#eng-learning
SICP Ch. 1.1

- Big picture thinking about the programming process
- Abstraction and building software from general patterns
- Functions as data
- Contains three programming paradigms (functional, OOP, declarative)
Scheme


ALGOL

Why Scheme?
- Procedures as data
- It's simple
(* 25 4 12)
1200
(+ (* 3 (+ (* 2 4) (+ 3 5))) (+ (- 10 7) 6))
(+ (* 3
(+ (* 2 4)
(+ 3 5)))
(+ (- 10 7)
6))(* (+ 2 (* 4 6))
(+ 3 5 7))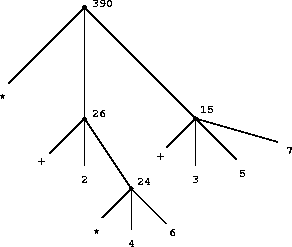
Procedures
(define (square x) (* x x))
(define (square x) (* x x))
| | | | | |
To square something, multiply it by itselfInterpreter & Substitution
(sum-of-squares (+ 5 1) (* 5 2))
(+ (square 6) (square 10))
(+ (* 6 6) (* 10 10))
(+ 36 100)
136Interpreter & Substitution
(sum-of-squares (+ 5 1) (* 5 2))
(+ (square (+ 5 1)) (square (* 5 2)) )
(+ (* (+ 5 1) (+ 5 1)) (* (* 5 2) (* 5 2)))
(+ (* 6 6) (* 10 10))
(+ 36 100)
136Normal-Order Evaluation
Conditionals
(define (abs x)
(cond ((> x 0) x)
((= x 0) 0)
((< x 0) (- x))))
(define (abs x)
(cond ((< x 0) (- x))
(else x)))
(define (abs x)
(if (< x 0)
(- x)
x))Block Structure
(define (sqrt x)
(define (good-enough? guess x)
(< (abs (- (square guess) x)) 0.001))
(define (improve guess x)
(average guess (/ x guess)))
(define (sqrt-iter guess x)
(if (good-enough? guess x)
guess
(sqrt-iter (improve guess x) x)))
(sqrt-iter 1.0 x))"... programmer's must learn to understand and to anticipate the consequences of their conjuring."
🧙