Test Driven Development
Andrey Kucherenko




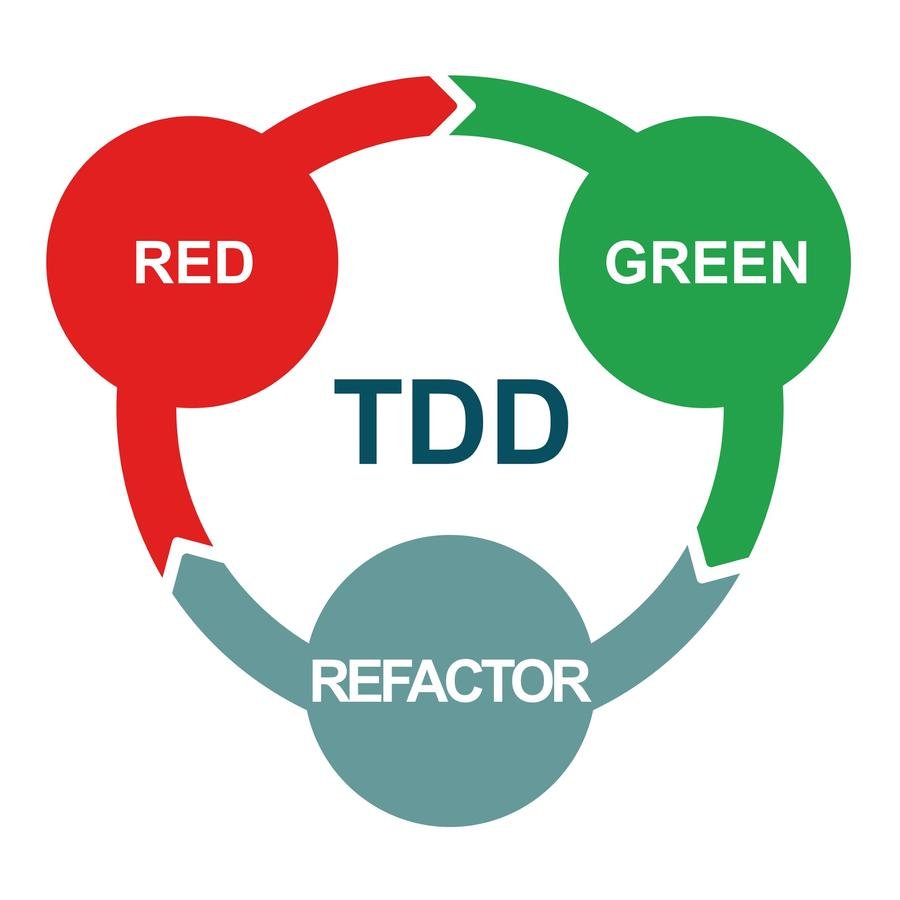
TDD
-
Navigation map
-
Test first
-
Assert first
-
Fail first

Navigation Map
- Decomposition of the task
- Less technical details
- Clear and ready to share with other teams members
- Can be changed during development
Test First
// calculator.spec.ts
test('should summarize two numbers',
(t: ExecutionContext) => {
}
);Assert First
// calculator.spec.ts
test('should summarize two numbers',
(t: ExecutionContext) => {
t.is(sum(1, 2), 3);
}
);Fail First
➜ ava-ts git:(master) ✗ npm test
> ava-ts@1.0.0 test /Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts
> ava
1 uncaught exception
Uncaught exception in __tests__/caclulator.spec.ts
__tests__/caclulator.spec.ts(4,8): error TS2304: Cannot find name 'sum'.
npm ERR! Test failed. See above for more details.Fail First
➜ ava-ts git:(master) ✗ npm test
> ava-ts@1.0.0 test /Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts
> ava
1 uncaught exception
Uncaught exception in __tests__/caclulator.spec.ts
__tests__/caclulator.spec.ts(5,20): error TS2345: Argument of type '3' is not assignable to parameter of type 'void'.Fail First
➜ ava-ts git:(master) ✗ npm test
> ava-ts@1.0.0 test /Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts
> ava
1 test failed
should summarize two numbers
/Users/andrii_kucherenko/Workspace/lab/tdd-training/ava-ts/__tests__/caclulator.spec.ts:5
4: test('should summarize two numbers', (t: ExecutionContext) => {
5: t.is(sum(1, 2,), 3);
6: });
Difference:
- 0
+ 3
npm ERR! Test failed. See above for more details.

TDD can:
- Reduce the costs
- Improve performance of development
- Help to change the project
- Reduce technical debt
Benefits
-
Bridge from task to implementation
-
Improved code
-
Tests as documentation
-
Safe refactoring
- No extra code
-
Increases assurance of correctness







Continuous Integration
- Short feedback loop
- Useful for all team (Dev, QA, BA, DM etc.)
- Reduce risks

Pair programming

Pair Programming Rules
- Ping Pong
- Silent coding
- Evil coder
- Baby steps
- ...
I don't use Pair Programming when:
- Build nonproduction code
- Work on spikes for future stories
- Learn new tool or technique
- Improve existing test coverage or fix code violations
Pair Programming Smells
- Unequal access
- Domination
- Unhealthy relationship
- Every player play his game
- Endless debate

Code Review
- Set goals & metrics
- Keep a positive code review culture
- Use checklists
- Use auto checkers (linters, style checkers, etc.)
- Small piece better than big
- Coding conventions
- ...


Emergent Design



Tools



coverage-blamer

Enzyme





https://jasmine.github.io/
describe("A suite is just a function", () => {
let a;
it("and so is a spec", () => {
a = true;
expect(a).toBe(true);
});
xit("will be skiped", () => {
a = true;
expect(a).toBe(true);
});
});
fdescribe("Focused suite", () => {
beforeAll(() => {
});
beforeEach(() => {
});
fit("focused test", () => {
expect("ololo").toEqual("test");
});
afterEach(() => {
});
afterAll(() => {
});
});expect(instance).toBe(instance);
expect(number).toBeCloseTo(number, decimalPlaces);
expect(mixed).toBeDefined();
expect(mixed).toBeFalsy();
expect(number).toBeGreaterThan(number);
expect(number).toBeLessThan(number);
expect(number).toBeNaN();
expect(mixed).toBeNull();
expect(mixed).toBeTruthy();
expect(mixed).toBeUndefined();
expect(array).toContain(member);
expect(mixed).toEqual(mixed);
expect(spy).toHaveBeenCalled();
expect(spy).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(number);
expect(spy).toHaveBeenCalledWith(...arguments);
expect(mixed).toMatch(pattern);
expect(fn).toThrow(string);
expect(fn).toThrowError(string);
spyOn(someObj, 'func').and.returnValue(42);
spyOn(someObj, 'func')
.withArgs(1, 2, 3)
.and
.returnValue(42);
someObj.func(1, 2, 3); // returns 42

https://mochajs.org/
http://www.chaijs.com/
describe('User', () => {
describe('#save()', () => {
it('should save without error', (done) => {
var user = new User('Luna');
user.save((err) => {
if (err) done(err);
else done();
});
});
});
});describe('hooks',() => {
before(() => {
// runs before all tests in this block
});
after(() => {
// runs after all tests in this block
});
beforeEach(() => {
// runs before each test in this block
});
afterEach(() => {
// runs after each test in this block
});
it.skip(() => {
// skipped cases
});
it.only(() => {
//focused tests
});
});import {assert} from 'chai';
const foo = 'bar';
const beverages = { tea: [ 'chai', 'matcha', 'oolong' ] };
// without optional message
assert.typeOf(foo, 'string');
// with optional message
assert.typeOf(foo, 'string', 'foo is a string');
assert.equal(foo, 'bar', 'foo equal `bar`');
assert.lengthOf(foo, 3, 'foo`s value has a length of 3');
assert.lengthOf(beverages.tea, 3, 'beverages has 3 types of tea');Assert
import {expect} from 'chai';
const foo = 'bar';
const beverages = { tea: [ 'chai', 'matcha', 'oolong' ] };
expect(foo).to.be.a('string');
expect(foo).to.equal('bar');
expect(foo).to.have.lengthOf(3);
expect(beverages).to.have.property('tea').with.lengthOf(3);Expect
import {should} from 'chai';
const foo = 'bar';
const beverages = { tea: [ 'chai', 'matcha', 'oolong' ] };
should();
foo.should.be.a('string');
foo.should.equal('bar');
foo.should.have.lengthOf(3);
beverages.should.have.property('tea').with.lengthOf(3);
Should

https://jestjs.io/
beforeAll(() => {
return initializeCityDatabase();
});
afterAll(() => {
return clearCityDatabase();
});
beforeEach(() => {
initializeCityDatabase();
});
afterEach(() => {
clearCityDatabase();
});
test('city database has Vienna', () => {
expect(isCity('Vienna')).toBeTruthy();
});
test('city database has San Juan', () => {
expect(isCity('San Juan')).toBeTruthy();
});beforeAll(() => console.log('1 - beforeAll'));
afterAll(() => console.log('1 - afterAll'));
beforeEach(() => console.log('1 - beforeEach'));
afterEach(() => console.log('1 - afterEach'));
test('', () => console.log('1 - test'));
describe('Scoped / Nested block', () => {
beforeAll(() => console.log('2 - beforeAll'));
afterAll(() => console.log('2 - afterAll'));
beforeEach(() => console.log('2 - beforeEach'));
afterEach(() => console.log('2 - afterEach'));
test('', () => console.log('2 - test'));
});
// 1 - beforeAll
// 1 - beforeEach
// 1 - test
// 1 - afterEach
// 2 - beforeAll
// 1 - beforeEach
// 2 - beforeEach
// 2 - test
// 2 - afterEach
// 1 - afterEach
// 2 - afterAll
// 1 - afterAlltest.only('this will be the only test that runs', () => {
expect(true).toBe(false);
});
test.skip('it is not snowing', () => {
expect(inchesOfSnow()).toBe(0);
});
test('this test will not run', () => {
expect('A').toBe('A');
});
xdescribe('All tests in this describe will be skipped', () => {
xtest('This test will be skipped', () => {
expect(true).toBe(true);
});
});describe('My work', () => {
it('works', () => {
···
})
})
expect(value)
.not
.toBe(value)
.toEqual(value)
.toBeTruthy()
expect(value)
.toThrow(error)
.toThrowErrorMatchingSnapshot()
expect(value)
.toBeInstanceOf(Class)
.toMatchObject(object)
.toHaveProperty(keyPath, value)
expect(value)
.toContain(item)
.toContainEqual(item)
.toHaveLength(number)
expect(value)
.toBeCloseTo(number, numDigits)
.toBeGreaterThan(number)
.toBeGreaterThanOrEqual(number)
.toBeLessThan(number)
.toBeLessThanOrEqual(number)expect(value)
.toMatchSnapshot()Snapshot
const fn = jest.fn();
const fn = jest.fn(n => n * n);
jest.fn().mockReturnValue('hello')
jest.fn().mockReturnValueOnce('hello')
expect(fn)
.toHaveBeenCalled()
.toHaveBeenCalledTimes(number)
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(arg1, arg2, ...)
.toHaveBeenLastCalledWith(arg1, arg2, ...)
expect(fn)
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(expect.anything())
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(expect.any(constructor))
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(expect.arrayContaining([ values ]))
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(expect.objectContaining({ props }))
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(expect.stringContaining(string))
.toHaveBeenCalledWith(expect.stringMatching(regexp))Mocks

https://github.com/avajs/ava
import test from 'ava';
test('foo', (t: ExecutionContext) => {
t.pass();
});
test.only('will be run', t => {
t.pass();
});
test('bar', async t => {
const bar = Promise.resolve('bar');
t.is(await bar, 'bar');
});
test.skip('will not be run', t => {
t.fail();
});test.before(t => {
// This runs before all tests
});
test.before(t => {
// This runs concurrently with the above
});
test.serial.before(t => {
// This runs after the above
});
test.serial.before(t => {
// This too runs after the above, and before tests
});
test.after('cleanup', t => {
// This runs after all tests
});
test.after.always('guaranteed cleanup', t => {
// This will always run, regardless of earlier failures
});
test.beforeEach(t => {
// This runs before each test
});
test.afterEach(t => {
// This runs after each test
});
test.afterEach.always(t => {
// This runs after each test and other test hooks, even if they failed
});
function macro(t, input, expected) {
t.is(eval(input), expected);
}
test('2 + 2 = 4', macro, '2 + 2', 4);
test('2 * 3 = 6', macro, '2 * 3', 6);Macros
// Passing assertion.
t.pass([message])
// Failing assertion.
t.fail([message])
// Assert that value is truthy.
t.truthy(value, [message])
//Assert that value is falsy.
t.falsy(value, [message])
// Assert that value is true.
t.true(value, [message])
// Assert that value is false.
t.false(value, [message])
// Assert that value is the same as expected. This is based on Object.is().
t.is(value, expected, [message])
// Assert that value is not the same as expected. This is based on Object.is().
t.not(value, expected, [message])
// Assert that value is deeply equal to expected. See Concordance for details.
// Works with React elements and react-test-renderer.
t.deepEqual(value, expected, [message])
// Assert that value is not deeply equal to expected. The inverse of .deepEqual().
t.notDeepEqual(value, expected, [message])
// Assert that an error is thrown.
t.throws(fn, [expected, [message]])Assertions
// Your component
const HelloWorld = () => <h1>Hello World...!</h1>;
export default HelloWorld;
// Your test
import test from 'ava';
import render from 'react-test-renderer';
import HelloWorld from '.';
test('HelloWorld component', t => {
const tree = render.create(<HelloWorld/>).toJSON();
t.snapshot(tree);
});Snapshot

https://sinonjs.org/
Standalone test spies, stubs and mocks for JavaScript. Works with any unit testing framework.
it("calls the original function", () => {
const callback = sinon.spy();
const proxy = once(callback);
proxy();
assert(callback.called);
});
Spies
it("returns the return value from the original function", () => {
const callback = sinon.fake.returns(42);
const proxy = once(callback);
assert.equals(proxy(), 42);
});Stubs
"test should call all subscribers when exceptions": () => {
var myAPI = { method: function () {} };
var spy = sinon.spy();
var mock = sinon.mock(myAPI);
mock.expects("method").once().throws();
PubSub.subscribe("message", myAPI.method);
PubSub.subscribe("message", spy);
PubSub.publishSync("message", undefined);
mock.verify();
assert(spy.calledOnce);
}Mocks
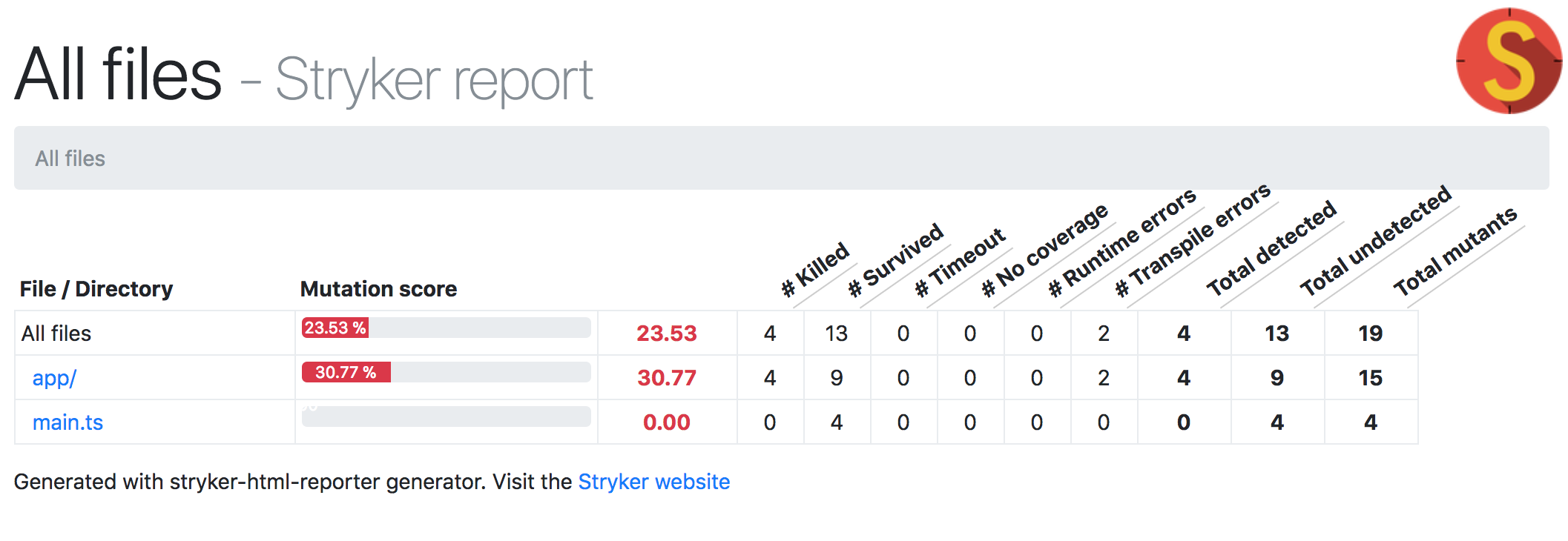
Mutation Testing

Mutation testing (or mutation analysis or program mutation) is used to design new software tests and evaluate the quality of existing software tests. Mutation testing involves modifying a program in small ways.[1] Each mutated version is called a mutant and tests detect and reject mutants by causing the behavior of the original version to differ from the mutant. This is called killingthe mutant. Test suites are measured by the percentage of mutants that they kill. New tests can be designed to kill additional mutants. Mutants are based on well-defined mutation operators that either mimic typical programming errors (such as using the wrong operator or variable name) or force the creation of valuable tests (such as dividing each expression by zero). The purpose is to help the tester develop effective tests or locate weaknesses in the test data used for the program or in sections of the code that are seldom or never accessed during execution. Mutation testing is a form of white-box testing.


and TypeScript

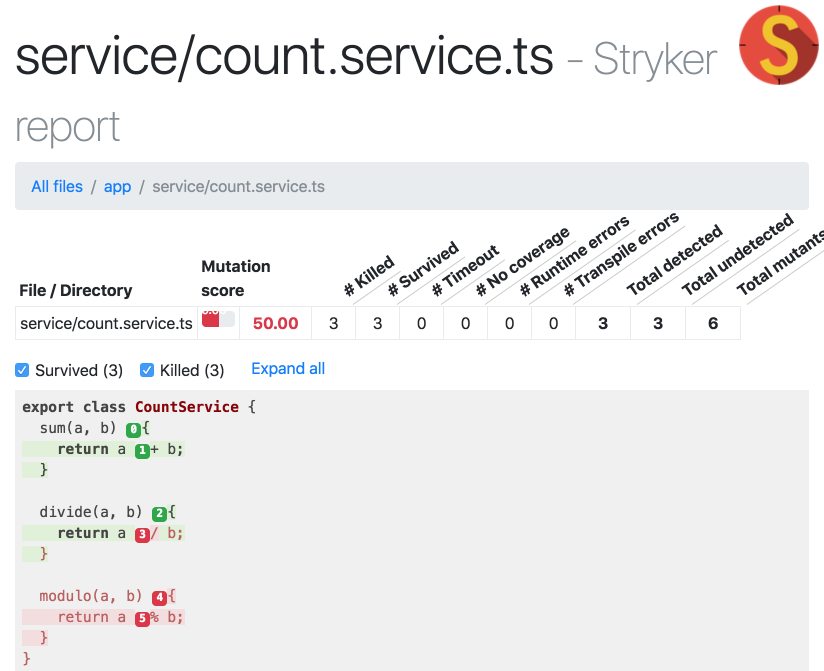
export class CountService {
sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
divide(a, b) {
return a / b;
}
modulo(a, b) {
return a % b;
}
}
describe('Count Service', () => {
let sut;
beforeEach(() => {
sut = new CountService();
})
it('should sum numbers', () => {
expect(sut.sum(2, 2)).toEqual(4);
});
it('should get divided numbers', () => {
expect(sut.divide(2, 1)).toEqual(2);
})
});

Unit Tests
Anti-patterns
Liar
Slow Poke
Giant
Mockery
Stranger
Inspector
Generous Leftovers
Local Hero
Nitpicker
Conjoined Twins
Anal Probe
Test-per-Method
https://github.com/kucherenko/tdd-training
String Calculator
Create a simple String calculator for extracting numbers from string and summarize them.
- The calculator can take 0, 1 or 2 numbers, and will return their sum (for an empty string it will return 0) for example "" or "1" or "1,2"

Create a simple String calculator for extracting numbers from string and summarize them.
- ...
- Allow the calculator to handle an unknown amount of numbers

Create a simple String calculator for extracting numbers from string and summarize them.
Allow the calculator to handle new lines between numbers (instead of commas).
- the following input is ok: “1\n2,3” (will equal 6)
- the following input is NOT ok: “1,\n” (not need to prove it - just clarifying)

Create a simple String calculator for extracting numbers from string and summarize them.
- ...
- ...
- ...
- Support different delimiters

Create a simple String calculator for extracting numbers from string and summarize them.
Calling Add with a negative number will throw an exception “negatives not allowed” - and the negative that was passed.
if there are multiple negatives, show all of them in the exception message.

Navigation maps #1
- return 0 if ""
- return number if "number"
- return a + b if "a,b"

Navigation maps #2
- Parse string by coma
- Validate parsed data
- Summarize results

Game Of Life
Flower Pot Application
Thank you
