Unit B - Installing and Configuring Flask
Lesson 2: Configuring Flask
Course Progress Review
This is lesson 4 of 8
Unit A Lesson A1 - Installing Python
Unit A Lesson A2 - Installing & setting up virtual environments
Unit B Lesson B1 - Installing Flask
Unit B Lesson B2 - Configuring Flask
Unit C Lesson C1 - Building your Flask Web application
Unit C Lesson C2 - Running your Flask Web application
Unit D Lesson D1 - Understanding Web Servers
Unit D Lesson D2 - Deploying to PythonAnyWhere
Configuring Flask
In order to best adapt Flask for the needs of your application, you may wish to change a number of settings to suit your development environment.
While it is possible to hardcode the configuration into Flask, there is a configuration tool within Flask that allows you to customise as you require.
The Config Object
Your chosen configurations are saved within a Config object in Flask.
All configuration values for Flask and any extensions you have installed are saved in this object.
The configuration tool is accessed through the "config" command.
Debug
Accessing the configuration file in Flask is completed by accessing the debug option.
This allows you to enter various configuration values for Flask to implement.
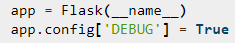
You can access the debug mode for your application by inputting the below command in Python, where (__name__) is the name of your application.
Configuration Values
Over the following slides, we will look at a few useful configuration values.
- DEBUG: Enables and disables the debug feature, which allows you to modify configuration settings.
- TESTING: Enables and disables the Test Mode feature, which allows you to test the functionality of your application in action.
- SERVER_NAME: displays the name and port number of the server in use.
- MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH: places a file size limit, in bytes, so that file submissions greater than this file size are rejected with an error.
Configuration Values
Text