Machine Learning in Intelligent Transportation
Session 2: Percepotron
Ahmad Haj Mosa
PwC Austria & Alpen Adria Universität Klagenfurt
Klagenfurt 2021

Machine Learning Tasks

1. Regression
Machine learning task are categorized by the target of the studies problems as follows:
is the problem of identifying the relationship (mathematical model) among different variables
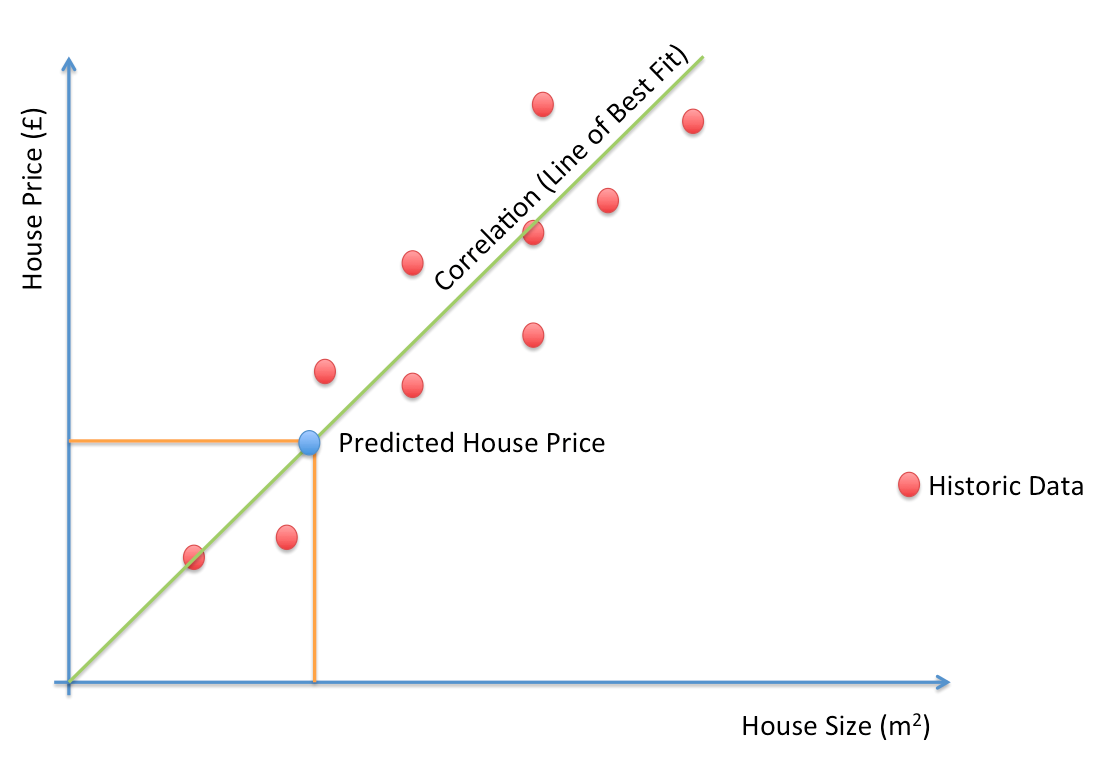
Linear Regression

A liner modeling of the relation between two or more variables
Text
\( \omega_1 \) , \( \omega_0 \) are the weights
\( x \) is the independent variable (input/feature)
\( y \) is the dependent variable (decision/output)
Linear Regression Training

The training target of a linear regression is to find the optimum weights \( \omega_1 \) , \( \omega_0 \) that minimize the mean square error \( mse \)
Text
Gradient Descent

The training target of a linear regression is to find the optimum weights \( \omega_1 \) , \( \omega_0 \) that minimize the mean square error \( mse \)
Text
Text
Gradient Descent

The training target of a linear regression is to find the optimum weights \( \omega_1 \) , \( \omega_0 \) that minimize the mean square error \( mse \)
Text
\( \ \frac{\partial J}{\partial \omega} \) is the gradient
\( \ \rho \) is the learning rate. Large \(\rho \) large steps
Gradient Descent

The training target of a linear regression is to find the optimum weights \( \omega_1 \) , \( \omega_0 \) that minimize the mean square error \( mse \)
\( \ \frac{\partial J}{\partial \omega} \) is the gradient
\( \ \rho \) is the learning rate. Large \(\rho \) large steps
def gradient_descent(alpha, x, y, ep=0.0001, max_iter=10000):
converged = False
iter = 0
m = x.shape[0] # number of samples
# initial theta
w0 = np.random.random(x.shape[1])
w1 = np.random.random(x.shape[1])
# total error, J(theta)
J = sum([(t0 + t1*x[i] - y[i])**2 for i in range(m)])
# Iterate Loop
while not converged:
# for each training sample, compute the gradient (d/d_theta j(theta))
grad0 = 1.0/m * sum([(w0 + w1*x[i] - y[i]) for i in range(m)])
grad1 = 1.0/m * sum([(w0 + w1*x[i] - y[i])*x[i] for i in range(m)])
# update the theta_temp
temp0 = w0 - alpha * grad0
temp1 = w1 - alpha * grad1
# update theta
w0 = temp0
w1 = temp1
# mean squared error
e = sum( [ (w0 + w1*x[i] - y[i])**2 for i in range(m)] )
if abs(J-e) <= ep:
print 'Converged, iterations: ', iter, '!!!'
converged = True
J = e # update error
iter += 1 # update iter
if iter == max_iter:
print 'Max interactions exceeded!'
converged = True
return w0,w1
Machine Learning Tasks

1. Classification
Machine learning task are categorized by the target of the studies problems as follows:
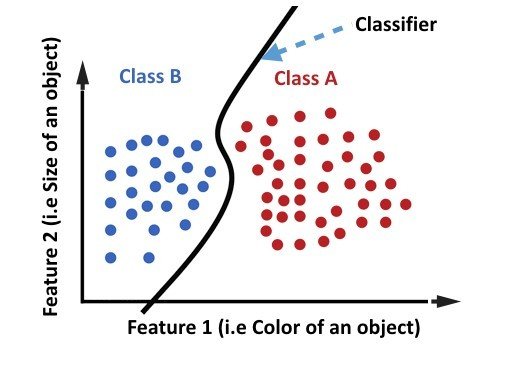
is the problem of identifying to which of a set of categories (sub-populations) a new observation
Linear Classifier

Text
From a linear Classifier to Neuron Models

Text
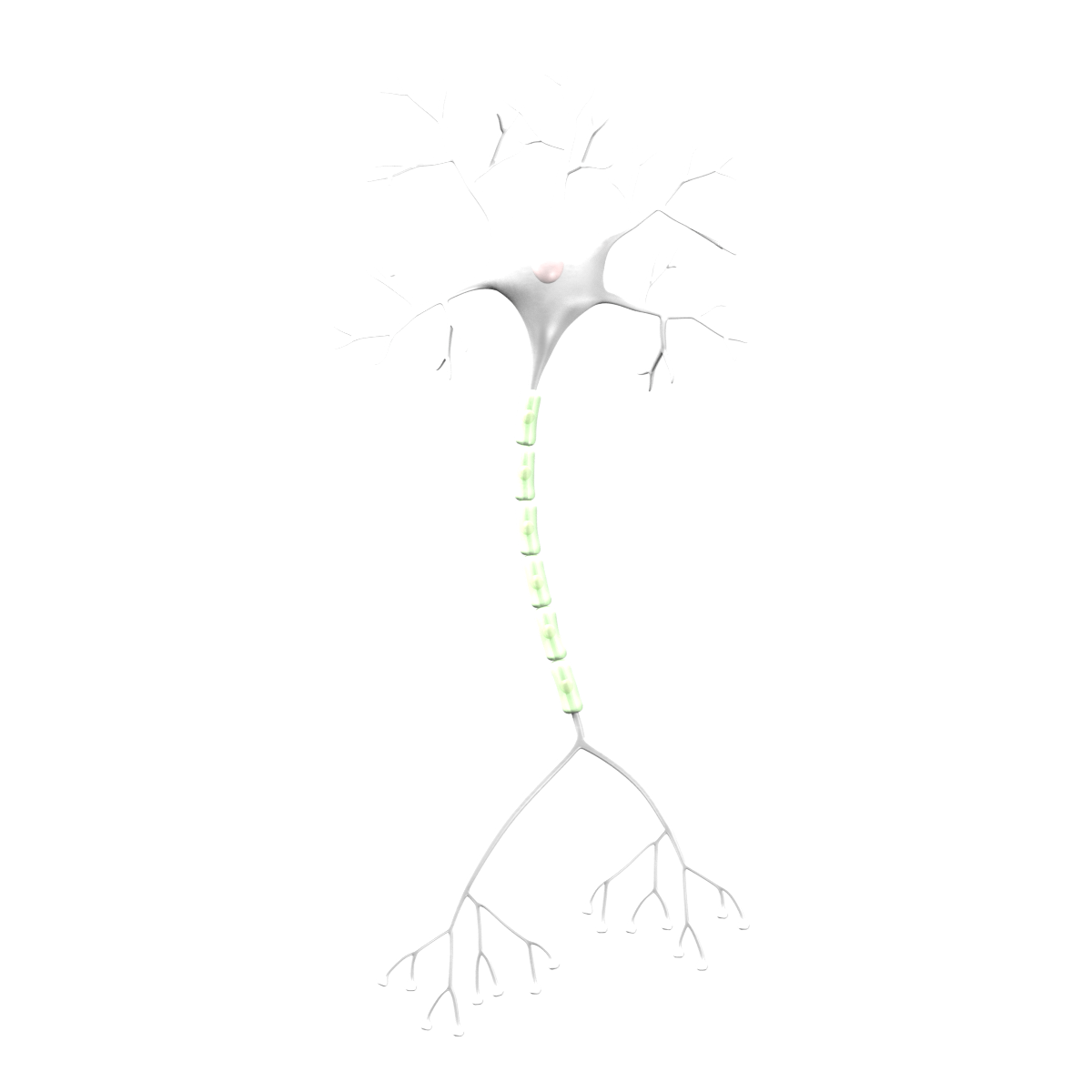
Dendrites
Axons
Cell body
\( x_1 \)
\( x_2 \)
\( y \)
Text
\( \omega= [\omega_1,\omega_2 ]^T \)
\( x=[x_1,x_2 ]^T \)
\( w_1 \)
\( w_2 \)
From a Neuron Model to Logistic Classification

Text

Dendrites
Axons
Cell body
\( x_1 \)
\( x_2 \)
\( y \)
\( w_1 \)
\( w_2 \)
\( \omega= [\omega_1,\omega_2 ,\omega_0]^T \)
\( x=[x_1,x_2,-1 ]^T \)
Text
\( -1 \)
\( w_0 \)
The Perceptron Algorithm

The perceptron algorithm is an optimization method to compute the unknown weights \( w^T \)
- Assume we have classification problem with two classes \( c_1, c_2 \)
- The perceptron cost is given by:
- Where \( Y \) is the subset of the samples, which are misclassified by the classifier
- The variable \( \delta_x \) is chosen so that \( \delta_x =-1 \) if \( x \epsilon c_1 \) and \( \delta_x =1 \) if \( x \epsilon c_2 \)
The Perceptron Algorithm

The perceptron algorithm is an optimization method to compute the unknown weights \( w^T \)
- Choose \( \omega_0 \) randomly
- Choose \( \rho_0 \)
- \( t=0 \)
- Repeat :
- \( Y = \phi \)
- For \(i=1\) to \(N\) :
- If \( \delta_{x_i}\omega(t)^Tx_i \geq 0\) then \( Y=Y \cup {x_i} \)
- End {For}
- \( \omega(t+1) = \omega(t) - \rho \sum_{x \epsilon Y}\delta_{x} x \)
- \(t=t+1\)
- Until \(Y= \phi \)
Nonlinear Classifiers

For nonlinear separable problems a single neuron/line model in not enough
Logical OR Modeling: linear classifier?

| OR | Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0
|
0 | 0 | B |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | A |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | A |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | A |
Text
\( y \)
\( w_2 =1 \)
Text
\( -1/2 \)
\( w_0 \)
\( w_1 =1 \)
\( y =x_1 +x_2 -0.5\)
Logical AND Modeling: linear classifier?

| AND | Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0
|
0 | 0 | B |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | B |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | B |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | A |
Text
\( y \)
\( w_2 =1 \)
Text
\( -3/2 \)
\( w_0 \)
\( w_1 =1 \)
\( y =x_1 +x_2 -3/2\)
Logical XOR Modeling: linear classifier?

| XOR
|
Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0
|
0 | 0 | B |
| 0 | 1 | 1
|
A
|
| 1 | 0 | 1
|
A
|
| 1 | 1 | 0
|
A
|
Text
\( y \)
\( -3/2 \)
\( 1 \)
\( y =(x_1 +x_2 -1/2)+2(x_1 +x_2 -3/2)- 1/2\)
Text
\( 1 \)
\( 1 \)
\( 1 \)
\( -1/2 \)
\( -1/2 \)
\( 2 \)
\( 1 \)
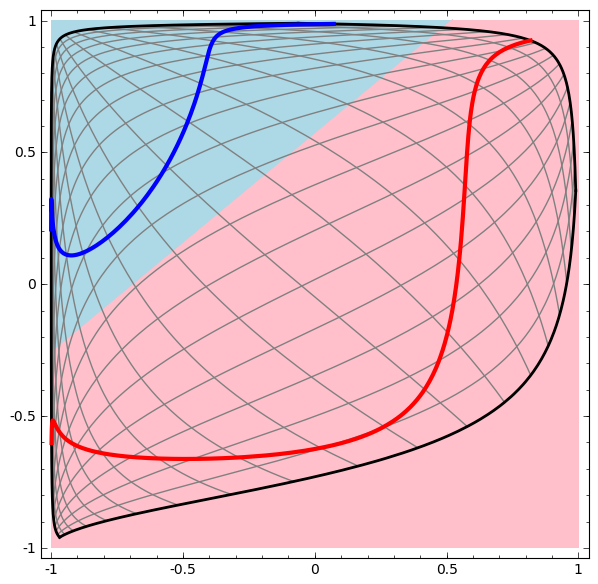
Neural Networks: topological representation

Topology is one field of mathematics that can be used to understand how neural networks work
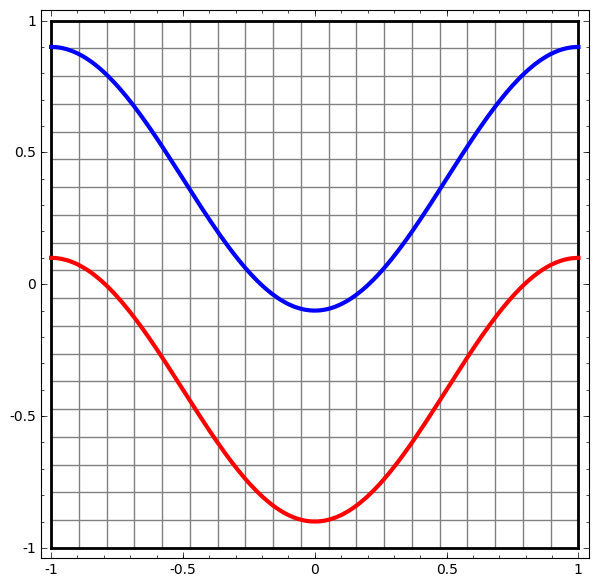
- A simple NN topology example: a very simple dataset, two curves on a plane. The network will learn to classify points as belonging to one or the other.
Text
Neural Networks: topological representation

Topology is one field of mathematics that can be used to understand how neural networks work
- The two regions can only be separated by a nonlinear curve
Text
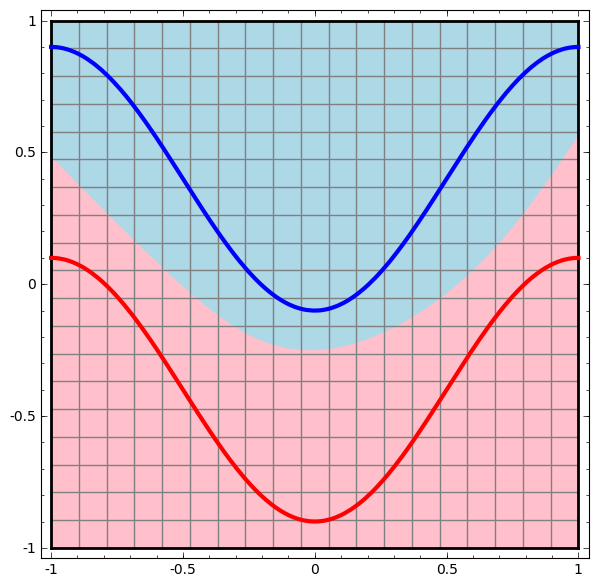
Neural Networks: topological representation

Topology is one field of mathematics that can be used to understand how neural networks work
- With each layer, the network transforms the data, creating a new representation

- When we get to the final representation, the network will just draw a line through the data (or, in higher dimensions, a hyperplane).