[F4CS] File formats and Compression
- show understanding that sound (music), pictures, video, text and numbers are stored in different formats
- show understanding of the concept of Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) files, JPEG files, MP3 and MP4 files
- show understanding of the principles of data compression (lossless and lossy) applied to music/video, photos and text files

Objectives
Data compression
- Reduce the size of data, using compression algorithm, during transmission or store in file
- Advantages:
- Faster transmission (less bandwidth required)
- Save storage space
- Disadvantages:
- Slower access time - data must be decompressed before use
- More memory and processing time is needed
Lossless compression
- The compressed data can be recovered (decompressed) without loss of data
- i.e. the original data before compression can be 100% retrieved after the data is compressed and decompressed
- Common application:
- File compression (.zip, .rar)
- Text file (.txt)
- Transmitting data through Internet (e.g. HTTP data are often compressed nowadays)
- Lossless compression are not very effective in multimedia files
How Lossless works?
- One lossless compression algorithm is called RLE (Run-length-encoding)
- e.g. consider the following string of pixels:
- BBBB BBBB WWWW BBWW - 16 Bytes
- RLE will only record the pattern and how many repetitions such that the compressed string became:
- B8 W4 B2 W2 - 8 Bytes
- Other lossless compression algorithm may work on longer repeating patterns (e.g. the word algorithm appears 3 times on this page, we can give that word an index (number) and replace all occurrences with that number)
Lossy compression
- During compression, some data is removed permanently (cannot retrieve after decompressed)
- Lossy compression works well in multimedia files,
- e.g. a 20MB picture can usually reduce to 1MB without sacrificing a lot detail using JPEG
- Common lossy compression files:
- JPEG (or jpg)
- NOTE: PNG is lossless
- MP4
- MP3
- JPEG (or jpg)
How Lossy compression works?
| 100 | 105 | 110 | 201 | 220 |
| 101 | 102 | 104 | 210 | 201 |
| 102 | 103 | 120 | 200 | 210 |
| 100 | 80 | 50 | 54 | 54 |
| 100 | 82 | 50 | 55 | 48 |
| 105 | 105 | 105 | 210 | 210 |
| 105 | 105 | 105 | 210 | 210 |
| 105 | 105 | 105 | 210 | 210 |
| 100 | 81 | 52 | 52 | 52 |
| 100 | 81 | 52 | 52 | 52 |
Original image (pixel value)
Lossy compressed
- Consider the above as a portion of an image, showing the value of individual pixel
- Lossy compression algorithm will group pixels with similar color (value), and assign them with same color (usually average)
- The image now consisted of many repeated pattern, so method such as RLE can be applied to reduce the size
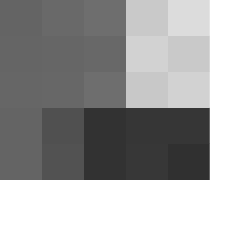


- The rightmost image is highest compressed so those color patch (neighbor considered as "similar" are grouped) are very obvious, while the middle one is almost not noticeable compare to original
- Note about the efficiency of lossy compression, the middle image is almost identical to the original but size is 85% smaller
Audio file formats
- Uncompressed sound waves are stored as .wav files, which stores the amplitude of the sound waves
- .mp3 is a type of lossy compression works on audio data
- e.g. a 3-minute CD quality audio file is about 30 MB in size, while compressed in mp3 is about 2-3 MB
- MP4 is a file format for audio and video, also a standard format for internet video nowadays
MIDI
- Musical Instrument Digital Interface
- A file format (.mid) and also refers to the protocol of electronic instruments
- When music is stored in MIDI, it is not recording the sound wave, but the followings:
- Types of instrument (e.g. Grand Piano)
- Note played
- Loudness
- Duration etc.
- MIDI can only store music (without vocal)
- Very small file size