Maths en échecs
Alexis Langlois-Rémillard
Hausdorff Center for Mathematics, Bonn
2024-01-09—11, ESMC, Québec
basé sur du travail avec Mia Müßig et Érika Roldán-Roa
https://slides.com/aliocha/maths-marche-echiquiers
Survol de ma vie scolaire
- Né à Saint-Athanase 1995
- Primaire Hamel 2000-07
- Secondaire ESMC 2007-12
- Cégep Saint-Jean 2012-14
- Bac maths Université de Montréal 2014-17
- Maîtrise maths Université de Montréal 2017-19
- Doctorat maths Gand (Belgique) 2019-23
Survol de ma vie professionnelle
- Moniteur de natation et sauveteur (2011-2017)
- Moniteur en sauvetage (2013-2017)
- Auxiliaire d'enseignement UdeM (2016-2019)
- Doctorat UGent (avril 2019-avril 2023)
- Visite de recherche, Leipzig (mai-sept 2023)
- Chercheur postdoctoral Bonn (oct 2023-2026)
En rafales
- Parle (mal) quatre langues:
- Français; anglais ; néerlandais (flamand); allemand
- Appris à crocheter pour une activité mathématique
- Finaliste concours du jeune écrivain de la francophonie 2021
- Visité 12 pays en 2023 (Danemark, Belgique, Pays-Bas, Angleterre, France, Islande, Allemagne, Japon, Suisse, Suède, Finlande, Canada)
- Joue aux échecs

En rafales

https://www.tiktok.com/@ayliean/video/7123658913794280709
Un polygone avec deux côtés?!
Maths


Durant la Covid: étude de problèmes classiques de maths et d'échecs -> deux articles (un avec Charles Senécal, UdeM, Cambridge)
https://accromath.uqam.ca/2022/02/huit-dames-et-un-echiquier/
https://accromath.uqam.ca/2022/09/des-dames-sur-detranges-echiquiers/
Échecs
A. L.-R. -- GM Bator Sambuev, 2018


Théorie des graphes
Petit puzzle
Un problème de Guarini (~16e):
Échanger les cavaliers blancs et noirs.

Petit puzzle
Un problème de Guarini (~16e):



Petit puzzle
Un problème de Guarini (~16e):



Domination maximale
Placer 8 dames sur l'échiquier de sorte à ce qu'elles ne puissent pas s'entre-capturer.
DominatioN
Problème des 5 dames
Placer 5 dames sur l'échiquier de façon à ce que chaque case soit gardée
- Aussi pour un échiquier \( n\times n \).
- Connu jusqu'à \(n=25\). (2017), et jusqu'à \(n=31\) (LR–Müßig–Roldán-Roa 2023). A075324
Conjecture (Hedetiemi ~1992)
Le nombre croît avec la taille de l'échiquier.
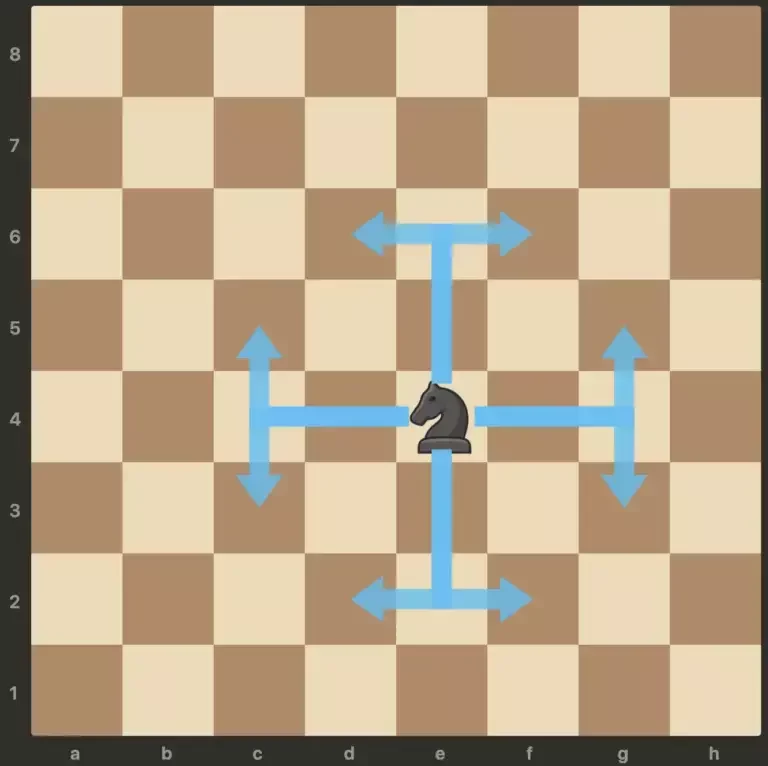
Een vrolijk paard
Grafentheorie heeft Euler geholpen om de Paardentour probleem op te lossen
Polyomino
Polyomino
Un polyomino est une sorte de grosse pièce de «Tetris».

12 pentominos avec leur réflexion
Polyomino
Mouvement sur un polyomino
Les pièces bougent normalement, mais ne peuvent sauter les trous.

Polyomino
Problemen
Minimal- en maximaldominantie
We kunnen het probleem niet exact oplossen. We willen het aantal dames begrenzen.
Polyomino
Stelling (Alpert–Roldán-Roa 2021)
- Voor een polyomino van \(n\geq 2\) velden, het minimale torensdominantiegetal zit tussen 1 en \(\lfloor \frac{n}{2}\rfloor\).
- Voor een polyomino van \(n\geq 3\) velden, het minimale damesdominantiegetal zit tussen 1 en \(\lfloor \frac{n}{3}\rfloor\).

Polyomino
Proposition (Alpert–Roldán-Roa 2021)
- Voor een polycube van \(n\geq 2\) velden, het minimale torensdominantiegetal zit tussen 1 en \(\lfloor \frac{n}{2}\rfloor\).
- Voor een polycube van \(n\geq 3\) velden, het minimale damesdominantiegetal zit tussen 1 en \(\lfloor \frac{n}{3}\rfloor\).
Bewijs 1:
Idee: wat maakt een schaakbord een schaakboard ?
Polycubes
Proposition (Alpert–Roldán-Roa)
- Voor een polycube van \(n\geq 2\) velden, het minimale torensdominantiegetal zit tussen 1 en \(\lfloor \frac{n}{2}\rfloor\).
- Voor een polycube van \(n\geq 3\) velden, het minimale damesdominantiegetal zit tussen 1 en \(\lfloor \frac{n}{3}\rfloor\).
Proof 2:

Spel

https://www.erikaroldan.net/queensrooksdomination
Nu dat jullie weten dat het moeilijk is, laten ons spellen!
Polycubes
3D en meer
Het kan ook in hogerdimensionalruimte!
De stellingen zijn ook geldig!
bijvoorbeeld: link rook link queen
Meer resultats
Proposition (LR-M-RR 2022)
MaxDomR and MaxDomQ are NP-complete on polycubes of dimension \(d\geq 3\).
Proof:
- Prove that verifying a solution is polynomial
- Reduce the problem to a known NP-complete problem in polynomial time.
Our results
Proposition (LR-M-RR 2022)
MaxDomR/Q are NP-complete on polycubes of dimension \(d\geq 3\).
Proof:
- Prove that verifying a solution is polynomial
Easy. Given a proposed placement, we check that everything is covered and it grows only polynomially with the size of the board.
Our results
Proposition (LR-M-RR 2022)
MaxDomR/Q are NP-complete on polycubes of dimension \(d\geq 3\).
Proof:
2) Reduce to a known NP-complete problem
This is harder. We go for P3SAT3
Our results
P3SAT3
- Set of Boolean variable
- Set of clauses with 2 or 3 literals
- Bipartite clause graph is planar
- Bipartite clause graph has exactly three edges per literals
Our results
We will go from an instance of P3SAT3 to a rook domination problem on polycubes.
We need:
- Literal gadgets
- Splitting gadget
- Clause evalutation gadgets
Literal gadgets

Splitting gadgets

Clause gadgets
\(x_1\vee x_2\) or \(\bar x_1\vee \bar x_2\)

Putting clauses

Translation
1. \(X\) an instance of P3SAT3
2. Construct polycube \(P(X)\)
3. From the gadgets, we know its guarding number \(N\) will respect:
4. The instance is true if and only \( N= M + x_{Clause}\). (All clauses are true.)
Translation
Sanity check: is the polycube too big?

Algorithm
Algorithm
We hebben een Integer Linear Programming algorithm met de methoden van Huangfu and Hall 2018, Math. Program. Comp. als solver
Over dames
Stelling
MaxDomQ is NP-complete voor polycubes \(d\geq 3\).

Example
Bedankt!
Het spel:

Boeken aanrader:
- Piktovic, Miodrag. Mathematics and chess
- Watkind, John. Across the Board: The Mathematics of Chessboard Problems
Artikel
Langlois-Rémillard, A., Müßig, M., and Roldán-Roa, É. (2022) Complexity of chess domination problems. 19p. arXiv:2211.05651