Test Automation
OBS -> OpenQA

OpenQA test group
By clicking colored circle we can access test settings

Assets Registration
- Every test has settings;
- Assets must be registered by present in job settings with corresponding prefix; (ISO_, REPO_, HDD_, ASSET_);
- Every test group has limit for combined assets size;
- Nightly job cleans up assets which exceed limit.

Settings are defined in REST

Automation challenges
- Every synced iso, hdd, repo, etc must be registered in isos post command. (For every architecture, flavor, build, etc).
- Synced files must be often renamed (e.g. include build or staging letter, etc).
- Cross repositories builds (E.g. test jeos with corresponding repos).
- Cross product builds (E.g. test RT build with corresponding SLE packages).
- Every product has own naming conventions.
- Huge repositories, often doesn't change much.
- Long running tests, failure needs to be reproducible.
- When and what is it safe to sync.
- Must be easy to troubleshoot.
- Must be easy to test.
3 step approach
-
Prepare - read file names from OBS.
-
Sync - sync files that were read in first step.
-
Invoke - call isos post commands.
Benefits
-
Easy to test (needs remote access only on the first step).
-
Preview commands before executing.
-
Eeasy to troubleshoot and alter (e.g. resync only one architecture)
In Sync and Invoke steps bash commands are generated, then executed.
Step 1
Prepare: read file list (no sync, no rest call)
Open Build Service -> files_iso.lst files_repo.lst
Step 2
Sync: (rsync, mv, bztar)
files_iso.lst files_repo.lst -> bash commands
Step 3
Invoke: (isos post, news generation)
files_iso.lst files_repo.lst -> bash commands
3 steps approach - config
Scripts for all 3 steps are generated from XML file, which must describe every asset, flavor and architecture.

3 steps approach -
testing and troubleshooting
No need neither OpenQA nor OBS for Step 2 and Step 3.
Just need .lst files
Store .lst files for each sync to understand if Sync is required
Sync Folders
Synchronization logs and scripts are stored in folders on openqa host.


Each folder is working area for sync of corresponding project and has list of current files, scripts for each step, logs, diagnostic info, etc.
Sync Dashboard
Information from sync folders is accessible in OpenQA UI (needs advanced access level)

Scripts and logs are accessible in UI as well

Starting sync
- Automatic - botmaster redirects Rabbit-MQ message (safe)
- Manual - UI button (safe)
- Manual - command line (less safe)
- Sync will do no action if list of files read on first step (Prepare) matches files in last sync (stored in .run_last link).
- To force re-sync of the same files .run_last link must be removed.
- When sync is started by OpenQA Plugin - it will wait for status of the project on OBS to be 'published'. (safe).
- If sync is started from command line - it may meet race condition with OBS building.
Starting sync - Automatic
- botmaster already receives Rabbit-MQ messages about project builds completion;
- botmaster asks OpenQA Plugin for list of projects which need to be notified.
# grep openSUSE:Factory:ToTest /var/log/apache2/access_log* | grep PUT
[24/Mar/2020:21:29:28] PUT /api/v1/obs_rsync/openSUSE:Factory:ToTest/runs?repository=images
[24/Mar/2020:22:49:11] PUT /api/v1/obs_rsync/openSUSE:Factory:ToTest/runs?repository=appliances
Prefixes of projects to notify are configured as parameter to call rabbit-repoid.py:
https://github.com/openSUSE/openSUSE-release-tools/blob/master/gocd/monitors.gocd.yaml
Starting sync - UI (needs admin access)
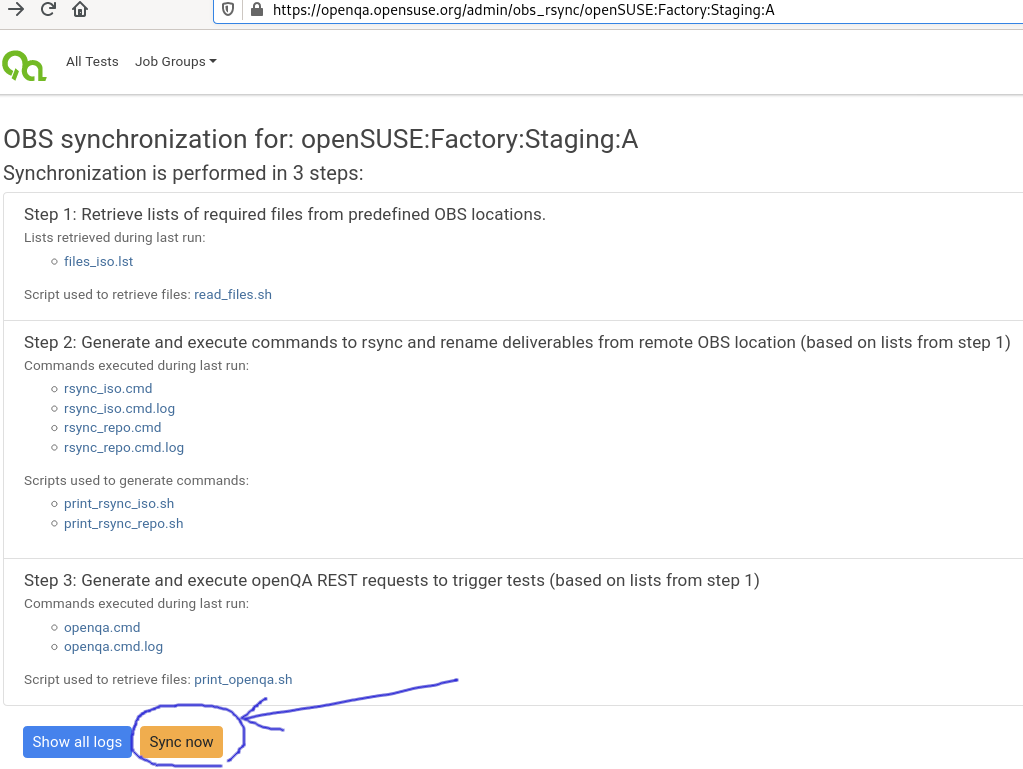
Starting sync - command line
# script/rsync.sh openSUSE:Factory:Staging:A
This is unsafe, because may meet race conditions when project files are changed on OBS during sync
If generated files are incorrect, it is possible to capture the commands for corresponding step and modify generated output. E.g. to modify output of rest commands - capture output of print_openqa.sh script and modify as needed. Then execute altered commands in shell.
To force resync - remove .run_last link first
# rm openSUSE:Factory:Staging:A/.run_last