[CSAL] Comm. and Internet Technologies
Network Topology
-
show understanding of a bus topology network and the implications of how packets are transmitted between two hosts
-
show understanding of a star topology network and the implications of how packets are transmitted between two hosts
In Data communications
- Sender
- Receiver
- Transmission medium - Carry the message, physical
- Message - Both ends required to have an agreed protocol to send
- Protocol
Network Topology - how physically devices connected in a single (isolated) network
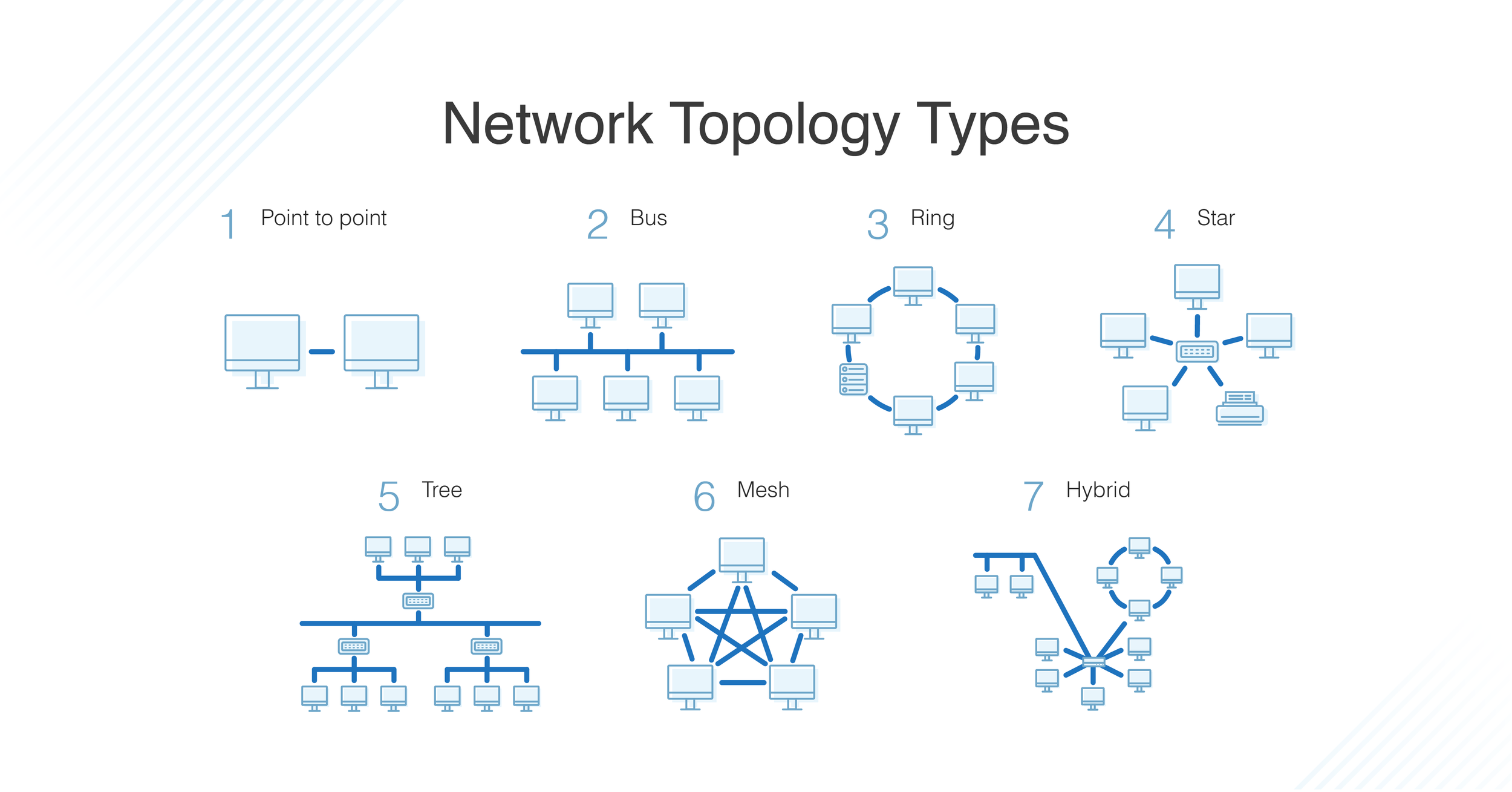
| Name and diagram | Description | Adv/Disadv | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point-to-point |
|||
| Bus |
|||
| Ring |
|||
| Star |
|||
| Mesh |
| Name and diagram | Description | Adv/Disadv |
|---|---|---|
| Point-to-point |
Two nodes connected directly | |
| Bus |
All devices shared a central "Bus", all data sent in a bus is broadcasted | |
| Ring |
Each end system has a point-to-point connection to the two adjacent end-systems | |
| Star |
All nodes connected to a central device | |
| Mesh |
Each node has a point-to-point connections to every single node |
Network Hardware Devices
-
show understanding of a wireless network
-
explain how hardware is used to support a LAN: switch, router, servers, Network Interface Cards (NICs), wireless access points
-
show understanding of Ethernet and how collision detection and avoidance (such as CSMA/CD) works
Wireless Networks
| Tech | Distance | Bandwidth | Radio Freq | Typical Usage | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth v2 | |||||
| Bluetooth v4 | |||||
| 802.11n | |||||
| 802.11ac | |||||
| 1G | Voice Comm. | Analog Only | |||
| 2G | Voice Comm. | ||||
| 3G | |||||
| 4G | |||||
| 5G |
Research and complete the table
LAN hardware
- Router
- Routes (path planning) for packet from one network to another
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- The hardware component that allows the device communicate with other devices
- Wireless Access Point (AP)
- Hardware device allow other WiFi device to connect to wired network
- Hub / Switch
- Provide wired connection to multiple devices, distribute packets to connected devices
- Central device in a Star network

Hub vs Switch
-
Hub
- "broadcast" all incoming message
- i.e. re-transmit to all connected devices
-
Switch
- inspect the packet to determine the destination of the packet
- Only forward the message to designated recipient
- Switch work in Layer 2 (Data link layer) of OSI model, and it inspect the MAC address of the packet
TCP/IP Protocols
- Show understanding of why a protocol is essential for
communication between computers - Show understanding of how protocol implementation
can be viewed as a stack, where each layer has its own
functionality - Show understanding of the TCP / IP protocol suite
- Show understanding of protocols (HTTP, FTP, POP3,
IMAP, SMTP, BitTorrent) and their purposes
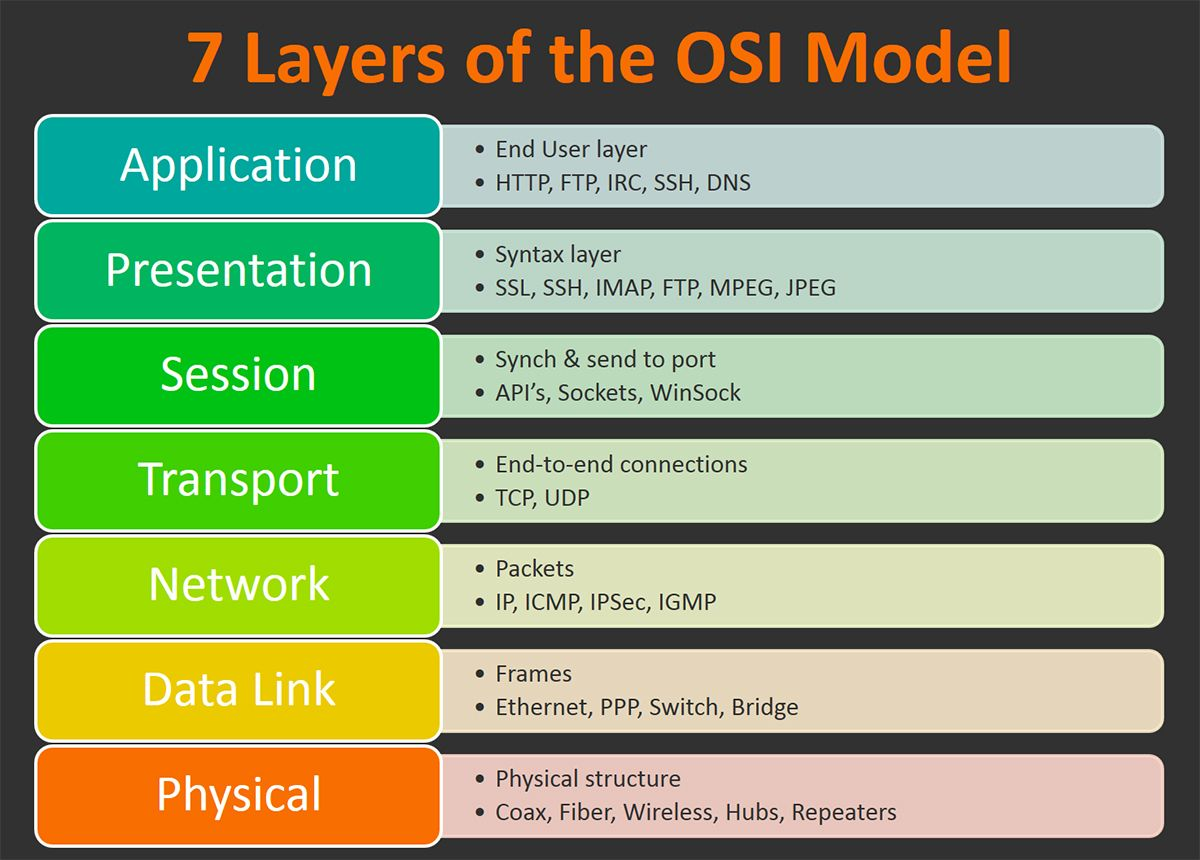
TCP/IP Protocols
- TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
- IP - Internet Protocol
- TCP/IP Suite is a stack of many different protocols:
- Link Layer (network interface)
- Network layer
- Transport layer
- Application layer
- Upper layer will communicate with the next immediate layer and relying on it to take care all lower level actions
- e.g. HTTP (application layer) can send data via any physical layer (e.g. ethernet, bluetooth) without changing any implementation, since it relies on TCP (transport layer) only
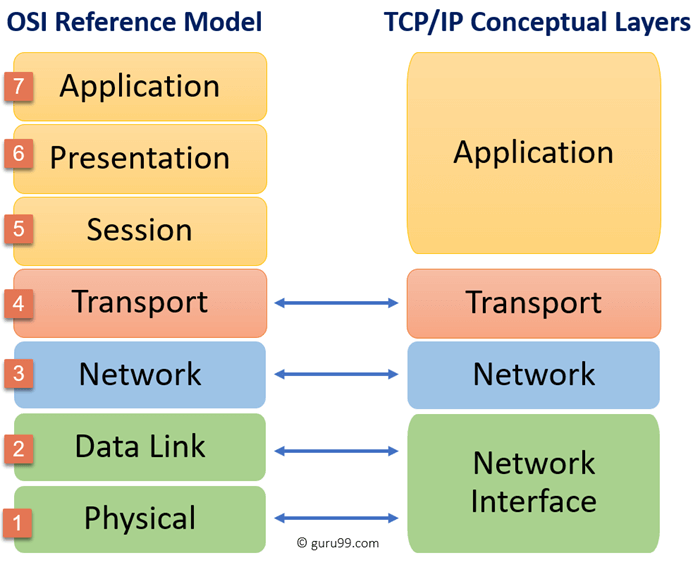
OSI compares to TCP/IP model
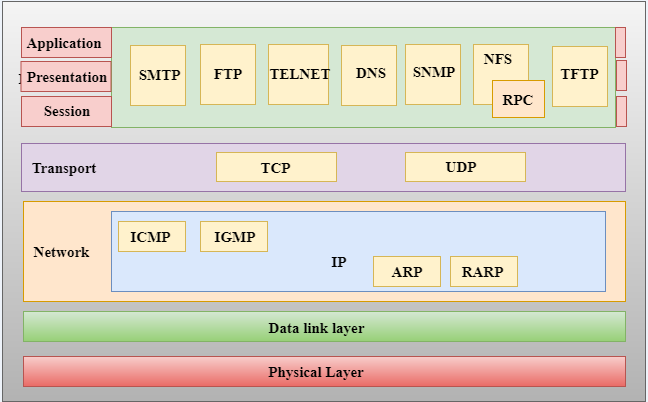
TCP/IP model with some example protocols
Network Layer (OSI layer 3)
- Data packets
- Internet Protocol, IP Address
- Ensure data packet correctly routed over the Internet
- Router is a layer-3 device which compares to switch is layer-2
- Router routes data packets (with IP address)
- Switch distributes data frames (with MAC address)
- What about hub?
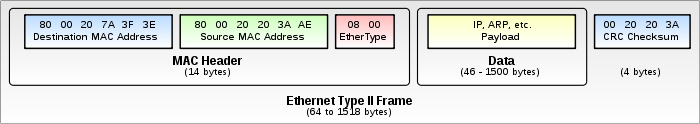
Ethernet Data Frame
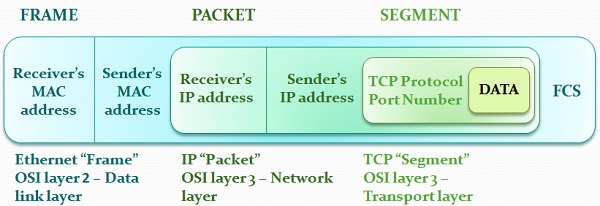
Dataframe vs Data packet
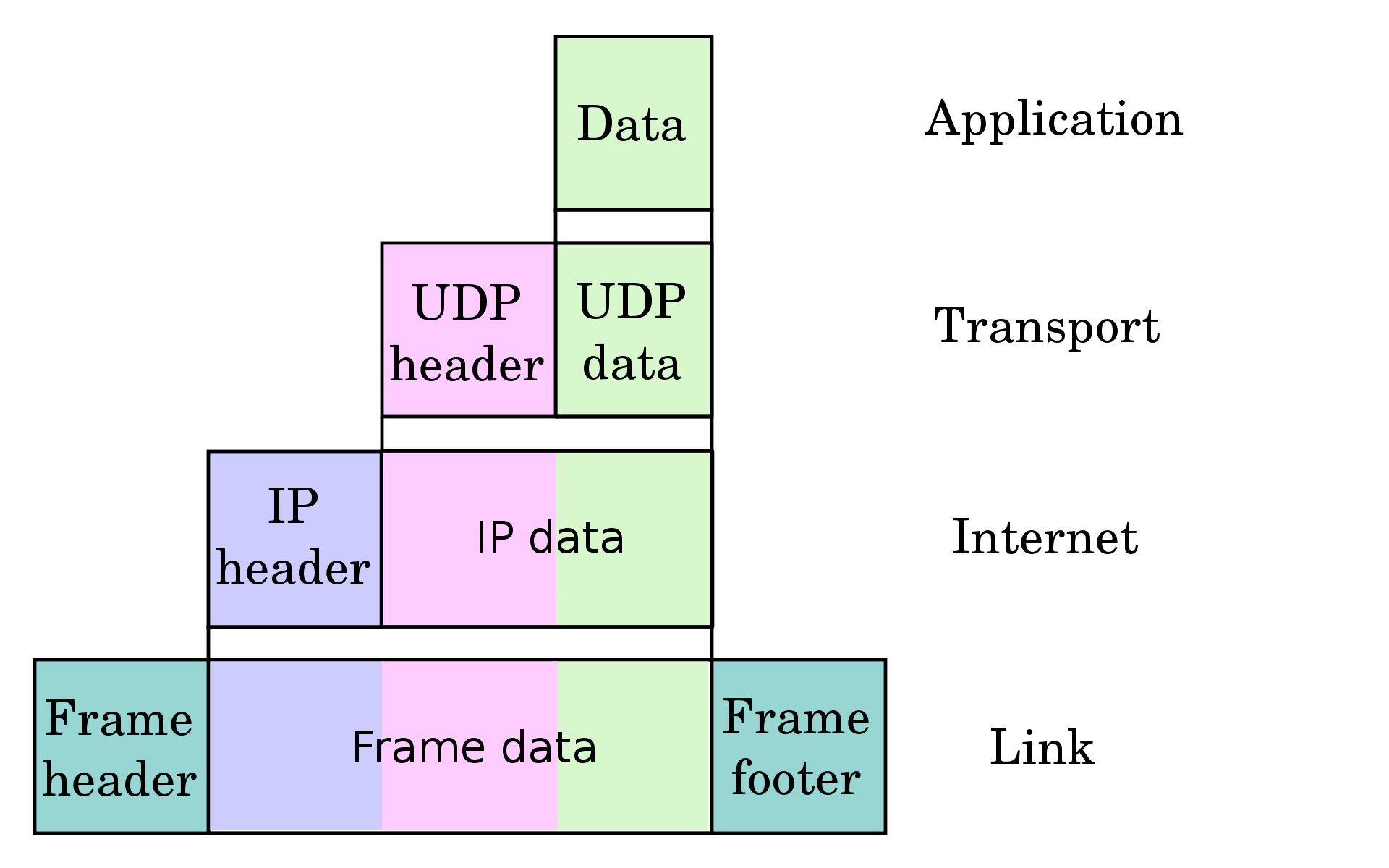
Data is wrapped in different layers across TCP/IP Suite
Transport Layer (OSI Level 4)
- TCP
- ensures message is safely delivered to the receiver
- also ensure response can be directed back to the application protocol
- On top of IP address, port is defined
- Port is virtual and refers to different communication channel over the same IP address
- TCP is connection-oriented, which means a virtual connection will establish between devices, while IP or lower levels are connection-less
Application Protocols
- HTTP/S
- FTP
- P2P
FTP
- File Transfer Protocol
- Design for clients to upload and download files from a file server
| POP3 | IMAP | SMTP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full name | |||
| Function Features |
Email Protocols
P2P Protocol
- BitTorrent is a peer to peer (p2p) protocol which allows files to be shared, without hosting the files in server
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6PWUCFmOQwQ
- Watch and answer:
- How BT different from downloading from server
- What is Tracker and Peer
Transmission Modes
- show understanding of circuit switching and where it is applicable
- show understanding of packet switching
- show understanding of the function of a router in packet switching
- explain how packet switching is used to pass messages across a network, including the Internet
Circuit Switching
- Circuit switching requires establishing dedicated physical connection between devices
- Example: Traditional Telephone switching system (PSTN)
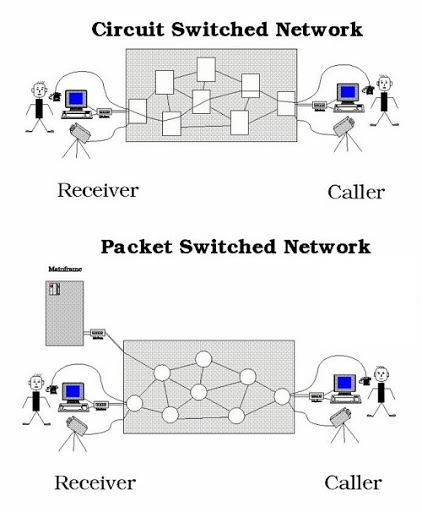
Packet Switching
- Instead of dedicated connection, connections are shared in packet switching
- Data is splitted into small chunks, call packets
- Each packet has headers identifying source and destination address, along with other control data
- Packets take different pathway to the destination
- On the Internet, packets are forwarded by Router