The Galactic Centre Murder Mystery

Supernova as a Murder Mystery



Rules of a
Criminal Investigation
Motive
Means
Opportunity

Rules of a
Galactic Investigation
Opportunity
Trivial for field supernovae, as coincidence probability is 1e-6

star forming regions, however...
Supernova Forensics 101
Energy = 1e51 erg
Sun's total radiative output
Most supernovae make neutron stars
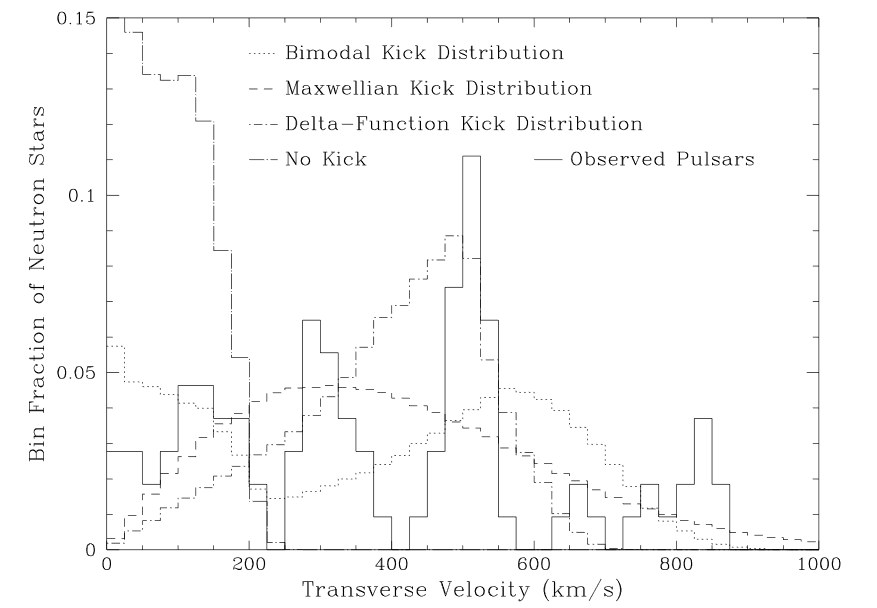
Neutron stars are kicked
Supernova Shock Propagation

Ejecta dominated phase
transition when
Sedov Taylor Phase
transition to snowplough when radiation kicks in
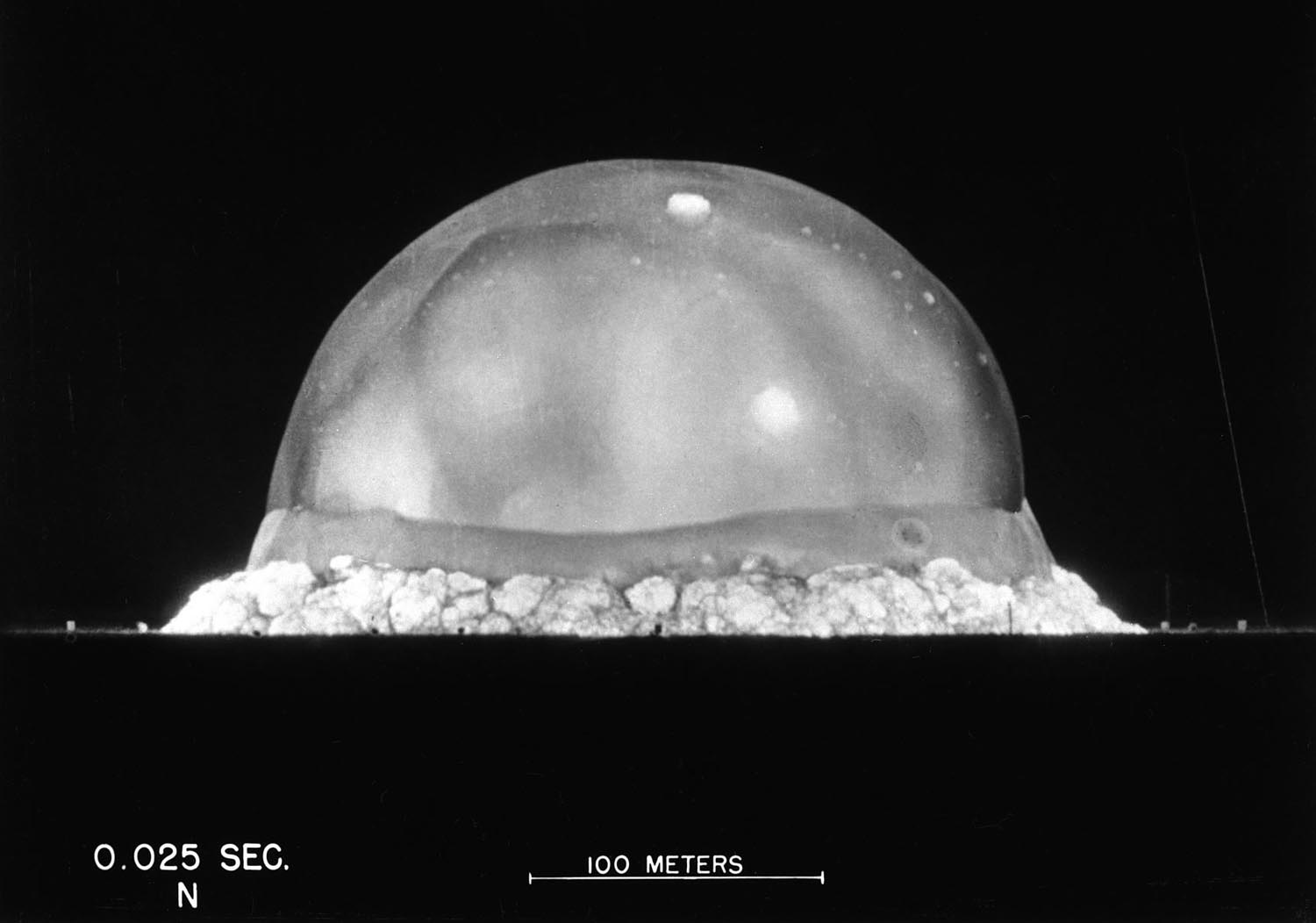

Neutron Star Natal Kicks
Slow and steady wins the race
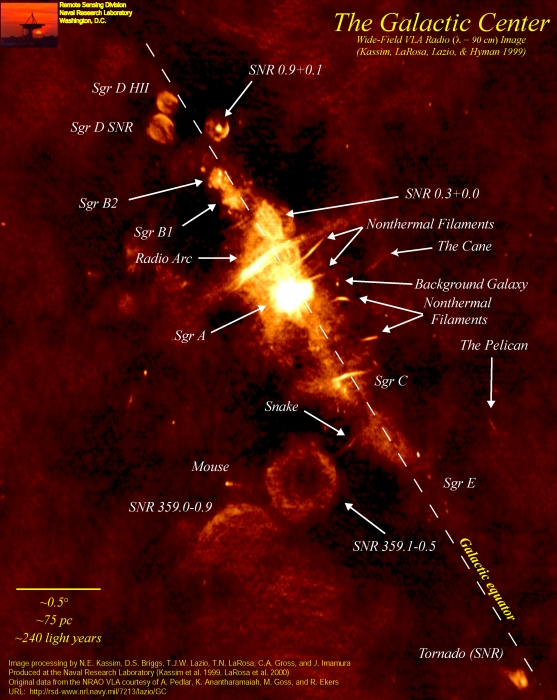
The Scene of the Crime
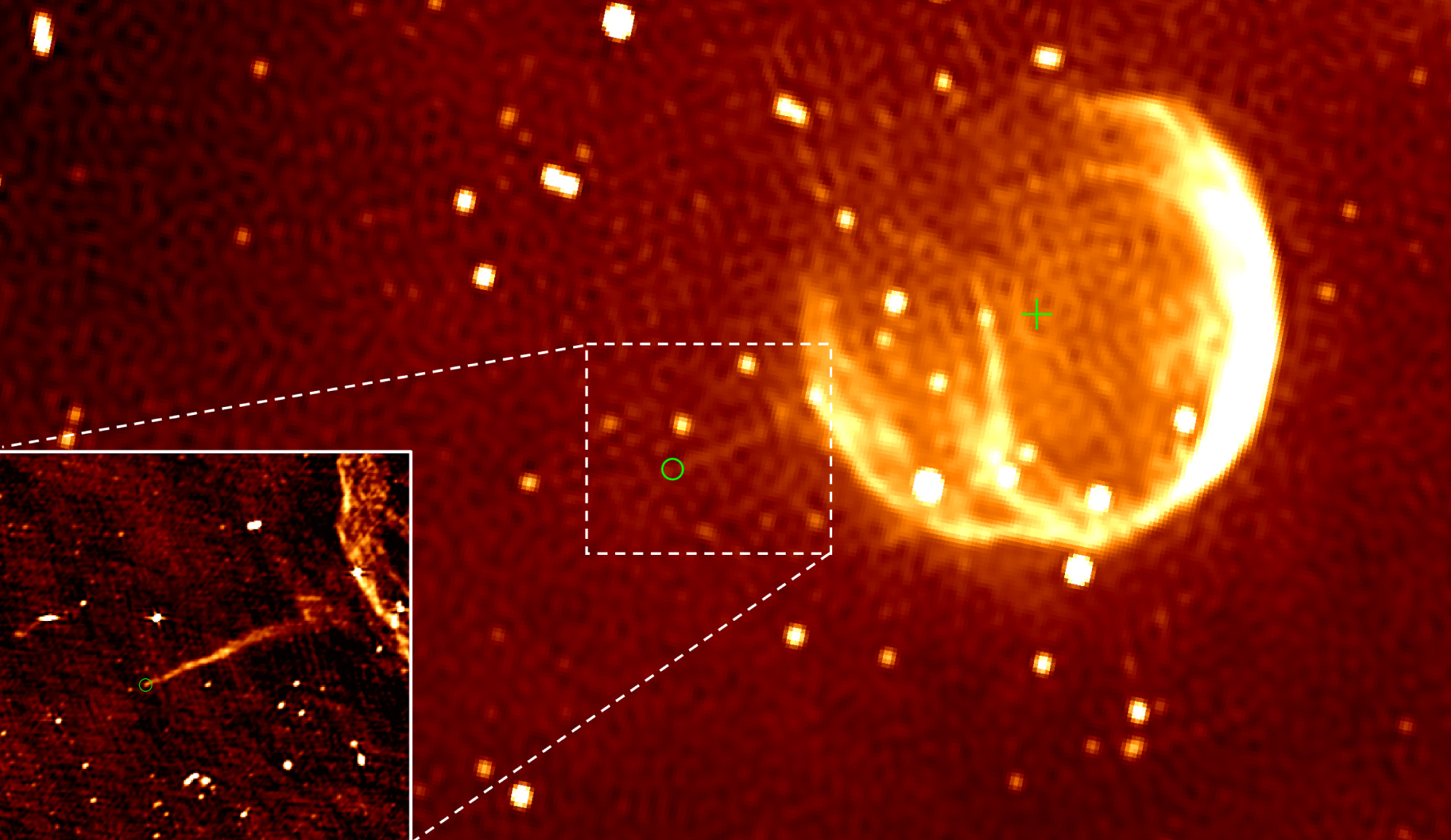
The Victims

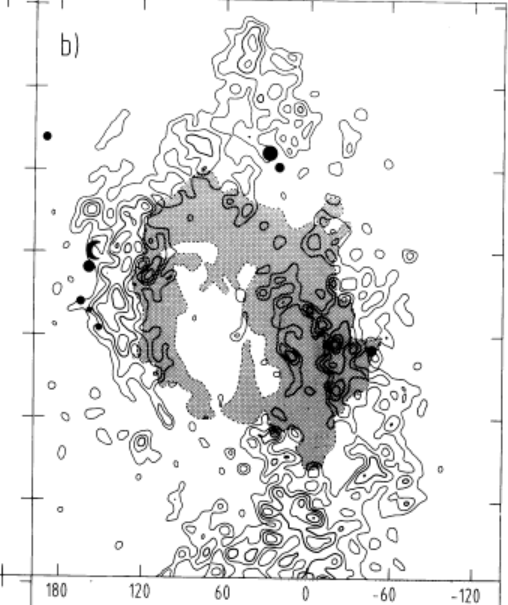
SGR A East
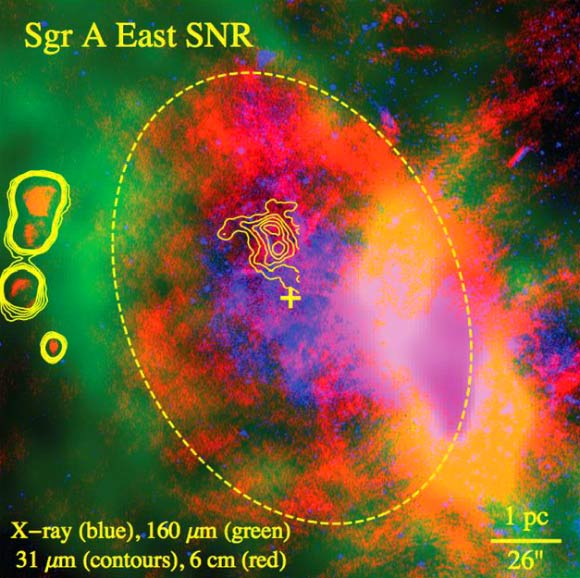
SGR X Ray Lobes

The Suspects

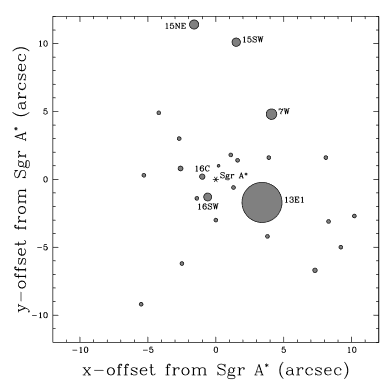
The Cannonball
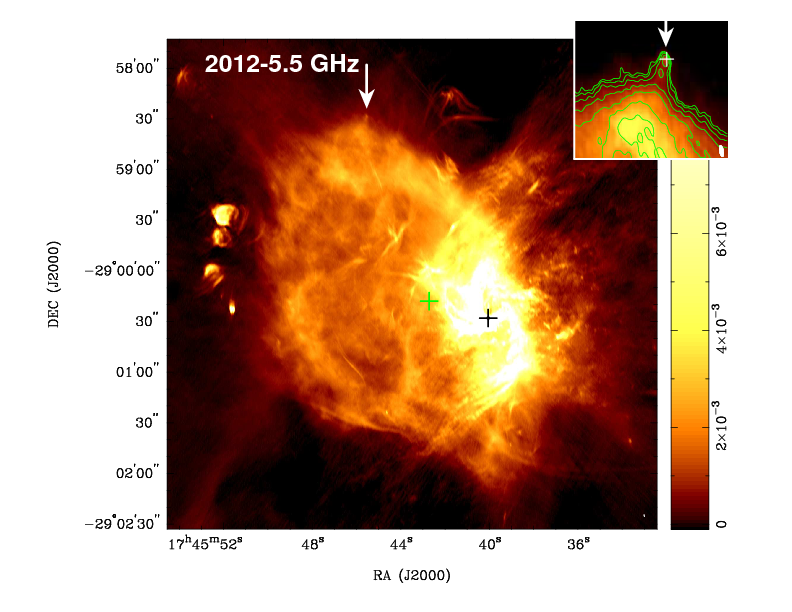
The Magnetar
Previous Investigation

Dust Extinction


First Detection of SGR East - 1989
Supernova Remnant!
Molecular lines!




Age Determination
Molecular clouds are very dense, around 1e2/cc
Sedov Taylor age 1e4 years
Bonus: the cannonball passes through the centre
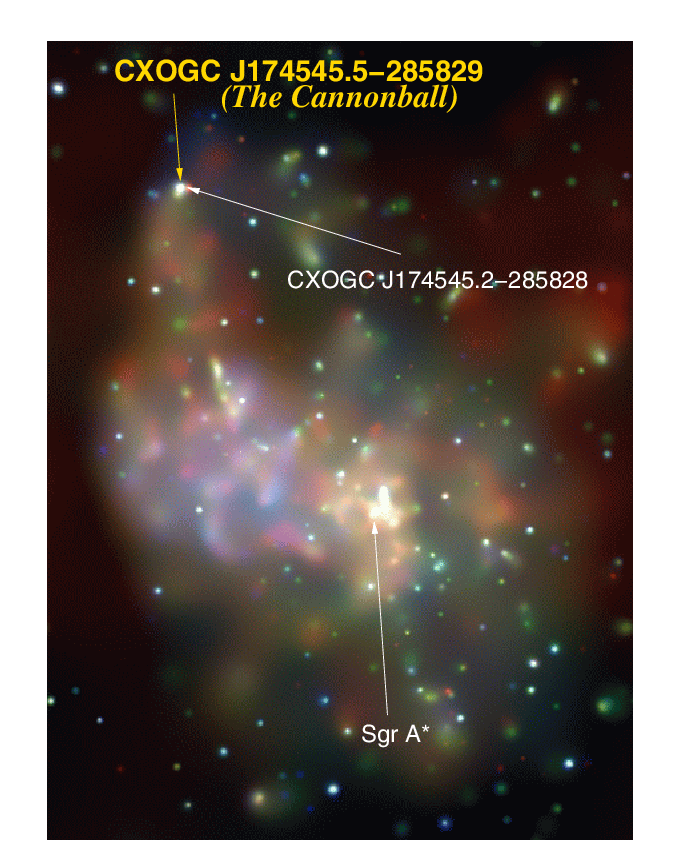

New Evidence
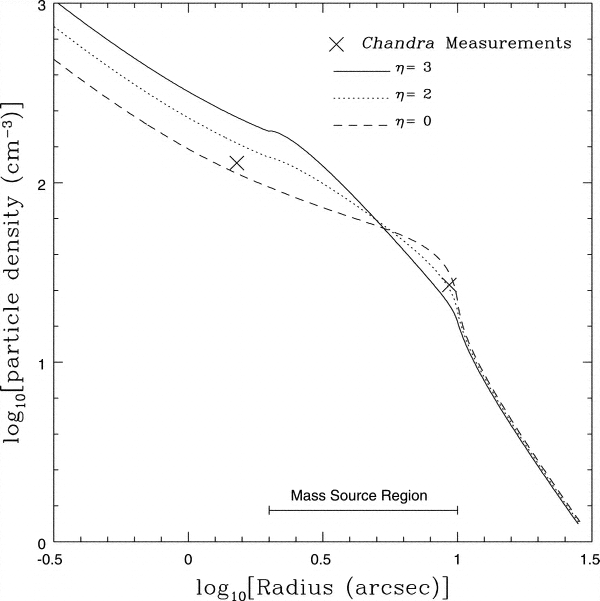
much smaller than molecular clouds!
Magnetar spin down age 1e4 years
SGR east is dusty - should have been destroyed in ST phase
Aeolian Environment
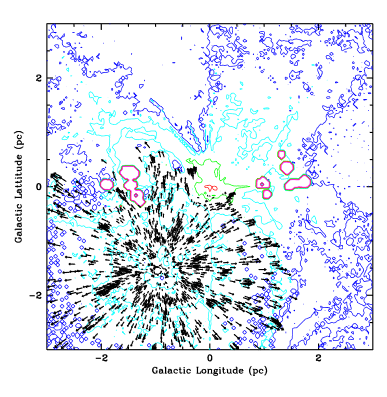
How do supernovae evolve in such environments?
star cluster
wind
supernova explosion
Numerical Simulations
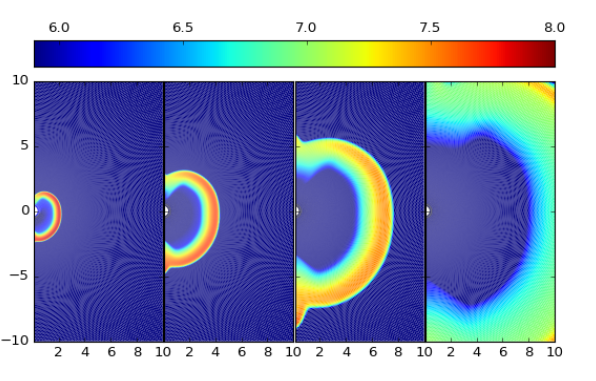
600y
1500y
6000y
9000y
Numerical Simulations
600y
1500y
6000y
9000y
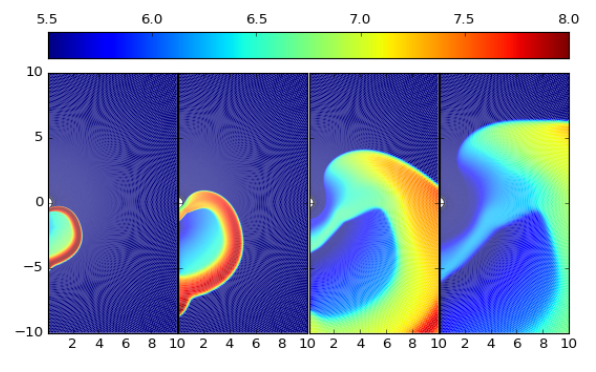
Numerical Simulations
600y
1500y
6000y
9000y
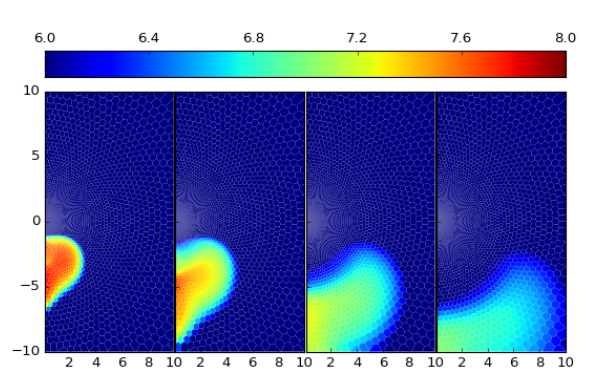
Phase Diagram
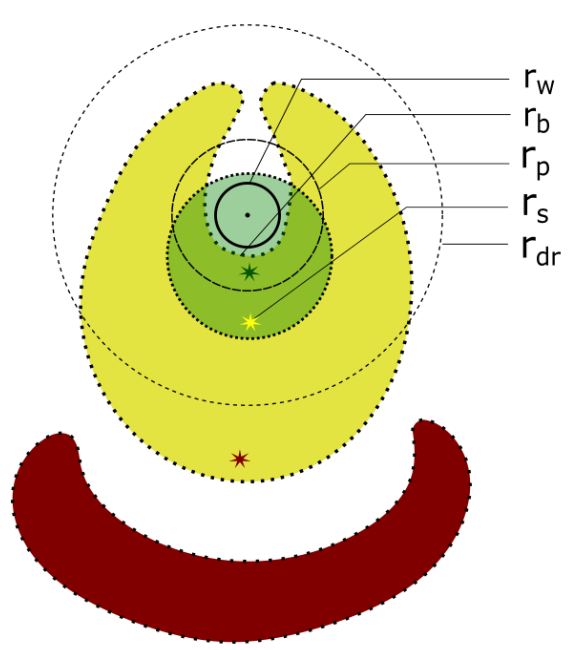
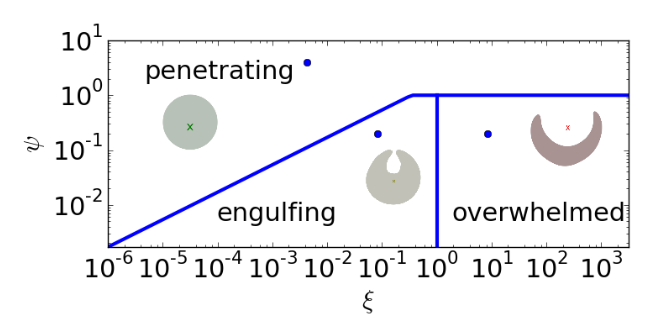
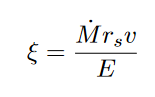
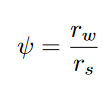
Implications for Relic - Remnant Associations
X - ray lobes - magnetar
age 1e4 years
SGR East only 1500 yo
Calls into question association with the cannonball
Crime Reconstruction
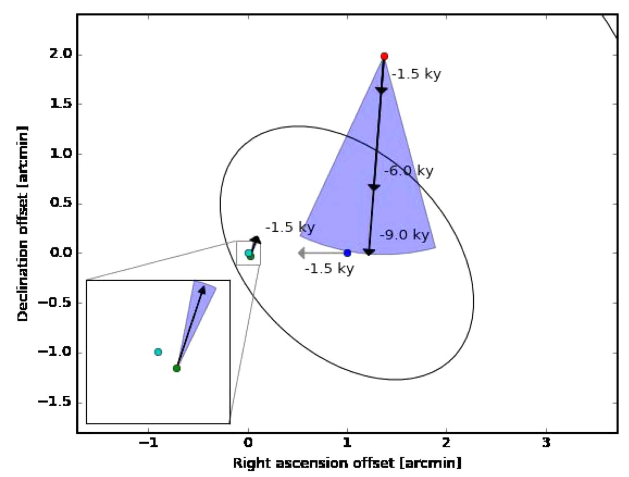
SGR East and the cannonball are not associated
Conclusion

SGR East - Cannonball association
X ray lobes - Magnetar association