
Environmental data:
extraction and interpolation
An open source tool-set for obtaining environmental data sets and aligning to your research requirements
Ann Gledson, Douglas Lowe, Manuele Reani, Caroline Jay, Dave Topping
The University of Manchester




-
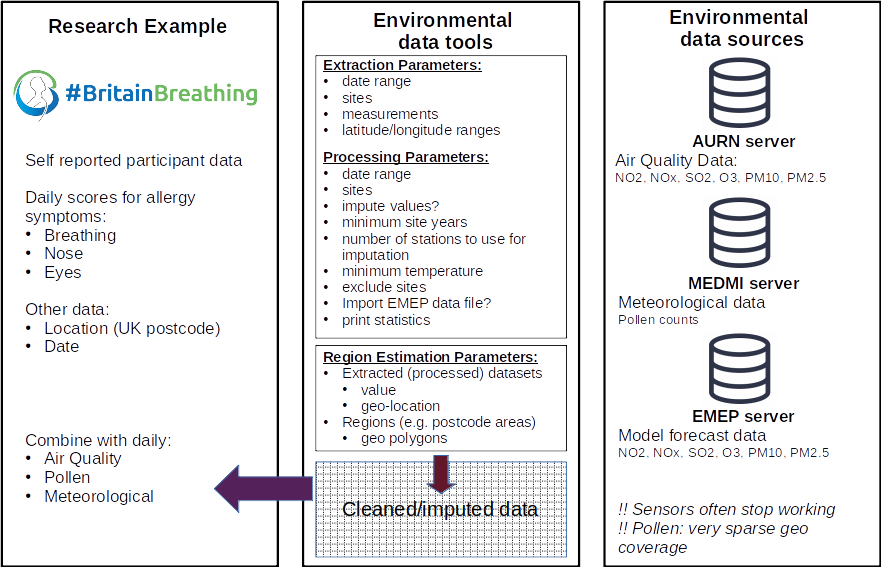
Automatic Urban and Rural Network (AURN)
- NOx, SO2, O3, NO2, PM10, PM2.5
-
Medical and Environmental Data (Mash-up) Infrastructure (MEDMI)
- Meteorological: temp, pressure, dewpoint temp, relative humidity
- Pollens: alnus, ambrosia, artemesia, ..., urtica
-
European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme (EMEP)
- Model forecast data
- NOx, NO2, SO2, O3, PM10, PM2.5
-
Complex extraction process:
- Multiple data sources
- Missing data (e.g. sensor down-time)
- Variable UK area coverage
Available data



Cleaning and Imputation
- Remove duplicate/unphysical values
- Select sites by minimum temporal data coverage
- scikit-learn (python) used to impute missing data using hourly time series
-
Imputation method
- Bayesian Ridge
- Quantile Transformer preprocessing
- Final data: daily mean / maximum values (or simple daily count)
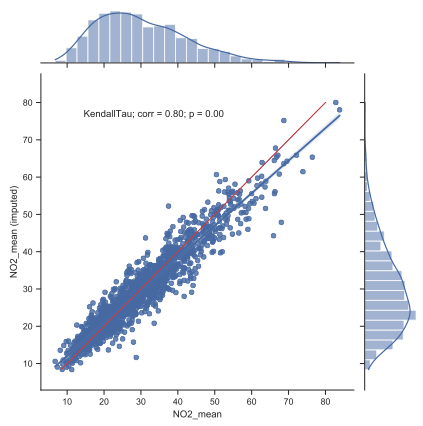
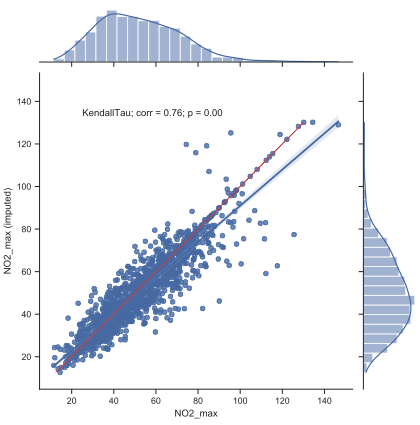

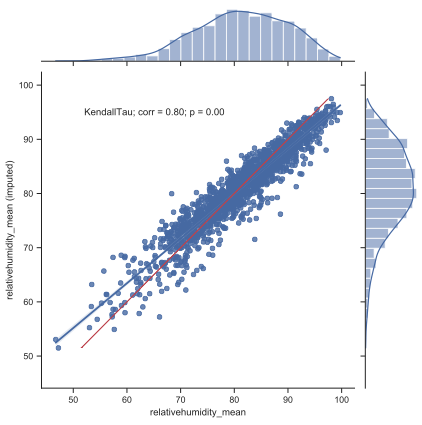



Regional estimations

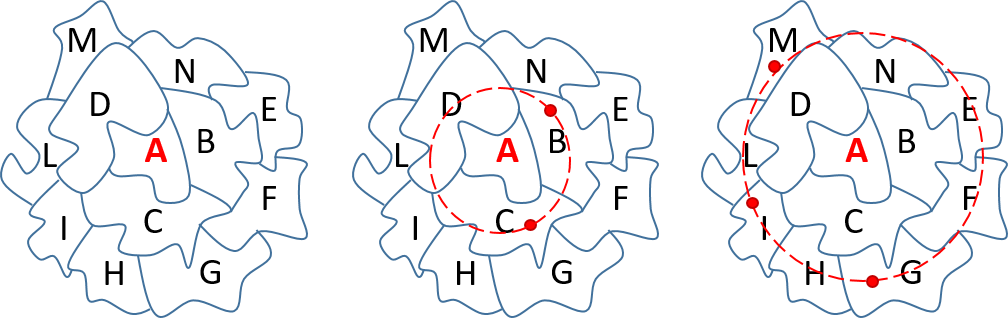
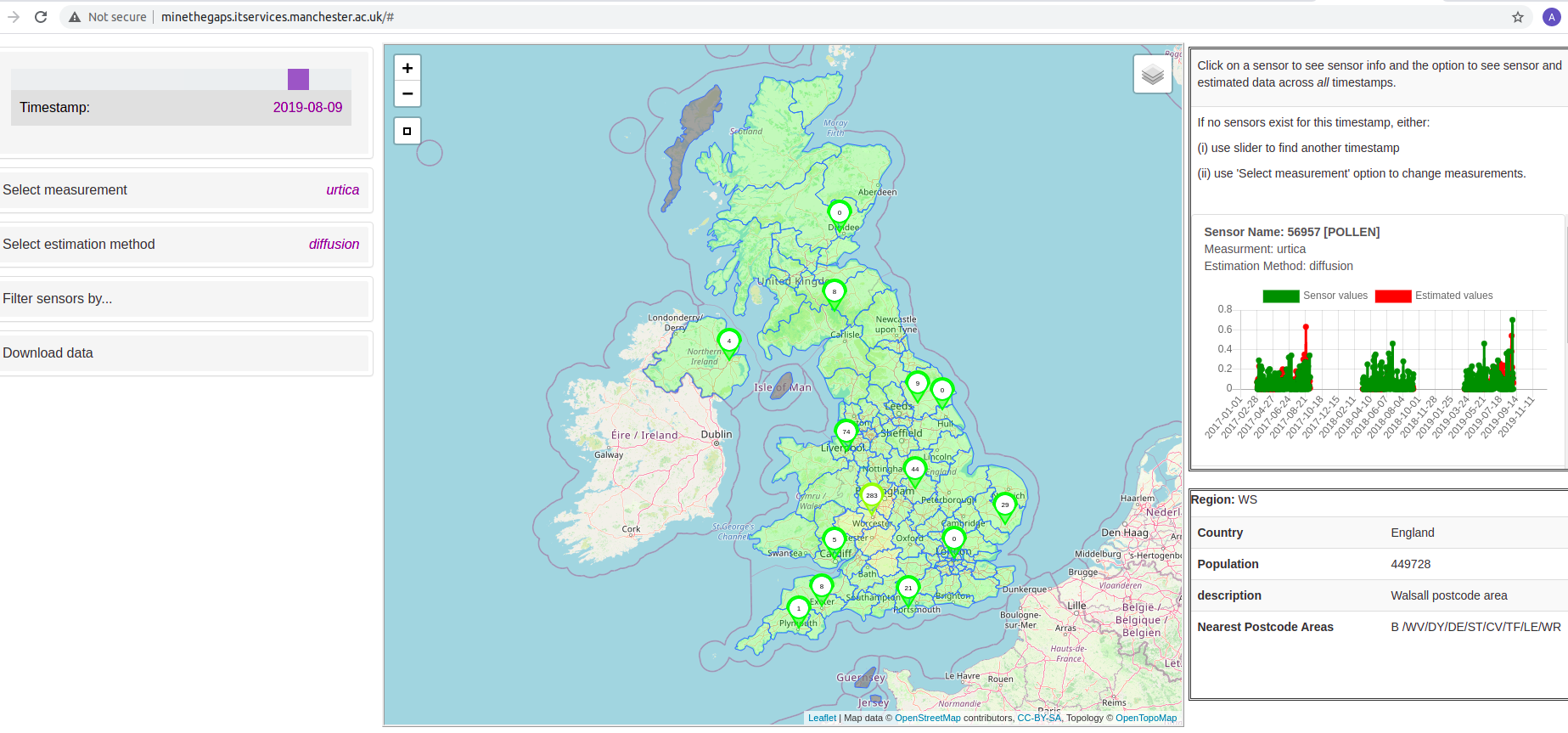
Diffusion method illustrated on fictional postcode regions
- Regions where sensors exist: take mean
- Regions with no sensors: take mean of surrounding regions
- Working outwards until sensors found


Filling the gaps



Links
- 2016-2019 dataset: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4315224
- Download the dataset
- Links to extraction and imputation tool set
- Mine the Gaps: minethegaps.manchester.ac.uk
- Data visualisation and example use case
