Paul Hersey & Ken Blanchard
Presenters are Shahin Shahabi, Sepehr Sa'dabadi and Ahmadreza Mozaffary
Leadership plays a critical role in the success of organizations. Unlike management, which focuses on planning and controlling, leadership emphasizes influencing and guiding people. Modern organizations require flexible leadership styles to deal with different individuals and situations.


Inroduction
Ken Blanchard
Paul Hersey
Presenter: Sepehr Sa'dabadi
Background of the Theory
The Situational Leadership Theory was developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Paul Hersey initially introduced the concept, and later, together with Ken Blanchard, refined and popularized the model through research, publications, and training programs.

Paul Hersey (1930–2013) was an American behavioral scientist, educator, and management theorist. He specialized in organizational behavior and leadership studies and is best known as the co-creator of the Situational Leadership Model.
Biography of Paul Hersey
Contributions of Paul Hersey
Hersey focused on understanding how leaders can adapt their behavior based on employee readiness. He wrote several books and articles on leadership and trained thousands of managers worldwide.

Ken Blanchard (born 1939) is an American author, leadership expert, and motivational speaker. He is one of the most influential figures in modern leadership studies and has worked with organizations around the world.
Biography of Ken Blanchard
Major Works of Ken Blanchard
Blanchard is the author of many bestselling books, including The One Minute Manager and Leadership and the One Minute Manager. He also founded The Ken Blanchard Companies, a global leadership training and consulting firm.
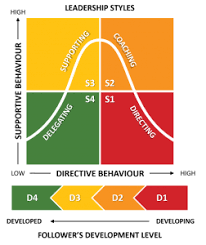
Core Idea of Situational Leadership
The main idea of the theory is that there is no single best leadership style. Effective leadership depends on the situation and, most importantly, on the development level of followers. Leaders must adapt their style accordingly.
Levels of Employee Development (D1–D4)
Presenter: Ahmadreza Mozaffary
Levels of Employee Development (D1–D4)
-
D1: Low competence, high commitment
-
D2: Some competence, low commitment
-
D3: High competence, variable commitment
-
D4: High competence, high commitment
D1 – Low Competence, High Commitment:
-
New to the role or task
-
Lacks required skills or experience
-
Highly motivated and eager to learn
-
Needs clear instructions and close guidance
D2 – Some Competence, Low Commitment:
-
Has basic skills but not fully proficient
-
Realizes the task is harder than expected
-
Confidence and motivation may drop
-
Needs coaching, encouragement, and feedback
D3 – High Competence, Variable Commitment:
-
Skilled and capable of performing independently
-
Motivation fluctuates due to doubt or boredom
-
May hesitate to take full ownership
-
Needs support, involvement, and recognition
D4 – High Competence, High Commitment:
-
Expert in the role or task
-
Confident, self-reliant, and motivated
-
Consistently delivers high performance
-
Needs autonomy and trust rather than supervision
Leadership Styles in the Model
- S1: Directing
-
S2: Coaching
-
S3: Supporting
-
S4: Delegating
The model identifies four leadership styles:
S1 - Directing Style
In this style, the leader provides clear instructions and closely supervises performance. The focus is high on task and low on relationship. This style is suitable for employees at the D1 level.
S2 - Coaching Style
The leader still provides direction but also offers support, encouragement, and explanations. The focus is high on both task and relationship. This style fits employees at the D2 level.
S3 - Supporting Style
Here, the leader shares decision-making with employees and focuses more on relationships than tasks. This style is appropriate for employees with high competence but lower confidence (D3).
S4 - Delegating Style
The leader provides minimal direction and support, allowing employees to take responsibility. This style works best with highly competent and committed employees at the D4 level.
Matching Style to Development Level
The effectiveness of leadership depends on correctly matching the leadership style to the employee’s development level. A mismatch can reduce motivation and performance, while proper alignment leads to growth and success.
Presenter: Shahin Shahabi
Advantages of the Model
-
Simple and easy to understand
-
Highly practical and flexible
-
Focuses on employee development
Criticisms and Limitations
-
Measuring development levels can be subjective
-
The model may oversimplify human behavior
-
Requires strong judgment and adaptability from leaders
Practical Applications
Situational Leadership is widely used in:
-
Team management
-
Coaching and mentoring
-
Project leadership
-
Training and development programs
Effective leadership requires flexibility. The Situational Leadership Theory by Hersey and Blanchard emphasizes adapting leadership style to follower readiness. There is no universally best style—successful leaders adjust to the situation.