Creating web widgets with
Module Federation
and Angular Elements
https://slides.com/agesteira/ng-india-web-widgets

Agenda
-
Microfrontends -
Modules -
Module Federation -
The User Story -
Demo
Andrés Gesteira
Twitter: @GeorgeKaplan_G
Born in Madrid.
Tech Lead Front End
Longer than 6 years playing with Angular.
Likes cinema, books, and food.

Microfrontends
Microfrontends architecture
-
Breaks up a FE app into smaller parts, called microfrontends.
-
Each MFE should be separately built and deployed.
-
Each MFE takes care of a different UI.
-
Each MFE can be handled by a different squad.
-
A MFE can be either:
-
An application.
-
A component.
-
There is not only 1 way
iframes are evil


Web Components (I)
-
They allow us to create reusable custom elements.
-
They contain an encapsulated DOM called Shadow DOM.
-
They build their markup with:
-
<template> & <slot>
-
-
They need to be registered in the DOM by using:
-
customElements.define('tag', HtmlElement)
-
wrapperElement.appendChild()
-
Web Components (II)


Web Components (III)


The Includes approach
-
A system creates the self-contained HTML fragments.
-
Depending on who assembles the fragments:
-
It can be Server-Side Includes (SSI)...
-
... or Client-Side Includes (CSI).
-
-
Module Federation uses this approach.
Modules
<script>
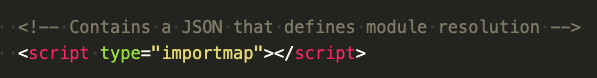
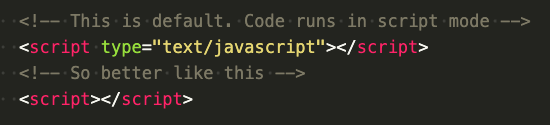

What do you mean "module mode"?
-
In JavaScript we have different execution contexts...
-
...we call them scopes.
-
If the code runs in script mode it uses the global scope.
-
But there are also 3 types of local scope
- Function scope.
- Block scope.
- Module scope.
So what is a module?
-
It is a mechanism to split JavaScript programs.
-
It it typically implemented in a separate file (js/mjs).
-
It must contain import and/or export declaration/s.
- ES modules can run in module mode.
- Non ES modules (e.g. CommonJS) cannot...
- Unless they are compiled to ES modules with a building tool...
- ...like Webpack.
Module Federation
It's a mental model...
...not an architecture.
-
Because it can produce multiple architectures.
-
The code is federated across different servers.
-
Each part of the federation is a module.
-
The host module wraps the other ones....
-
...which are called remote modules.
-
Any module can communicate with any module.
-
So circular dependencies are allowed.
Federation
Shell / Host
Remote 1
Remote 1
import()
Remote 2
import()
Remote 3
import()
remoteEntry.js
remoteEntry.js
-
It is not a module.
-
It is a manifest...
-
...that enables the dynamic sharing.
-
It includes fine-grained information about:
-
Modules.
-
Libraries.
-
Considerations
-
PROS:
-
No code duplication (better than Webpack's default).
-
Shared libraries.
-
Version control.
-
-
CONS:
-
Cross-framework not guaranteed.
-
In Angular, it creates several root scopes.
-
The User Story
My manager told me to.

Requirements
-
You need to do it with Angular.
-
You need to deploy self-contained HTML fragments.
-
BUT You don't have the routing app. And you will never have it.
You need to find a solution.

Module Federation Web Components
Web Component
Shell
Remote
Web Component
Shell
Remote
Any Web App