Fragments

Fragments
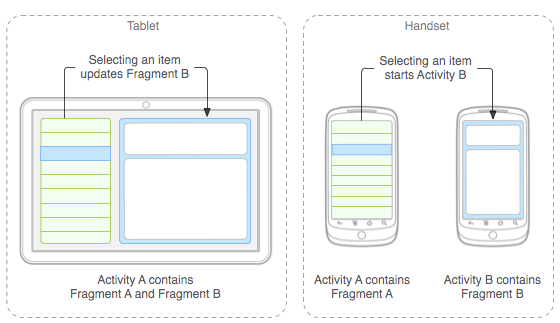
- Los fragments son porciones de interfaz en una
activity (una especie de «sub-activity») - Tienen sus propios ciclos de vida, inputs del usuario
y se pueden añadir, eliminar o reemplazar mientras
la activity está activa. - Se crearon para android 3.0 para pantallas más
grandes (tablets), y se han adaptado para 4.0
permitiendo mostrar distinto contenido según el
tamaño de la pantalla del dispositivo.
Fragments
Ciclo de Vida
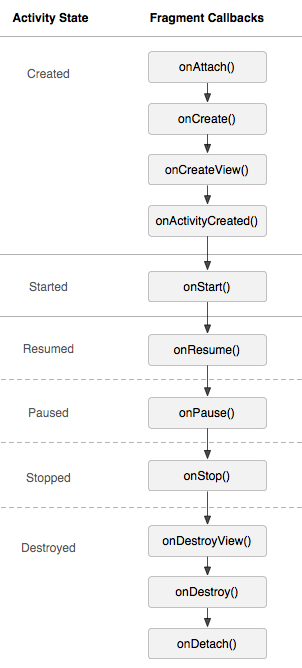
Nuevas llamadas
- OnAttach(..): Se llama cuando se associa a la activity
-
OnCreateView(..): Se llama para generar la vista del Fragment
- Lo implementa el programador
-
onActivityCreated(...): Se llama cuando la activity esta creada
- Solo se llama si l'activity pasa por onCreate()
- onDestroyView(...): Se llama para limpiar recursos de la vista
- OnDetach(...): Se llama cuando se retira de la activity
Ejemplo(I)
public static class ExampleFragment extends Fragment{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.hello_world, container, false);
}
}Añadir un fragment
- 2 metodos
- estático: poniendo el fragment en el layout xml
- dinámico: por codigo
Añadir un fragment
Estático
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<fragment android:name="com.example.android.fragments.HeadlinesFragment"
android:id="@+id/headlines_fragment"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<fragment android:name="com.example.android.fragments.ArticleFragment"
android:id="@+id/article_fragment"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentById( R.id.static_fragment );
Al añadir fragments de este modo, no se pueden eliminar en runtime.
Añadir un fragment
Dinámico
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fragment_container"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fragment_container2"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>Podemos usar FrameLayouts e inflar los fragments más tarde.
Añadir un fragment
Dinámico
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.fragment_container, firstFragment).commit();
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.element, firstFragment).commit();
Remplazando otro elemento
Comunicación de fragments
- Podemos usar la activity para comunicarnos con el resto de fragments de la activity
- Para ello hemos de:
- Definir una interface en el fragment
- Implementar dicha interface en la activity
Comunicación de fragments
Ejemplo
public class HeadlinesFragment extends Fragment {
OnHeadlineSelectedListener mCallback;
//La activity ha de implementar esta interface
public interface OnHeadlineSelectedListener {
public void onArticleSelected(int position);
}
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
// Nos aseguramos que la activity implementa la interface
try {
mCallback = (OnHeadlineSelectedListener) activity;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
throw new ClassCastException(activity.toString()
+ " must implement OnHeadlineSelectedListener");
}
//podemos llamarlo para comunicarnos con la activity
mCallback.onArticleSelected(pos);
}
}Fragments sin UI
- Podemos añadir un fragment sin layout (por ejemplo un dialog), pero entonces debemos definir un Tag en el fragment para poder identificarlo desde el código para editar o eliminar ese fragment.
- Para ello haremos: .add(Fragment, String tag)
- y lo buscaremos con: findFragmentByTag (String tag)