Data Science for Finance Professionals
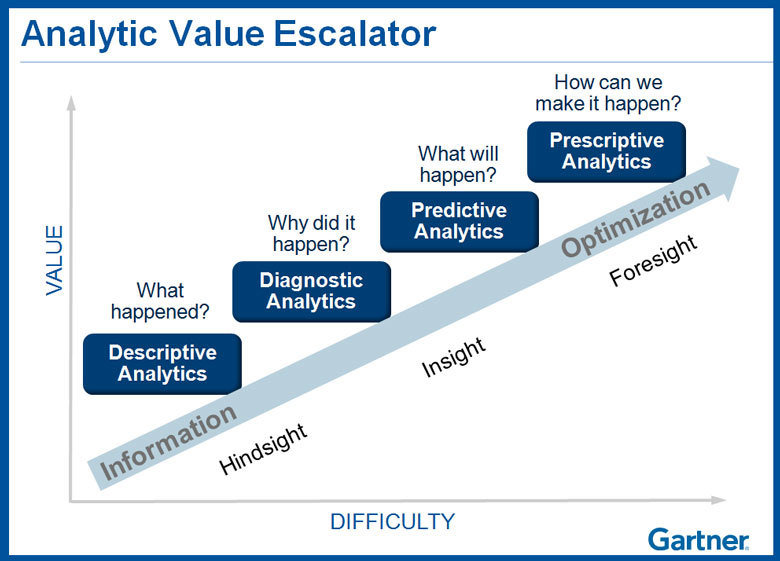
Types of Analytics
Types of Analytics
-
Descriptive Analytics
-
Make use of data aggregation and data mining to provide insight into the past and answer: “What has happened?”
-
-
Predictive Analytics
-
Make use of statistical models and forecasts techniques to understand the future and answer: “What could or will happen?”
-
-
Prescriptive Analytics
-
Make use of optimisation and simulation algorithms to advice on possible outcomes and answer: “What should we do?” or "How can we make it happen?"
-
Types of Analytics
Diagnostic Analytics
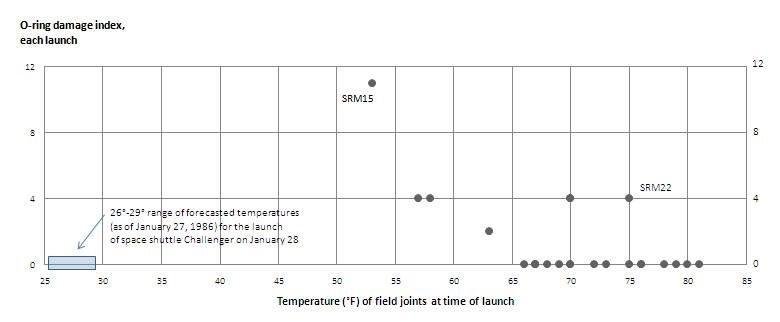
Example
Historical Data
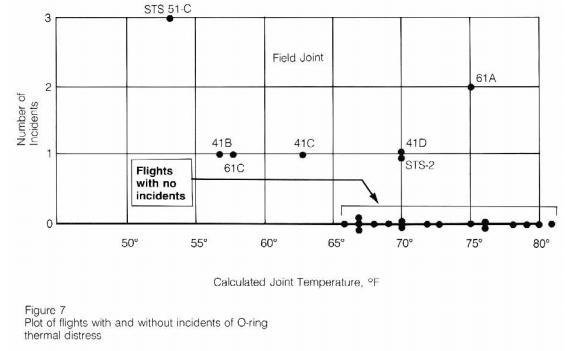
Launch Day
What is Machine Learning?
What is Machine Learning?
[Machine Learning is the] field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
Arthur Samuel, 1959
Why Machine Learning?
Why Machine Learning
-
The problem of a rule-based system against an evolving world. E.g., Spam filtering
-
Set rules versus ML
-
-
ML is great for:
-
Problems the requires a lot of hand-tuning or long list of rules
-
Complex problems
-
Evolving environment: Adapts to new data
-
Pattern discovery / Provides insights
-
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
-
Supervised
-
Regression
-
Linear Regression, Penalised Methods, Tree-based
-
-
Classification
-
Logistic Regression, Tree-based, Bagging, Boosting
-
-
-
Unsupervised
-
Clustering
-
Visualisation / Dimensionality Reduction
-
Association rule learning
-
-
Semi-supervised
-
Reinforcement Learning
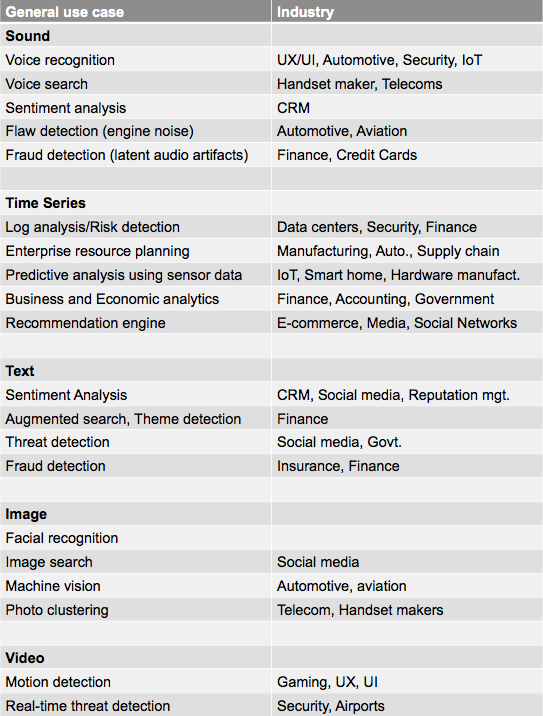
Deep Learning Use Case
Source: deeplearning4j
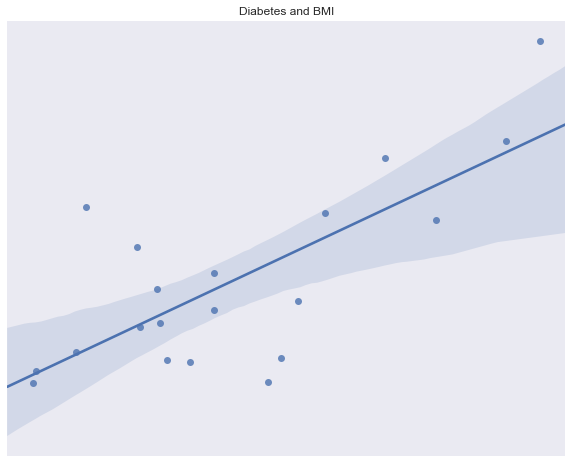
Regression -
Continuous Variable
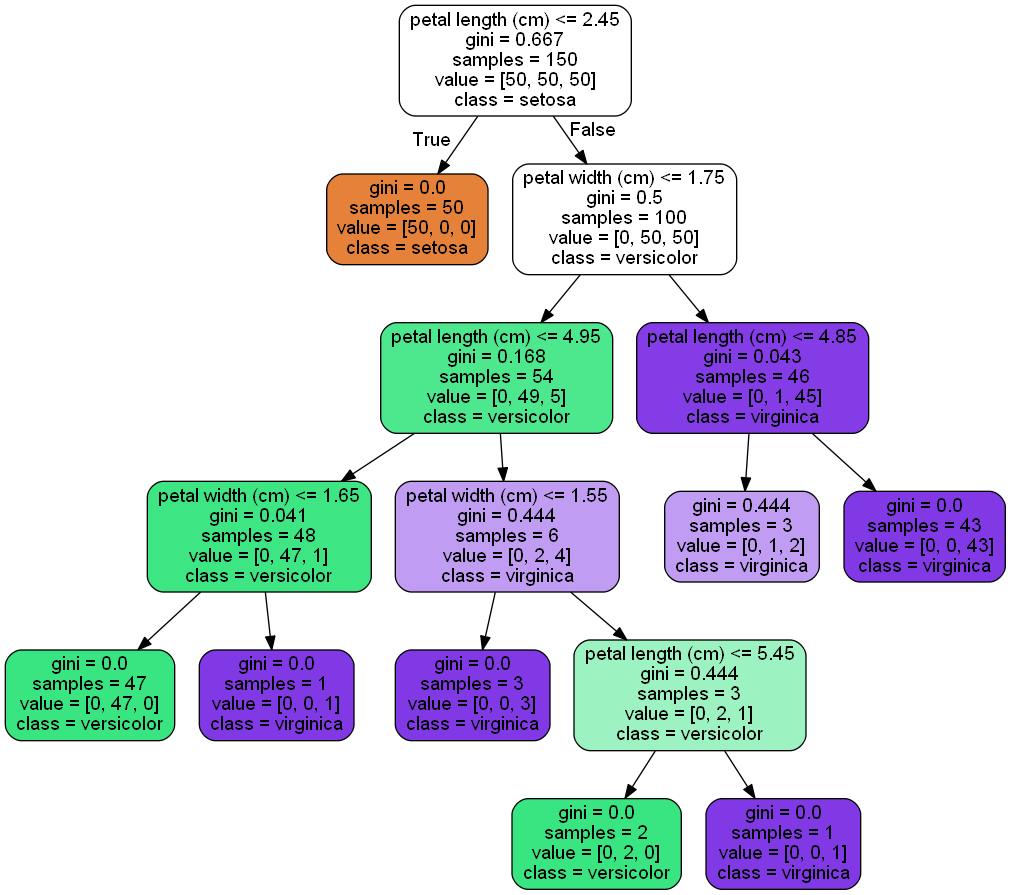
Classification
Classification with Deep Learning

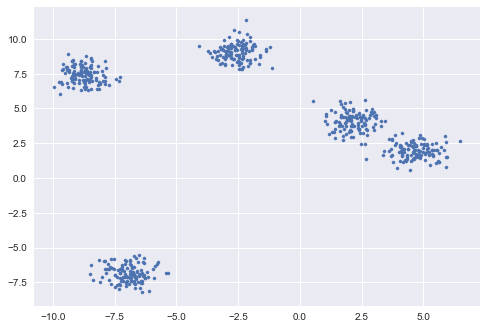
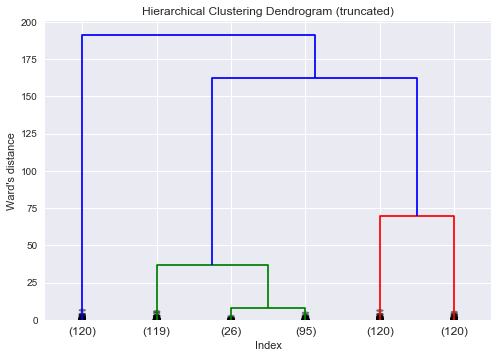
Unsupervised
Reinforcement Learning - 2015
Reinforcement Learning - 2017
Machine Learning Checklist
Machine Learning Checklist
-
Frame the problem and look at the big picture.
-
Get the data.
-
Explore the data to gain insights.
-
Prepare the data to better expose the underlying data patterns to Machine Learning algorithms.
-
Explore many different models and short-list the best ones.
-
Fine-tune your models and combine them into a great solution.
-
Present your solution.
-
Launch, monitor, and maintain your system.
Source: Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems By Aurélien Géron