Introduction To OpenStack

What is OpenStack?
The OpenStack project is an open source cloud-computing platform for private, public and hybrid clouds that’s simple to implement, massively scalable, and feature rich. OpenStack provides an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) solution through a set of interrelated services.
OpenStack was started in 2010 as a joint venture between RackSpace Hosting and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Today more than 200 companies have joined the project, including AMD, Canonical, Cisco, Dell, EMC, Ericsson, Groupe Bull, HP, IBM, Inktank, Intel, NEC, Red Hat, SUSE Linux, VMware, and Yahoo!
The project is now managed by the OpenStack Foundation, a non-profit corporate entity established in September 2012 to promote OpenStack software and its community. The community collaborates around a six-month, time-based release cycle with frequent development milestones.
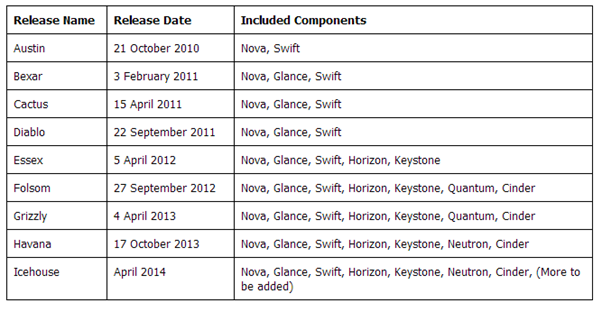
Releases
Overview
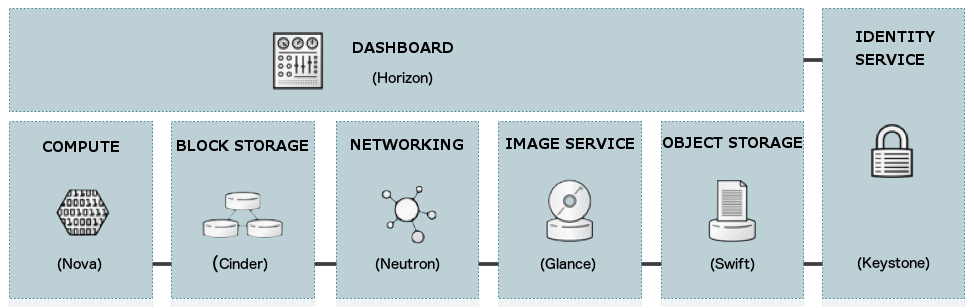
Keystone
The OpenStack Identity Service (Keystone) provides authorization and authentication for users and also manages service catalogs. It’s equivalent to AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Glance
The OpenStack Image Storage Service (Glance) stores and manages virtual machine images in different formats. These images are used by compute service to provision instances. It’s comparable to AWS AMI (Amazon Machine Image).
Cinder
The OpenStack Block Storage Service (Cinder) provides persistent block storage to guest virtual machines for expanded storage, better performance and integration with enterprise storage platforms. It’s similar to AWS EBS (Elastic Block Storage).
Neutron
The OpenStack Network Service (Neutron) enables network-connectivity interface devices managed by Compute. It enables users to create and attach interfaces to networks. It corresponds to AWS Networking.
Nova
The OpenStack Compute Service (Nova) provisions instances on user demand. It supports most virtualization technologies. It’s analogous to Amazon's EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) environment.
Swift
The OpenStack Object Storage Service (Swift) provides a cost effective, scale-out, redundant, scalable and fully-distributed API-accessible storage platform that can be integrated directly into applications or used for backup, archiving and data retention. It’s equivalent to Amazon’s S3.
Ceilometer
The OpenStack Metering/Monitoring Service (Ceilometer) monitors and meters the OpenStack cloud for billing, benchmarking, scalability, and statistics gathering. It’s comparable to AWS CloudWatch.
Heat
The OpenStack Orchestration Service (Heat) is a template-driven engine that allows automated infrastructure the deployment through both an OpenStack-native REST API and a CloudFormation-compatible Query API. It’s similar to AWS CloudFormation.
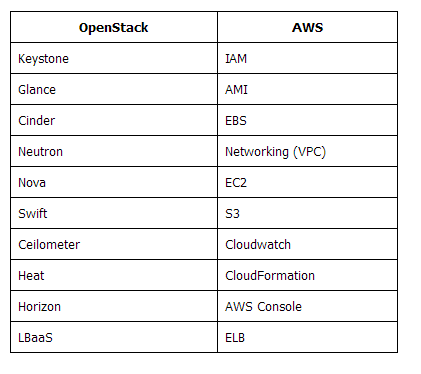
Comparison of OpenStack Services with AWS services
Abayomi Ayoola
aoayoola
abayomi@corvio.co
07053049104
Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
“ A model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers,storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.”
~~The National Institute of Standards and Technology
Features
On-demand self-service - Service consumer can procure or enable computing resources such as storage as needed without requiring personnel contact with the service provider
Broad network access - These computing resources are available over the network and accessed through various form of standard devices
Resource pooling - Computing resources such as memory, processing, bandwidth, storage are pooled together by service providers to serve multiple consumers under the multi-tenant model, assigning and re-assigning such resources according to demand
Rapid elasticity - This is so that services can scale rapidly outward and rapidly released to scale inward on demand
Measured service - Cloud systems leverage a metering capability to automatically manage and optimize resource usage at level of abstraction suitable to that level of
service
Service Models
Software as a Service (SaaS) - Service provisioning under this model is for users or consumers to use a provider’s application running on its infrastructure at a remote location on demand, in that, a single instance of the application is available to multiple end-users. In other cases, different instances of the same application are deployed for different consumer.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) - The service provision on this model is the deployment of applications acquired or developed by end-user onto the infrastructure of service provider using tools and programming languages supported by such.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - The provisioning of computing resources such as operating system, storage, servers, processing, bandwidth, datacenter space and sometimes applications are pooled together and made available by service providers to
handle tasks and processes.
Deployment Models
Private Cloud - A cloud infrastructure built entirely for a single organization and its business units and managed either by its own human resource or third party organization.
Community Cloud - A cloud infrastructure set up for several organizations with common interest and concern. Like private cloud, it can be managed either by member of its staff or third party organization.
Public Cloud - The provisioning of cloud services is rendered by an organization to the public.
Hybrid Cloud - The provisioning of two or more cloud deployment models networked by standards or proprietary protocols that allow portability of traffic such as cloud bursting activity between clouds