)] # how many courses need to finish if we want to take the course
pre = [[] for _ in range(numCourses)] # I am who's the prerequisites
for i, j in prerequisites: # O(E)
degrees[i] += 1
pre[j].append(i)
cur = []
for i in range(numCourses): # O(V)
if degrees[i] == 0: # the courses doesn't need to prerequisites
cur.append(i)
ans = []
while (cur): # O(V + E)
next = []
for i in cur:
for x in pre[i]:
degrees[x] -= 1
if degrees[x] == 0:
next.append(x)
ans += cur
cur = next
return len(ans) == numCourses
# TC, SC: O(V+E)Alien Dictionary
There is a new alien language which uses the latin alphabet. However, the order among letters are unknown to you. You receive a list of words from the dictionary, where words are sorted lexicographically by the rules of this new language. Derive the order of letters in this language.
For example,
Given the following words in dictionary,
[ "wrt", "wrf", "er", "ett", "rftt"]
The correct order is: "wertf".
Alien Dictionary
What do we need to do?
Use the words to get the priority between two letters
Use topology sort to get the information of the order of these letters
Note:
You may assume all letters are in lowercase.
If the order is invalid, return an empty string.
There may be multiple valid order of letters, return any one of them is fine.
Alien Dictionary
public String alienOrder(String[] words) {
Map<Character, Set<Character>> pre = new HashMap<>();
Map<Character, Set<Character>> post = new HashMap<>();
// Build the graph
for (int i = 0; i < words.length - 1; i++) {
String a = words[i];
String b = words[i + 1];
boolean foundDifference = false;
for (int j = 0; j < Math.min(a.length(), b.length()); j++) {
if (a.charAt(j) != b.charAt(j)) {
pre.putIfAbsent(b.charAt(j), new HashSet<>());
post.putIfAbsent(a.charAt(j), new HashSet<>());
pre.get(b.charAt(j)).add(a.charAt(j));
post.get(a.charAt(j)).add(b.charAt(j));
foundDifference = true;
break;
}
}
// If we finished a longer word and didn't find a difference, the order is invalid
if (!foundDifference && a.length() > b.length()) {
return "";
}
}
// Get all unique characters
Set<Character> allChars = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : words) {
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
allChars.add(c);
}
}
// Initialize the queue with characters that have no prerequisites
Queue<Character> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (char c : allChars) {
if (!pre.containsKey(c)) {
q.add(c);
}
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// Perform topological sort
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
char cur = q.poll();
res.append(cur);
if (post.containsKey(cur)) {
for (char neighbor : post.get(cur)) {
pre.get(neighbor).remove(cur);
if (pre.get(neighbor).isEmpty()) {
q.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
// Check if the topological sort is valid
if (res.length() == allChars.size()) {
return res.toString();
}
return "";
}
Alien Dictionary
def alienOrder(self, words: List[str]) -> str:
pre = collections.defaultdict(set)
post = collections.defaultdict(set)
for a, b in zip(words, words[1:]):
for i in range(len(a)):
if i >= len(b):
return ""
if a[i] != b[i]:
pre[b[i]].add(a[i])
post[a[i]].add(b[i])
break
allchars = set("".join(words))
q = [x for x in allchars if x not in pre]
res = []
while q:
next_q = []
for cur in q:
res.append(cur)
for neighbor in post[cur]:
pre[neighbor].remove(cur)
if len(pre[neighbor]) == 0:
next_q.append(neighbor)
q = next_q
if len(res) == len(allchars):
return "".join(res)
return ""Clone Graph
clone an undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of its neighbors.
class UndirectedGraphNode {
int label;
List<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
UndirectedGraphNode(int x) { label = x; neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>(); }
};
Clone Graph
Use BFS/DFS to go through all the nodes
Use Hashmap to remember which nodes has been visited
Clone each node with its label and is neighbors
A B
C D
A' B'
C' D'
D''
Clone Graph
public class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Node, Node> maps = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(node, maps);
}
private Node dfs(Node node, Map<Node, Node> maps) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (maps.containsKey(node)) {
return maps.get(node);
}
Node copy = new Node(node.val);
maps.put(node, copy);
for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) {
Node copyNeighbor = dfs(neighbor, maps);
copy.neighbors.add(copyNeighbor);
}
return copy;
}
}Clone Graph
def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if node is None:
return None
maps = {}
def dfs(node, maps):
if node is None:
return None
if node in maps:
return maps.get(node)
copy = Node(node.val)
maps[node] = copy
for child in node.neighbors:
copy_child = dfs(child, maps)
copy.neighbors.append(copy_child)
return copy
dfs(node, maps)
return maps.get(node) Reconstruct Itinerary
You are given a list of airline tickets where tickets[i] = [fromi, toi] represent the departure and the arrival airports of one flight. Reconstruct the itinerary in order and return it.
All of the tickets belong to a man who departs from "JFK", thus, the itinerary must begin with "JFK". If there are multiple valid itineraries, you should return the itinerary that has the smallest lexical order when read as a single string.
Reconstruct Itinerary
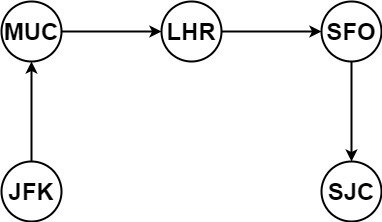

Input: tickets = [["MUC","LHR"],["JFK","MUC"],["SFO","SJC"],["LHR","SFO"]]
Output: ["JFK","MUC","LHR","SFO","SJC"]
Input: tickets = [["JFK","SFO"],["JFK","ATL"],["SFO","ATL"],["ATL","JFK"],["ATL","SFO"]]
Output: ["JFK","ATL","JFK","SFO","ATL","SFO"]
Explanation: Another possible reconstruction is ["JFK","SFO","ATL","JFK","ATL","SFO"] but it is larger in lexical order.
Reconstruct Itinerary
All the edges are given. How do we know which way we should go?
Use DFS -> iterate all the possible ways and try to find all the ways
And use a certain way to compare the result to get the best results
How should we store the data -> use Adjacent list
public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {
Map<String, List<String>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (List<String> ticket : tickets) {
String src = ticket.get(0);
String dest = ticket.get(1);
graph.putIfAbsent(src, new ArrayList<>());
graph.get(src).add(dest);
}
// Sort the destinations for each source lexicographically
for (List<String> destList : graph.values()) {
Collections.sort(destList);
}
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<String> cur = new LinkedList<>();
cur.add("JFK");
dfs(cur, res, graph, tickets.size(), "JFK");
return res;
}
private boolean dfs(LinkedList<String> cur, List<String> res, Map<String, List<String>> graph, int n, String city) {
if (n == 0) {
res.addAll(new ArrayList<>(cur));
return true;
}
List<String> neighbors = graph.getOrDefault(city, new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < neighbors.size(); i++) {
String neighbor = neighbors.get(i);
cur.add(neighbor);
neighbors.remove(i);
if (dfs(cur, res, graph, n - 1, neighbor)) {
return true;
}
neighbors.add(i, neighbor);
cur.removeLast();
}
return false;
}
def findItinerary(self, tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for src, des in tickets:
graph[src].append(des)
## sort the the graph for each src
for src in graph:
graph[src].sort()
def dfs(cur, res, graph, n, city):
if n == 0:
res.append(list(cur))
return True
for index, neighbor in enumerate(graph[city]):
cur.append(neighbor)
del graph[city][index]
if dfs(cur, res, graph, n - 1, neighbor):
return True
graph[city].insert(index, neighbor)
cur.pop()
n = len(tickets)
res, cur = [], ["JFK"]
dfs(cur, res, graph, n, "JFK")
return res[0]Minimum Height Trees
For a undirected graph with tree characteristics, we can choose any node as the root. The result graph is then a rooted tree. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height are called minimum height trees (MHTs). Given such a graph, write a function to find all the MHTs and return a list of their root labels.
Examples
Given n = 4, edges = [[1, 0], [1, 2], [1, 3]], return [1].
Given n = 6, edges = [[0, 3], [1, 3], [2, 3], [4, 3], [5, 4]], return [3, 4]
0
|
1
/ \
2 3
0 1 2
\ | /
3
|
4
|
5
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, List<List<Integer>> edges) {
if (n == 1) {
return Collections.singletonList(0);
}
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
int[] indegree = new int[n];
// Build the graph and indegree array
for (List<Integer> edge : edges) {
int x = edge.get(0);
int y = edge.get(1);
graph.putIfAbsent(x, new ArrayList<>());
graph.putIfAbsent(y, new ArrayList<>());
graph.get(x).add(y);
graph.get(y).add(x);
indegree[x]++;
indegree[y]++;
}
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 1) {
q.add(i);
}
}
int count = q.size();
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> nextLevel = new ArrayList<>();
for (int cur : q) {
seen.add(cur);
if (seen.size() == n) {
return new ArrayList<>(q);
}
for (int neighbor : graph.get(cur)) {
indegree[neighbor]--;
if (indegree[neighbor] == 1) {
nextLevel.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
q = new LinkedList<>(nextLevel);
}
return new ArrayList<>();
}
def findMinHeightTrees(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
if n == 1:
return [0]
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
indegree = [0] * n
for x, y in edges:
graph[x].append(y)
graph[y].append(x)
indegree[x] += 1
indegree[y] += 1
q = []
for i in range(n):
if indegree[i] == 1:
q.append(i)
count = len(q)
seen = set()
while q:
next_level = []
for cur in q:
seen.add(cur)
if len(seen) == n:
return q
for neighbor in graph[cur]:
indegree[neighbor] -= 1
if indegree[neighbor] == 1:
next_level.append(neighbor)
q = next_level