FORMATION GIT
Présentation originale par Tristan Roussel @theodo
Qu'est-ce que GIT?
- Version Control System (VCS)
- Distribué et non-linéaire
- Outil génial
VCS
sauvegarde des versions
D'un projet
DISTRIBUÉ
Partage de ces versions sur un réseau.
Non-LinÉaIrE
v1
v2
v3
v4
v3'
v4'
outil
ce n'est pas une religion, Cela doit servir un objectif.
le mien est
de gagner du temps
pourquoi Vous
Devriez apprendre?
cela vaut-il le coup ?
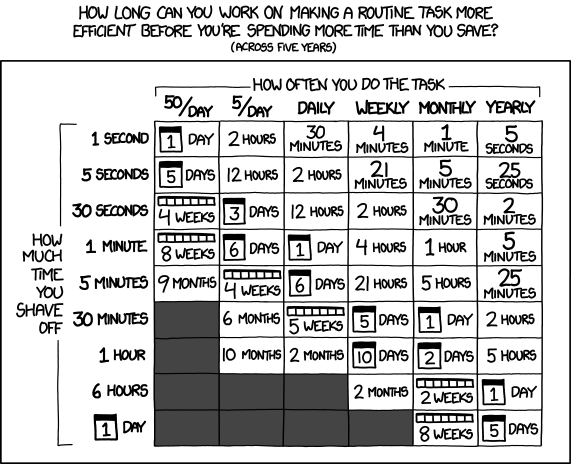
Text
Text
https://xkcd.com/1205/
comment faire pour apprendre?
- Lire l'output de git
- Lire la documentation
- Regarder sur Internet
- Être attentif à cette présentation :)
- Faire des dessins !
Commits

qu'est-ce qu'un commit?
- Un tree (arborescence)
- fait de trees et de blobs (binary large object i.e. un fichier)
- Un timestamp (date)
- Un message
- 0 parents ou plus
- Un hash unique (ex ea21f8d3464a6464a897b489133a7babd493d9ed)
qu'est-ce qu'un commit?
Commit parent
…
Commit
ea21f8d
snapshot du projet
Commit parent
Comment VOIR UN commit ?
git show
$ git show --format=raw
commit ea21f8d3464a6464a897b489133a7babd493d9ed
tree 6fa3613d5dbeff329364595abe8f9d823acf8162
parent 09d9b29e1d649a5eb27c233f0f6891436ceed610
author Tristan Roussel <troussel@notmyrealmail.com> 1449279238 +0100
committer Tristan Roussel <troussel@notmyrealmail.com> 1449315422 +0100
Document constraint validator alias optional
diff --git a/cookbook/validation/custom_constraint.rst b/cookbook/validation/custom_constraint.rst
index a248a84..1adf5ed 100644
--- a/cookbook/validation/custom_constraint.rst
+++ b/cookbook/validation/custom_constraint.rst
@@ -167,7 +167,7 @@ Constraint Validators with Dependencies
If your constraint validator has dependencies, such as a database connection,
it will need to be configured as a service in the Dependency Injection
Container. This service must include the ``validator.constraint_validator``
-tag and an ``alias`` attribute:
+tag and may include an ``alias`` attribute:
.. configuration-block::
@@ -195,21 +195,14 @@ tag and an ``alias`` attribute:
->register('validator.unique.your_validator_name', 'Fully\Qualified\Validator\Class\Name')
->addTag('validator.constraint_validator', array('alias' => 'alias_name'));
-Your constraint class should now use this alias to reference the appropriate
-validator::
+As mentioned above, Symfony will automatically look for a class named after
+the constraint, with ``Validator`` appended. You can override this in you constraint class::
public function validatedBy()
{
- return 'alias_name';
+ return 'Fully\Qualified\Class\Named\ConstraintValidator'; \\ or 'alias_name' if provided
}
-As mentioned above, Symfony will automatically look for a class named after
-the constraint, with ``Validator`` appended. If your constraint validator
-is defined as a service, it's important that you override the
-``validatedBy()`` method to return the alias used when defining your service,
-otherwise Symfony won't use the constraint validator service, and will
-instantiate the class instead, without any dependencies injected.
-
Class Constraint Validator
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
COMMENT FAIRE Un commit?
- git commit
- git merge
- git cherry-pick
- git rebase (awesomeness lvl++)
git commit
git add changes
git commit -m "my commit with changes"git Add?
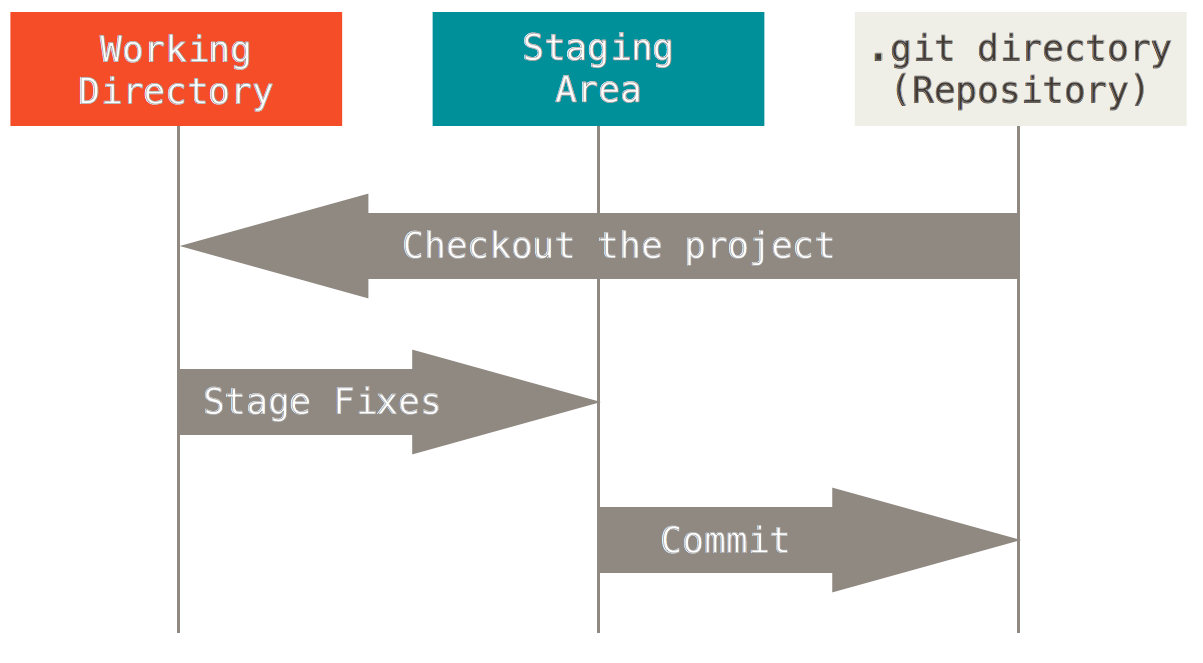
https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Git-Basics#The-Three-States
git add
git commit
git checkout (not seen yet)
git merge
…
Commit de merge
Ancêtre commun
Second parent
Premier parent
Un commit de merge prend le diff entre l'ancêtre commun et le premier commit parent et le diff entre l'ancêtre commun et le second commit parent et les applique ensemble.
git merge
Il peut y avoir 2 parents… ou moins !
…
Second parent
…
Premier parent
= commit de merge
Second parent
…
Premier parent
+
=
(ancêtre commun)
Git Merge
Si on merge 2 commits où le premier est un parent (direct ou non) du second, git fait un fast-forward merge.
Il prend simplement le second commit parent comme un commit de merge.
…
Premier parent
(ancêtre commun)
Commit de merge
Second parent
Ainsi, git merge est une généralisation de git commit.
Git CHERRY-pick
…
…
…
+
=
Un commit de cherry-pick prend le diff entre un commit et son parent direct et l'applique à un autre commit pour faire un tout nouveau commit.
Diff à appliquer
Branches
Une branch ?
un pointeur sur un commit
… c'est tout !
…
master branch
déplacer des Branches
…
master branch
Quand on est sur une branch pointant sur un commit, et que l'on fait un nouveau commit, la branch suit le nouveau commit.
master branch
être sur une branch?
…
master branch
Git a un pointer spécial appelé HEAD, qui pointe la branch (ou plus généralement le commit) sur laquelle on se trouve.
HEAD
À chaque fois que l'on fait un nouveau commit, HEAD pointe ce nouveau commit.
déplacer les branches
master branch
…
master branch
On peut changer le commit pointé par une branch en utilisant git reset.
d1d9ab7
git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working directory clean
git reset --hard d1d9ab7CHANGer de branche
…
staging branch
On peut changer la branch sur laquelle on est avec git checkout.
git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working directory clean
git checkout staging
Switched to branch 'staging'
master branch
HEAD
HEAD
Merger des branches
On peut utiliser une branch dans un commit de merge, cela utilisera le commit pointé par cette branch.
git merge staging
…
staging branch
HEAD
HEAD
voir les branches
git branch
2.3
2.7
2.8
* fix-constraint-validator-alias-requiredvoir l'état des branches
git log --decorate --graph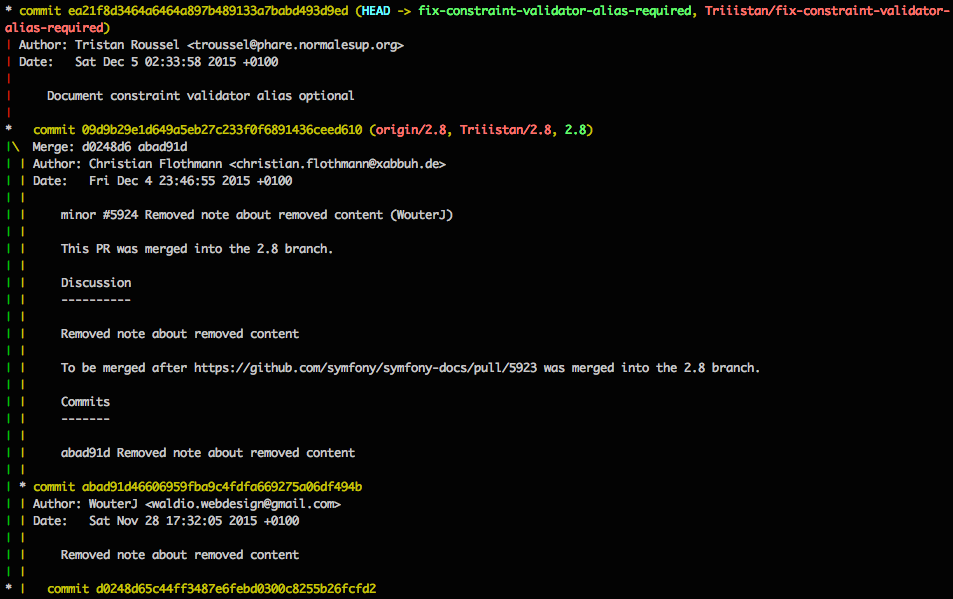
GIT REBASE
git rebase
Un rebase fait une sauvegarde des commits entre l'ancêtre commun et le second commit parent, applique les commits entre l'ancêtre commun et le second commit parent puis cherry-pick un à un les commits précédemment sauvegardés.
git rebase
git rebase master add-selenium-tests
Premièrement, rembobinons head pour rejouer votre travail par-dessus...
Application : Improve FeatureContext
Application : Add test about price computation
Application : Test ambulatory condition
Application : Patient can set a guardianship
Application : Test ARE popup
Application : Check person to notify
Application : Check registration form
Application : Test print document pageGit CHECKOUT add-selenium-tests
+ GIT RESET --hard master
+ Git cherry-pick ...
git rebase
…
Ancêtre commun
Second parent
Premier parent
master branch
featurebranch
HEAD
HEAD
git rebase
…
Ancêtre commun
Premier parent
master branch
featurebranch
HEAD
HEAD
git rebase
…
Ancêtre commun
Premier parent
featurebranch
HEAD
Second parent
HEAD~4
git rebase --interactive HEAD~4
pick 3030af7 Check registration form
pick 83a0fc2 Test print document page
pick 9ed1c25 Improve pull request
pick 1636a91 Change tests order
# Rebase 196bb70..1636a91 onto 196bb70
# p, pick = use commit
# r, reword = use commit, but edit the commit message
# e, edit = use commit, but stop for amending
# s, squash = use commit, but meld into previous commit
#
# These lines can be re-ordered; they are executed from top to bottom.
# If you remove a line here THAT COMMIT WILL BE LOST.Remotes
qu'est-ce qu'une remote?
une version du projet (repository) hébergée sur le réseau
qu'est-ce qu'une remote ?
- Un nom
- Une URL git pour le fetch
- Une URL git pour le push
git remote --verbose
Triiistan git@github.com:Triiistan/symfony.git (fetch)
Triiistan git@github.com:Triiistan/symfony.git (push)
origin git@github.com:symfony/symfony.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:symfony/symfony.git (push)pourquoi travailler avec des remotes ?
- Sauvegarder le travail en ligne.
- Partager du code avec d'autres, collaborer.
- Déployer le projet sur plusieurs machines, être sûr d'avoir le même code.
remote tracking branches
…
origin/master branch
C'est une réplique de la branch master distante sur la remote origin qui est hébérgée localement.
Sur le repository hébergé sur le réseau, il y a une branch master avec les mêmes commits. Probablement.
Probablement ?
remote tracking branches
Les remote tracking branches doivent rester synchronisées avec les branches réellement présentes sur le réseau pour qu'elles aient les mêmes commits.
git fetch
git push
git pull
git Fetch
…
origin/master branch
…
master branch
origin/master branch
origin
local
git fetch origin mastergit push
…
origin/master branch
…
master branch
origin
local
git push origin d1d9ab7:mastermaster branch
d1d9ab7
d1d9ab7
origin/master branch
Git Pull?
= Git Fetch + git merge
git pull
…
origin/master branch
…
master branch
origin
local
git pull origin masterorigin/master branch
Fetch
+
Merge
HEAD
HEAD
pull fast-forward
…
origin/master branch
…
master branch
origin
local
git pull origin masterorigin/master branch
HEAD
HEAD
Fetch
+
Merge
WORKFLOWS
NO FLOW
Impossible à plusieurs
feature flow
…
MAIS... Qu'une seule version
GIT FLOW
-
Plusieurs environments : master, staging...
-
Un process de release/hotfix extrêmement bien défini
-
Tous les avantages du Feature Flow
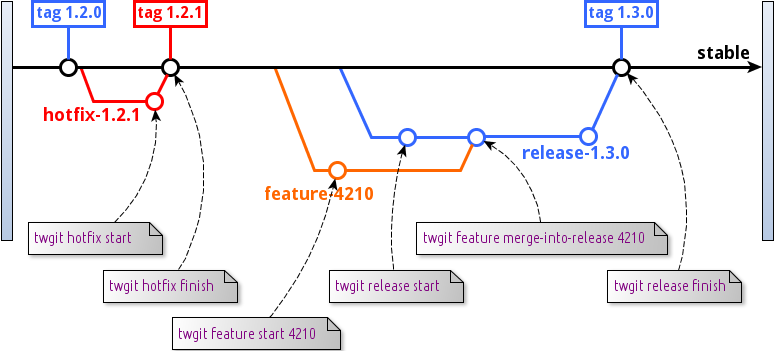
TWGIT Flow
-
Sélection des features par release
-
Branches de démo
-
Un process de release/hotfix extrêmement bien défini
-
Tous les avantages du Feature Flow
qu'est-ce qu'il y a d'autre à découvrir ?
- diff
- archive
- checkout
- patch
- hooks
- rerere
- bisect
- stash
- --patch
- reflog
- gc
- hub
- plumbing vs porcelain
- internals