Test Driven Development



My activities




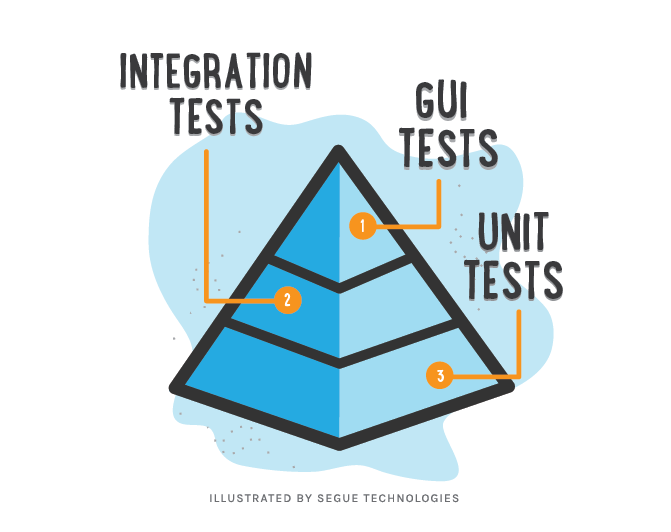
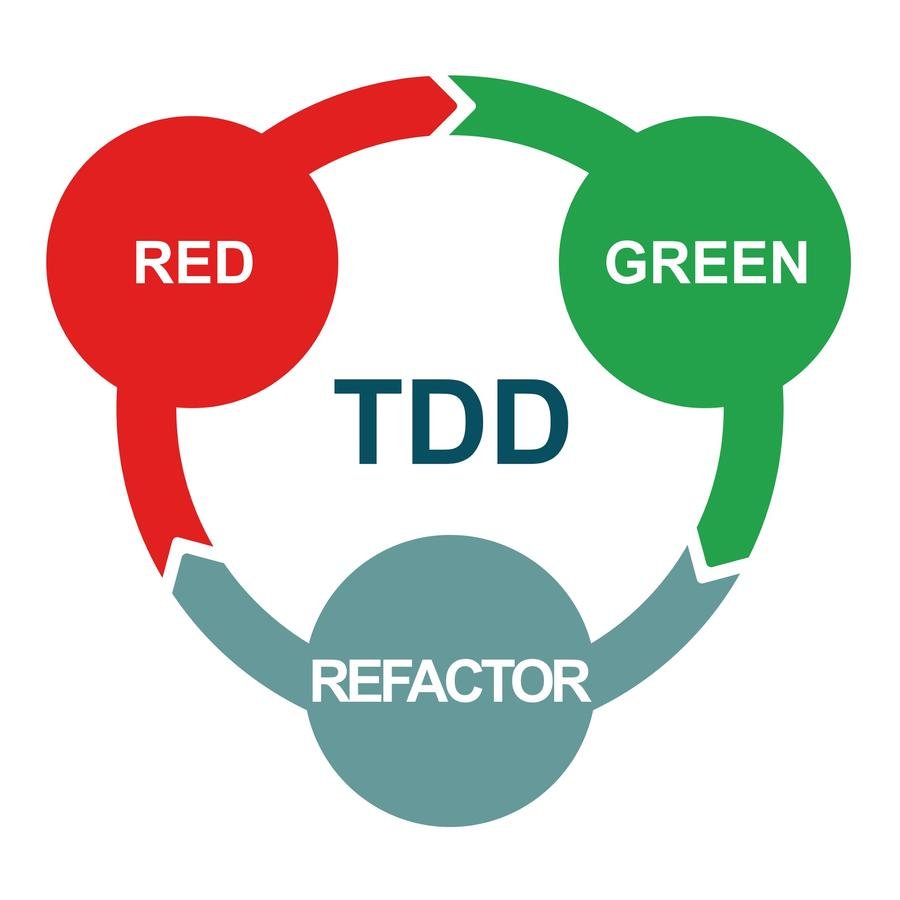
TDD
-
Navigation map
-
Test first
-
Assert first
-
Fail first

Navigation Map
- Decomposition of the task
- Less technical details
- Clear and ready to share with other teams members
- Can be changed during development
Test First
// calculator.spec.ts
test('should summarize two numbers',
(t: ExecutionContext) => {
}
);Assert First
// calculator.spec.ts
test('should summarize two numbers',
(t: ExecutionContext) => {
t.is(sum(1, 2), 3);
}
);Fail First
➜ ava-ts git:(master) ✗ npm test
> ava-ts@1.0.0 test /Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts
> ava
1 uncaught exception
Uncaught exception in __tests__/caclulator.spec.ts
__tests__/caclulator.spec.ts(4,8): error TS2304: Cannot find name 'sum'.
npm ERR! Test failed. See above for more details.Fail First
➜ ava-ts git:(master) ✗ npm test
> ava-ts@1.0.0 test /Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts
> ava
1 uncaught exception
Uncaught exception in __tests__/caclulator.spec.ts
__tests__/caclulator.spec.ts(5,20): error TS2345: Argument of type '3' is not assignable to parameter of type 'void'.Fail First
➜ ava-ts git:(master) ✗ npm test
> ava-ts@1.0.0 test /Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts
> ava
1 test failed
should summarize two numbers
/Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts/__tests__/caclulator.spec.ts:5
4: test('should summarize two numbers', (t: ExecutionContext) => {
5: t.is(sum(1, 2,), 3);
6: });
Difference:
- 0
+ 3
npm ERR! Test failed. See above for more details.
TDD can:
- Reduce the costs
- Improve performance of development
- Help to change the project
- Reduce technical debt
Benefits
-
Bridge from task to implementation
-
Improved code
-
Tests as documentation
-
Safe refactoring
- No extra code
-
Increases assurance of correctness







Emergent Design



Tools



coverage-blamer

Enzyme




import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@DisplayName("A special test case")
class DisplayNameDemo {
@Test
void addition() {
assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Custom test name containing spaces")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpaces() {
}
@Test
@DisplayName("╯°□°)╯")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpecialCharacters() {
}
@Test
@DisplayName("😱")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingEmoji() {
}
}XUnit
RSpec.describe "Using an array as a stack" do
def build_stack
[]
end
before(:example) do
@stack = build_stack
end
it 'is initially empty' do
expect(@stack).to be_empty
end
context "after an item has been pushed" do
before(:example) do
@stack.push :item
end
it 'allows the pushed item to be popped' do
expect(@stack.pop).to eq(:item)
end
end
endRSpec

https://sinonjs.org/
Standalone test spies, stubs and mocks for JavaScript. Works with any unit testing framework.

describe("PubSub", () => {
it("should call subscribers on publish", () => {
const callback = sinon.spy();
PubSub.subscribe("message", callback);
PubSub.publishSync("message");
assertTrue(callback.called);
});
});
spy
describe("stubbed callback", () => {
it("should behave differently based on arguments", () => {
const callback = sinon.stub();
callback.withArgs(42).returns(1);
callback.withArgs(1).throws("name");
assert.isUndefined(callback()); // No return value, no exception
assert.equals(callback(42), 1); // Returns 1
assert.exception(() => {
callback(1);
}); // Throws Error("name")
});
});stub
"test should call all subscribers when exceptions": () => {
const myAPI = { method: () => {} };
const mock = sinon.mock(myAPI);
mock.expects("method").once().throws();
PubSub.subscribe("message", myAPI.method);
PubSub.publishSync("message", undefined);
mock.verify();
}mock


Mutation testing (or mutation analysis or program mutation) is used to design new software tests and evaluate the quality of existing software tests. Mutation testing involves modifying a program in small ways.[1] Each mutated version is called a mutant and tests detect and reject mutants by causing the behavior of the original version to differ from the mutant. This is called killingthe mutant. Test suites are measured by the percentage of mutants that they kill. New tests can be designed to kill additional mutants. Mutants are based on well-defined mutation operators that either mimic typical programming errors (such as using the wrong operator or variable name) or force the creation of valuable tests (such as dividing each expression by zero). The purpose is to help the tester develop effective tests or locate weaknesses in the test data used for the program or in sections of the code that are seldom or never accessed during execution. Mutation testing is a form of white-box testing.


and TypeScript

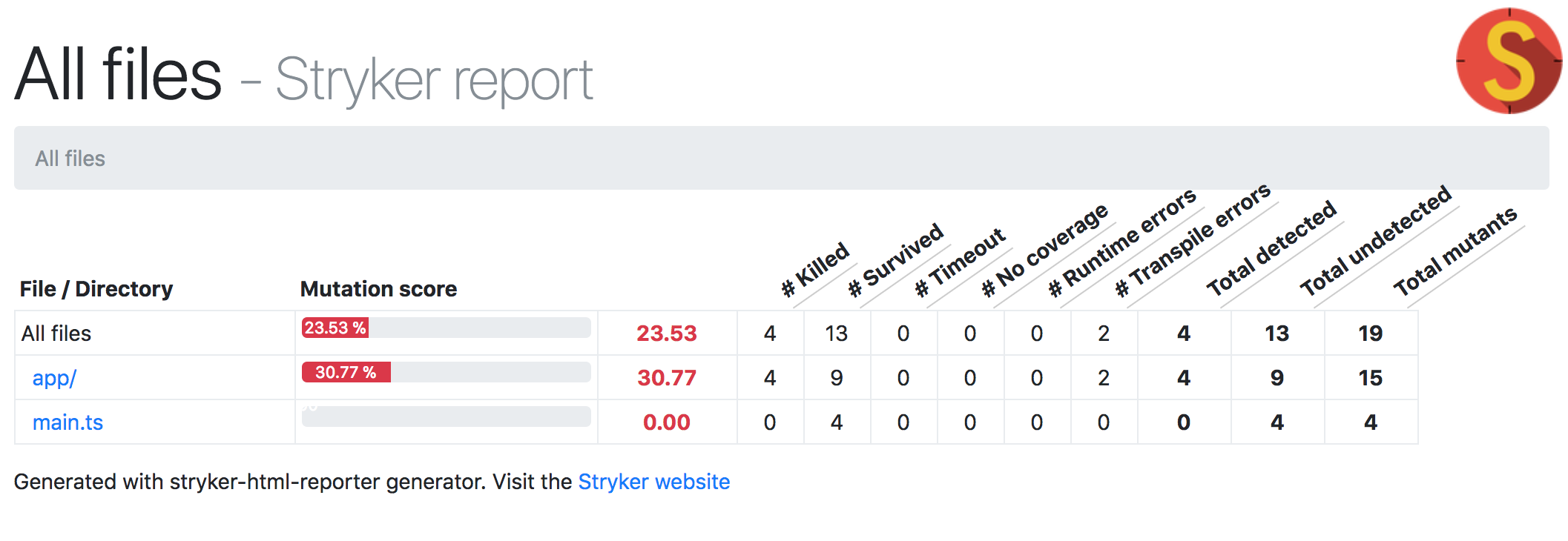

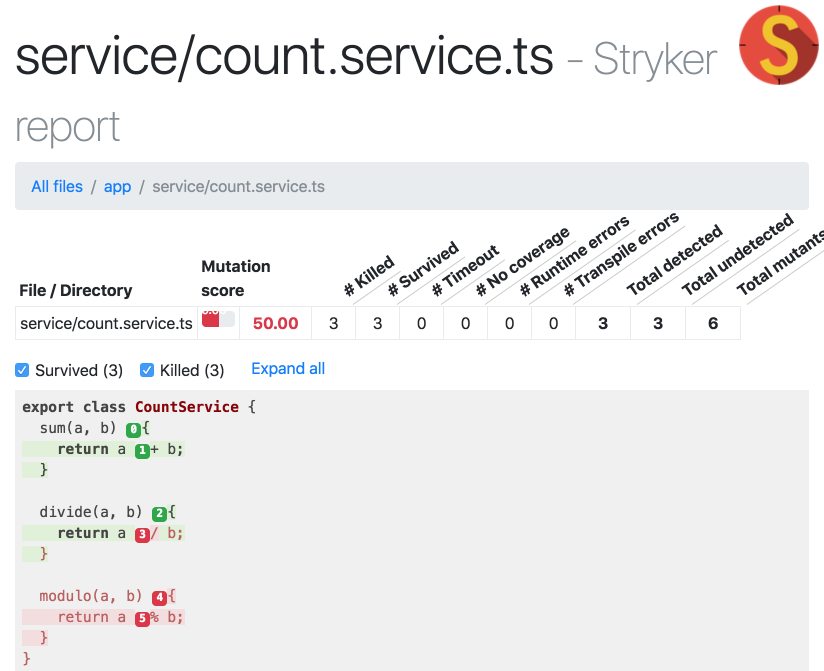
export class CountService {
sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
divide(a, b) {
return a / b;
}
modulo(a, b) {
return a % b;
}
}
describe('Count Service', () => {
let sut;
beforeEach(() => {
sut = new CountService();
})
it('should sum numbers', () => {
expect(sut.sum(2, 2)).toEqual(4);
});
it('should get divided numbers', () => {
expect(sut.divide(2, 1)).toEqual(2);
})
});

Anti-patterns



Coverage First

TDD Terror
The Liar
Excessive Setup
Giant
The Mockery
The Inspector
Generous Leftovers
The Local Hero
The Nitpicker
The Secret Catcher
The Dodger
The Loudmouth
The Greedy Catcher
The Sequencer
Hidden Dependency
The Enumerator
The Stranger
The Operating System Evangelist
Success Against All Odds
The Free Ride
The One
The Peeping Tom
The Slow Poke

