[ITal] Communication Technology
Types of network
- https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/6152aed02d1b75001da773cb
Network Components
- Objectives:
- The role of components in a network:
- network interface cards and wireless network interface cards repeaters, hubs, and switches wireless access points, gateways, bridges and routers firewalls (hardware and software)
- The operations of networking components:
- how each component carries out its role
- how each component works with the others in a network
- The role of components in a network:
Refer to Worksheet - no difference from F4 ICT
Routing data in network
- https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5f7c191d0e6742001b1371f8
Networking Server and protocols
- Objectives
- Types of network server
- The role of servers in a network
- The operations of servers in a network
- Advantages and disadvantages of each type of server for a given scenario
- The definition of a protocol
- The purposes and uses of protocols in the preparation, addressing, sending and receiving of data across networks including the internet
Network Server
- Servers "serves" data, content or provide services to networked devices
- Use the Client-Server Model:
- Client make "request" from server
- Server "response" to client
- Server computer are usually more powerful computer that able to serve multiple clients
(Network) Protocol
- A network protocol is an established set of rules that determine how data is transmitted between different devices in the same network
- include: data format, sequence of communication, command etc...

Example of how client-server works - HTTP Server
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kBXQZMmiA4s
- HTTP Client (e.g. Browser) initiate connection to server, and send a request to server
- HTTP Server received the request from client, and response with appropriate content / data
- Note:
- In order for client to connect to server, the "IP Address" of server is required
- Server will NOT initiate connection in client-server model, any communication must start with client
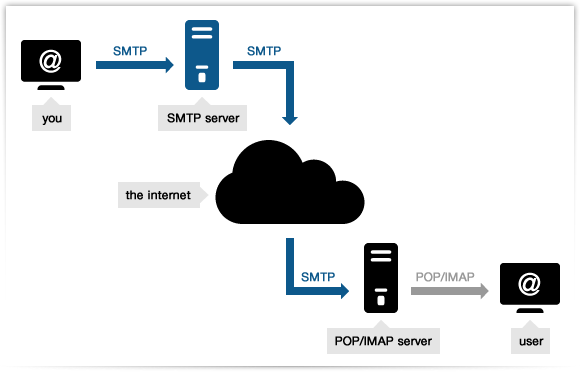
Mail Server and Protocol
Overview on how mail server works
Email Protocols
- There are 3 major protocols in Email:
- SMTP - sending email from client to server / server to server
- IMAP and POP3 - client receiving emails that is stored in server
- POP / POP3 - mail client (e.g. outlook) get the email from server and server will not keep copy (just like how a physical mailbox behave)
- IMAP - mail client can read / retrieve email from server and copy stays in the server unless user request to delete
- Note: Web based email client like Gmail may work differently, but SMTP still required to move data between mail servers
FTP
- FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol
- Which is superseded by FTPS or SFTP for added security
- FTP intended for transferring and managing files
- Allow upload, download, delete, rename etc. operations
- Files are stored in, FTP Server
- File access can be controlled by authentication (username and password)
- Note:
- While HTTP is more frequently used in file sharing nowadays (e.g. Cloud drives), FTP is designed to work better with large files
- Not commonly used, but some business users will use FTP
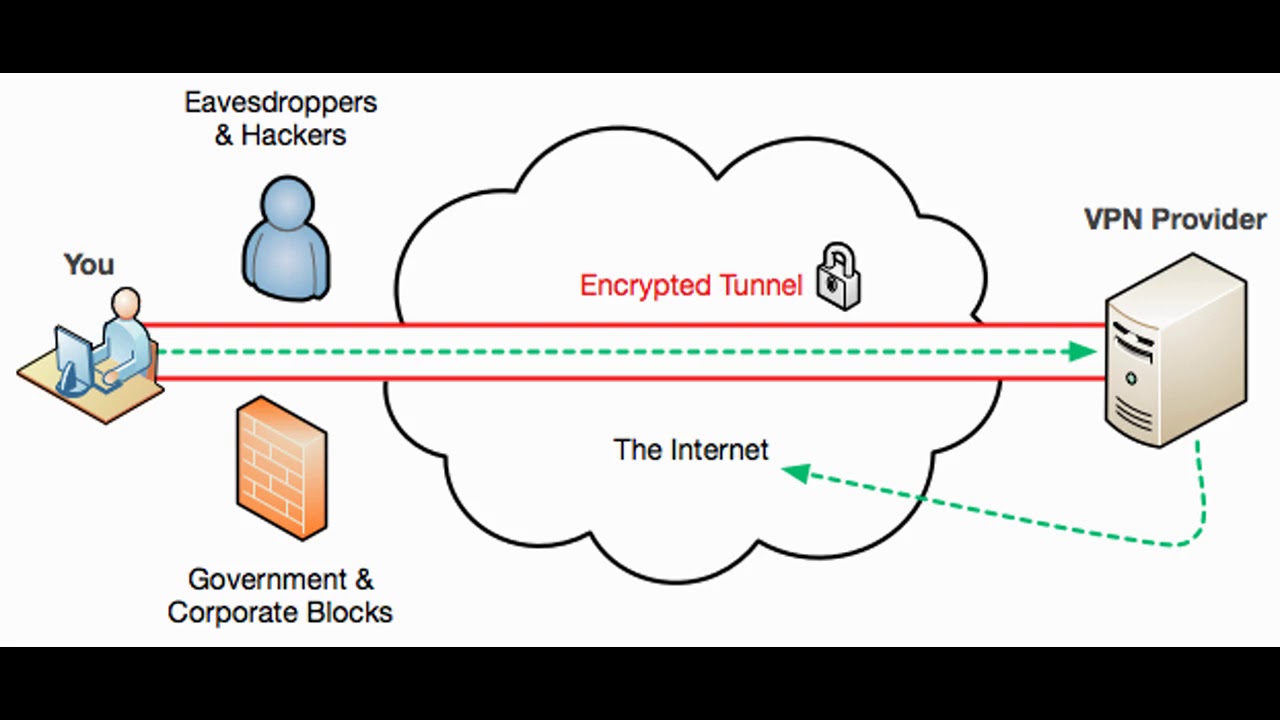
Tunneling Protocols
- Protocols to connect to a VPN server, one example is L2TP
- Tunnels is encrypted
- User can access to LAN (which VPN server locates) from outside or hiding his real location since accessing Internet is done by the VPN server (similar to proxy in this case)
Virtual Server
- Virtual server allows multiple "virtual machines" to run on the server, each machine has it's own virtual hardware like CPU, RAM etc.
- Each VM is running their own operating system, which basically isolated from each other

Virtual Server (cont'd)
- OS, application software running on VM did not aware it is running on VM. i.e. identical to running on dedicated hardware
- Hardware like CPU or RAM is shared amount those VMs
- Advantages:
- VMs can have better utility on the physical machine
- Different VMs have different copies of OS, hence they won't affect each other => Secure
- Cheaper hardware cost and maintenance compare to multiple physical machine
- Allows full (virtual) machine backup in host server
- Disadvantages:
- Slight discount on hardware performance
- Not suitable for already heavily loaded servers
OSI Layers, WAN and LAN Protocols
- https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5f83e012afd3e8001b492819
- Worksheet on additional protocols
- https://www.dummies.com/programming/networking/layers-in-the-osi-model-of-a-computer-network/
Data Transmission methods
- The properties, features and characteristics of different transmission methods
- Typical applications of each method
- Advantages and disadvantages of each method
Satellite System
- How satellite communication systems are used for transferring data
- in global positioning systems (GPS), in global mapping
systems, in surveillance, in telecommunications (e.g.
television and radio broadcasting, telephones) - how communications data is prepared, sent and received by satellite communication systems
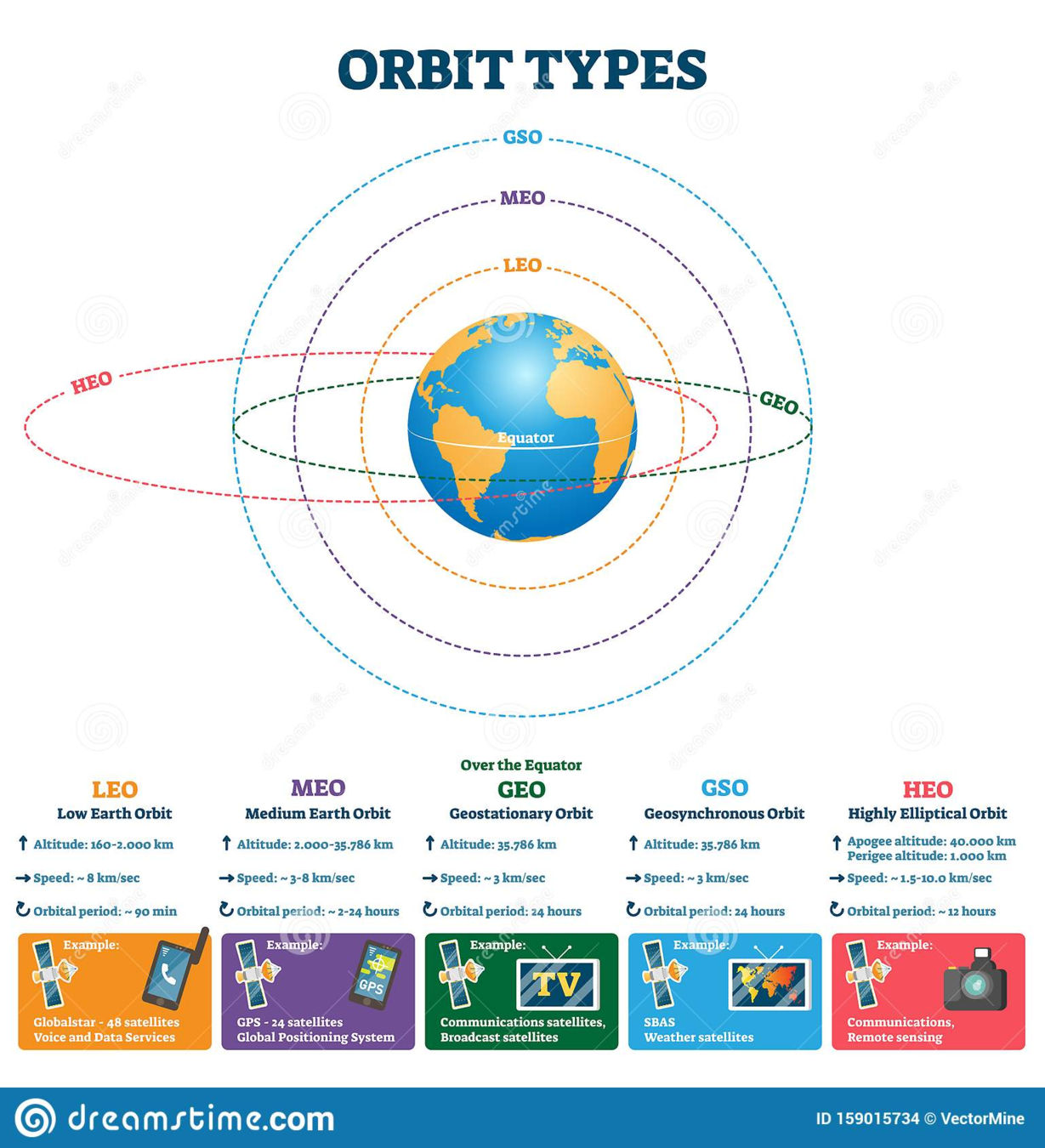
Types of Satellites
- Which is defined by how far away from earth:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO), < 2000 km
- e.g. Voice and data services
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), between LEO and GEO
- e.g. GPS
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO), about 35,700 km
- GEO orbits in synchronous with the earth, so from ground it seems it is not moving
- e.g. Satellite TV
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO), < 2000 km
- The further the satellite, the less you can cover the whole planet
- But it also increase latency, e.g. light/Em Wave takes about 0.1s from ground to GEO, which is <0.01s on LEO
Satellite TV
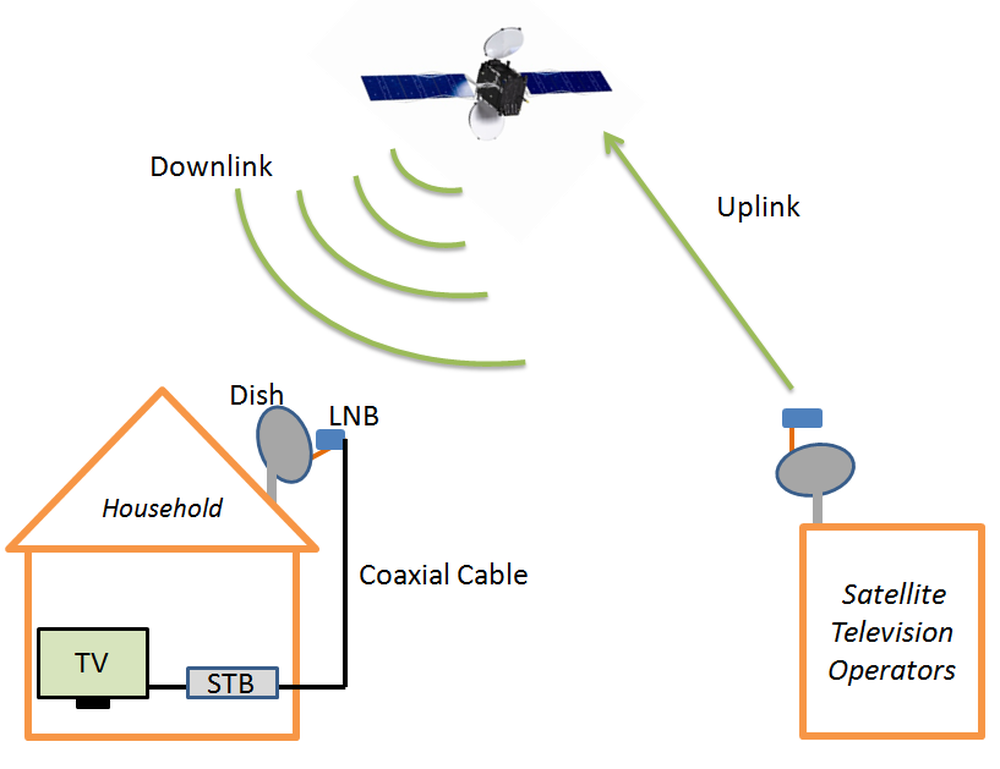
Satellite TV
- Program source create the content and pay the broadcast company to air their content
- Broadcast Center collects signals (channels) from sources and beam (uplink) the signal to the GEO satellites
- GEO satellites received the signal and send back to earth (downlink)
- Viewer's dish antenna is setup to face the satellite direction, and receive the signal from it
- Signal passes to home, usually decoded by set-top box and view on TV
- GEO is used since it is "fixed" from viewer/broadcaster's point of view, also only 5-6 is needed for global coverage
Satellite Phone
- Provides voice call service similar to mobile phones, but data is transmitted through satellites instead of cell towers
- Depending on carrier, some are using LEO and some are GEO
- Compare to mobile phone it can cover remote area where there's no mobile cell tower coverage
Satellite Data
- Most home Internet connection is by broadband (telephone line) or optical fiber nowadays
- Telephone line are much lower in terms of bandwidth, while optical fiber is very expensive
- Not cost effective to cover remote areas
- Starlink - by SpaceX is a project that sends thousands of LEO (550km) satellites to provide high speed and low latency Internet connection
- Also other types of satellite data provider, mainly for field survey / scientific research purpose
- Bei Dou, the Chinese (GPS) satellite system, can also provide two-way data transmission services
GPS
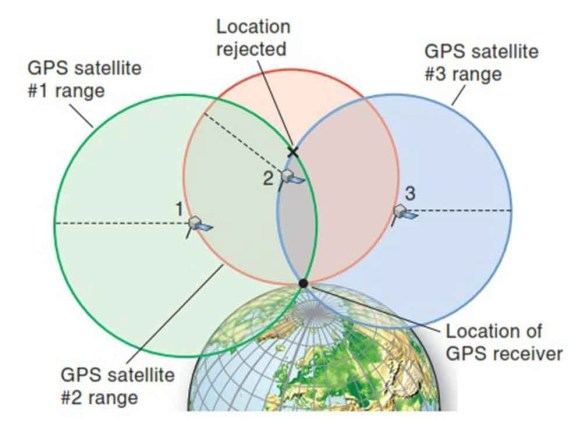
Global Positioning system
- GPS satellites are MEO, there are 24 GPS satellites altogether
- GPS receiver (e.g. smartphone) picks up the signal from at least 3 GPS satellites which includes:
- time of sending, location of the satellite
- Receiver compares the time of receiving that particular signal, calculate the time of travel of that signal
- With the time of travel and position, it can use to calculate it's location on earth
- Usually 4th satellite signal is needed for verification purpose
- Note GPS receiver will NEVER send data to GPS satellites, it only receives
- Since the signal travel in light speed, the time must be calibrated accurately (with 0.1 ms), calibration data also comes from GPS satellites
Security threats
- Networking security threats to stored data and files
- Impact of network security threats on individuals and organisations
- Prevention of network security issues using physical and software methods
- Advantages and disadvantages of the various methods
Activity
- On each card, put the name and draw the security measure / threats to network computer system
- On the back, write the description (how it works) and:
- threats: impact of the threat, what measure can protect it from
- security measure: what can it protect from