Binary Classifier Two-Sample Test (C2STs) with Logistic Regression
CPSC 532S - Danica Sutherland
James, Amin, James
Spring 2022
Two Sample Tests - Motivation
P = Q?
Two Sample Tests - Motivation

Two Sample Tests - The Basics
Two Sample Tests - The Basics cont.
Steps to the standard two-sample test:
1) determine a significance level as input to the test
2) manually compute the test statistic
3) compute p-value
4) reject the null hypothesis if our calculated p value is less than alpha, and fail to do so otherwise.
C2STs - Classifier Two Sample Tests
Shuffle D at random and split it into training and test subsets
"Revisiting Classifier Two-Sample Tests "[Lopez-Paz and Oquab, 2016]
C2STs - Classifier Two Sample Tests cont.
Train a binary classifier
C2STs - Classifier Two Sample Tests cont.
From here we develop the p value as is traditionally done in normal two sample tests
Theoretical Motivation
Finding bounds for p-value
- Imagine we have trained a classifier on our data.
- We then compute the (pseudo) t-statistic using a test set .
- Then we calculate the p-value using the following function:
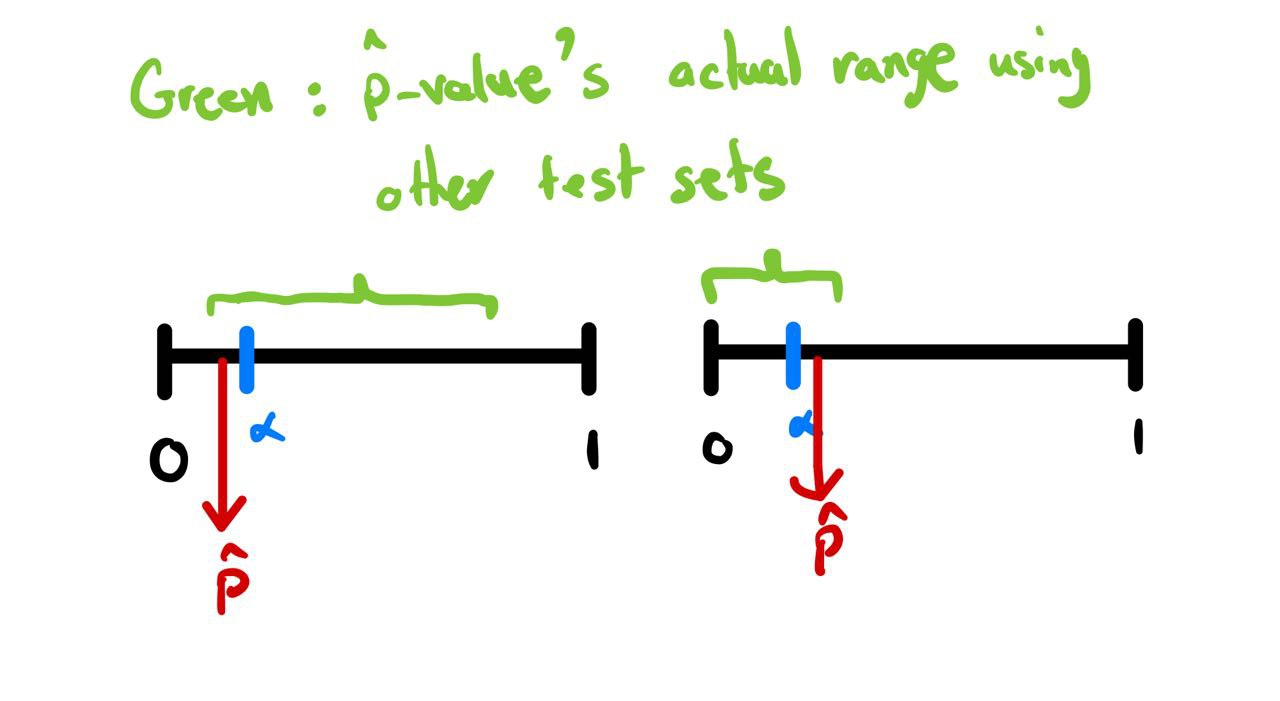
- But, how confident are we that our p-value will be almost the same, if we change the test set?
- Possible scenarios in the next slide.
Finding bounds for p-value
Finding Bounds: Linear Classifiers
- Let's start with a simple case:
- Take the space of linear classifiers:
- Use 0-1 loss:
- Let's derive the (pseudo) t-statistic of this classifier:
- Note that:
- Idea: if we find some bounds for , we can use them to find bounds for our reported p-value.
Finding Bounds for Linear Classifiers: Test Loss
- Let's start with the Uniform Convergence of Linear Classifiers trained with 0-1 loss:
-
We have the assumptions that:
-
We know that
-
Thus: [https://cse.buffalo.edu/~hungngo/classes/2011/Fall-694/lectures/rademacher.pdf]
-
Using this, we can derive the uniform convergence bounds:
Finding Bounds for Linear Classifiers: Test Loss
- But, how do we derive bounds for test loss?
-
Remember that:
-
Combining this with the uniform convergence property, we get:
- Remember that
- We get:
- Note that is a monotonically decreasing function, Thus:
Finding Bounds for Logistic Regression
- But, we can't really train classifiers on 0-1 loss.
- How about logistic loss? (Logistic Regression)
- Well, the (pseudo) t-statistic and the p-value computations are based on 0-1 loss...
- We would have to design a new test for other (pseudo) t-statistics.
- Idea: Use logistic loss as a surrogate loss for 0-1 Loss.
- The good: bounds for logistic regression!!!
- The ugly: One-sided bounds for logistic regression :(
- Because the surrogate loss bounds 0-1 loss only on one side
Finding Bounds for Logistic Regression
-
We showed that:
-
Note that:
-
Thus:
-
Which gives us:
- We have derived a one-sided bound on the p-value of our test, when our classifier is a linear classifier trained with logistic loss (logistic regression).
Experiments
Experiment Detail
-
Implemented Logistic Regression in Pytorch
-
Tested on synthetic data sampled from 1D distributions
-
Trained for 200 epochs on 400 generated examples
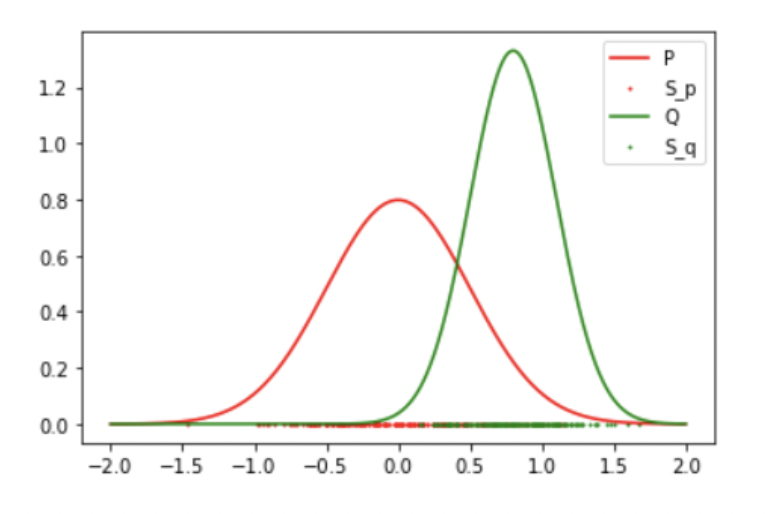
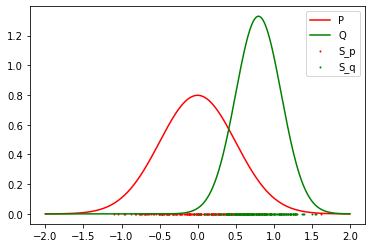
Results: 2 Gaussian (Success)
-
Result: Reject the Null Hypothesis, P != Q
-
Mean: 0 std: 0.5
-
Mean: 0.8 std: 0.3
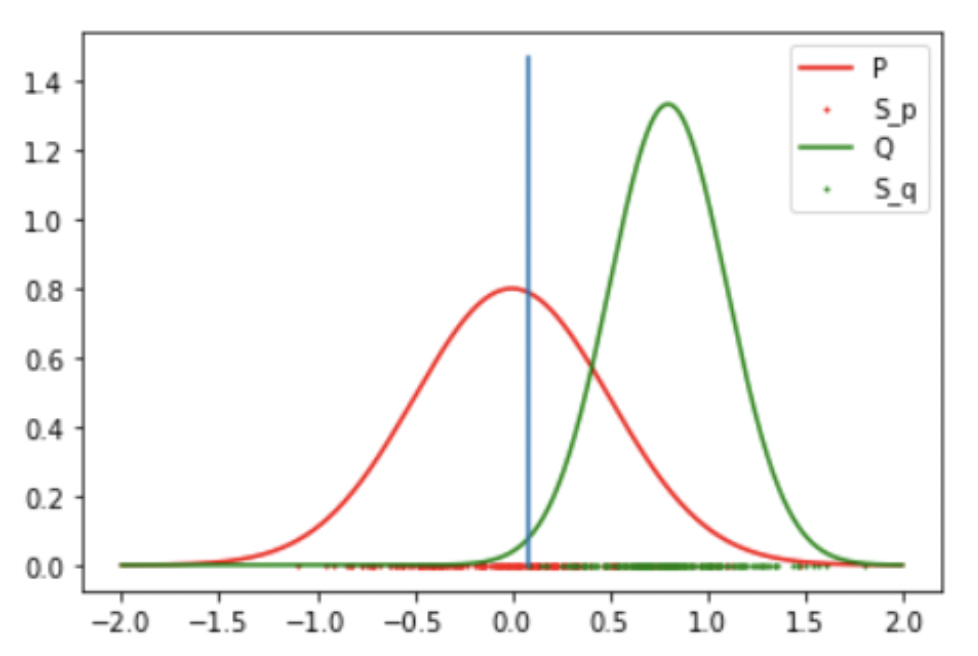
Result 3: Gaussian and Student T (Success)
-
Result: Reject the Null Hypothesis, P = Q
-
Mean: 0 std: 0.5
-
Student T: DoF: 4 mean: 1.5
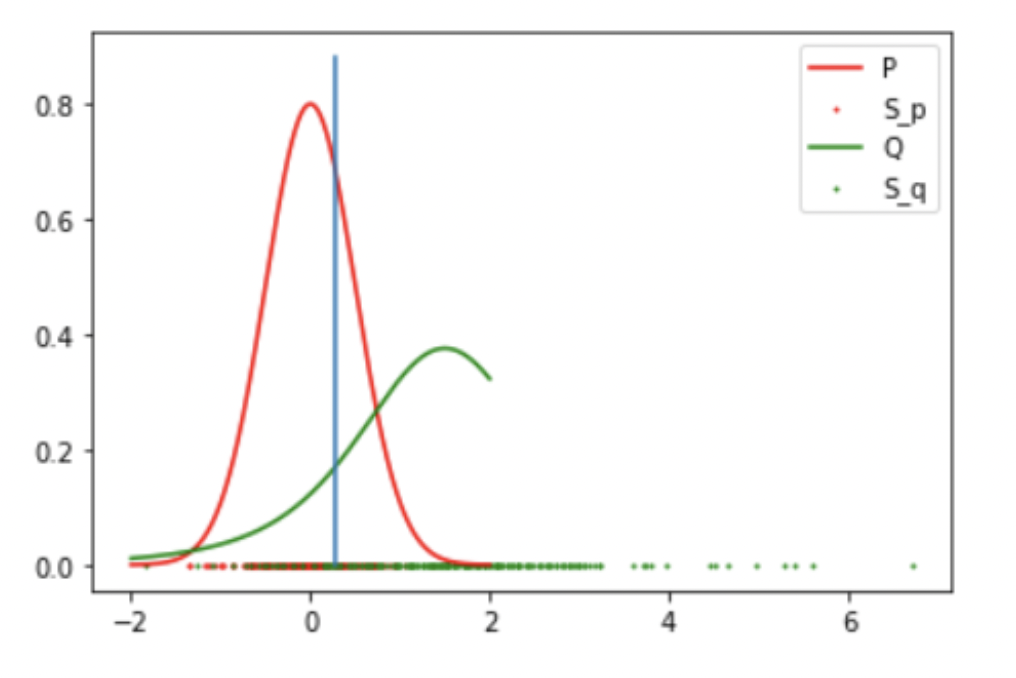
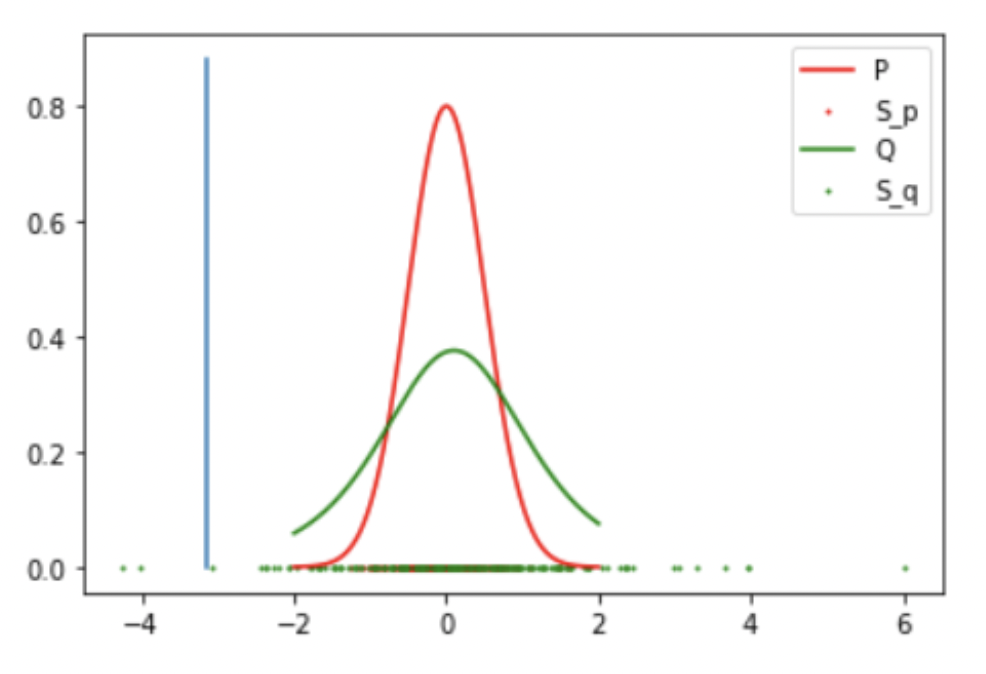
Results: 1 Gaussian (Success)
-
Result: Accept the Null Hypothesis, P = Q
-
Mean: 0 std: 0.5
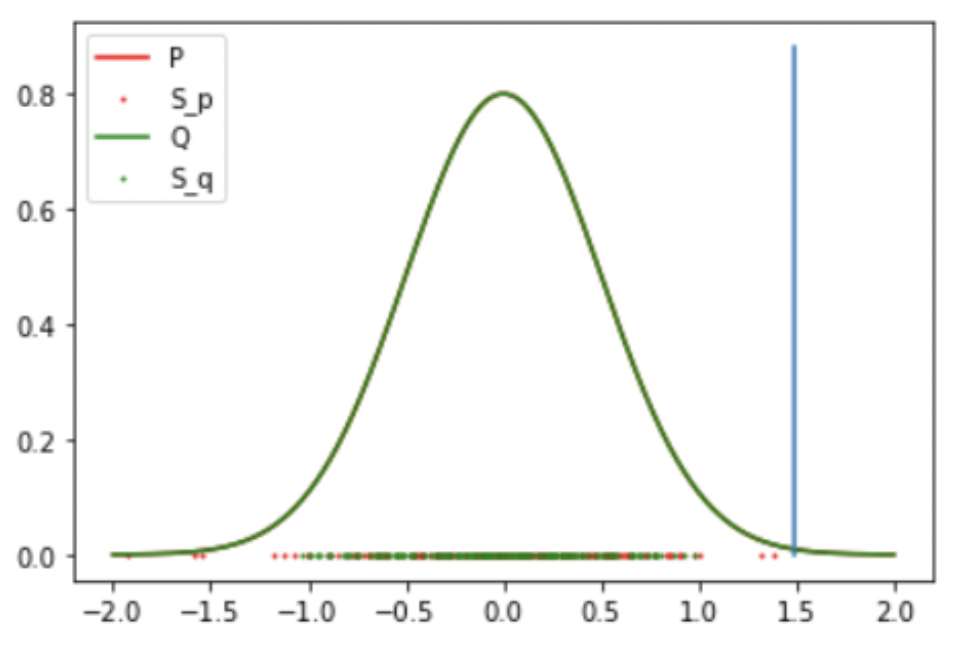
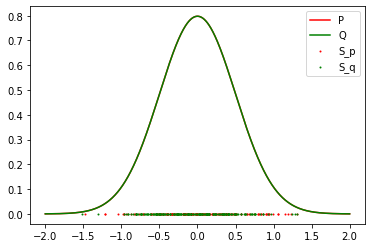
Result 3: 2 Gaussian (False Negative)
-
Result: Accept the Null Hypothesis, P = Q
-
Gaussian: Mean: 0 std: 0.5
-
Student T: DoF: 4 mean: 0.1
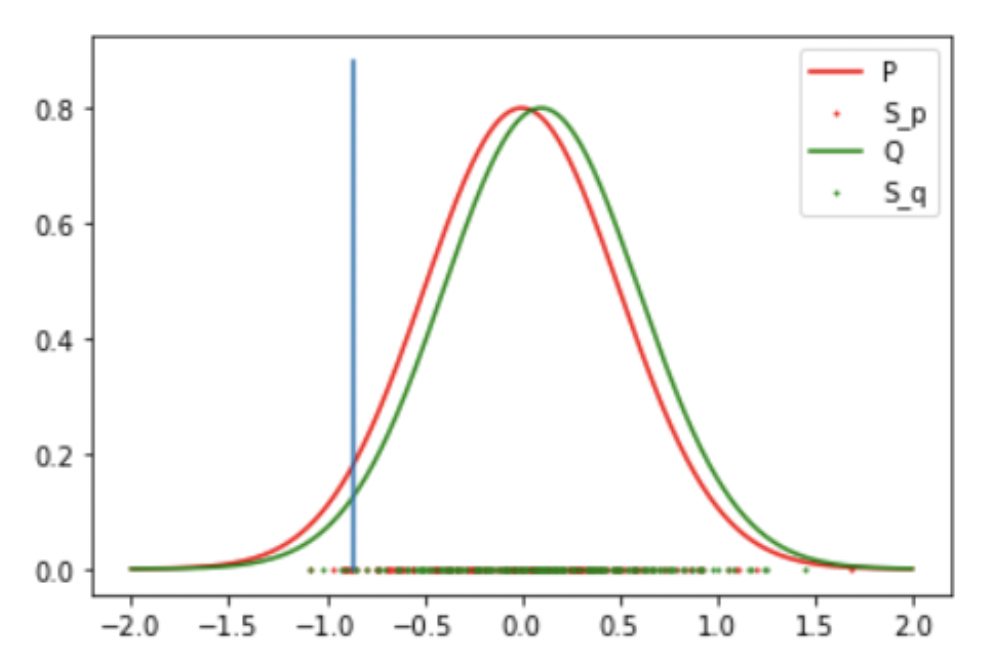
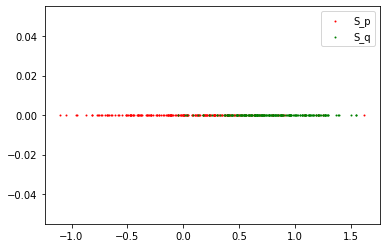
Result 3: Gaussian and Student T (False Negative)
Result: Accept the Null Hypothesis, P = Q
-
Gaussian: Mean: 0 std: 0.5
-
Student T: DoF: 4 mean: 0.1