Introduction to
web apps & React
Lesson 3: Intro to React
November 2019
Amsul Naeem
twitter.com/amsul_
slides.com/amsul
HTML, Javascript, & React
Topics
React Components
React RenderING
First of all...
HTML, JavaScript, & React
- HTML & JavaScript are languages
- React is a UI library
React uses JavaScript & HTML to keep your application UI in sync with your application state.
HTML
HTML, JAVASCRIPT, & REACT
Elements
REACT
Elements
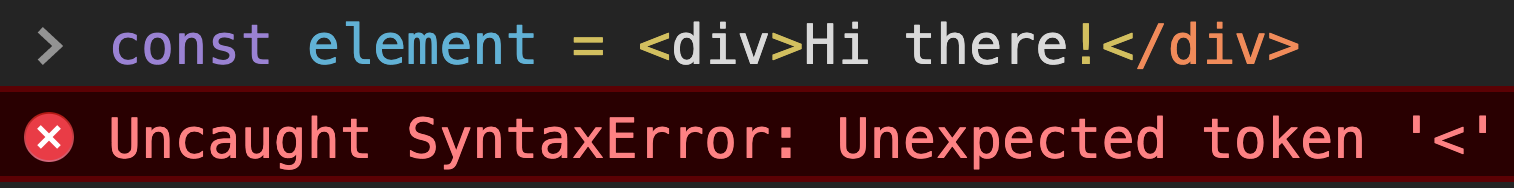
<div>Hi there!</div>const element = <div>Hi there!</div>Note the assignment
Attributes
<div id="Title">Hi there!</div>Props (short for properties)
const element = <div id='Title'>Hi there!</div>Rendering & Updates
- Manual
- Managed with JavaScript
- DOM querying
- DOM updating
Rendering & Updates
- Automatic
- All in JavaScript
- No querying
- Declarative updating
React *Uses* JavaScript
HTML, JAVASCRIPT, & REACT
JSX !== JavaScript
&& JSX !== HTML
JSX is an additional syntax on top of JavaScript to mimic HTML.
JSX compiles to JavaScript in a build step.
var element = React.createElement("div", null, "Hi there!");Why use React?
HTML, JAVASCRIPT, & REACT
- DOM updates are slow
- Updating elements for every change
- Recalculate UI for every update
- Repaint UI for every pixel change
- React components are fast
- Just functions
- DOM updates in batches
- Atomic updates
React Components
HTML, JAVASCRIPT, & REACT
const element = <div>Hi there!</div>function Component() {
return <div>Hi there!</div>
}Components encapsulate logic & markup to be reused and return the composed element to be rendered.
Exercise 1
HTML, JAVASCRIPT, & REACT
Recreate form with pre-filled values:
- 👉 No styling
- 👉 No change handlers
- First Name, Last Name
- Above 19+
- Diet Restrictions: Vegetarian, Vegan, Halal/Kosher, None
- Current Year
Starting point:
- github.com/amsul/george-brown
- Under the
lesson-03directory
15 minute break
Handlers & State & Hooks
REACT COMPONENTS
- Handlers: Manage user actions to trigger a state change.
- State: Maintains a record of the component’s rendered result.
- Hooks: Create states and handle component lifecycle.
HANDLERS & STATE & HOOKS
REACT COMPONENTS
function Component() {
// Create some state..
const handleButtonClick = () => {
// Do something to the state..
}
// Use the state to show the ### count
return <button onClick={handleButtonClick}>Clicked ### times!</button>
}function Component() {
const [clicked, setClicked] = React.useState(0)
const handleButtonClick = () => {
// Do something to the state..
}
// Use the state to show the ### count
return <button onClick={handleButtonClick}>Clicked ### times!</button>
}function Component() {
const [clicked, setClicked] = React.useState(0)
const handleButtonClick = () => {
setClicked(clicked + 1)
}
// Use the state to show the ### count
return <button onClick={handleButtonClick}>Clicked ### times!</button>
}function Component() {
const [clicked, setClicked] = React.useState(0)
const handleButtonClick = () => {
setClicked(clicked + 1)
}
return <button onClick={handleButtonClick}>Clicked {clicked} times!</button>
}Props are used to:
- Bind handlers
- Share state between components
- Set attributes of an HTML element
Hooks
REACT COMPONENTS
- State management
useState() - Component lifecycle
useEffect()- More on this in future lessons
- Other built-in hooks as well
Custom Hooks
- Wrappers for custom logic around existing hooks
- Naming convention:
use*
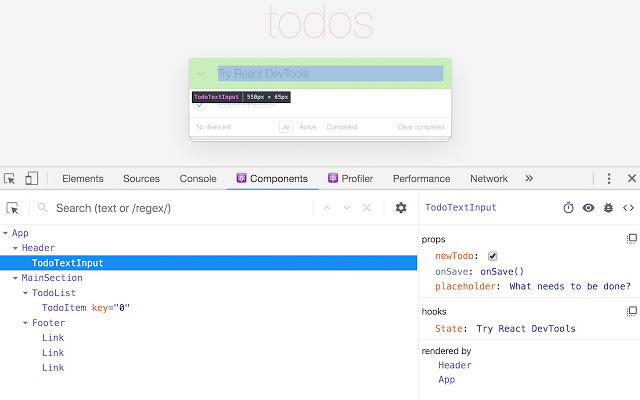
React Dev Tools
REACT COMPONENTS
Exercise 2
REACT COMPONENTS
Refactor previous exercise with state & handlers:
- Define state within correct component(s)
- Pass props to correct components
- Add side-effects
- Hooks
- Event handlers
- HINT: Current year requires different handling
- (Optional) Add gender select menu
5 minute break
Top-down Approach
React Rendering
- Initiated from state changes
- Every subcomponent re-renders
- Atomic DOM updates
- React has an internal Virtual DOM
- Not every re-rendered component results in DOM updates
- V-DOM diffs the resulting tree to do atomic updates in batches
Rules Of Hooks
REACT RENDERING
- Only at top-level scope
- Not inside for-loops
- Not inside if-statements
- Not after an early return
- Only from React Functions
- Not within React Class Components
- Can be wrapped easily
Conditional Rendering
React Rendering
Using if statements
Using && conditionals
Using ternary (cond ? a : b) operators
function Component({ someCondition }) {
if (someCondition) {
return <div>Condition met</div>
}
return <div>Condition not met</div>
}function Component({ someCondition }) {
return (
<div>
<div>Some content</div>
{someCondition && <div>Condition met</div>}
</div>
)
}function Component({ someCondition }) {
return (
<div>
{someCondition ? <div>Condition met</div> : <div>Condition not met</div>}
</div>
)
}Looped Rendering
React Rendering
function Component() {
const list = [
/*list of items*/
]
return (
<ul>
{list.map(item => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
)
}Un-Rendering & Un-Mounting
React Rendering
- Both remove element from DOM
- Un-rendering: maintains component logic
- Un-mounting: resets component logic
function ParentComponent() {
const [someCondition, setSomeCondition] = React.useState(false)
if (someCondition) {
return <SubComponentOne />
}
return <SubComponentTwo />
}Exercise 3
React Rendering
Read “Thinking in React”:
- reactjs.org/docs/thinking-in-react.html
- Good way of framing the problem of building any piece of UI.
End of Lesson
Lesson 3: Intro to React
November 2019
Amsul Naeem
twitter.com/amsul_
slides.com/amsul