An application of VAR model in Brain Imaging
Aiying Zhang & Gemeng Zhang
Department of Biomedical Engineering
April 27, 2018
Intro to fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging(fMRI) is a medical imaging form to measure human brain activity. This techniques can detect the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast which is closely coupled with neuronal activation. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases.
https://www.neurologyadvisor.com/epilepsy/epilepsy-surgery-evaluation-with-functional-mri-guidelines/article/
Data Description
Type
1.Resting state fMRI (rs-fMRI)
2.Emotion identification fMRI (task fMRI)
Timepoints (T)
124
210
Brain parcellation:
Power Atlas -- 264 regions of interest (ROIs)
- Default Mode
- Visual
- Fronto-Parietal Control
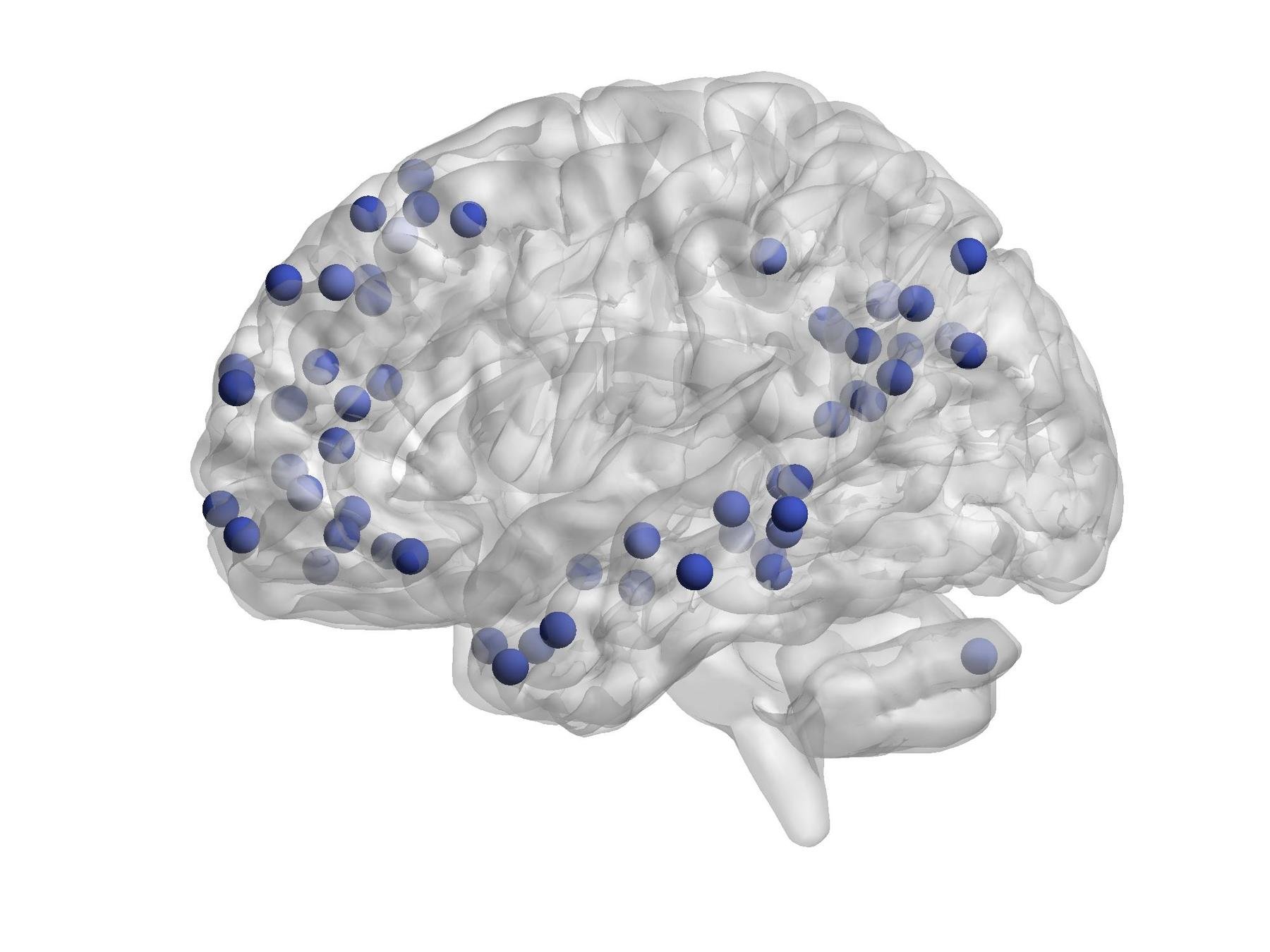
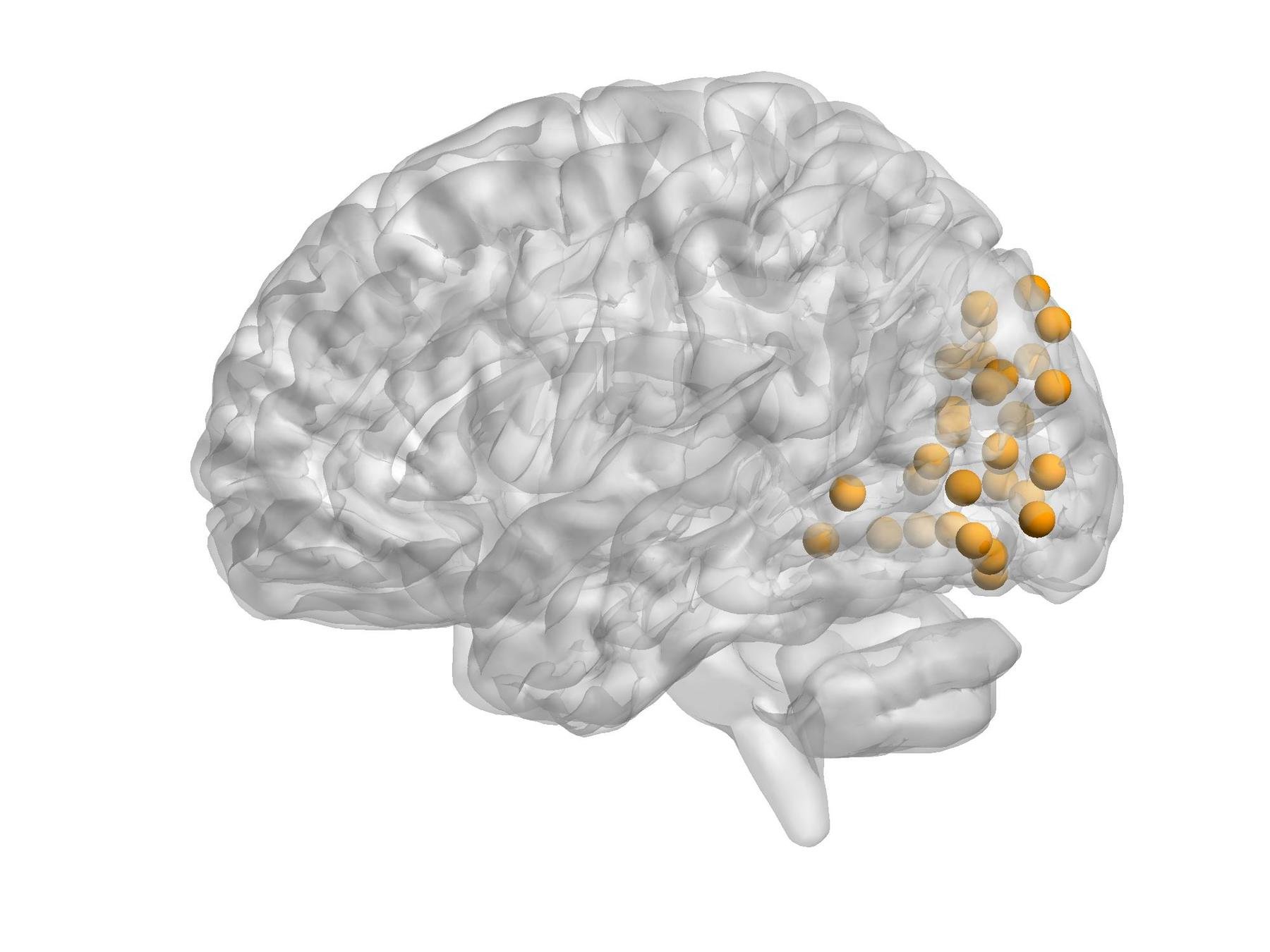
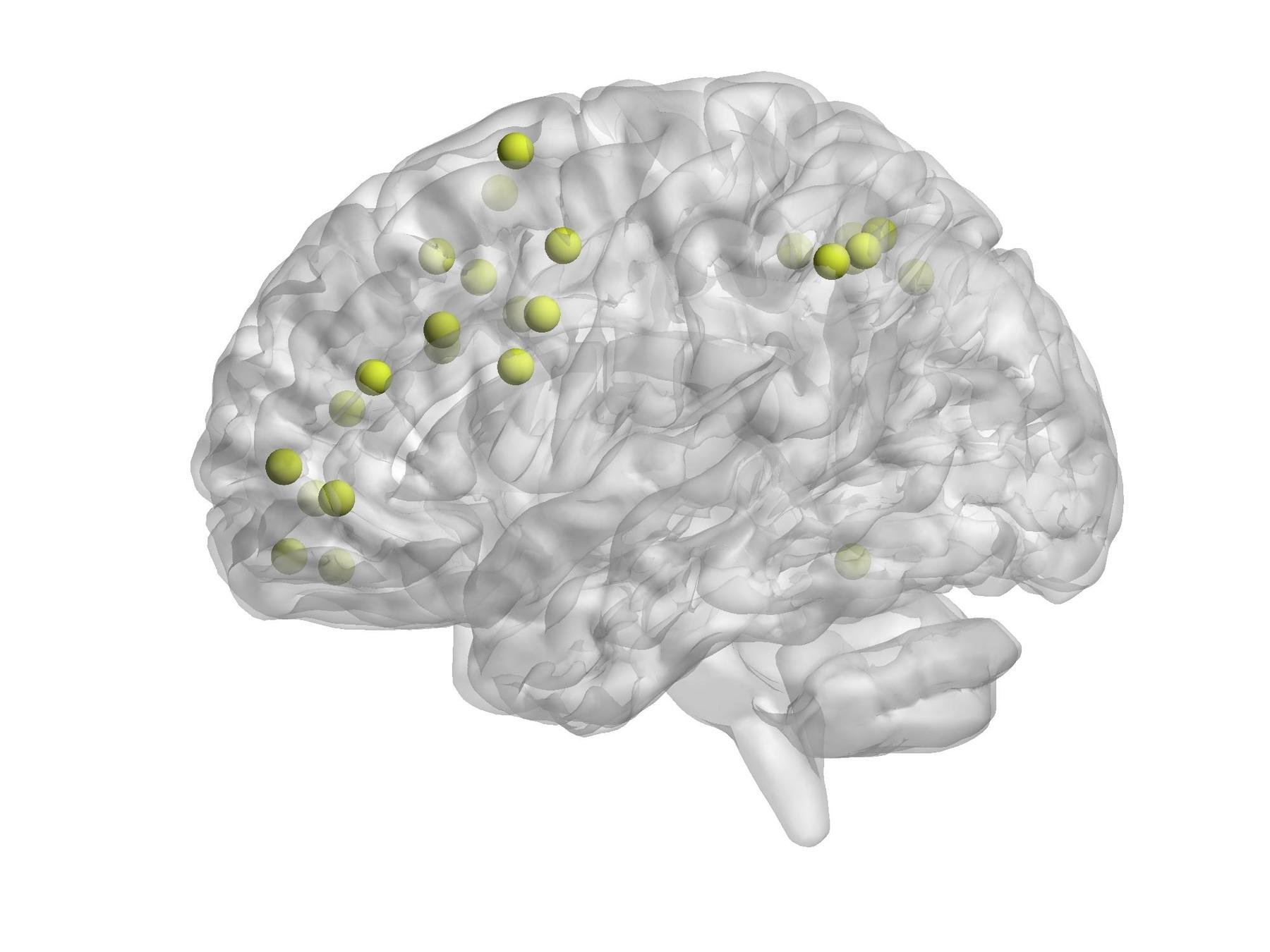
Some functional Modules
Source: Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort (PNC)
Data Description
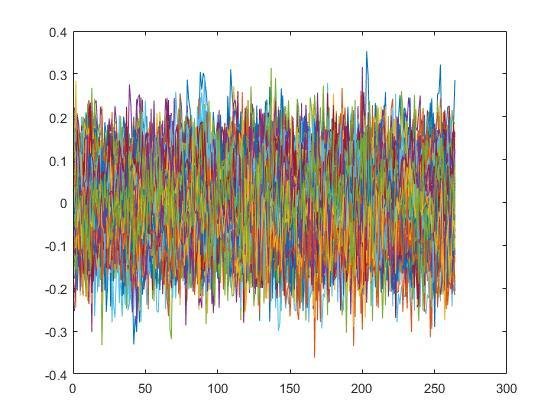
Data in time series for rs-fMRI (up) and task-fMRI (down)
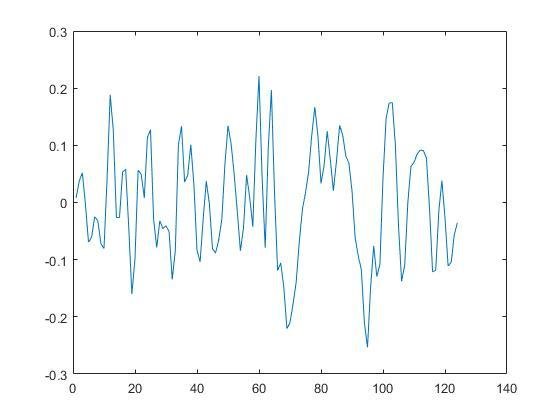
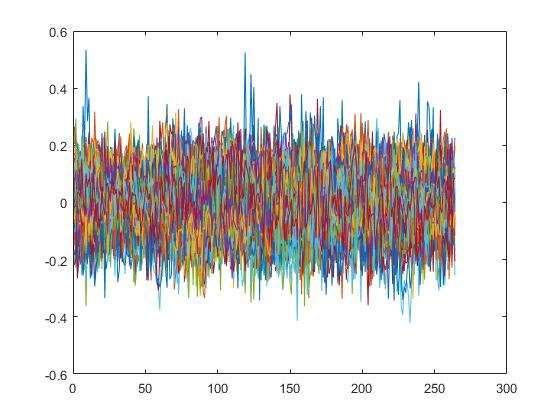
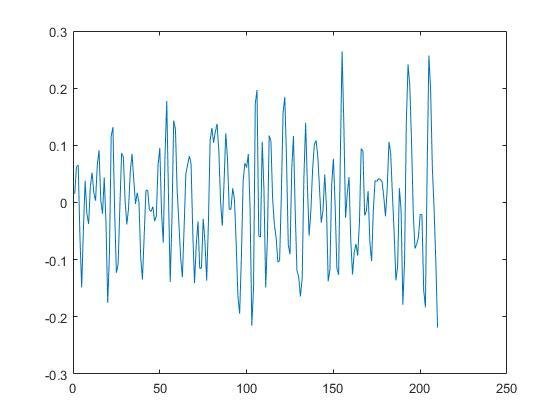
Normality Test
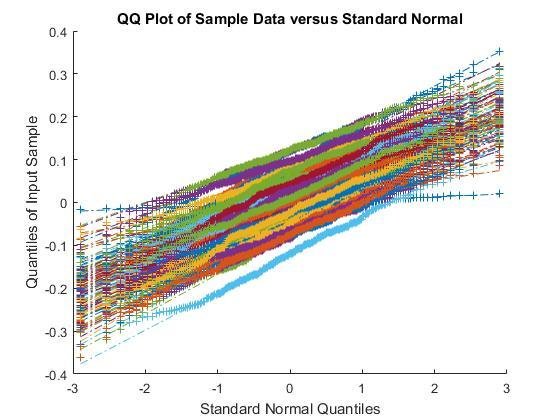
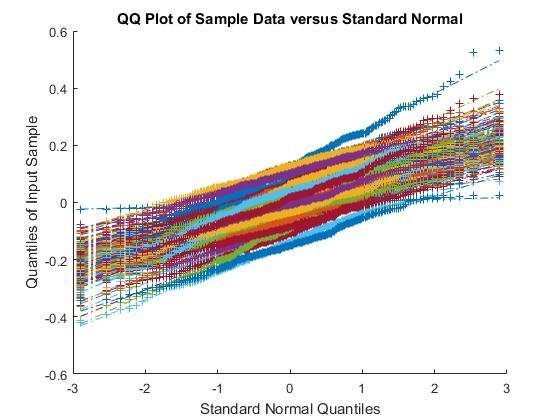
QQ plots for rs-fMRI (left) and task-fMRI (right)
AR(1) Model
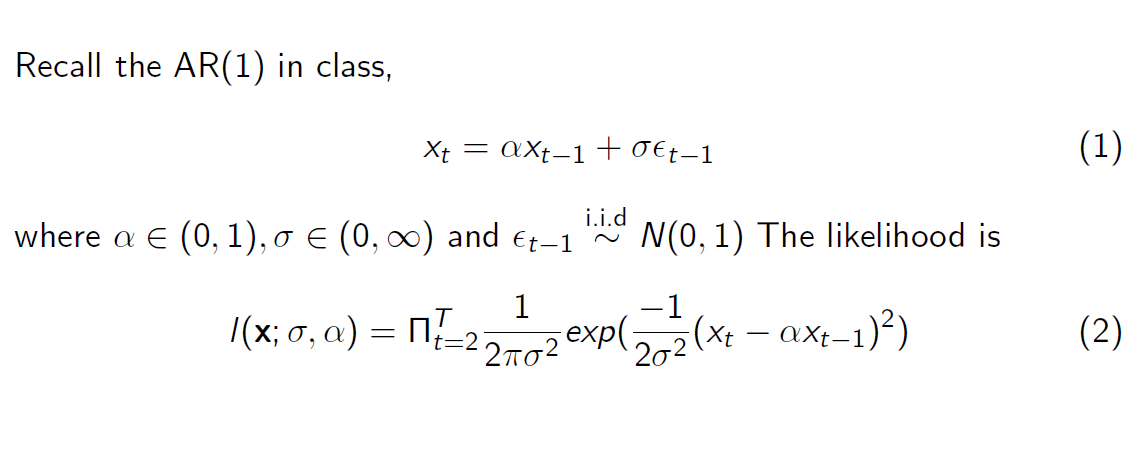
Consider 2 cases:
Resting state: T = 124
Task: T = 210
Variables:
p = 264
p = 264
AR(1) with Gibbs Sampler
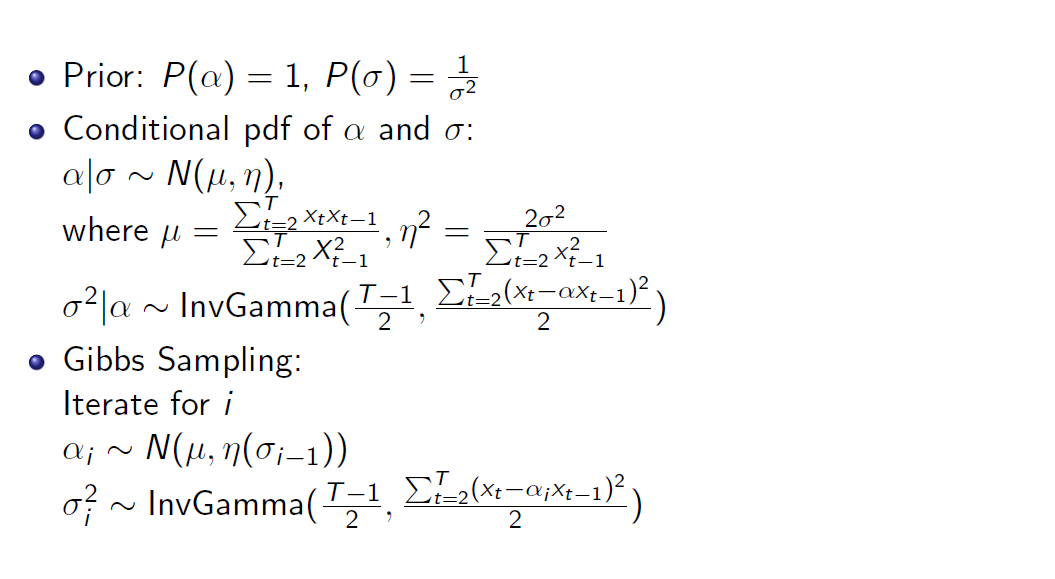
AR(1) Model
TRUTH:
1. The brain is constantly active with a high level of activity even when the person is not engaged in focused mental work (the resting state).
2.The brain, even during rest, contains information about its functional organization.
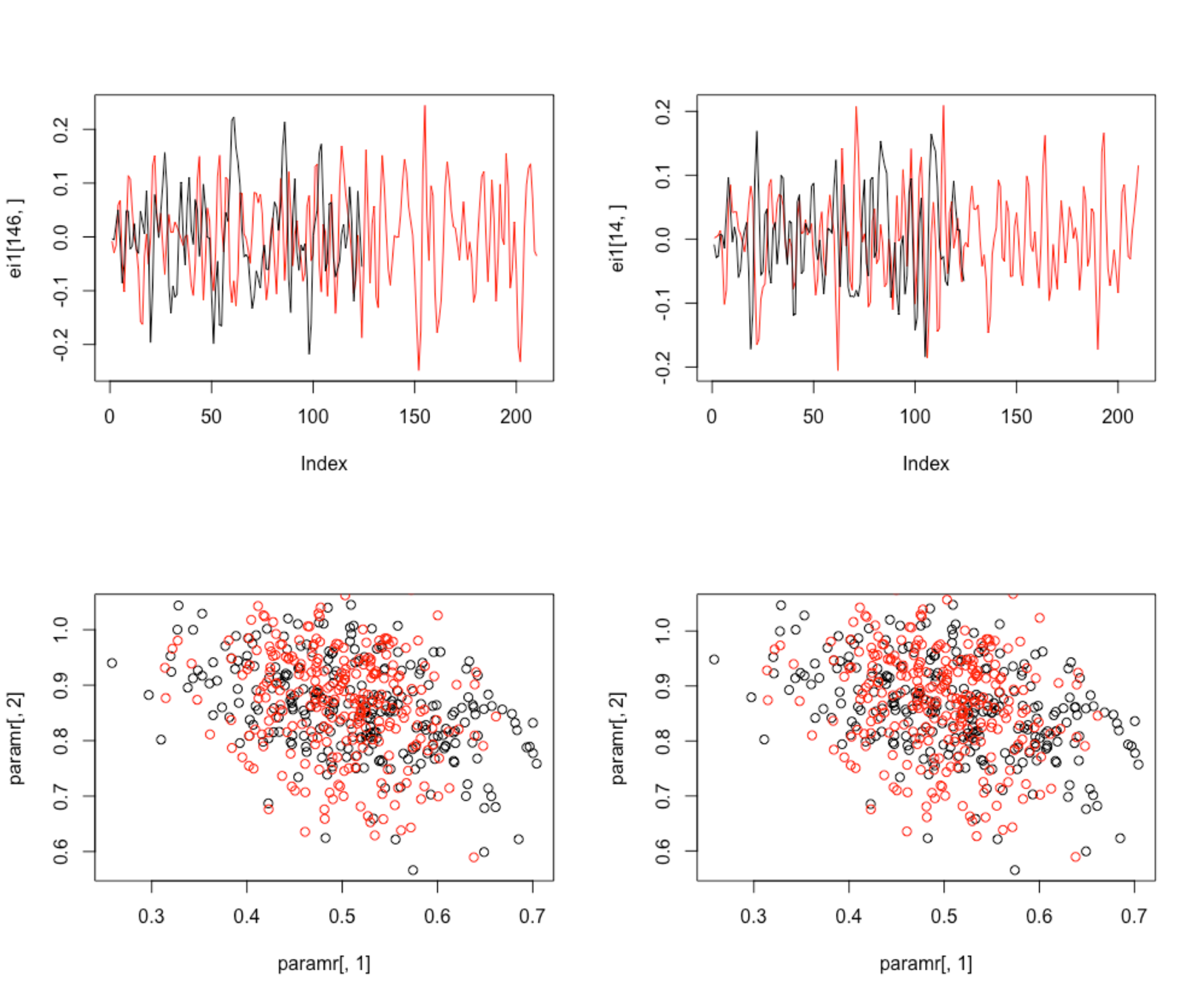
1-dimension AR(1) Model fails to discriminate two signals
VAR Model
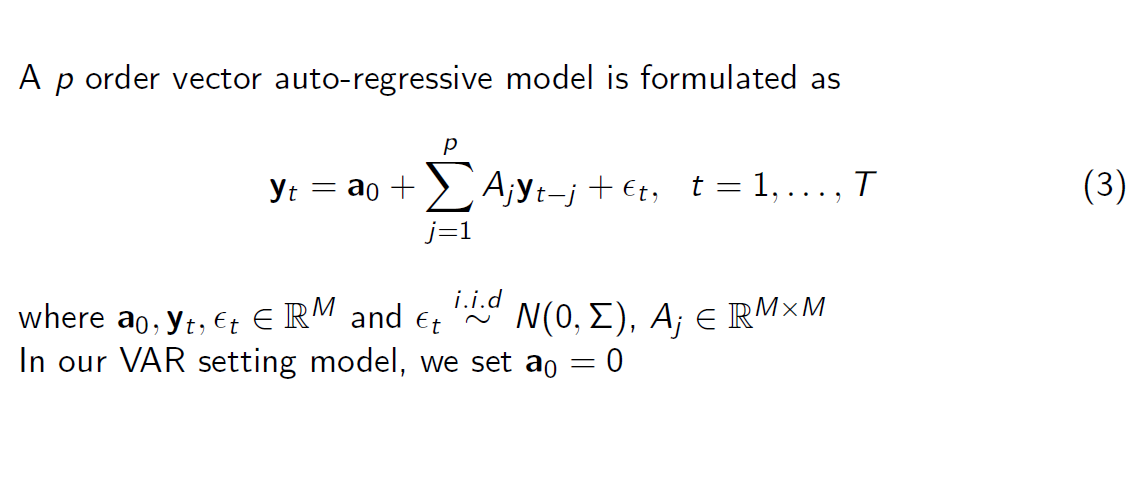
VAR Model
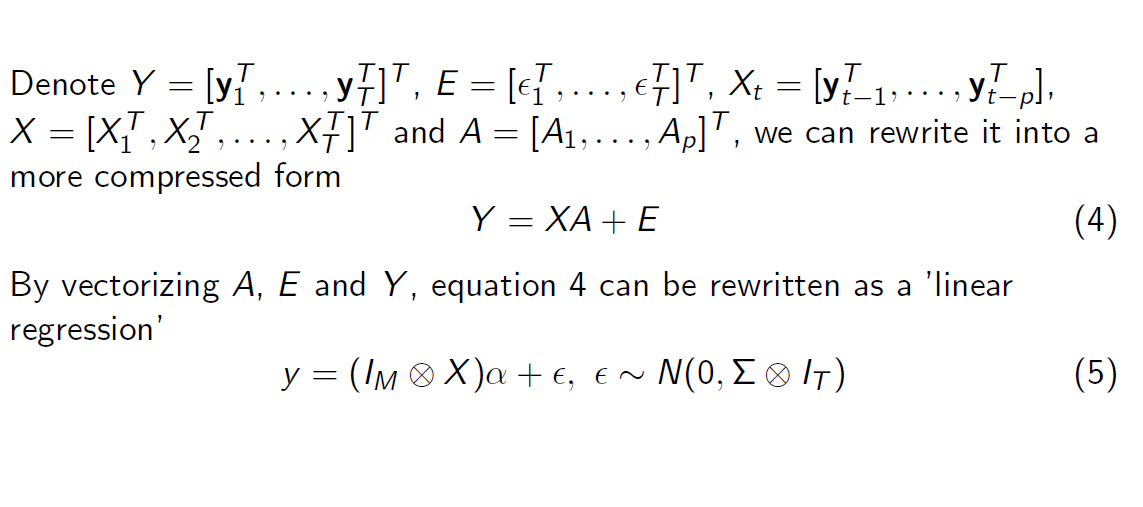
VAR Model
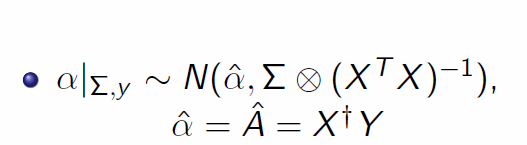
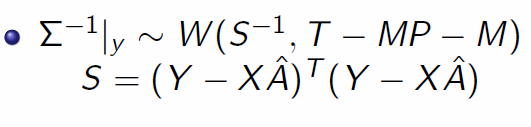

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wishart_distribution
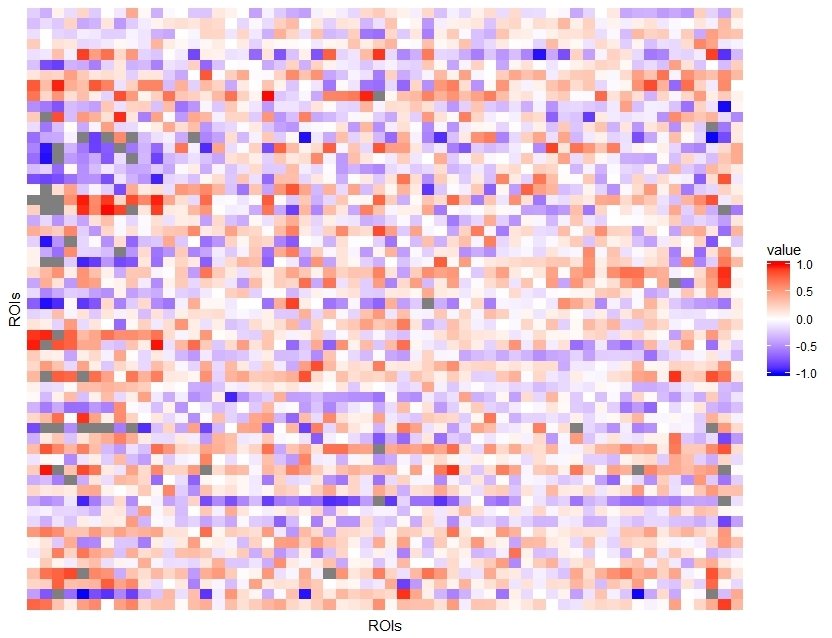
VAR(1) Model
- Apply to 3 different functional modules,respectively
- R package: vars
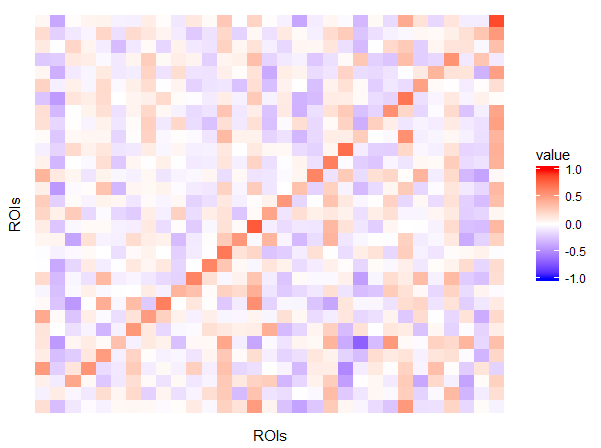
Default Mode Network (DMN):
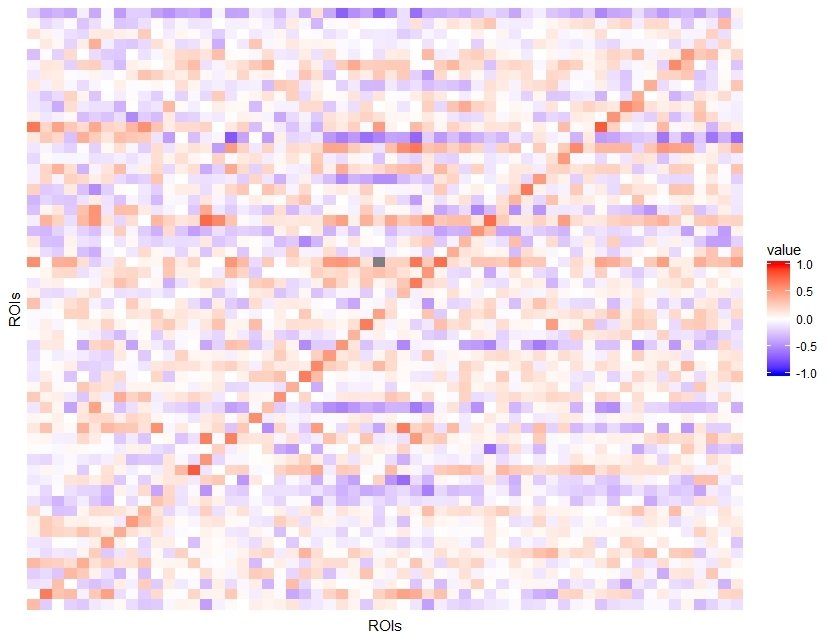
TRUTH:
DMN is active during passive rest and mind-wandering;
BUT is deactivate during external goal-oriented tasks (e.g. visual attention or cognitive working memory tasks)
DMN -- "Task-negative network"
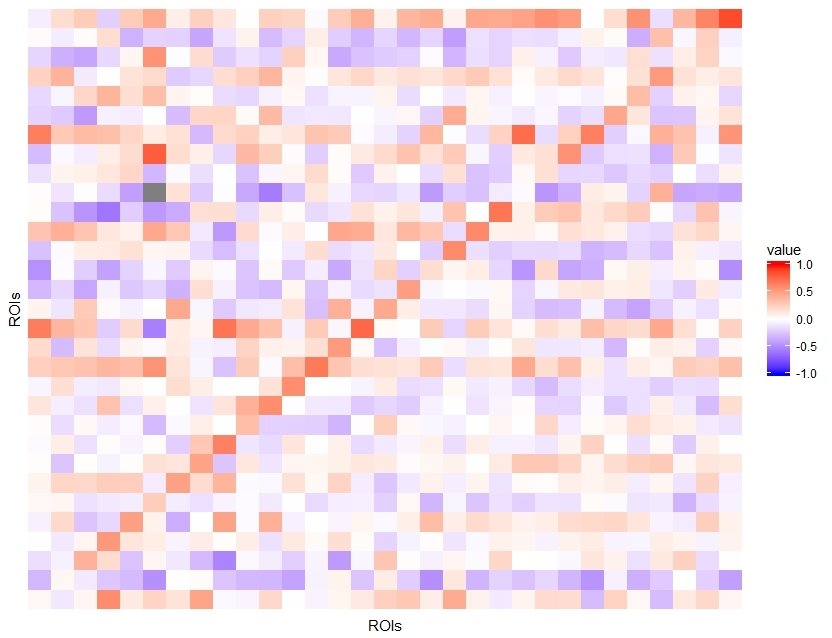
VAR(1) Model
Visual
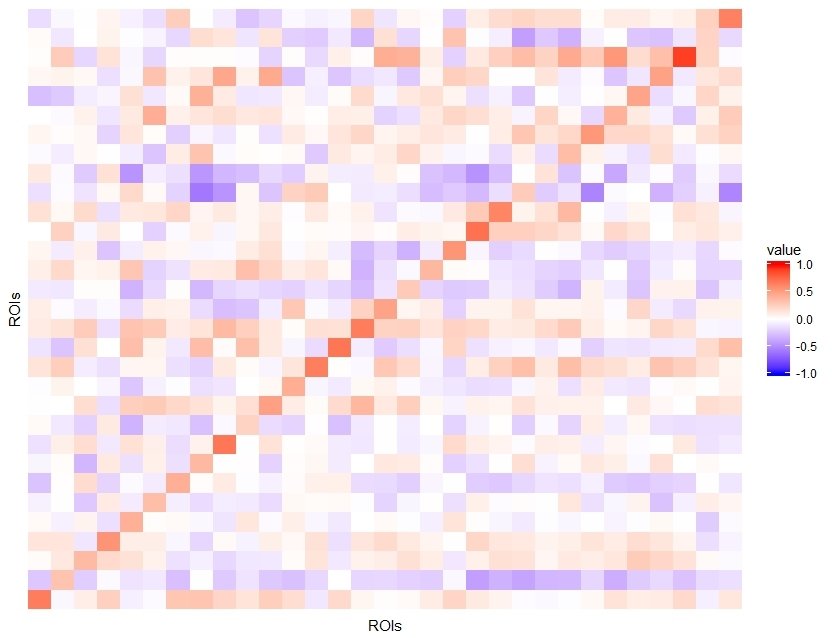
TRUTH:
Visual module is one of the neural networks that are strongly functionally connected during rest.
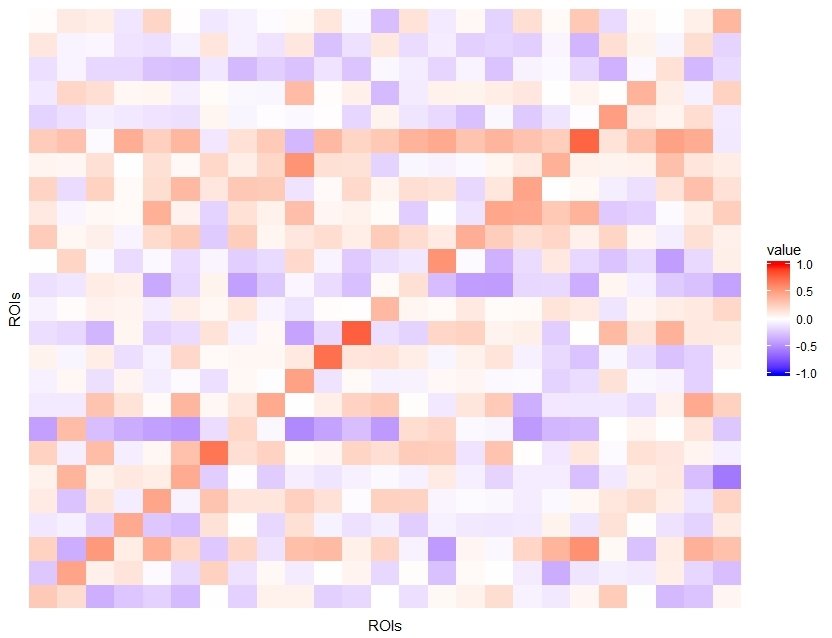
VAR(1) Model
fronto-parietal control
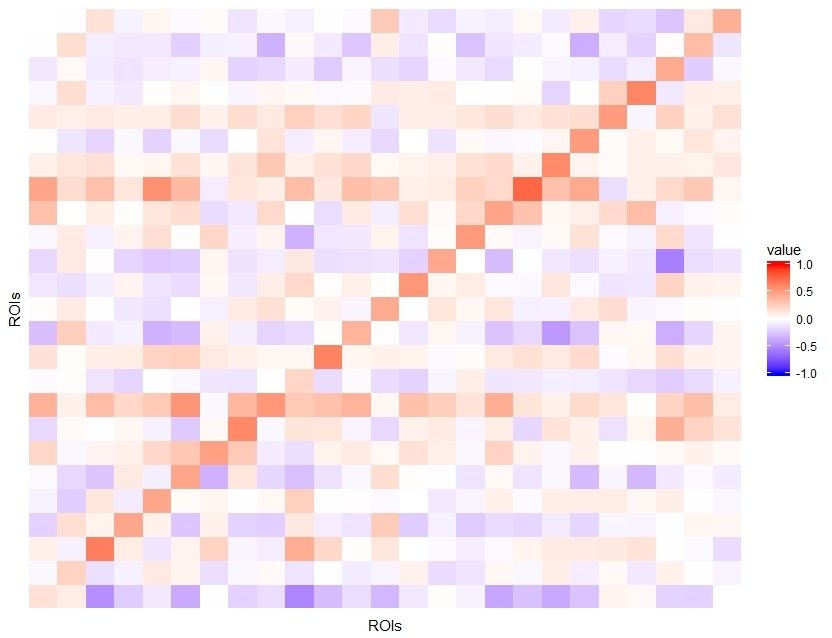
Role of frontal lobe:
voluntary movement/integrating memories
Role of parietal lobe:
Integrating sensory information
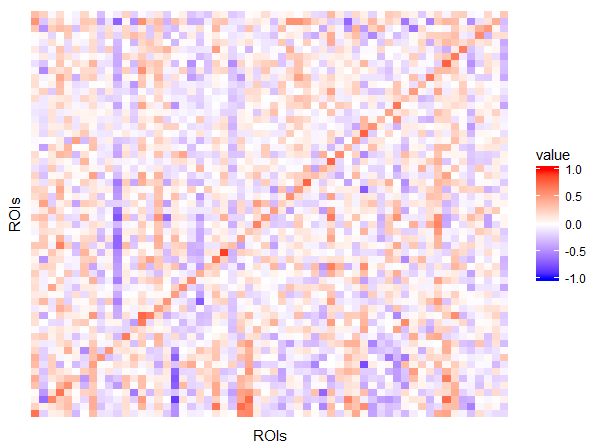
BVAR Model
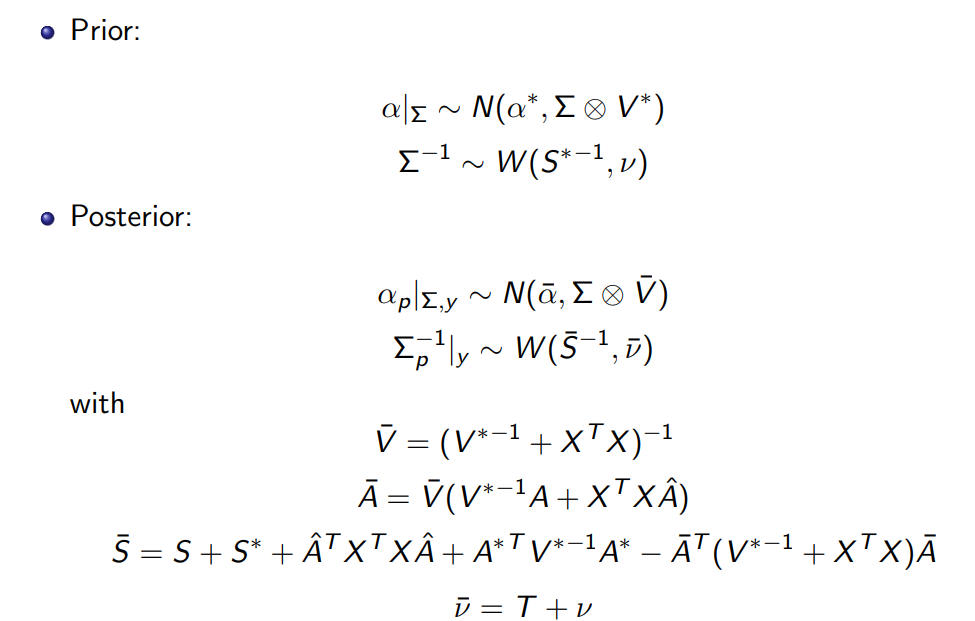
BVAR(1) Model
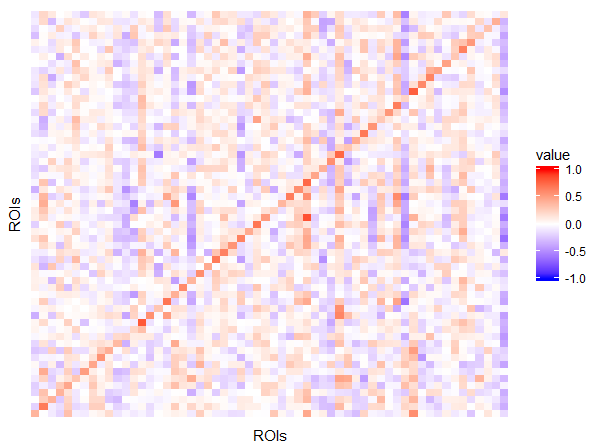
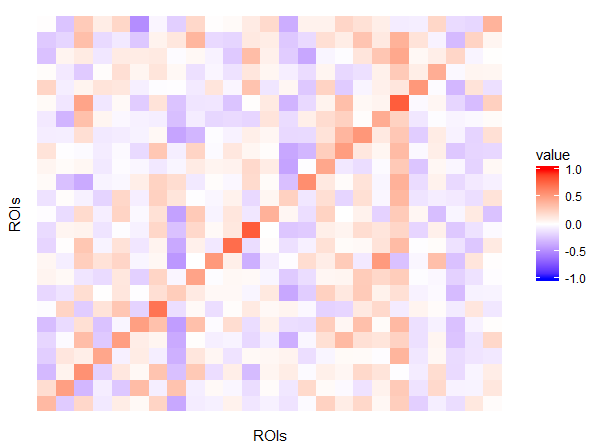
Default Mode Network (DMN):
R package: MSBVAR
BVAR(1) Model
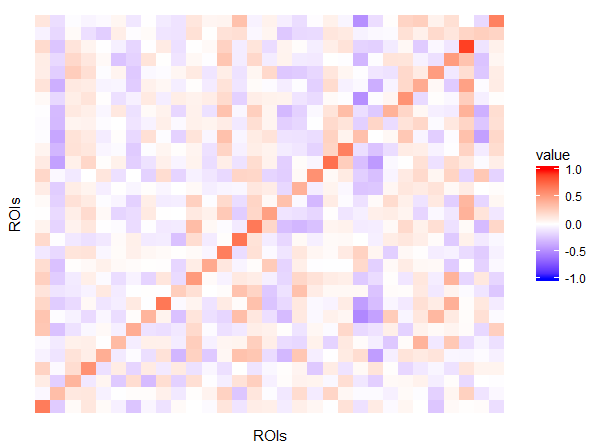
Visual
BVAR(1) Model
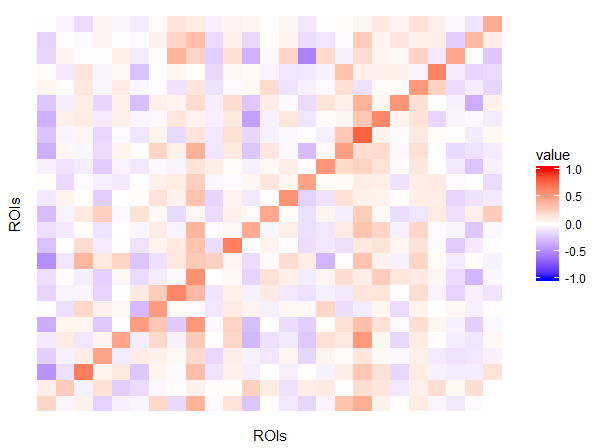
fronto-parietal control