Reactive Back-end
With Node.js + ReactiveX (RxJS)
whoami
Alwin Arrasyid
Back-end developer, DyCode
Background story
Handling Real-time data
We need to process periodic & real-time data from IoT devices asynchronously.
We are using MQTT protocol to subscribe for incoming data from IoT devices.
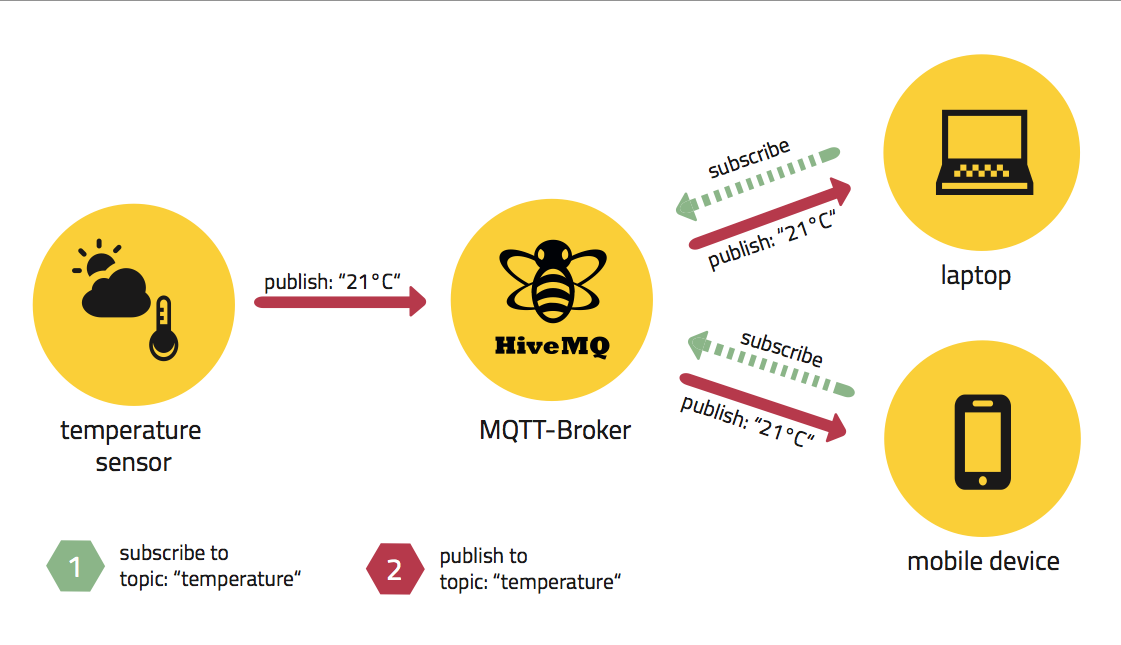
A little bit about MQTT
Is a lightweight protocol built on top of TCP/IP that is designed for M2M (machine-to-machine) communication.
Unlike HTTP, MQTT uses pub/sub model instead of request/response
MQTT.js
MQTT client for Node.js
https://www.npmjs.com/package/mqtt
const mqtt = require(`mqtt`);
const client = mqtt.connect(`mqtt://localhost:1883`);
client.on(`connect`, () => {
client.subscribe(`temperature_data`);
});
client.on(`message`, (topic, msgBuffer) => {
if (topic === `temperature_data`) {
// handle temperature message
}
});
client.on(`error`, (err) => {
console.error(err);
process.exit(1);
});It uses event system. So we need to listen to events, if we wish to know what's happening.
All messages that come to our client are emitted through an event emitter.
Dealing with those messages requires different approach.
Dealing with Async
Frequently used ways of dealing with async:
1. Callback function
2. Promise
Let's say that,
We have temperature sensors and we want to write each message that's sent by those sensors to our database.
How do we do that?
Callback Function
Most of async functions are using callback as a mechanism of signaling a completition.
Node's callback are usually the last argument to our async function.
Easy to deal with at first.
client.on(`message`, (topic, msgBuffer) => {
const msgObject = JSON.parse(msgBuffer.toString()); // don't do this
if (topic === `temperature_data`) {
return db.temperatures.insert(msgObect, (err, insertResult) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return false;
}
});
}
});It's pretty easy, right? Until...
We also need to send alert to the notification service whenever the temperature value is above 30 degrees
const request = require(`superagent`);
// ...
client.on(`message`, (topic, msgBuffer) => {
const msgObject = JSON.parse(msgBuffer.toString()); // don't do this
if (topic === `temperature_data`) {
return db.temperatures.insert(msgObect, (err, insertResult) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return false;
}
if (msgObject.temp > 30) {
return request.post(notifServiceUrl).send(msgObject).end((err, response) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return false;
}
});
}
});
}
});You'll eventually run into a "callback hell" or "pyramid of doom".
What's wrong?
1. Once things got complicated, it becomes harder to maintain.
2. Hard to handle errors.
3. try-catch is pretty much useless here
Promise
Represents the future result of an async operation.
It's realtively easy to:
1. Handle error
2. Avoid callback hell
Promise
function sendRequest(url, payload) {
return request.post(url).send(payload).end();
}
db.temperature.insert(msgObject)
.then((insertionResult) => {
// do something
if (msgObject.temp > 30) {
return sendRequest(notifServiceUrl, msgObject);
}
return true;
})
.then((responseOrBoolean) => {
if (typeof resposneOrBoolean === `boolean`) {
console.log(`Not sending anything to notification service`);
} else {
console.log(`Sent alert to notification service`);
}
return true;
})
.catch((ex) => {
console.error(ex);
});Errors / exceptions inside Promise can be propagated to `catch` handler. We get try-catch like feature here!
To chain a promise, you need to return another promise inside `then`.
No callback hell this way.
But,
Not every library / module supports promise yet. (Really?)
In my opinion mixing event, callback, and promise is a no.
So, can we do better?
Wait!
Before we continue, remember Array's high order functions?
forEach
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].forEach(item => console.log(item));
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5Map
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].map(x => x * 2);
// output:
// [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]Filter
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].filter(x => x % 2 === 0);
// output:
// [2, 4]What if I told you that you can process incoming messages using these simple functions, asynchronously.
Introducing RxJS
RxJS
Library for composing asynchronous and event-based programs by using observable sequences.
Provides one core type, Observable.
And satellite types (Observer, Scheduler, Subject)
Using operators inspired by Array's HoF (map, filter, etc)
Lodash for events
Observable
Lazy push collection of multiple values.
Collection of values over time.
What's the difference with function and promise?
You can create Observable almost from everything
Using .create operator
const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
const myObservable = Rx.Observable.create((observer) => {
observer.next(17);
setTimeout(() => {
observer.next(12);
observer.complete();
}, 300);
});
myObservable.subscribe(
(data) => {
// data will be: 17 12
},
(err) => {
// Any error during execution will be handled here
},
() => {
// fires when complete
}
);Using .from operator
const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
const fromArray = Rx.Observable.from([1, 2, 3, 4]);
const fromObject = Rx.Observable.from({ name: `winter` });
fromArray.subscribe(data => console.log(data));Callback, Event, Promise
const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
const writeData = Rx.Observable.bindNodeCallback(db.temperature.insert);
writeData(data) // returns observable of db.temperature.insert result
const message = Rx.Observable.fromEvent(client, `message`);
Rx.Observable
.fromPromise(db.temperature.insert(data));Applying Operators
const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
Rx.Observable
.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
.map(item => item * 2)
.filter(item => item % 2 === 0)
.subscribe((data) => {
console.log(data);
});We can do the same to our `message` event!
Handling message event (then)
const request = require(`superagent`);
// ...
client.on(`message`, (topic, msgBuffer) => {
const msgObject = JSON.parse(msgBuffer.toString()); // don't do this
if (topic === `temperature_data`) {
return db.temperatures.insert(msgObect, (err, insertResult) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return false;
}
if (msgObject.temp > 30) {
return request.post(notifServiceUrl).send(msgObject).end((err, response) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return false;
}
});
}
});
}
});const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
const writeDb = Rx.Observable.bindNodeCallback(db.temperature.insert);
function sendRequest(url, payload) {
return request.post(url).send(payload).end();
}
Rx.Observable
.fromEvent(client, `message`, (topic, message) =>
({ topic, message: JSON.parse(message) })
)
.filter(data => data.topic === `temperature_data`)
.mergeMap(data => writeDb(data), (original, writeResult) => original)
.filter(data => data.message.temp > 30)
.mergeMap(data => sendRequest(url, data.message), (original, response) => original)
.subscribe({
next: (data) => console.log(`Incoming data:`, data.message),
error: (err) => console.error(`Error happens: ${err.message}`),
complete: () => console.log(`I'm done`),
});Handling message event (now)
What kind of sorcery is this?
const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
const jsonMessage$ = Rx.Observable
.fromEvent(client, `message`, (topic, message) => ({ topic, message }));
.map(data => {
try {
return { topic: data.topic, message: JSON.parse(data.message.toString()) };
} catch (ex) {
return { topic: data.topic, message: message.toString() };
}
})
.filter(data => typeof data.message !== `string`);
jsonMessage$
.filter(data => data.topic === `temperature_data`)
.mergeMap(data => writeDb(data), original => original)
.filter(data => data.message.temp > 30)
.mergeMap(data => sendRequest(url, data.message), original => original)
.subscribe({
next: (data) => console.log(`Incoming data:`, data.message),
error: (err) => console.error(`Error happens: ${err.message}`),
complete: () => console.log(`I'm done`),
});const Rx = require(`rxjs`);
const temperatureData$ = jsonMessage$.filter(data => data.topic === `temperature_data`);
temperatureData$
.map(data => toFahrenheit(data.message.temp))
.subscribe((data) => {
console.log(`Temperature in Fahrenheit: ${data}`);
});
temperatureData$
.map(data => toKelvin(data.message.temp))
.subscribe((data) => {
console.log(`Temperature in Kelvin: ${data}`);
});