SFD
Software Freedom Day (SFD) is an annual worldwide celebration of Free Software. SFD is a public education effort with the aim of increasing awareness of Free Software and its virtues, and encouraging its use.
Let's start Networking...
Topics
- Networking Basics
- OSI
- Types of Network and Networking Devices
- Ports
- IP Concepts
- Protocols
- Network Security
- Wireshark
Networking
Networking is connecting devices together so that they can communicate with each other, in order to share data, files, and computing resources.
Networking happens all around us, In our PCs, ATMs, cell phones, and much more.
Networking Communication
1- Broadcasting refers to transmitting a packet that will be received by every device on the network.
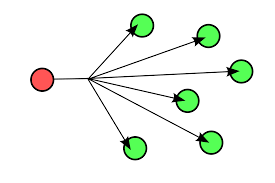
Networking Communication
2- Unicast is communication between a single sender and a single receiver over a network.
3- Multicast (one-to-many or many-to-many distribution) is group communication where information is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously.
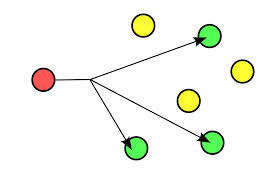
Networking-Types
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
Text

Text

HUB/REPEATER
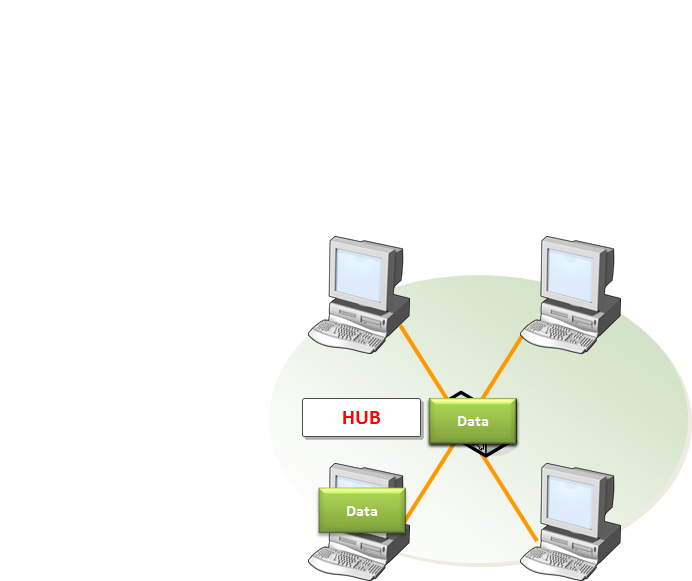
Functions of Hub
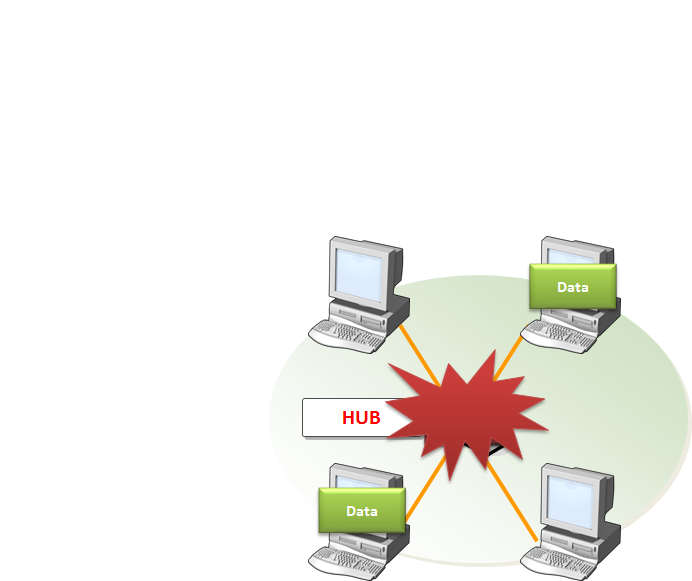
Functions of Hub

Switch
Functions of a Switch

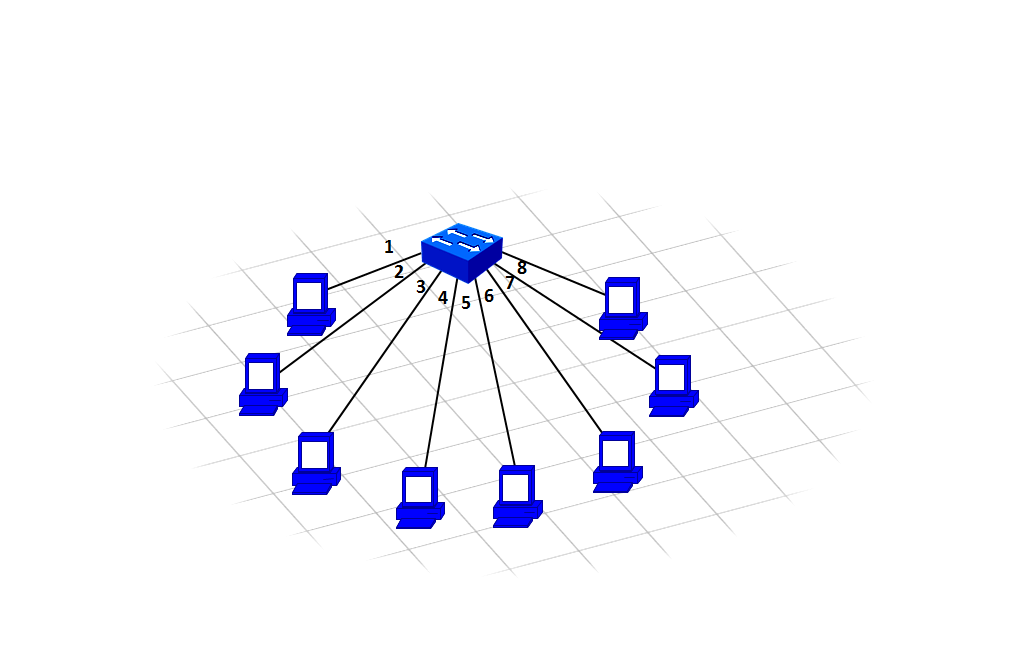
Function of a Switch
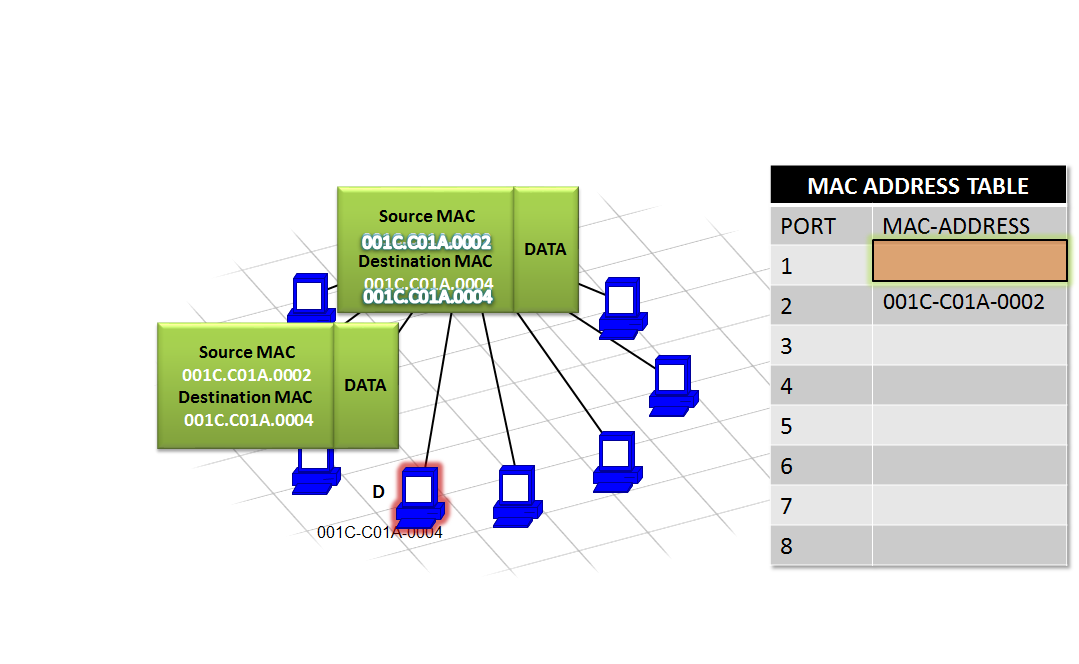
Functions of a Switch
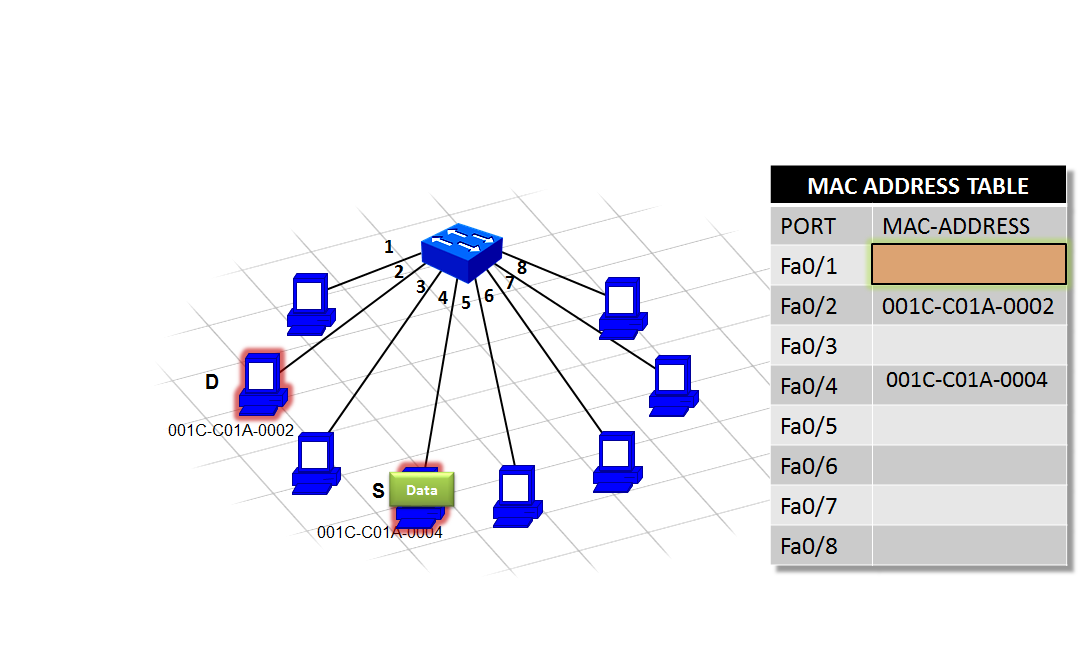
Functions of Switch

Router

IP Address

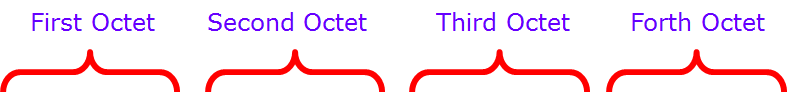
IP Version 4
IP Concepts
There are five classes of available ip ranges.
class A: ip ranges - 1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254
class B: ip ranges - 128.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254
class C: ip ranges - 192.0.1.1 to 223.255.255.254
class D: ip ranges - 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.254
Reserved for multicast
class E:ip ranges - 240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254 Reserved for research and future use
OSI
- OSI was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and introduced in 1984.
- It is a layered architecture (consists of seven layers).
- Each layer defines a set of functions which takes part in data communication.
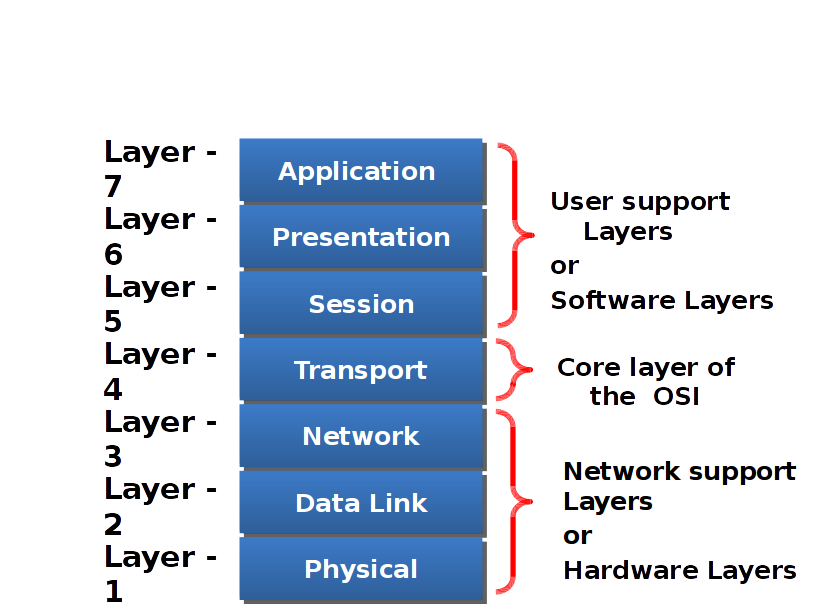
OSI Model Layer
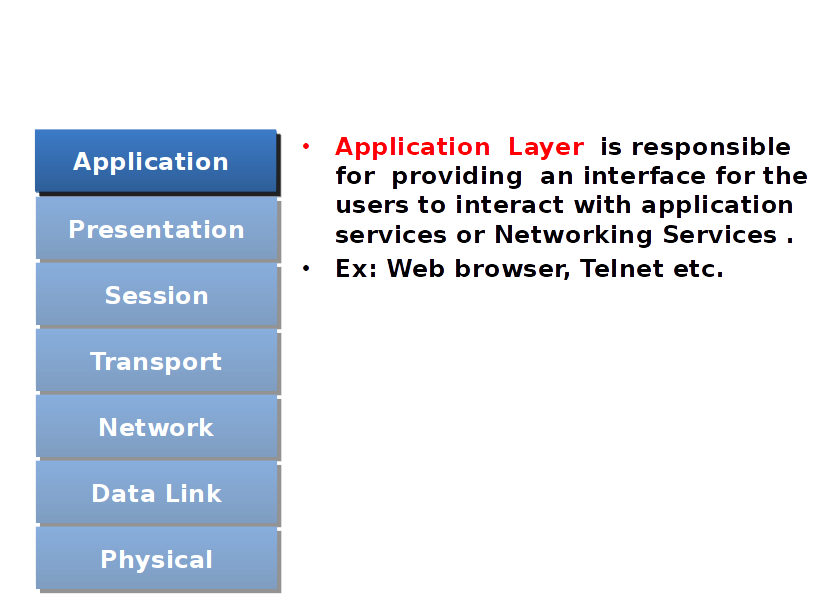
Application Layer

Networking Services
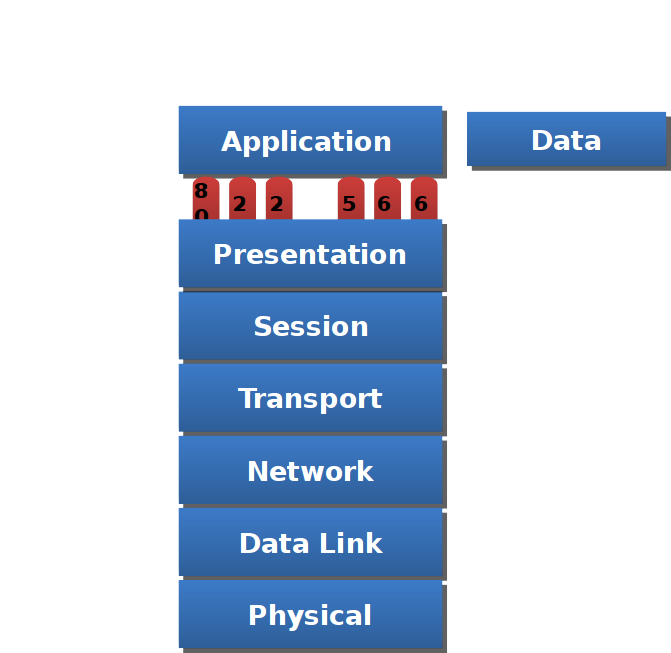
Data flow from Application layer
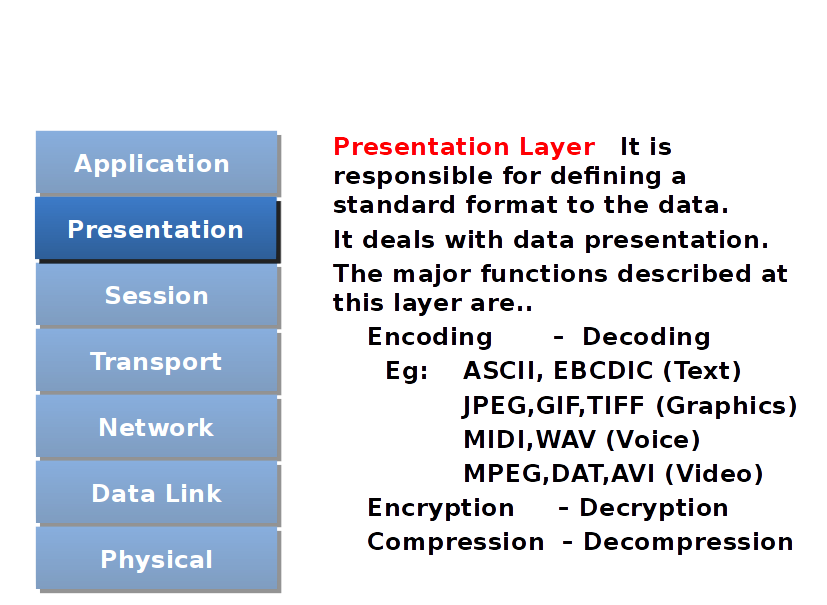
Presentation Layer
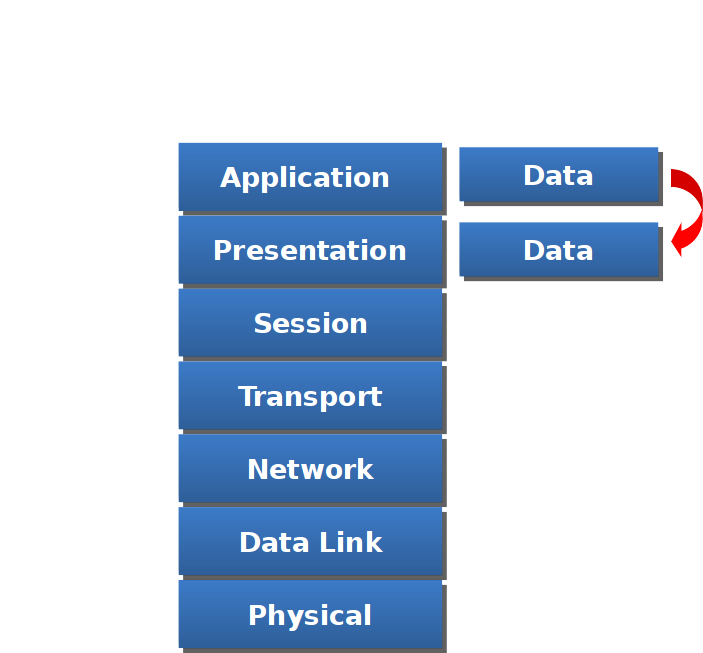
Data flow from Presentation Layer
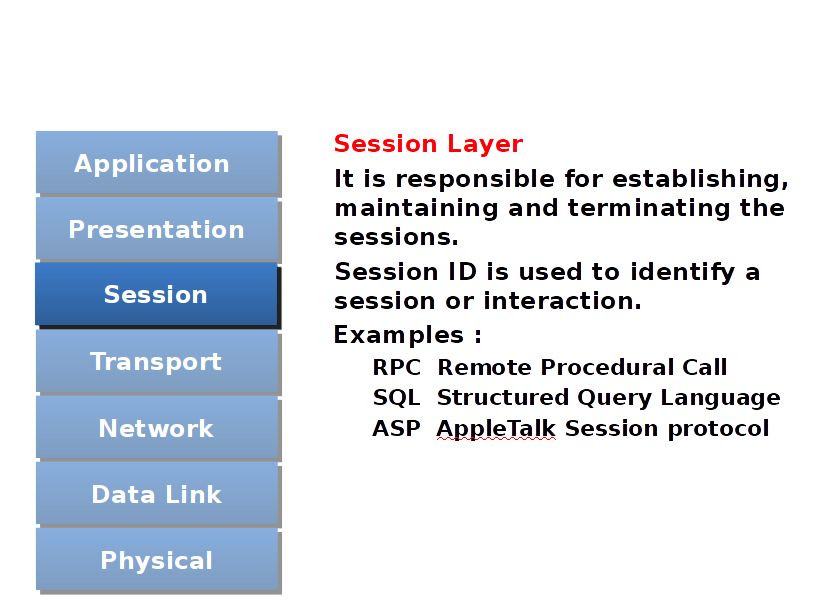
Session Layer
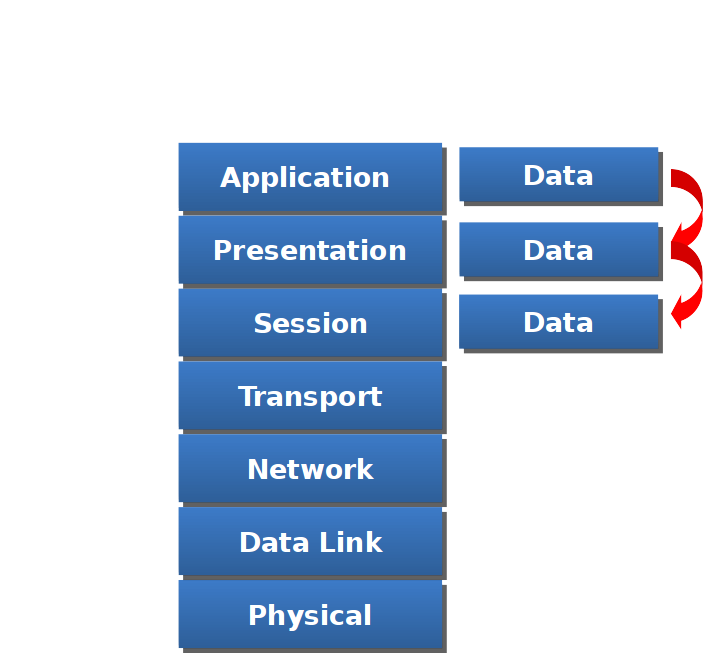
Data flow from Session layer
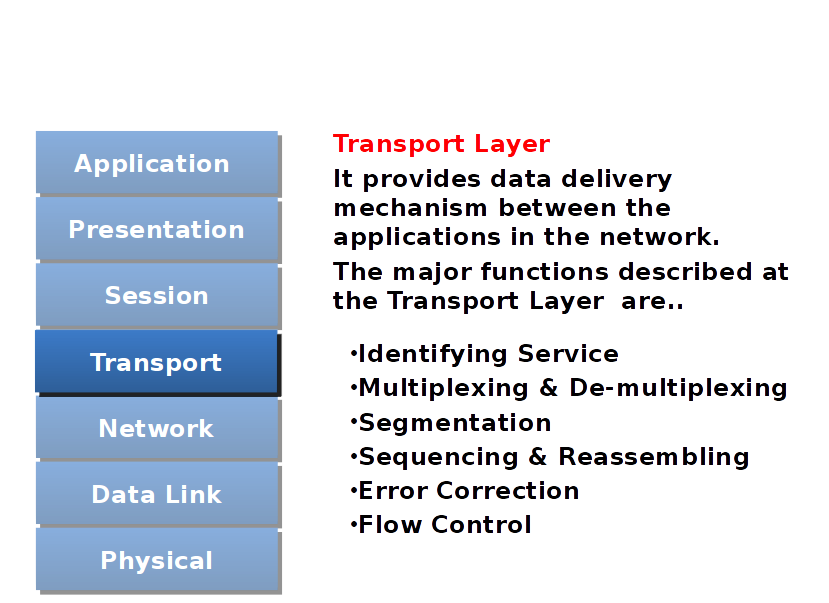
Transport Layer

Identifying a Service
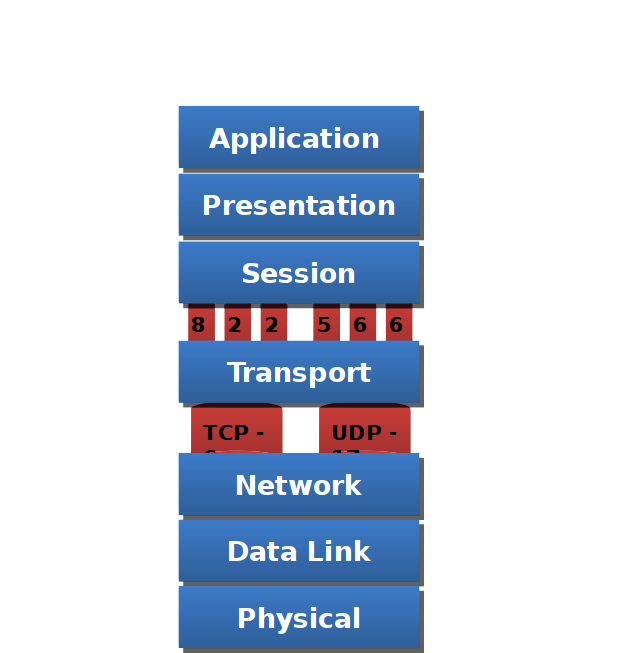
Multiplexing and De-multiplexing
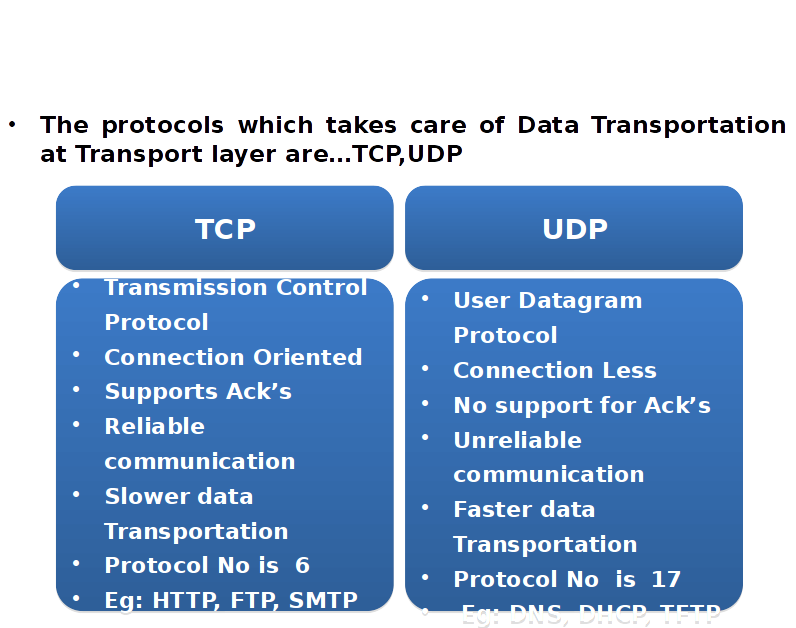
Transport Layer Protocol
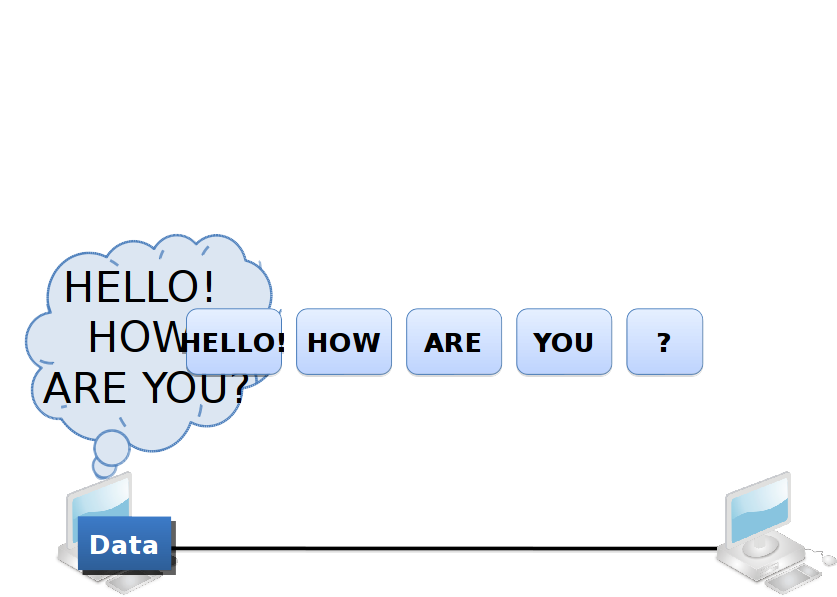
Segmentation
Sequencing
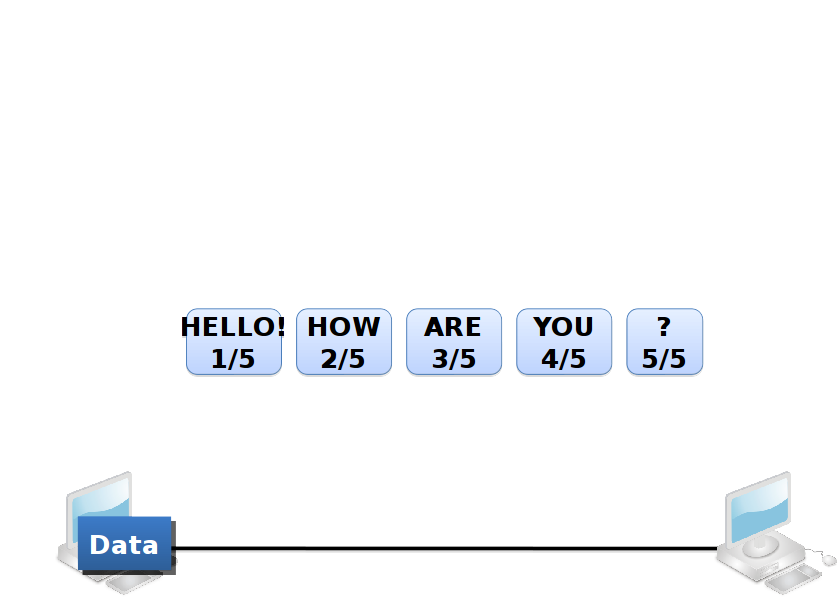
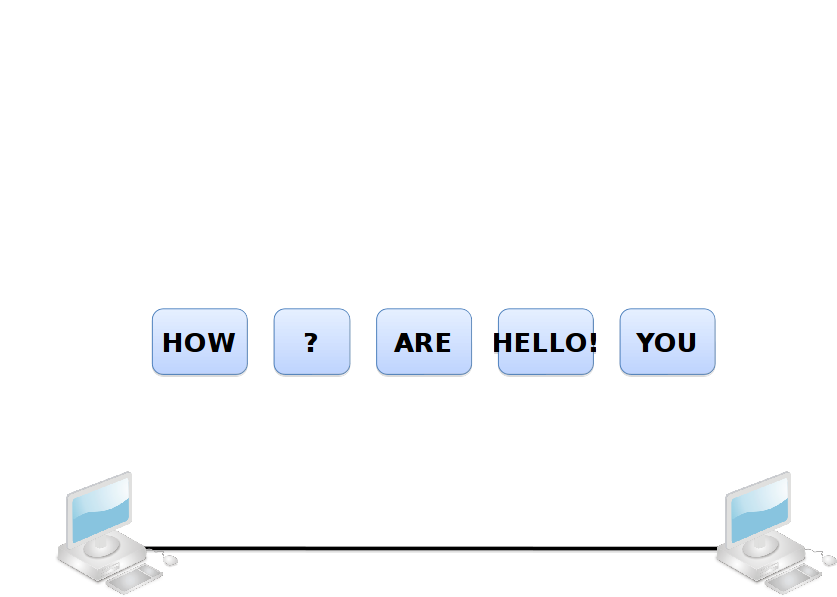
Sequencing
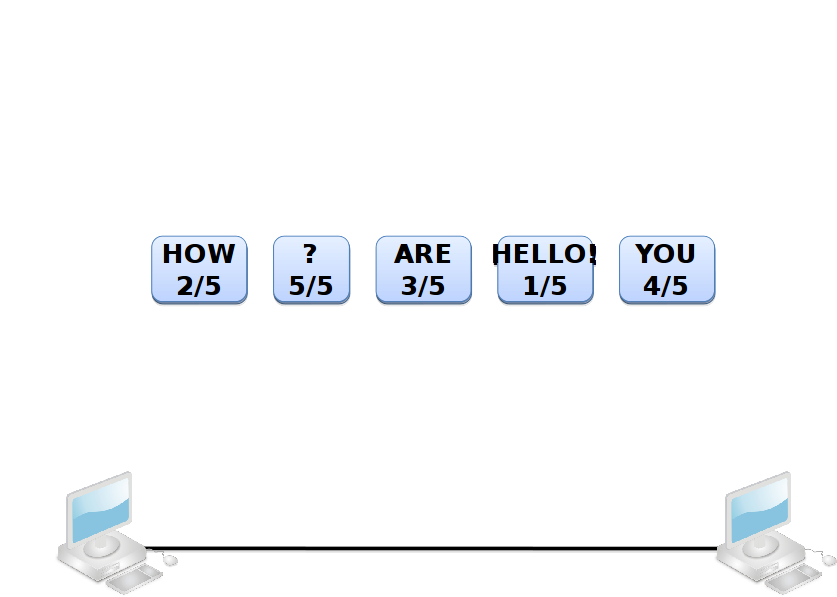
Sequencing
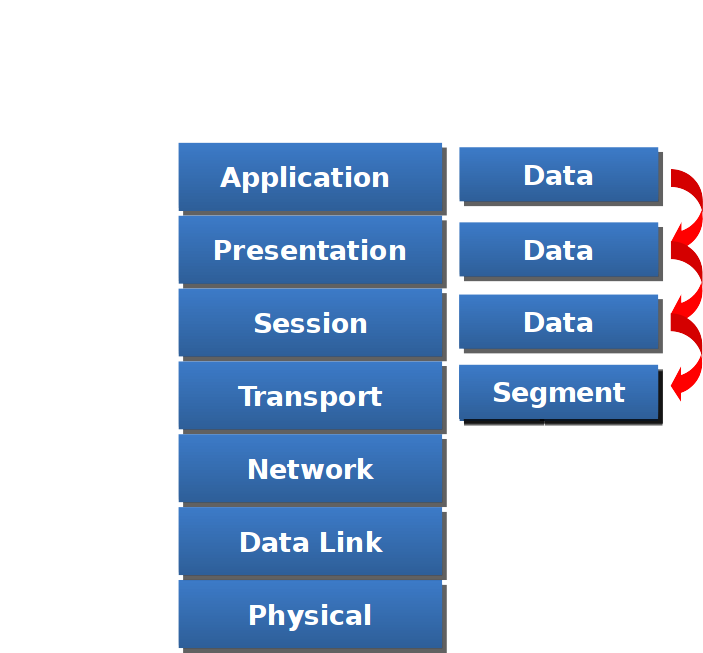
Data flow from Transport layer
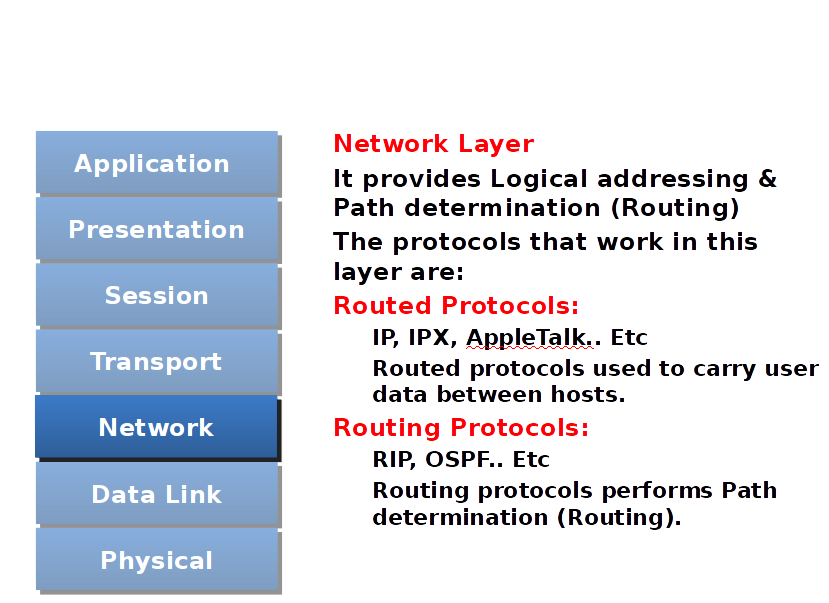
Network Layer
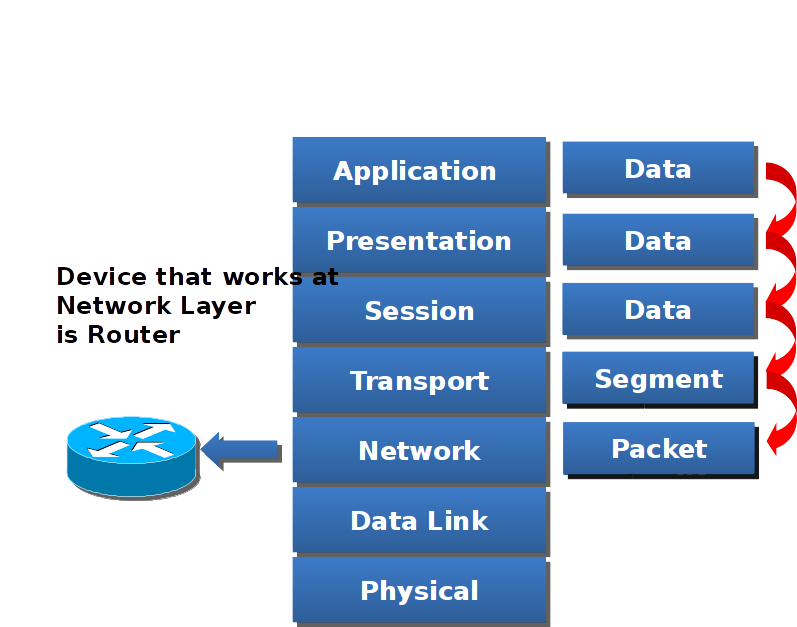
Data flow from Network layer
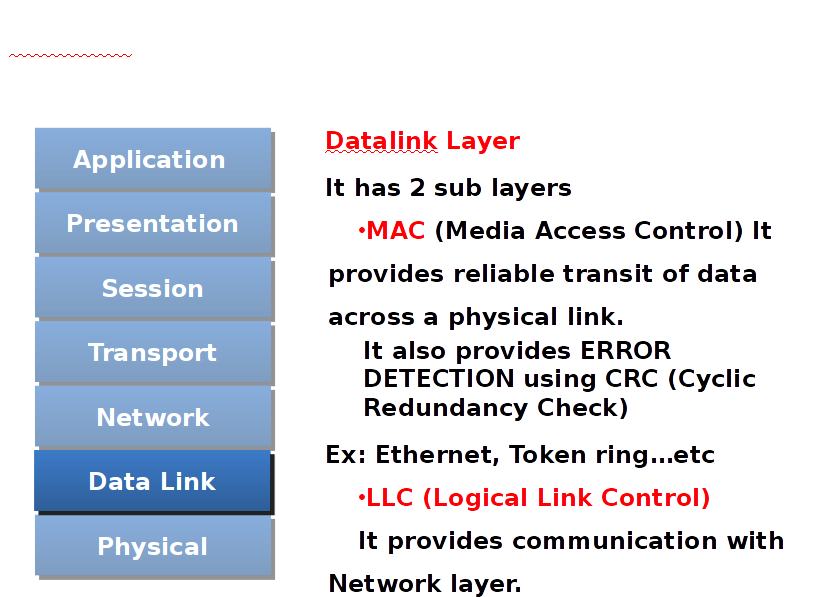
Datalink layer
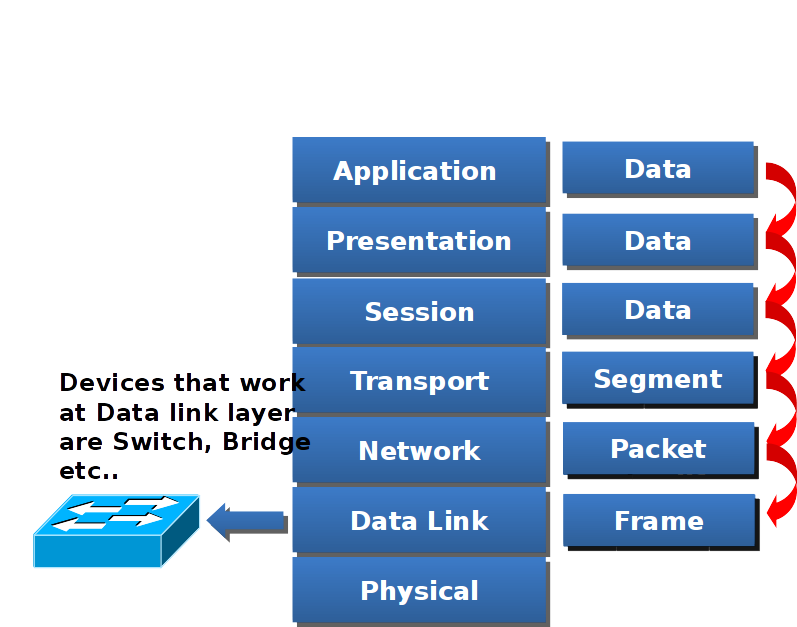
Data flow from Datalink layer
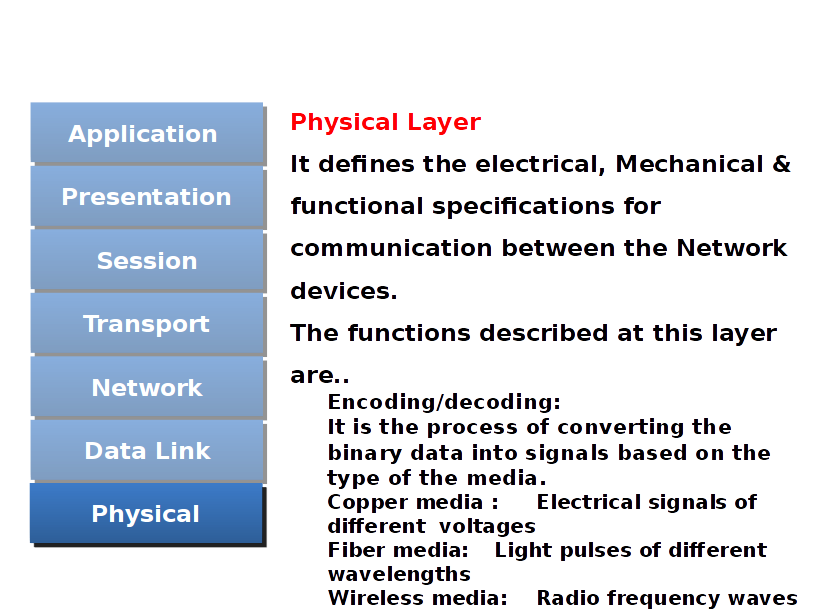
Physical layer
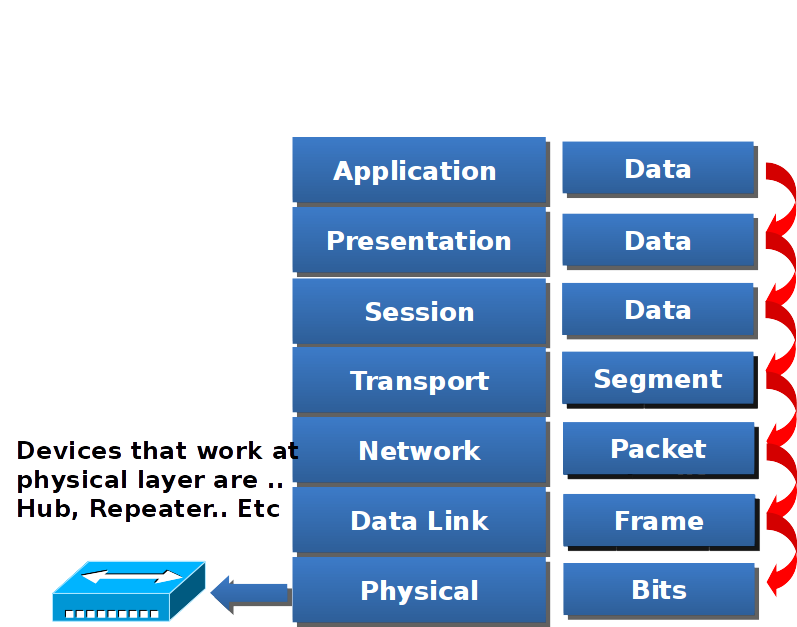
Data flow from Physical layer
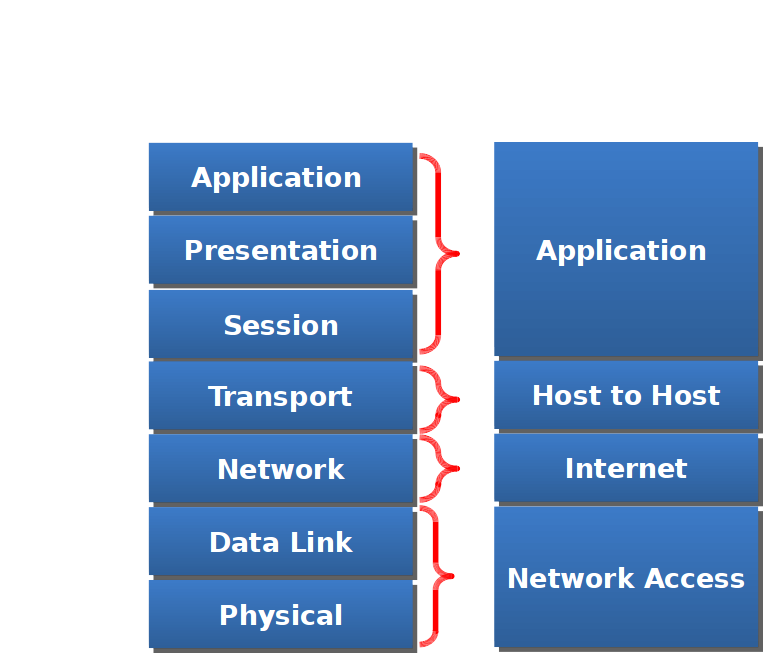
OSI vs TCP/IP
Cisco Packet Tracer
Cisco Packet Tracer is a network simulation program that allows students to experiment with network behavior and ask “what if” questions.
- Cryptography
Cryptography is a method of storing and transmitting data in a particular form so that only those for whom it is intended can read and process it.
Security
Encryption Idea
Plaintext: plaintext is information a sender wishes to transmit to a receiver.
Ciphertext: ciphertext (or cyphertext) is the result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm, called a cipher.
ex. ciphertext: vgzs hr xntq mzld
plaintext: what is your name
Q- ciphertext: oa pcog ku 999999999
Wireshark
Wireshark is a network packet/protocol analyzer.
A network packet analyzer will try to capture network packets and tries to display that packet data as detailed as possible.
Wireshark is perhaps one of the best open source packet analyzers available today for UNIX and Windows.
Some Intended Purposes
- Network administrators use it to troubleshoot network problems.
- Network security engineers use it to examine security problems.
- Developers use it to debug protocol implementations
people use it to learn network protocol internals
- Wireshark isn't an intrusion detection system.
- Wireshark will not manipulate things on the network, it will only "measure" things from it.
Websites must visit
- professormesser.com/security-plus/sy0-401/sy0-401-course-index/
- https://security.stackexchange.com/
- http://www.securityfocus.com/
- http://www.cisco.com/
- https://www.microsoftvirtualacademy.com/en-US/training-courses/networking-fundamentals-8249
- https://www.quora.com/
Any Question
Please ask.....
Thank you
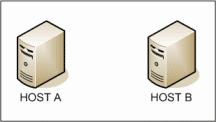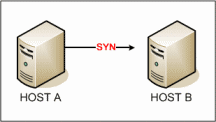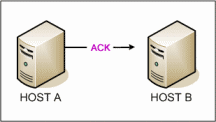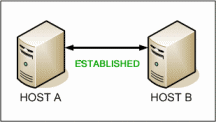
- TCP 3-Way Handshake (SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK)
- Host A sends a TCP SYNchronize packet to Host B
- Host B receives A's SYN
- Host B sends a SYNchronize-ACKnowledgement
- Host A receives B's SYN-ACK
- Host A sends ACKnowledge
- Host B receives ACK.
- TCP socket connection is ESTABLISHED.