Comparison of properties affecting the performance of Hypercube Interconnection
Presented By: Abdullah Alshammari
Authors
- K. Karthik
- Dr. Sudarson Jena
- Dr. T. Venu Gopal
Telangana state, India
Publisher
- Electrical, Electronics, Signals, Communication and Optimization (EESCO), 2015 International Conference
- Date of Conference : 24-25 Jan. 2015
Interconnection Networks
- Important in many area such as Parallel Computing and WSNs as a virtual backbone.
- In Parallel Computing:
- interconnection of processors and linking the memory module to them effectively is not an easy task.
- A single bus is not a perfect solution ( one message at a single point of time
- crossbar is not a practical solution ( each process is linked to another one).
- The solution is custom topologies such as Hypercube topology.
Hypercube Variants
- Hypercube Network.
- Folded Hypercube Network.
- Multiply Twisted Cube Network.
- Multiple Reduced Hypercube Network.
- Half Hypercube Network.
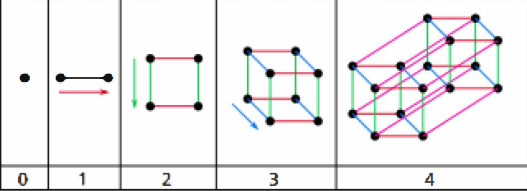
Hypercube Network
- it's n dimensional figure similar to cube in 3 Dimension and square in 2 Dimension.
- Diameter : the minimum number of steps it takes for one processor to send a message to the farthest processor. ( it's 2 in C2 and 3 in C3 and n in Cn)
- Nodes: 2^n
- Degree: n.
Hypercube Network Example
Folded Hypercube Network
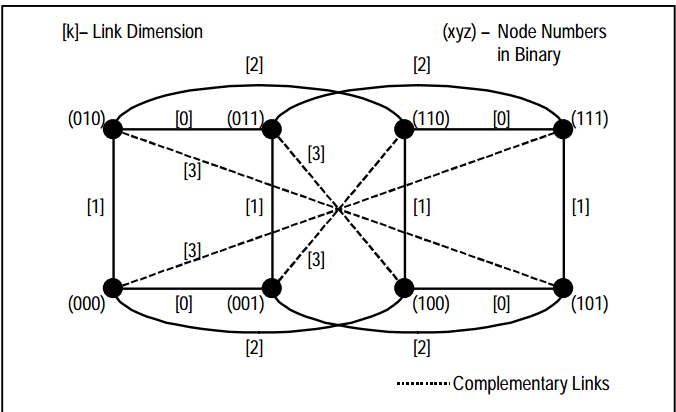
- it is a standard hypercube with some extra links established between its nodes.
- it can be constructed from a standard n-dimension hypercube by connecting each node to the unique node that is farthest from it ( for example 111 to 000 ).
- Diameter : the minimum number of steps it takes for one processor to send a message to the farthest processor. ( n/2)
- Nodes: 2^n
- Degree: n+1
FHC example
Multiple Reduced Hypercube Network
- It's based on hypercube with better diameter.
- The edges of MRH(n) are expressed in three forms. Based on the methodology of connection, they are named as Hypercube edge, Exchange edge and Complement edge
- Diameter : (n/2) + ( (n/2) + 1)/3)+ 1
- Nodes: 2^n
- Degree: n
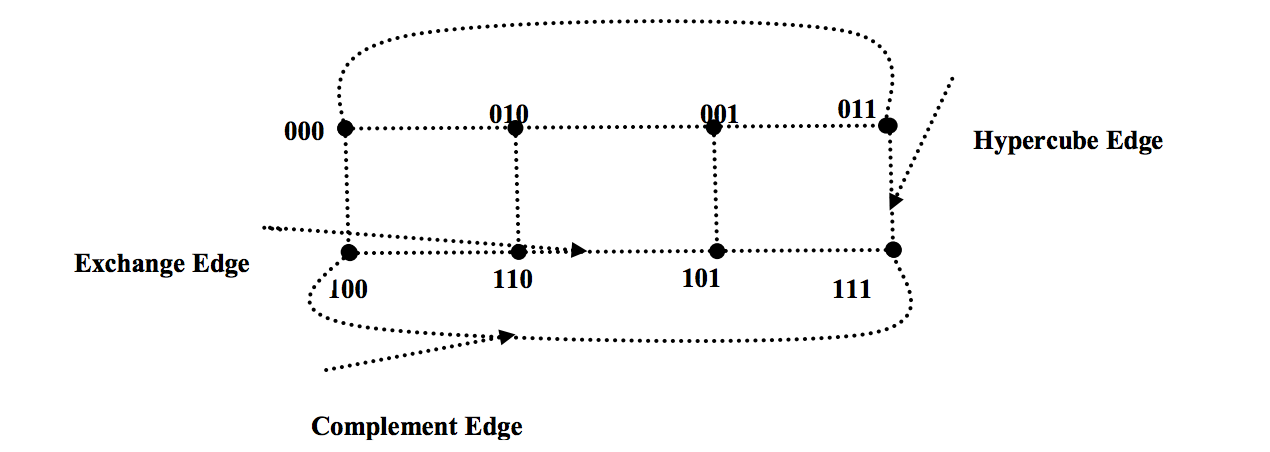
Multiple Reduced Hypercube Network
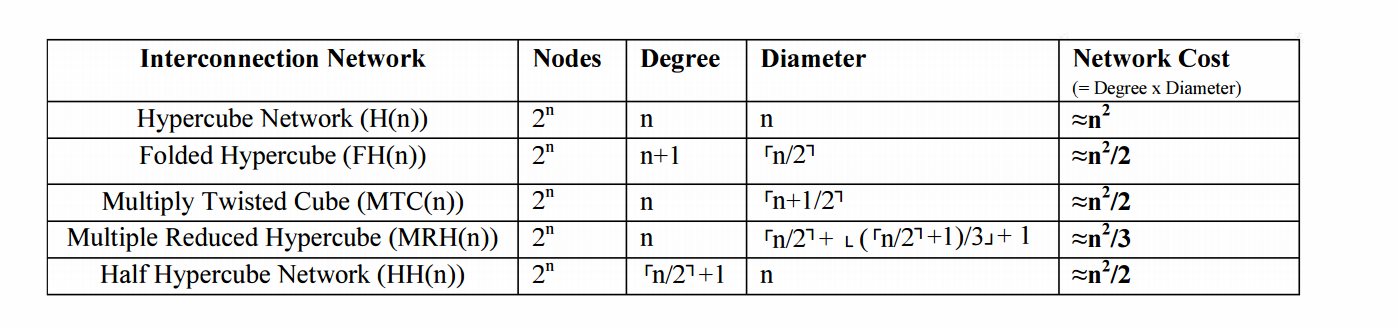
ANALYSIS OF PROPERTIES OF INTERCONNECTION NETWORKS
References
- Comparison of properties affecting the performance of Hypercube Interconnection Networks
- MODELING THE FOLDED HYPERCUBE NETWORK WITH OPNET
- ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE REDUCED HYPERCUBE INTERCONNECTION NETWORK PROPERTIES OF BOTH DIAMETER AND NETWORK COST