Blockchain
vs.
Database


Contents:
- Overview
- Architecture
- Reason to use
- Best use cases
Overview
What is Database?
- Database is a data structure for storing & working with data.
- Managed by single administrator (Centralized).
- Support CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operation.
- Uses a Client/Server architecture.
- Admin or authorized user able to edit the data stored in it.
- Data can be deleted and will have no records if not backed up.
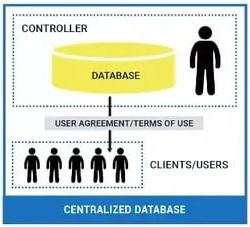
What is Blockchain?
- Uses a distributed ledger network architecture based on P2P model.
- Stores data or information in blocks that are linked using cryptography.
- Each block contains hashed info from the previous block (Chained).
- No administrator (Decentralized).
- Supports Read & Write only. (Cannot Update/Delete data)
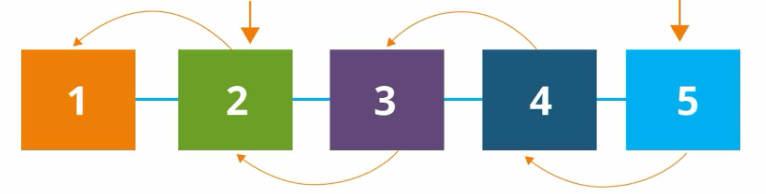
Block 2 carries the info of Block 1's data.
Block 5 is the current data contains all information from all blocks.
Blockchain Simple Analogy
This is how data is stored, added and 'edited' in Blockchain.
If someone request latest data using Blockchain, the result will take the latest 'Name = Ali. Address = Pahang. Spouse = Fatimah.' with the ability to view the previous entries.
This is not just a way to store data, but also a record of what has been added.
"Just like bank account ledger.. New transaction will be added to the new line.."
- Entry 3 states that I have changed my name. Instead of editing Entry 1, I created a new entry with new data. No entries are changed or removed.
- Entry 5 does the same thing to Entry 2.
- Name = Alex.
- Address = Kuala Lumpur.
- Name = Ali.
- Spouse = Fatimah.
- Address = Pahang
1. Name = Alex.
1. Name = Alex. Address = KL.
1. Name = Ali. Address = KL.
1. Name = Ali. Address = Pahang.
1. Name = Ali.
How about Database?
| BLOCKCHAIN | DATABASE | |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Blockchain is decentralized. No centralized authority. |
Database is centralized. Controlled by the administrator. |
| Architecture | Peer-to-Peer (P2P) | Client/Server |
| Data Handling | Read and Write operations. | CRUD operations. |
| Integrity | Supports integrity. | Exposed to data alterations. |
| Transparency | Offers transparency. | Not transparent. |
| Performance | Slow down by the validation of consensus algorithm. | Extremely fast and offer great scalability. |
| Cost | New technology, harder to implement and maintain. | Established technology, easy to implement and more supports. |
| Data Privacy | The block header is public, but only the owner of data has the key to access own data. | Controlled access. |
Architecture
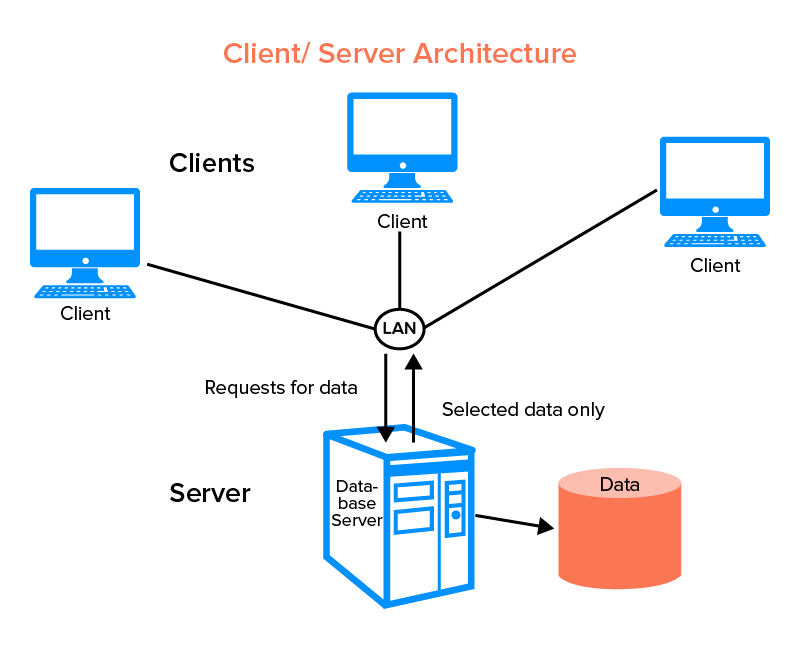
Database Architecture
- Database are based on a Client/Server architecture.
- Clients are end-users of the service that request access to a particular set of data.
- This request goes through a server that hosts the database.
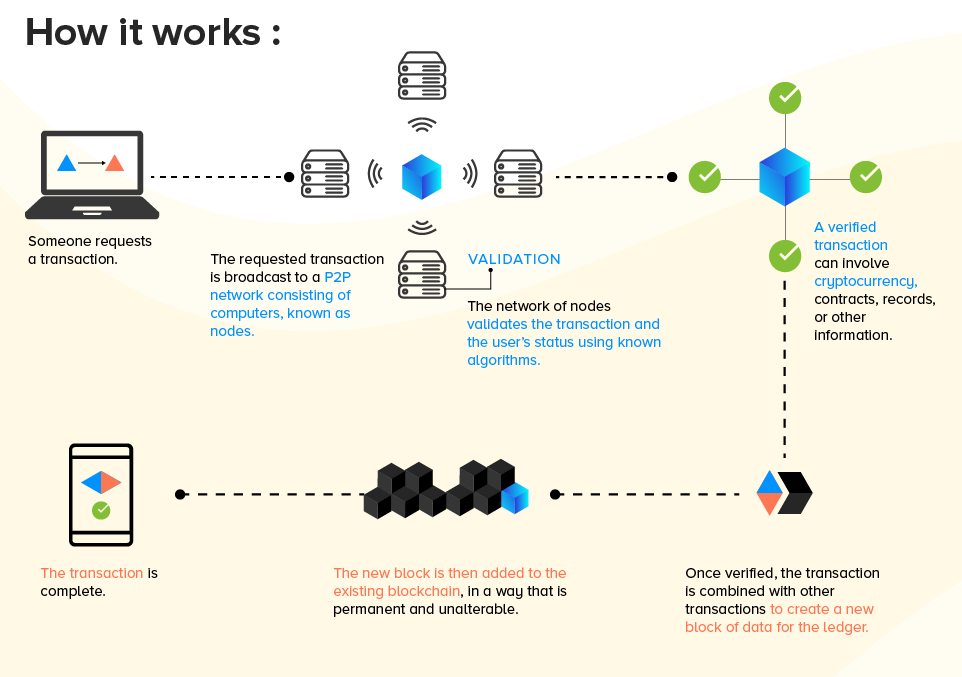
Blockchain Architecture
- Blockchain uses a distributed ledger network achitecture.
- They operate on a Peer-to-Peer, P2P, model.
- Data transaction is validated by consensus algorithm to ensure no invalid transaction is executed.
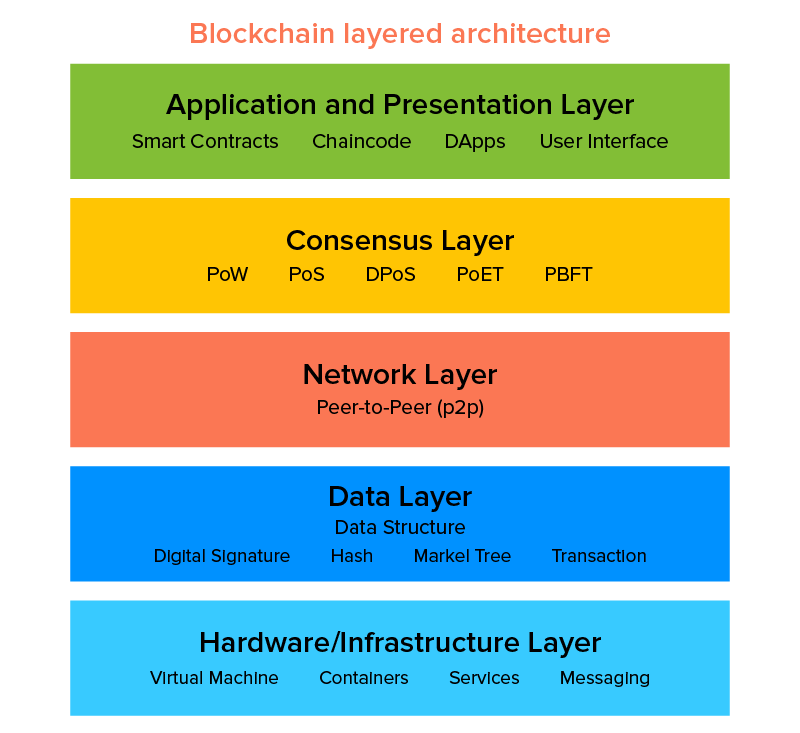
- Timestamps are created to ensure each transaction can be traced back and verified.
- Such features add value to data transparency, immutability and security.
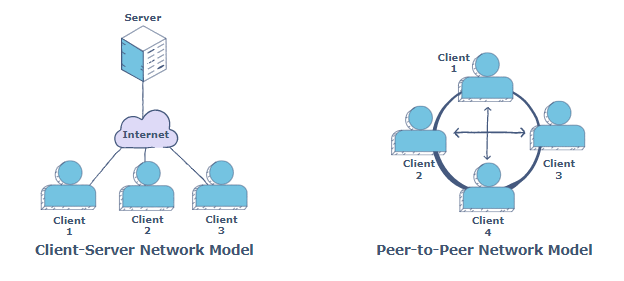
| Database (Client/Server) | Blockchain (P2P) |
|---|---|
| Multiple clients, one server. | Each nodes acts as a server and a client. |
| Clients request the data, server responds back with the data. | Each node can request and provide the data. |
| Data is stored at server side only. | Each node store its own data. |
| Server more stable and scalable. | Stability reduces when the no. of nodes increase. |
| Exposed to data alteration and system failure. | Records will be kept forever and cannot be tempered. |
Architecture at a glance..
Reason to use Database
1. Customizable
Since database is centralized administered, permissions, privileges and requirements can be customized easily.
The architecture and backup practices make database server can be relocated anywhere.
Developers can add plugins to the database server and system and improve the security and front end for customer centric.

2. Stable
Database can tolerate high volumes of data transactions per second.
Client/Server architecture reduces nodes dependency with standalone server centers.
But in the event of power outage or downtime, backup acts as an option to reset to the last version.

3. Speed
Database has been design for a long time to suit faster delivery times and high-end analytical operations.
Big data analytics is the case where database is best used.

Reason to use Blockchain
1. Fault Tolerant
Blockchain's uptime is not reliant on a few server centers but hundreds and thousands of nodes that offer processing input to run the system.
In the scenario that a few nodes are turned off, the overall efficiency of the network would remain the same.

2. Secure
Blockchain can survive any malicious attack. This is because attacking the system is more expensive for hackers and not an easy solution. So, it’s less likely to breakdown.
As the system runs on algorithms, there is no chance for people to scam you out of anything.

3. Transparency
Anyone with the right tool can verify the data once written into the blockchain. Transparency ensures that the public can trust the network.
Data, once stored cannot be corrupted or changed in any possible way, which means that the data integrity and authenticity is maintained at any cost.
Best Use Cases
Database: Best Use Cases
Database Use Cases:
- Apps or systems that utilize the continuous flow of data
- Confidential data
- Quick online transaction
- Big Data Analytics
- Relational data
Databases are undoubtedly user-friendly and are already supported by many popular management systems for developers and administrators.
The scalability is what makes databases such a good choice for the enterprises out there.
It doesn’t have to go through verification during the write or read process which can process fast transaction.

Blockchain: Best Use Cases
Any system that requires proper verification can utilize blockchain. The key here is transparency as it enables businesses to follow every single movement without introducing more complexity.
Blockchain is also ideal for automating tasks within a platform. E.g. Smart contracts which brings in the ability to utilize stored procedures. If a certain condition is met, the code is automatically executed.
Blockchain Use Cases
- Financial services
- Identifying and authenticating records
- Trusted data verification
- Voting systems
- Decentralized apps (dApps)
Future Application of Blockchain
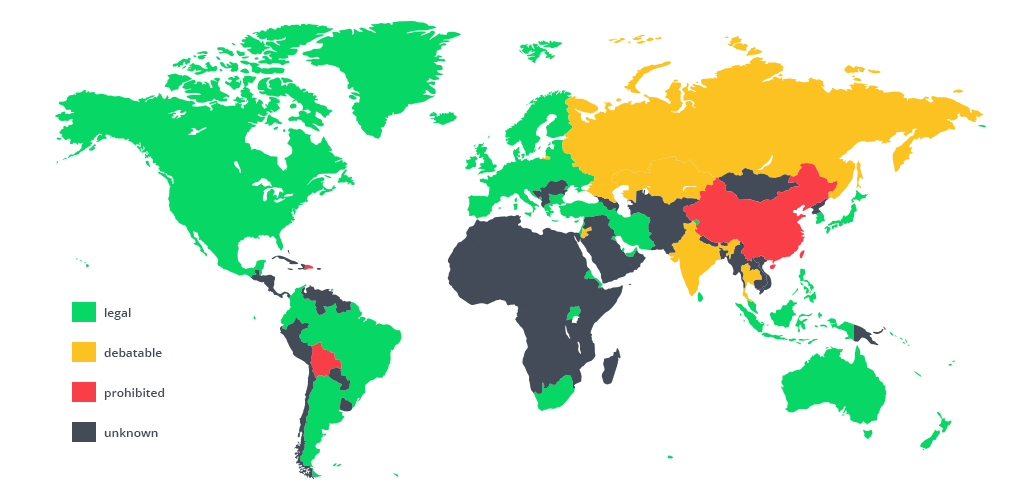
Worldwide Adoption of Blockchain
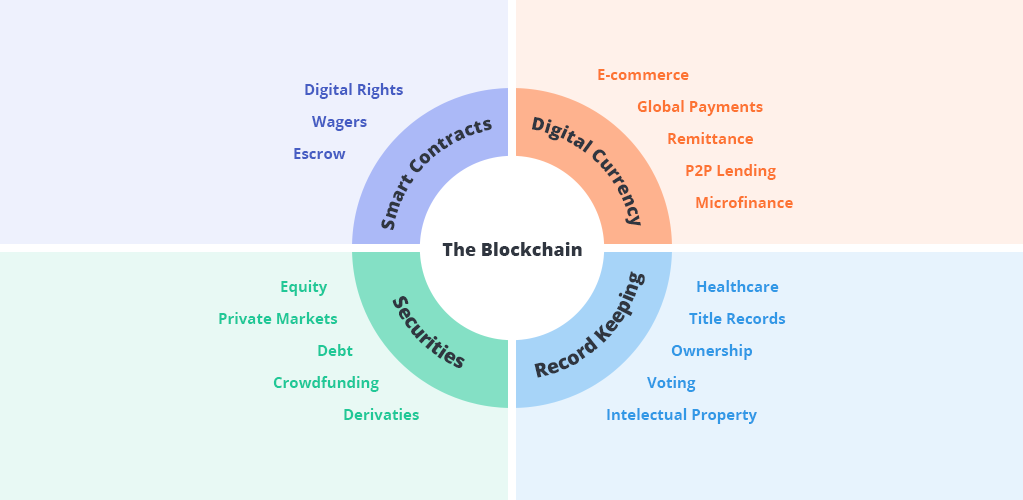
Malaysia Use Case of Blockchain
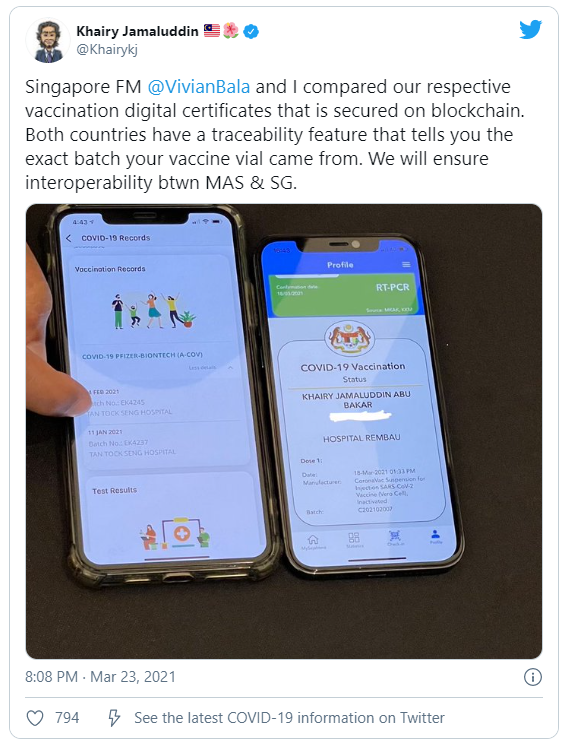
Malaysia & Singapore To Use Blockchain Technology To Record Your Vaccination Certs
Top 3 Blockchain Open Source Projects
- Developed by Linux Foundation.
- All projects developed are Private & Permissioned Blockchain.
- Built around the Etherium codebase.
- Permissioned & highly customizable.
- Strict transaction privacy.
- Smart contract can be written in JVM language & Java.
(Click title for the link)
In conclusion...
Database is a winner when it comes to utility, speed, and accuracy.
Blockchain is also a winner when it comes to innovation, verification, and automation.
Blockchain gets a performance penalty because of its verification method. Avoid blockchain where fast execution time is an essential factor.
Databases are a great choice where the critical business process needs to be supported or scaled at the same time.
In short, choose blockchain if you are looking for trust, transparency, and verification. Database, on the other hand, is ideal for high-performance apps or services.

Thank You