
Neural Symbolic Learning
Ahmad Haj Mosa
Fabian Schneider
ahmad.haj.mosa@pwc.com
LinkedIn: ahmad-haj-mosa
schneider.fabian@pwc.com
LinkedIn: fabian-schneider-24122379



Marvin Minsky
The definition of intelligence
Our minds contain processes that enable us to solve problems we consider difficult.
"Intelligence" is our name of those processes we don't yet understand.
Marvin Minsky
The definition of intelligence
Our model contain processes that enable us to solve problems we consider difficult.
"Black-box" is our name of those processes we don't yet understand.

source: DARPA
Is it explainability vs accuracy?
Explainability
(notional)
Explainability
Prediction Accuracy
Neural Nets
Deep
Learning
Statistical
Models
AOGs
SVMs
Graphical
Models
Bayesian
Belief Nets
SRL
MLNs
Markov
Models
Decision
Trees
Ensemble
Methods
Random
Forests
Learning Techniques (today)

Non relational inductive bias
Spatial and Temporal relational inductive bias
Attention based Spatial and Temporal relational inductive bias
Multi relational inductive bias
explanatory factors
Disetangled Representation
Graph Neural Networks
Attention Mechanism
ConvNets
Feed Forward
Performance
Explainability
Current
Future
Is it explainability vs accuracy?

What is next in Deep Learning?
Slow
Fast
Automatic
Effortful
Logical
Emotional
Conscious
Unconscious
Stereotypic
Reasoning
| System 1 | System 2 |
|---|---|
| drive a car on highways | drive a car in cities |
| come up with a good chess move (if you're a chess master) | point your attention towards the clowns at the circus |
| understands simple sentences | understands law clauses |
| correlation | causation |
| hard to explain | easy to explain |
Thinking fast and slow
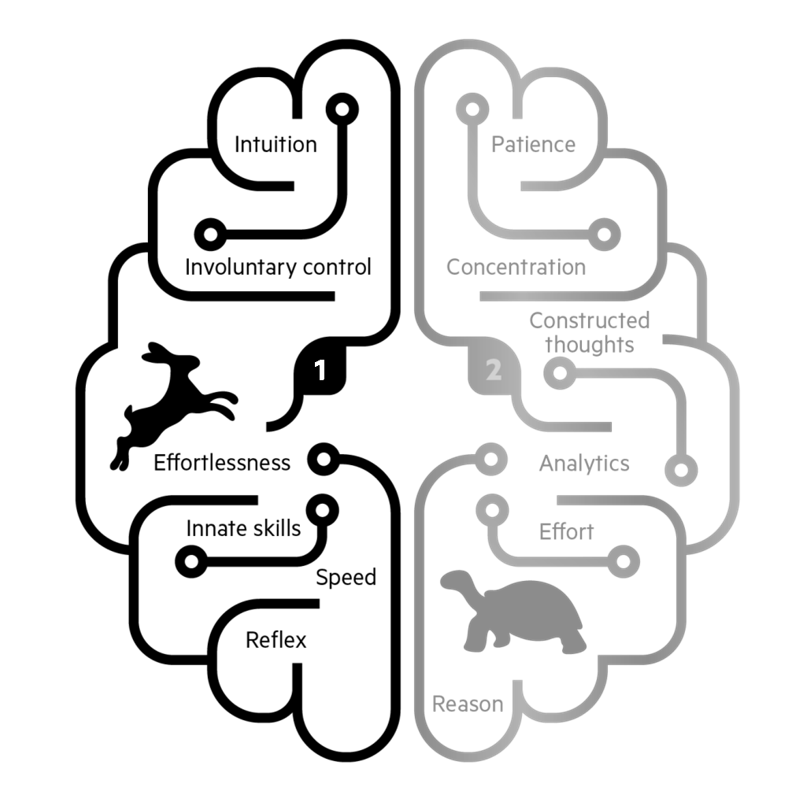

source: Thinking fast and slow by Daniel Kahneman
thinking fast
thinking slow
consciousness prior
learning slow
learning fast
hard explanation
easy
explanation
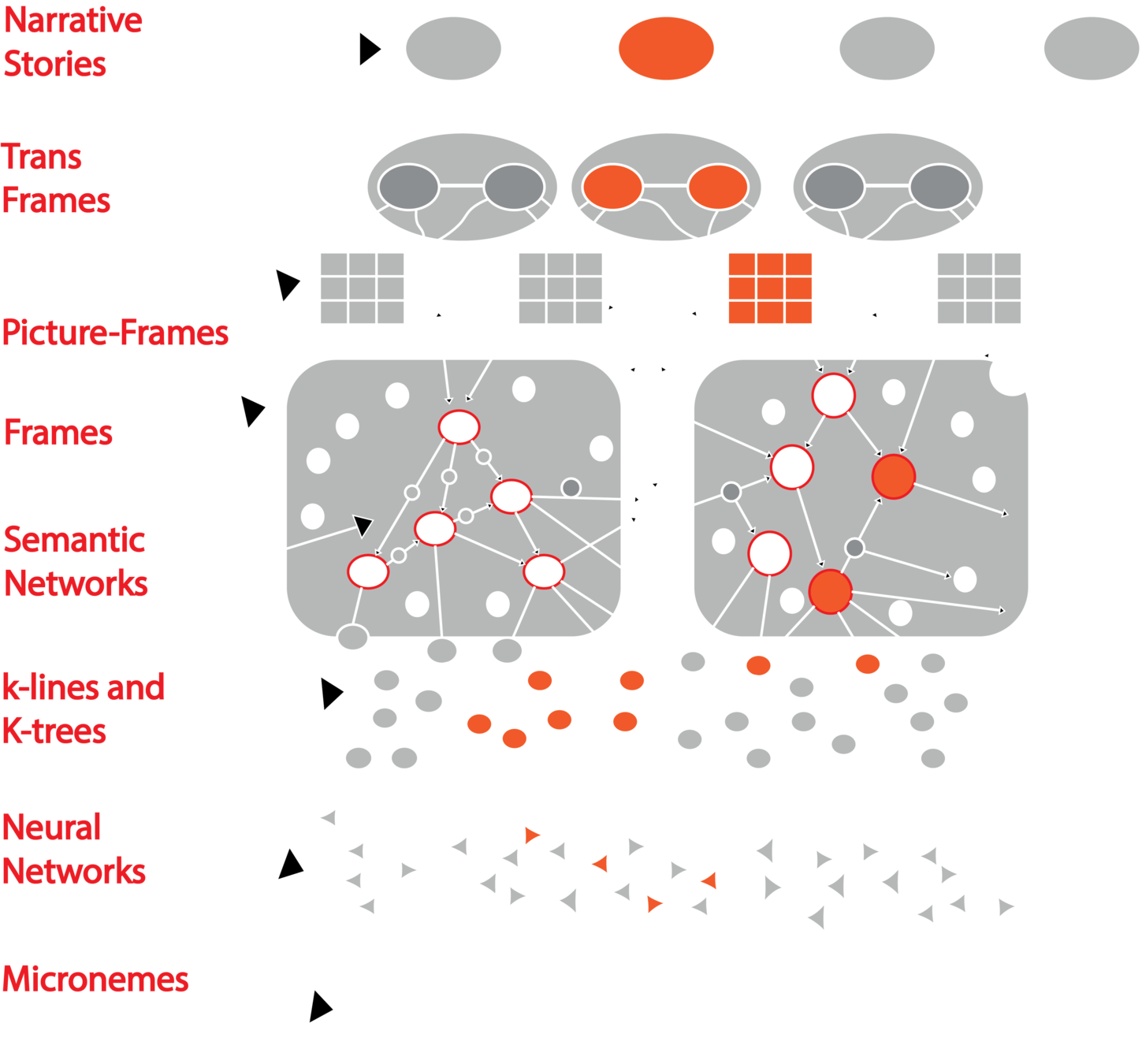
A framework for representing knowledge


Neural Symbolic Learning


Neural Symbolic AI Models
Sym
ML
Sym
ML
ML
ML
Sym
Sym
Sym
Sym
Data
Data
Data
RE
RE
- Sym: Symbolic representation ( graph and/or knowledge base)
- ML: Statistical Machine Leaning ( mainly deep learning )
- RE: Logical Reasoning Engine
- Data: raw data ( image, voice, structured data .etc)
RE
Sym

Data
Data
ML
Sym
ML
RE
Sym
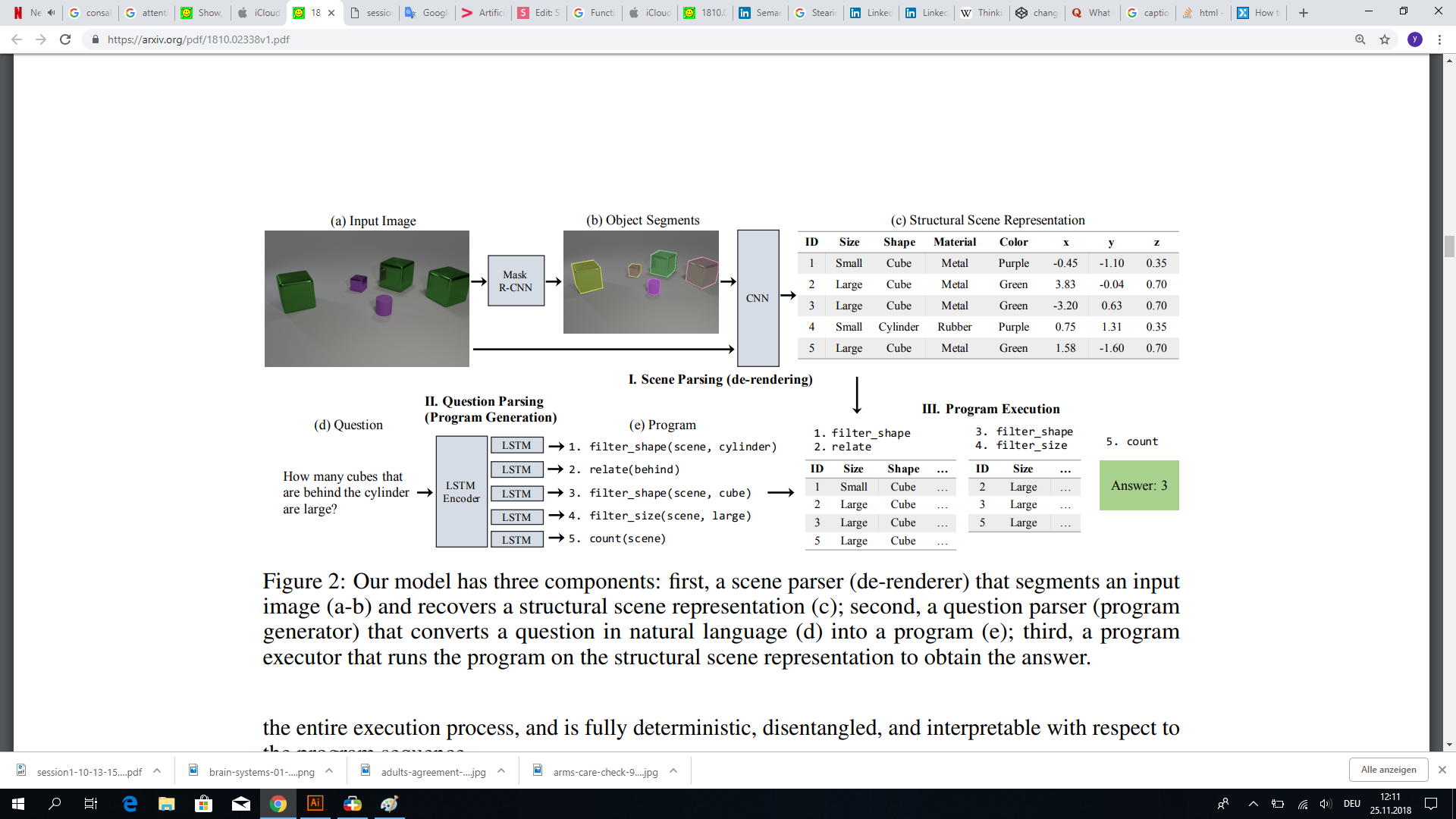
source: arXiv:1810.02338: Neural-Symbolic VQA: Disentangling Reasoning from Vision and Language Understanding
Neural symbolic and disentangled reasoning


Sym
Sym
Sym
RE
ML
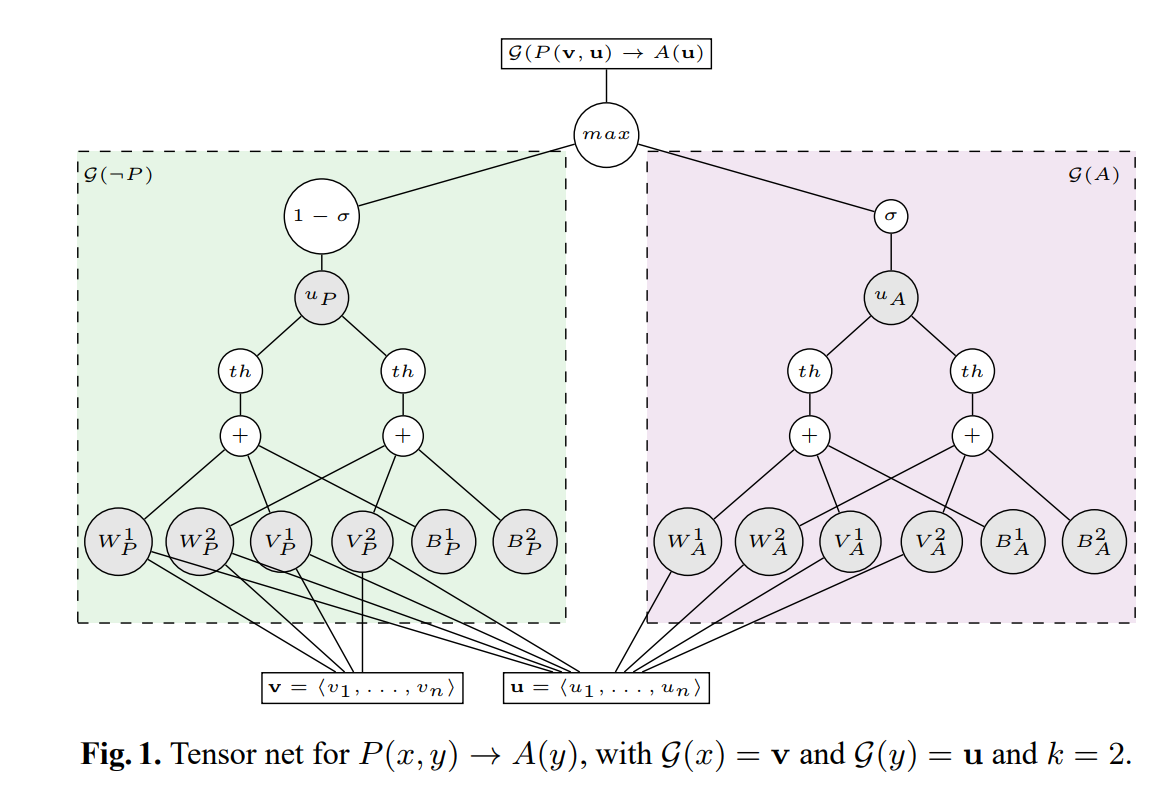
Logic Tensor Networks

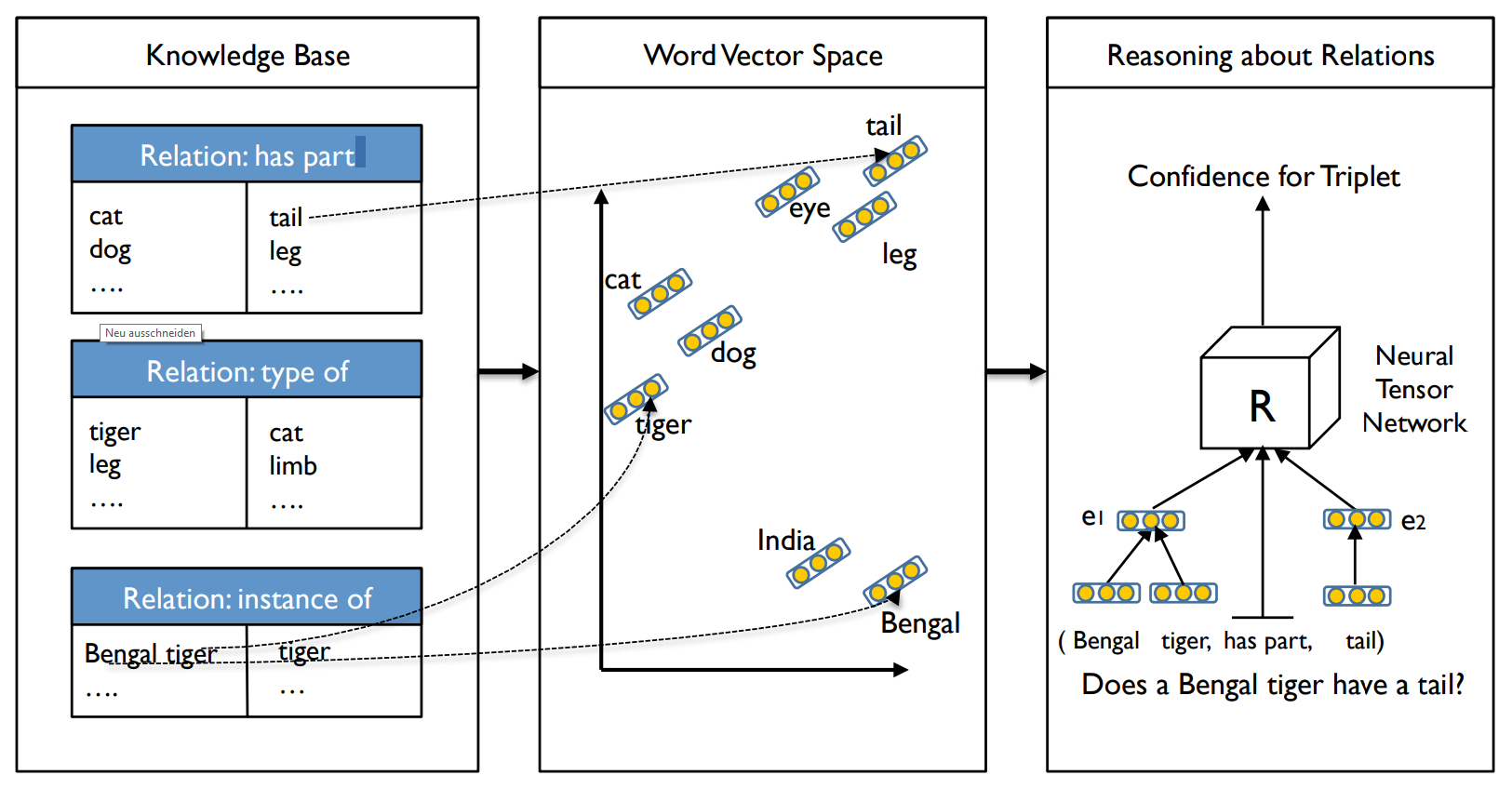
- Defined FOL for real valued vectors (RealLogic)
- Defined semantic grounding for RealLogic
- Using Neural Tensor Network (NTN) for inferring new knowledge
NTN: learning representation of entities and their relations in a KB unsupervised using tensor representation
Logic Tensor Networks

- Defined FOL for real valued vectors (RealLogic)
- Defined semantic grounding for RealLogic
- Using Neural Tensor Network (NTN) for inferring new knowledge
NTN: learning representation of entities and their relations in a KB unsupervised using tensor representation

Data
ML
Sym
Sym
RE
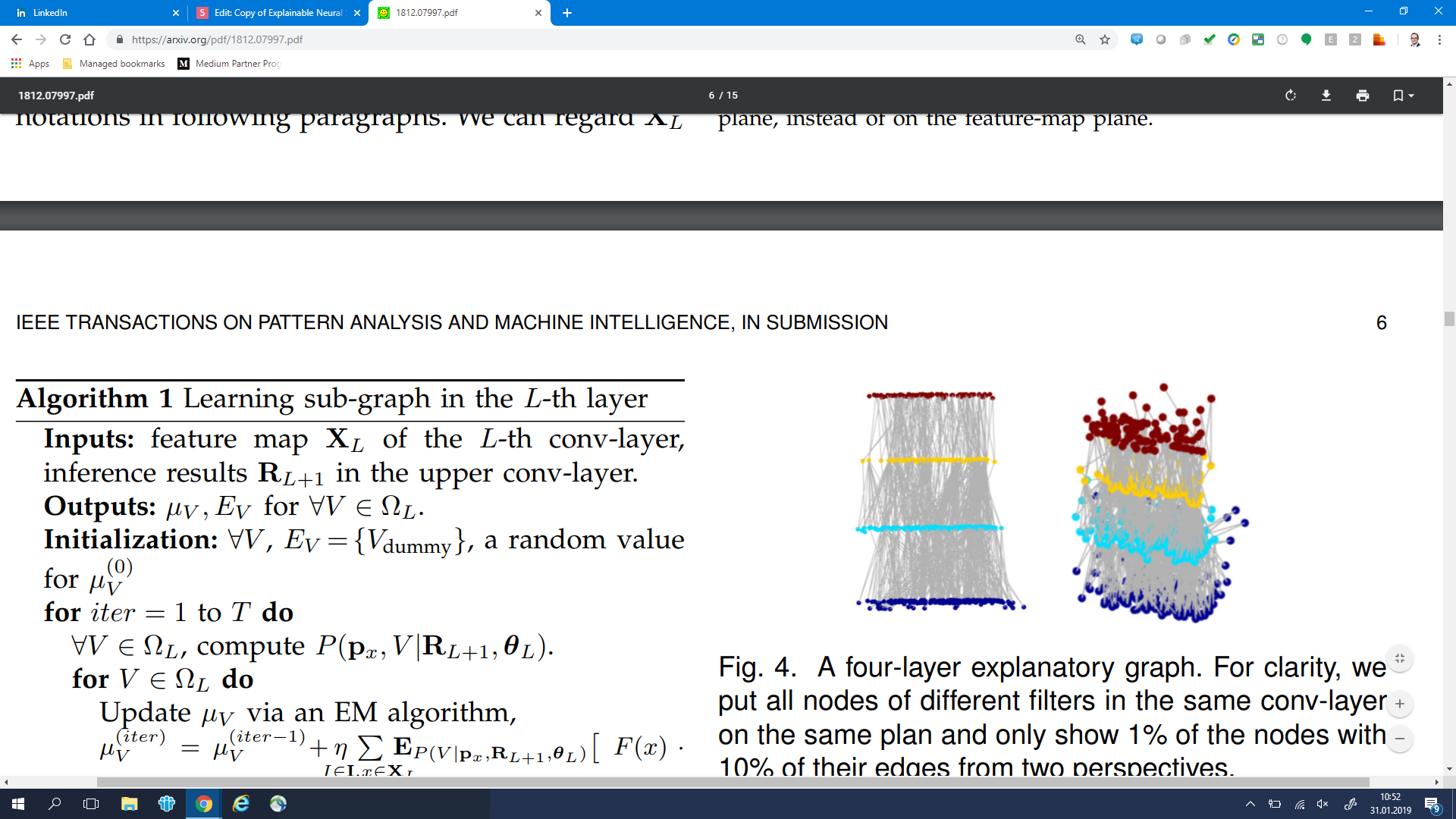
Explanatory Graphs for CNNs

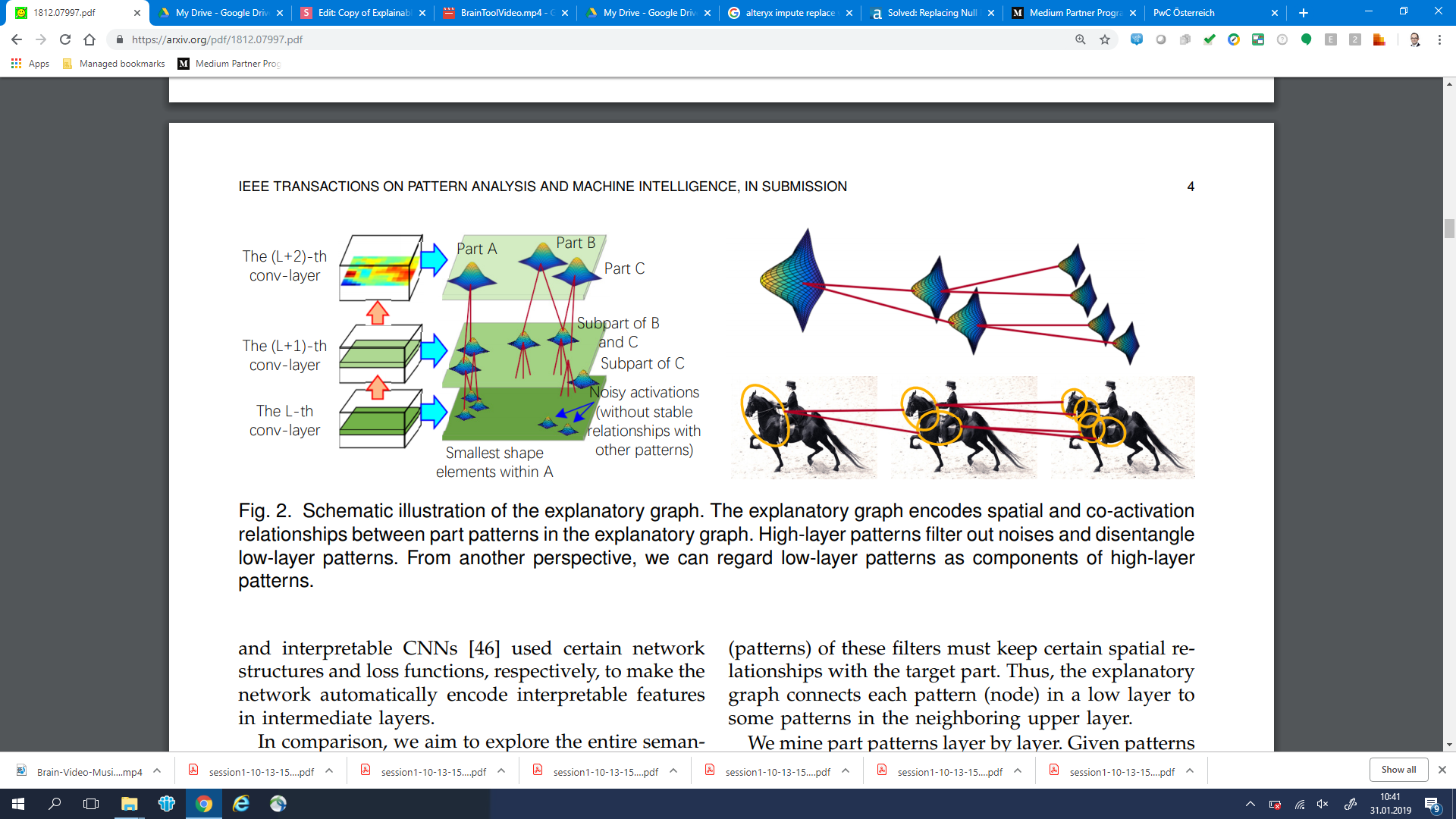
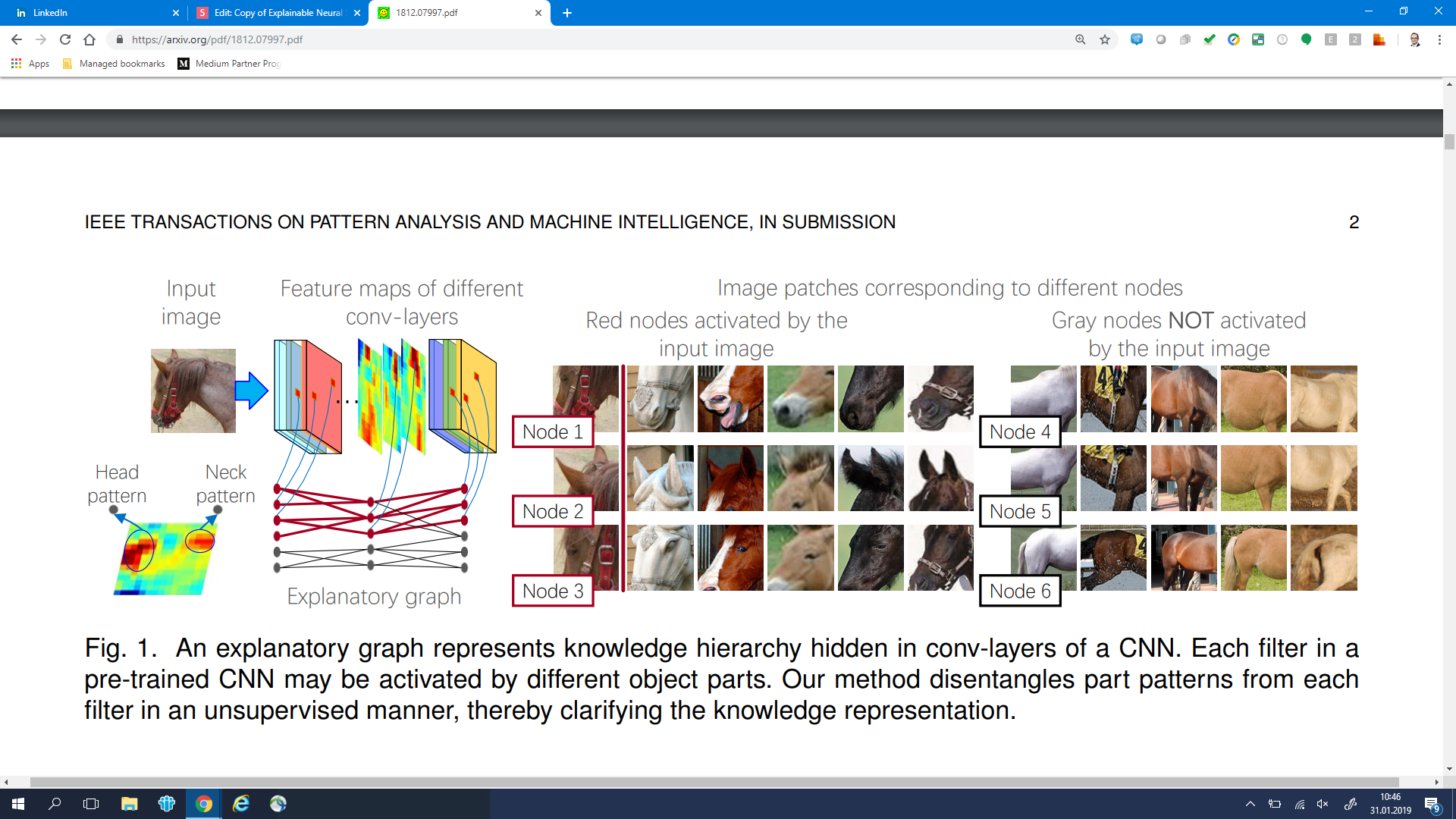
source: arXiv:1812.07997: Explanatory Graphs for CNNs
Framework 1: Logical Simplification using Tree Search, Graph Neural Network and Reinforcement Learning
Logical Simplification using TS, GN and RL

Initial
Target
Truth Table
Graph Representation
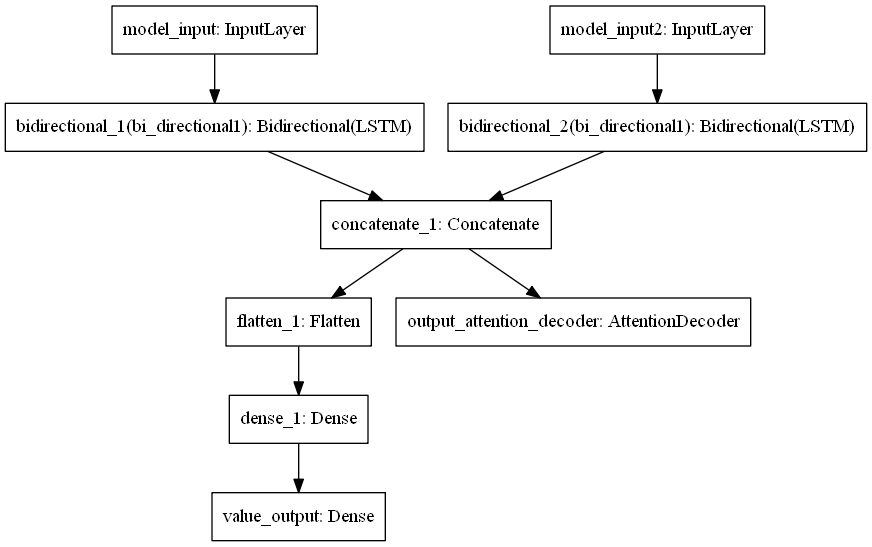
Logical Simplification using TS, GN and RL
Shared Layer
Value Layer
Policy Layer
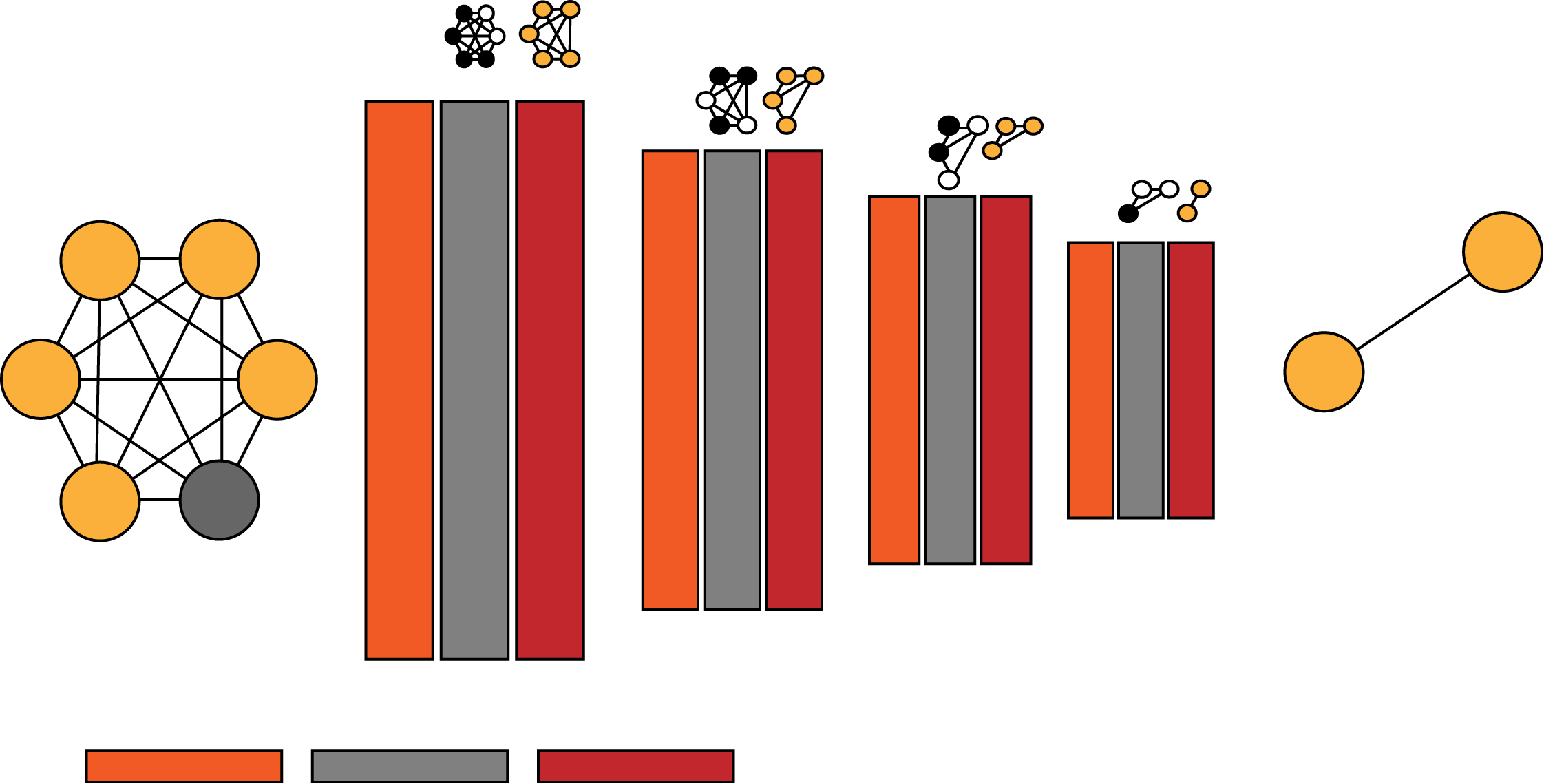
Shared Weights along the features space and the depth
Convolution over the Graph
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM
Atten-LSTM
Flatten
Dense
Dense
Bi-LSTM
-
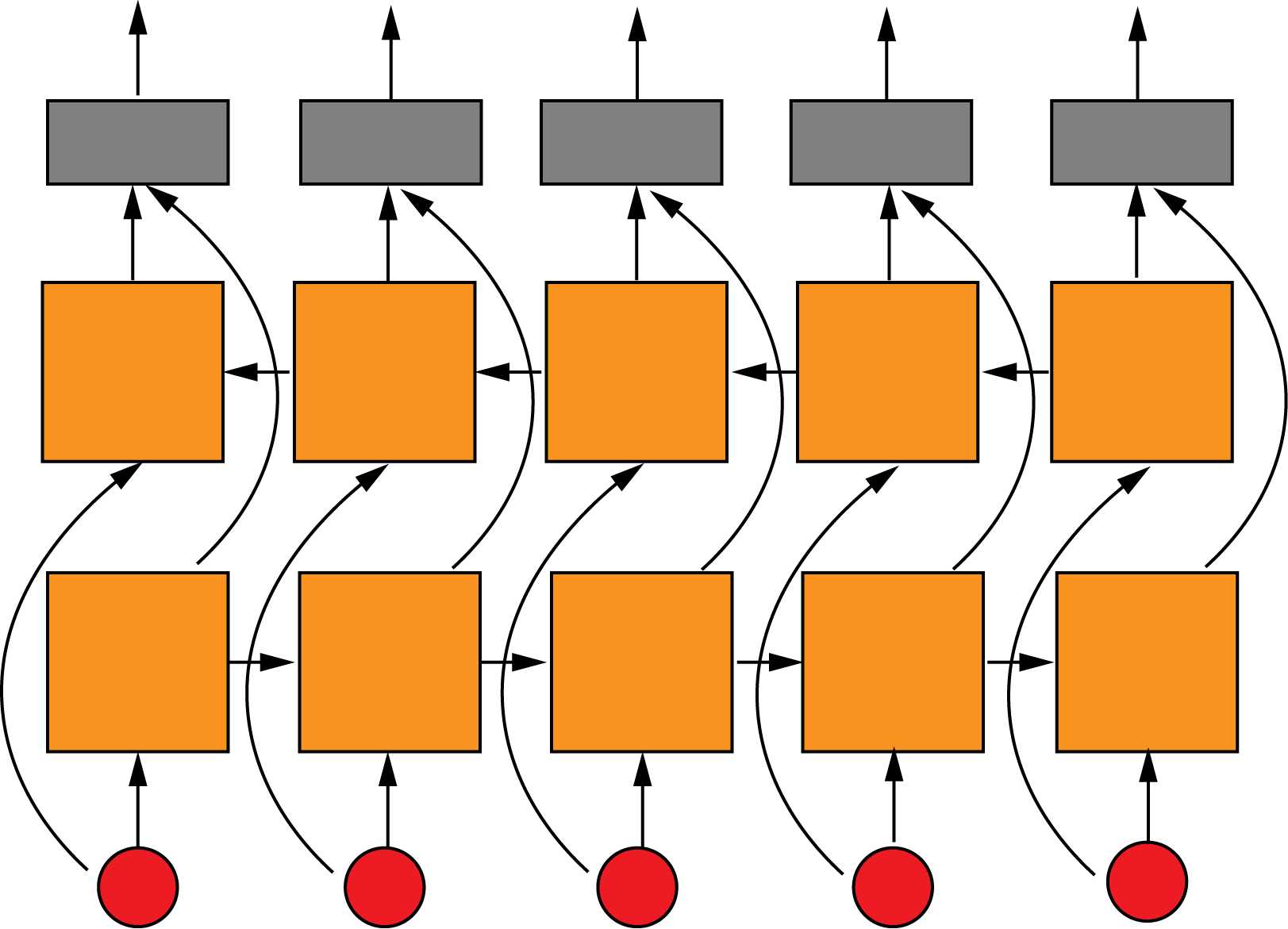
Apply the simplifier block on every pair of nodes
-
In case of large graph, apply the block locally on adjacent nodes
Simplifier Block
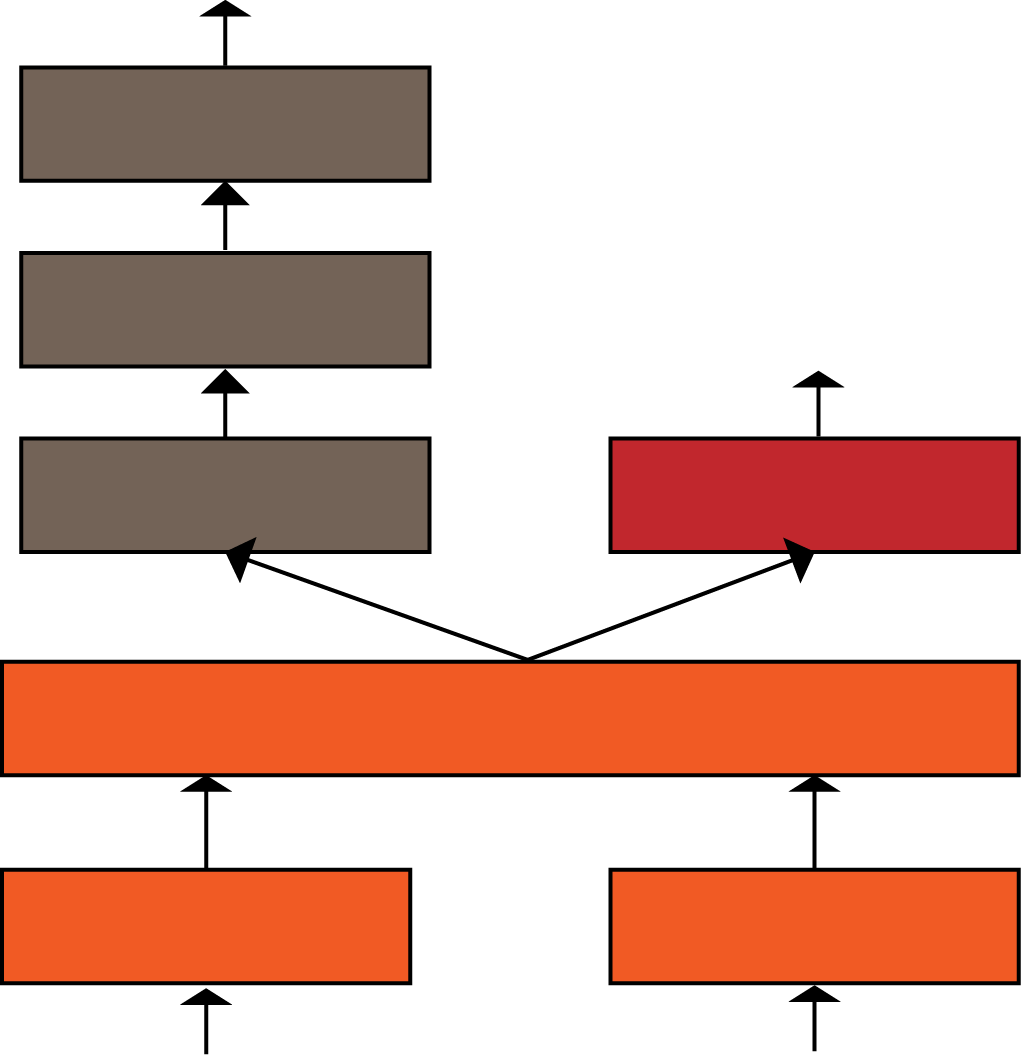
Shared Layer
Value Layer
Policy Layer
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM
Atten-LSTM
Flatten
Dense
Dense
Concatenation
Value of the selection [-1,1]
Simplifier Block
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM

| 0 |
| 1 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM
Atten-LSTM
Flatten
Dense
Dense
Bi-LSTM
Concatenation

| 0 |
| 1 |
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |
| 0 |

Concatenation
Node Features
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM
Atten-LSTM
Flatten
Dense
Dense
Bi-LSTM
Concatenation
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Binary Logic
Multivariate Logic
Monte Carlo Tree Search

Bi-LSTM
Atten-LSTM
Concatenation
Value of the selection [-1,1]
N W
Q P
Accumulated value W = W + v
Number of visits N = N + 1
Mean value Q = W / N
Prior probability of an action P
Active nodes in the graph: G
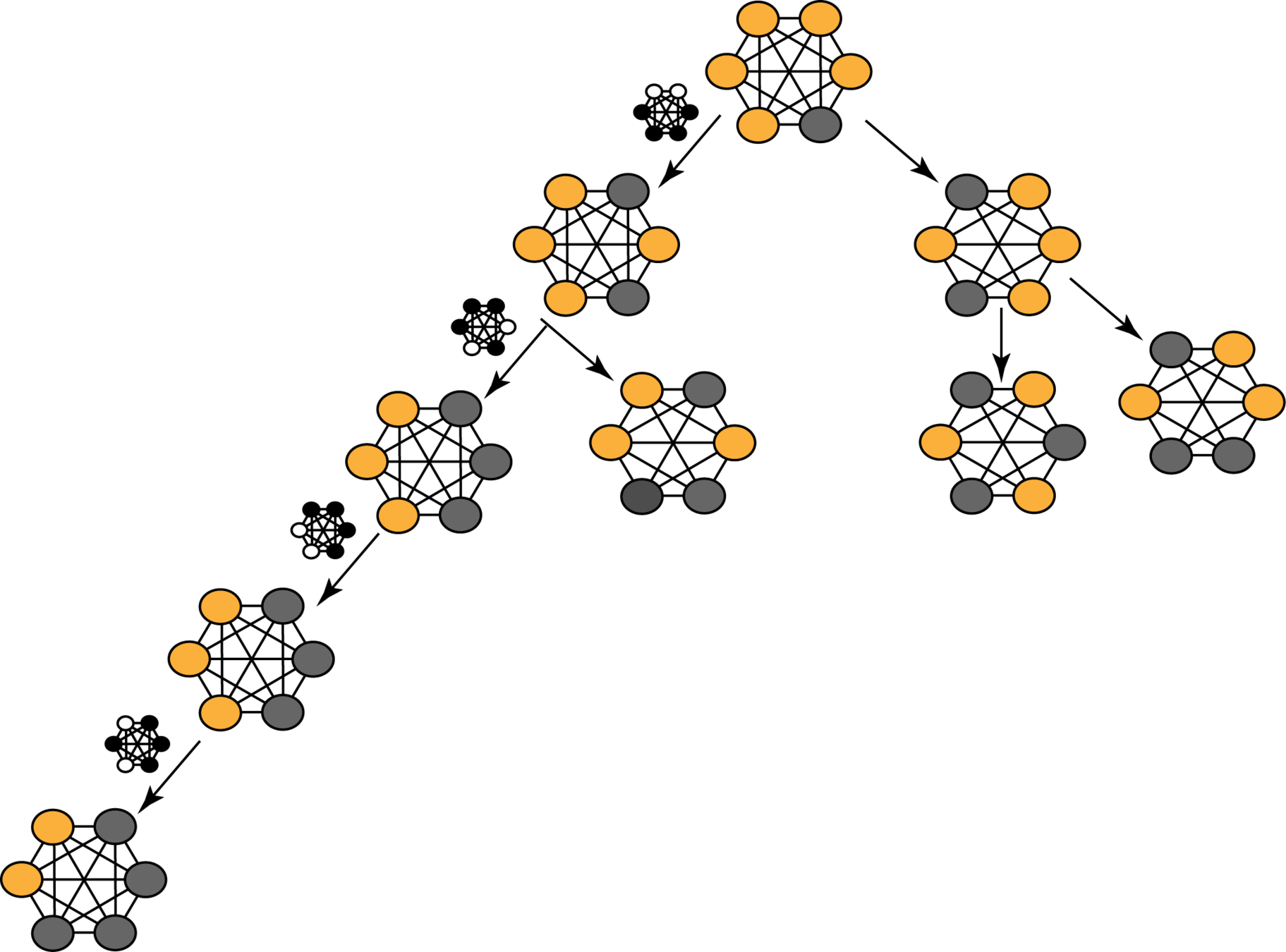
MCT + RL
Bi-LSTM
N W
Q P
Accumulated value W = W + v
Number of visits N = N + 1
Mean value Q = W / N
Prior probability of an action P
Repeate the follwoing steps for M time:
-
Generate Binary data
-
Generate Target Rule
-
Simulate the MCT:
-
Choose the action that maximises Q + U
-
Continue until the leaf node is reached
-
Rollout W, N, Q, P
-
Train the policy layer using policy gradient
-
Train the value layer by minimizing MSE between W and the predicted W
-
Active nodes in the graph: G

Logical Simplification using TS, GN and RL
Shared Layer
Value Layer
Policy Layer
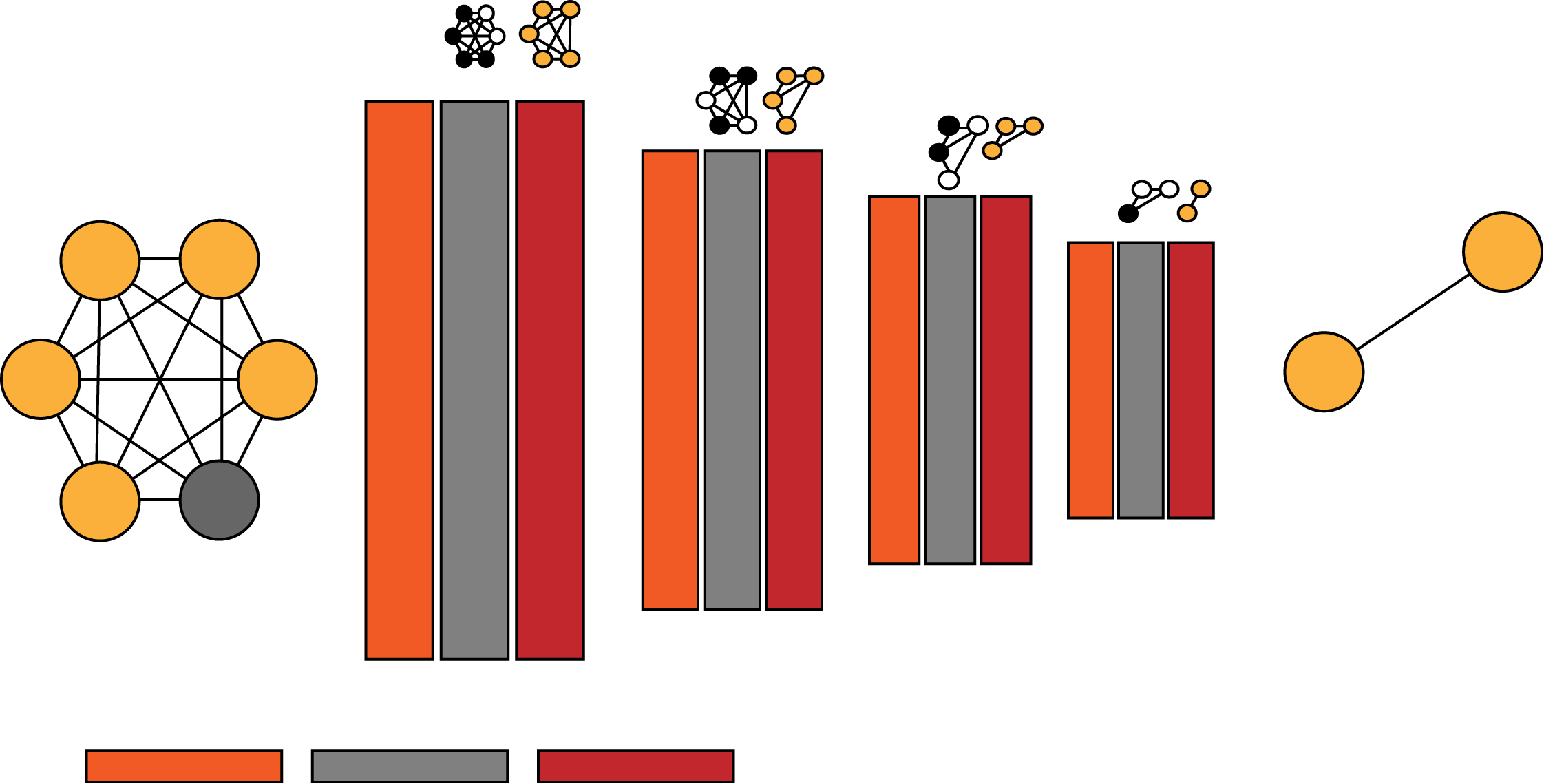
Shared Weights along the features space and the depth
Framework 2: DL Disentangled Representation + Functional Programming Computaiotnal Graph
Framework 2: DL representation + CGN reasoning
Bi-LSTM
Atten-LSTM
Dense
Dense

Variational Disentagled AE
Dense Classifier
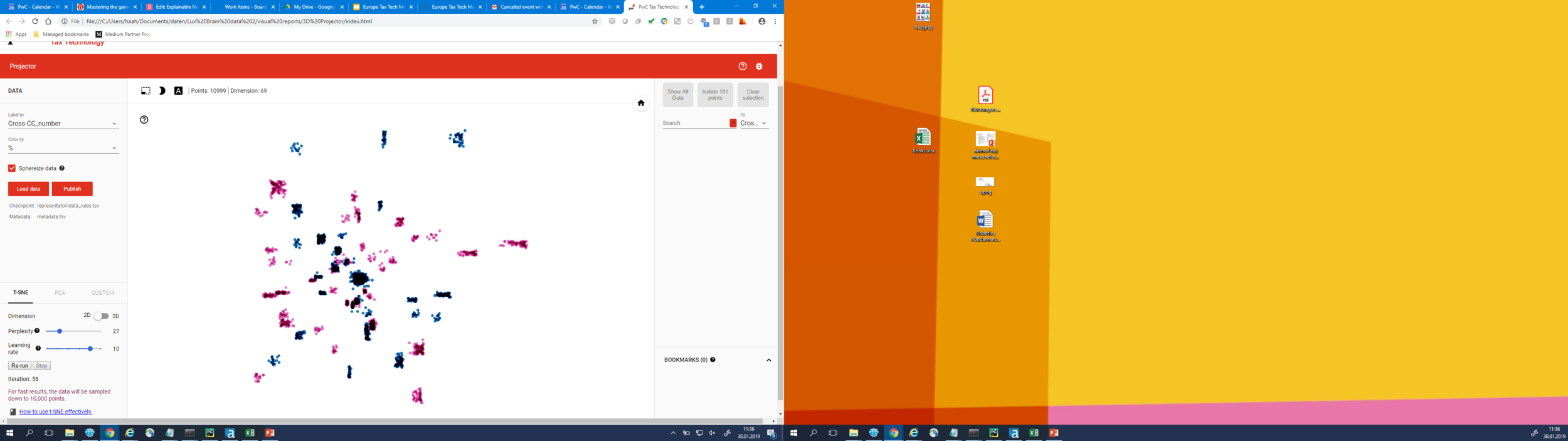
TSNE
LIME
LIME
CGN
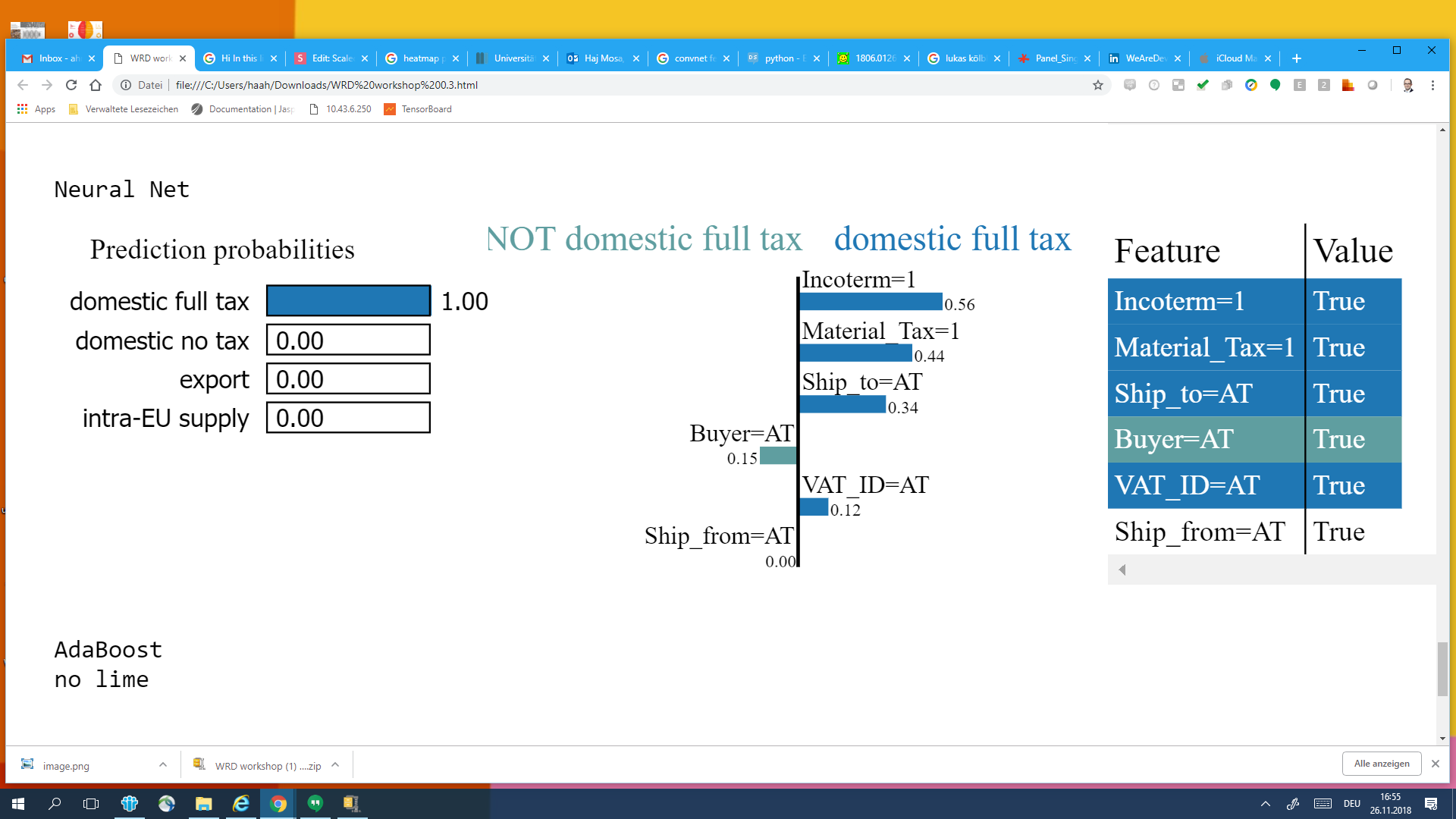
(Ship_to = AT) & (Material_Tax =1) & (IncoTerm =1)
& (VAT_ID =AT) --> domestic full tax
Computational Graph Network


[ not ( A || C ) || ( C && not ( B && E ) ) , f7 ( f1 ( A ) ) , not ( f8 ( f7 ( f1 ( A ) ) ) ) , not ( A || B ) || implication( C, D ) , ... ]
Haskell

(.-) [[a] -> [b]] -> ([[b]] -> [a] -> [c]) -> [a] -> [c] (.-) funcList newFunc inp = newFunc (map ($inp) funcList) inp -- where -- funcList = Previous Node Function List -- newFunc = Node Function -- inp = Sample Input
Usage of CGN

predicted rules
searching for best fitting rules
re-validate rules
- Accuracy is not enough to trust an AI
- Accuracy vs Explainability is not a trade-off
Look for solutions in weird places:
- Try Functional Programming & Category Theory
Trends in XAI:
- closing the gap between Symbolic AI and DL
- disentangled representation
- Object-Oriented-Representation
- Computational Graph Networks
Conclusion

+ Don't let your robot read legal texts ;)
Thank you for your attention


Fabian Schneider
PoC-Engineer & Researcher
schneider.fabian@pwc.com
Ahmad Haj Mosa
AI Researcher
ahmad.haj.mosa@pwc.com