Medical Image Registration for Glioblastoma MRI Using Constrained Metamorphosis.



Anton François
Advised by
Alain Trouvé


Advised by
Joan Glaunès & Pietro Gori




Introduction
Metamorphosis
Implementation
Constrained Metamorphosis
Future
works
Metamorphosis
Background












Comparing shapes


On Growth and Form, [D'arcy Thompson, (1917,1942)]
Compare species organs by the amount of deformation needed to match them.



Anton François - 05/03/2024

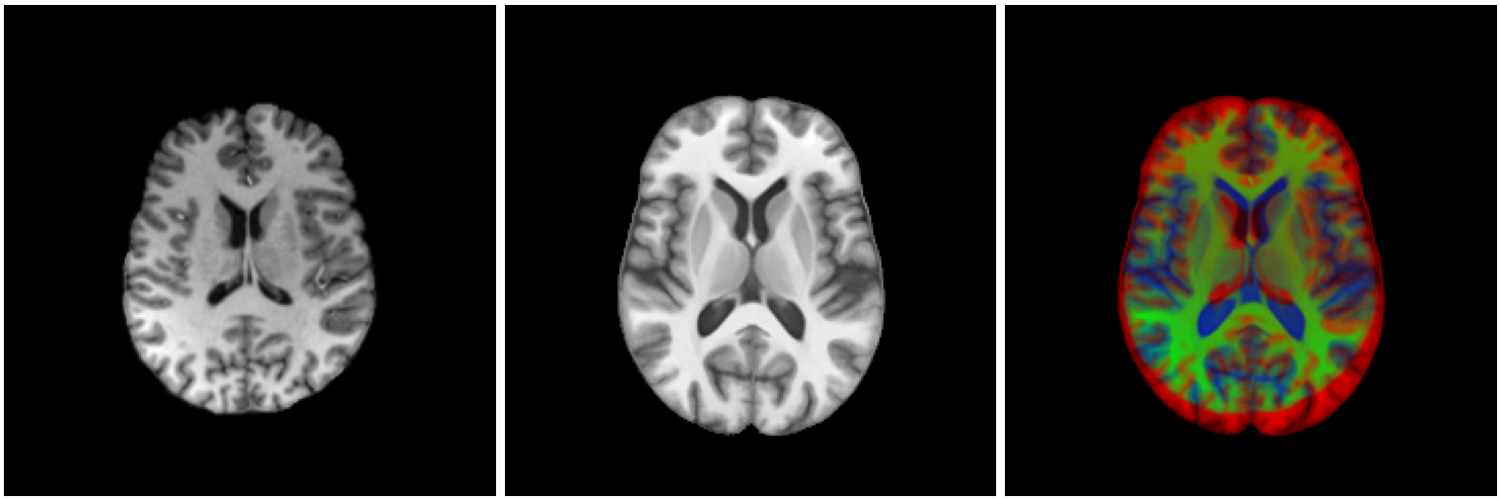
Image registration of medical images is an important step in many medical applications:
- motion tracking
- longitudinal studies
- pre/post-surgical normalisation
- statistical analysis (atlas construction)...
Before
registration:
After
Image registration
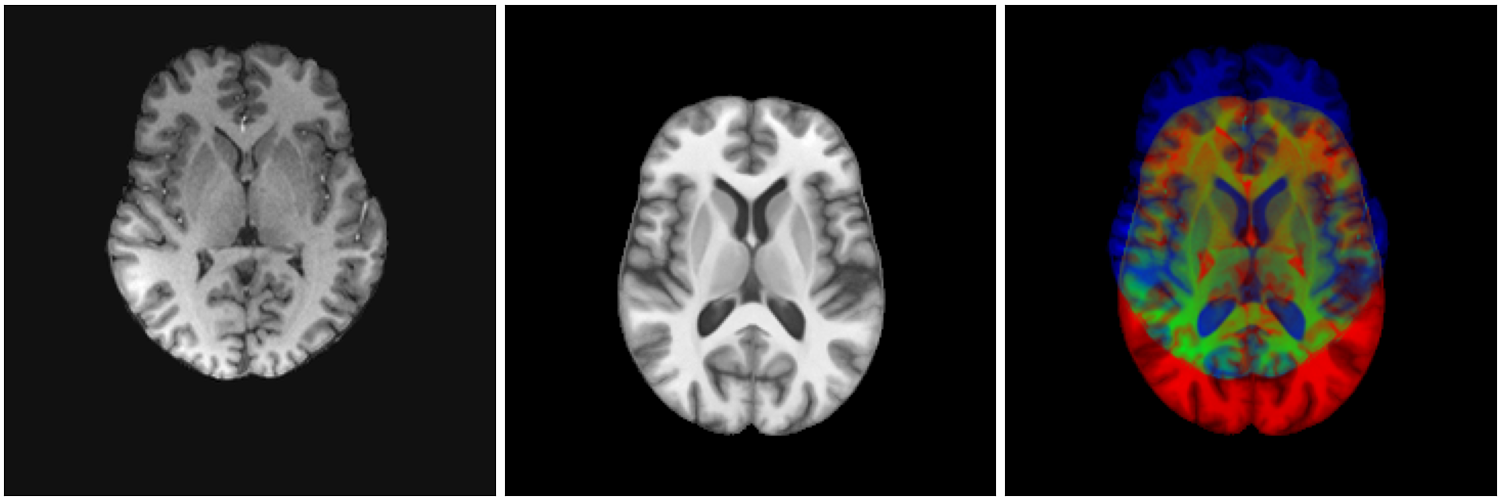













Anton François - 04/06/2024


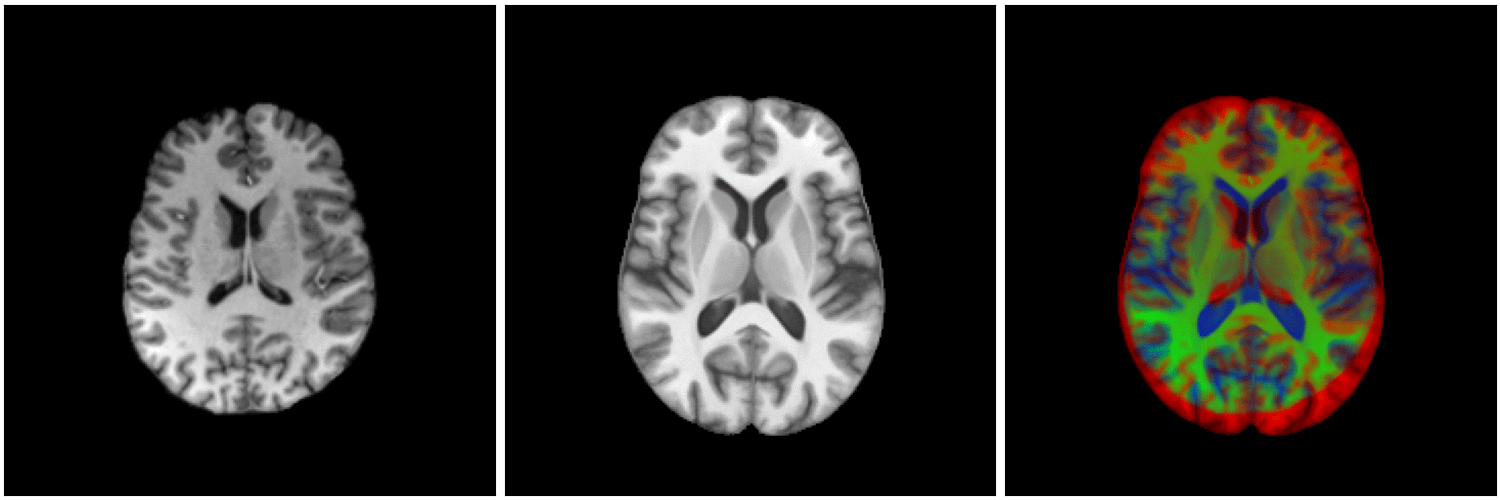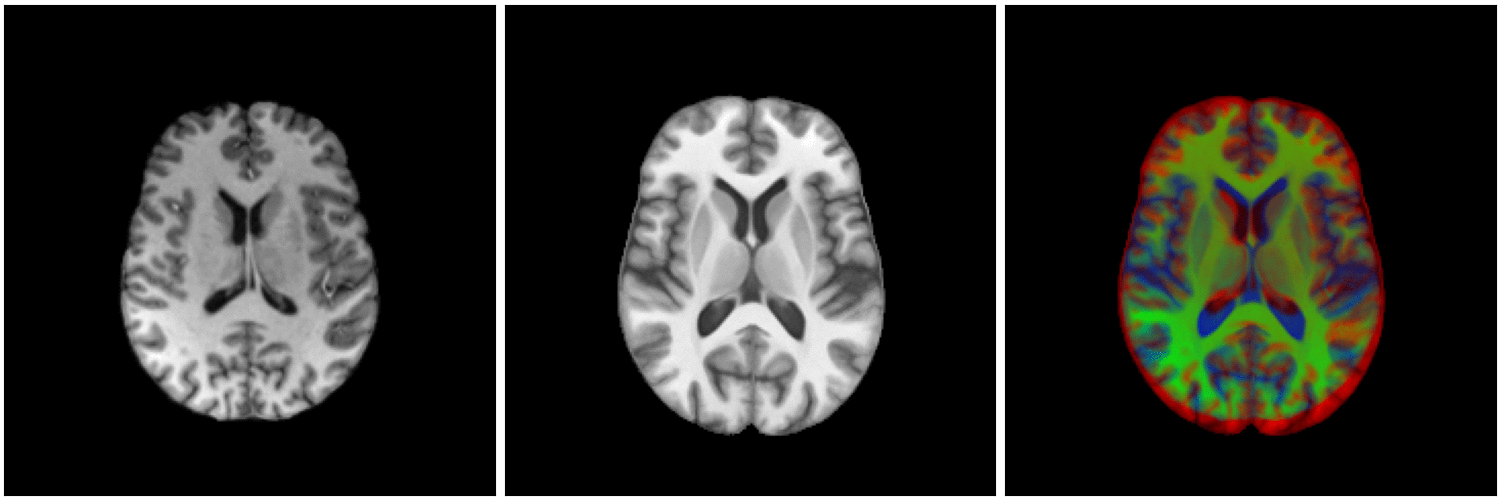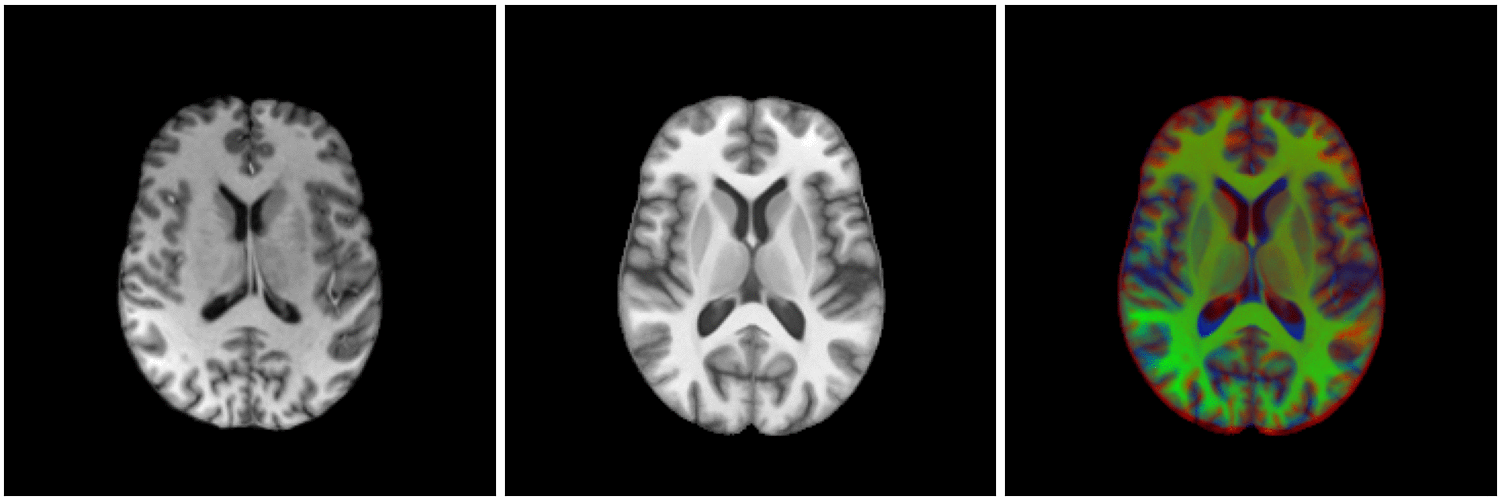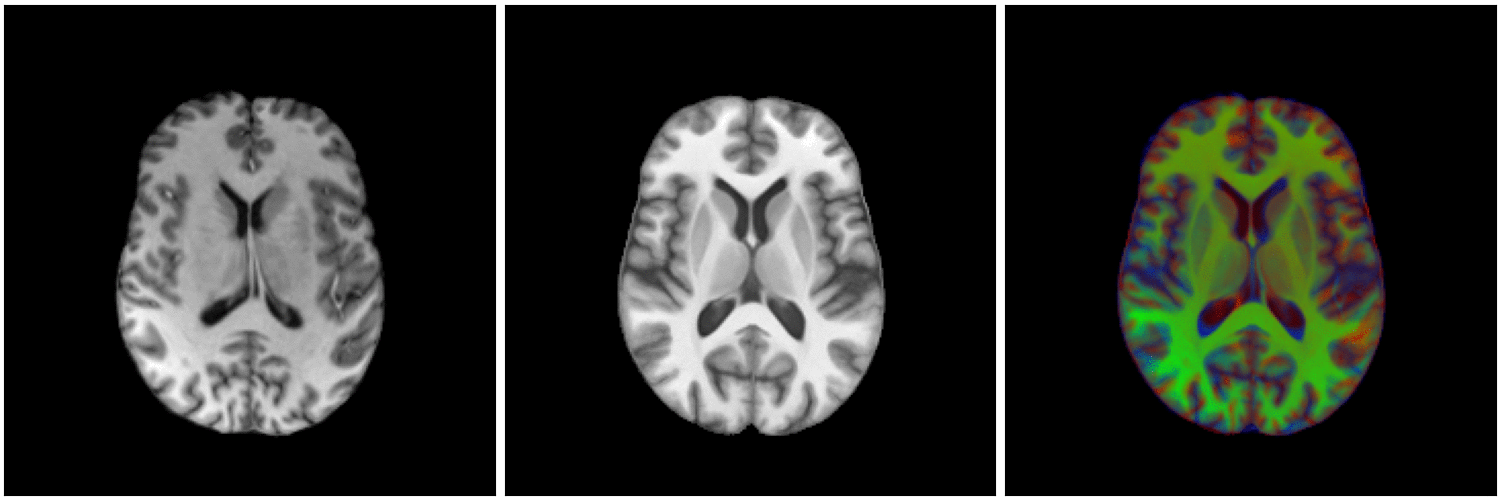
non-linear image registration:
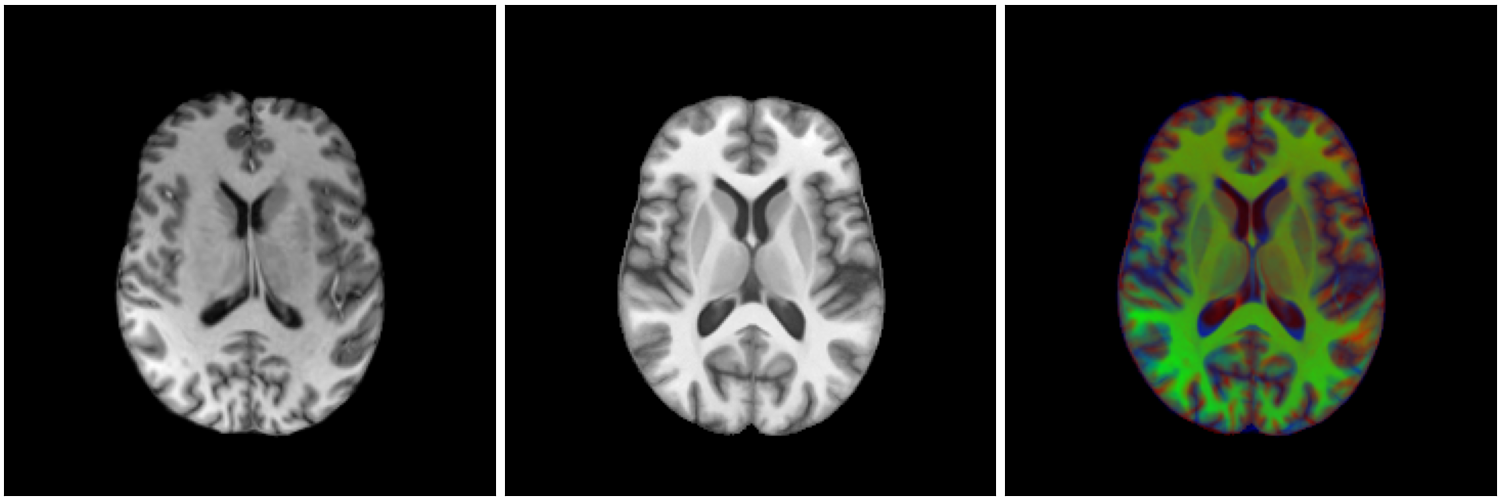
Image registration
temporal













Anton François - 04/06/2024

Deformation from vector fields
Let \(I\) and \(J\) be two images defined on \(\Omega\), we search for the deformation \(\varphi\) such that:
$$I = \varphi \cdot J$$
One can define, for any \(x \in \Omega, \varphi(x) = x + v(x)\) where \(v\) is a smooth vector field.
Limit: When \(v\) is large, \(\varphi\) can be not invertible anymore.















Anton François - 04/06/2024



Diffeomorphic image registration:
Finding a smooth one-to-one (non-linear) deformation to be biologically plausible (no holes, shearing, tearing...)

Image registration













Anton François - 04/06/2024



Source
Target
Automatic non-linear
matching
With modern methods
LDDMM













Anton François - 04/06/2024



Source
Target
Automatic non-linear
matching
LDDMM: Large Diffeomorphic Deformation Metric Mapping
With modern methods













Anton François - 05/03/2024

Let \(V\) be the Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space (RKHS) of vector fields whose kernel is \(K\). We denote \(L: V \rightarrow V^*\) the Riesz operator such that \(\|v\|^2_V = ( Lv,v)\) .
Let \(K\) be the Gaussian reproducing kernel with \[K(x,y) = \exp\left( -\frac{|x -y|^2}{2\sigma^2}\right) \cdot \mathrm{Id}_{\mathbb{R}^d}\]
V is an admissible RKHS of vector fields.
Deformation as a flow of vector field
$$\left\{\begin{array}{rl}\partial_t \varphi_t &= v_t \circ \varphi_t\\ \varphi_0&= \mathrm{Id}\end{array}\right.$$
\(v_t \in V, \forall t\in [0,1]\)













Definition of \(V\)?
Anton François - 04/06/2024


\(G\) is a group of diffeomorphisms
The deformation defined from the ordinary differential equation:
\[\partial_t \varphi_t = v_t \circ \varphi_t; \quad \varphi_0 = \mathrm{Id}\]
with \(v_t \in V,\forall t\in [0,1]\), is a diffeomorphism. We note \(\varphi^v \in G\) such a diffeomorphism.
\(G\) := Space of Deformations
Deformation as a flow of vector field













Anton François - 04/06/2024



\[\partial_t \varphi_t = v_t \circ \varphi_t; \quad \varphi_0 = \mathrm{Id}\]
Image transport (advection): \[\partial_t I_t = v_t \cdot \nabla I_t \]
Deformed image
\(I_t = I_0 \circ (\varphi^v)^{-1}\)
The deformation acts on images.
Geodesic := Shortest path for the exact matching:
\[\mathrm{inf}_v \int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 dt\]













Anton François - 04/06/2024

\[\partial_t \varphi_t = v_t \circ \varphi_t; \quad \varphi_0 = \mathrm{Id}\]
Image transport (advection): \[\partial_t I_t = v_t \cdot \nabla I_t \]
Deformed image
\(I_t = I_0 \circ (\varphi^v)^{-1}\)
The deformation acts on images.
Geodesic := Shortest path for the exact matching:
\[\mathrm{inf}_v \int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 dt\]
Distance between two images
$$d(I,J) = \mathrm{min}_{v} \frac12 \int_0 ^1 \|v_t \|_V^2dt,$$
$$\text{s.t. }I_0 = I; I_1 = \int_0^1 v_t \cdot\nabla I_t dt = J$$













Anton François - 04/06/2024
The average Atlas builder.
Karcher mean : Given a group of image \(I^1,\dots,I^n\) and the Riemannian metric \(d\) we compute the template \(I\) by minimising:
$$\mathcal M(I) = \frac{1}{2n} \sum_{k=1}^{n} d(I,I_1^k)^2$$
















Anton François - 04/06/2024

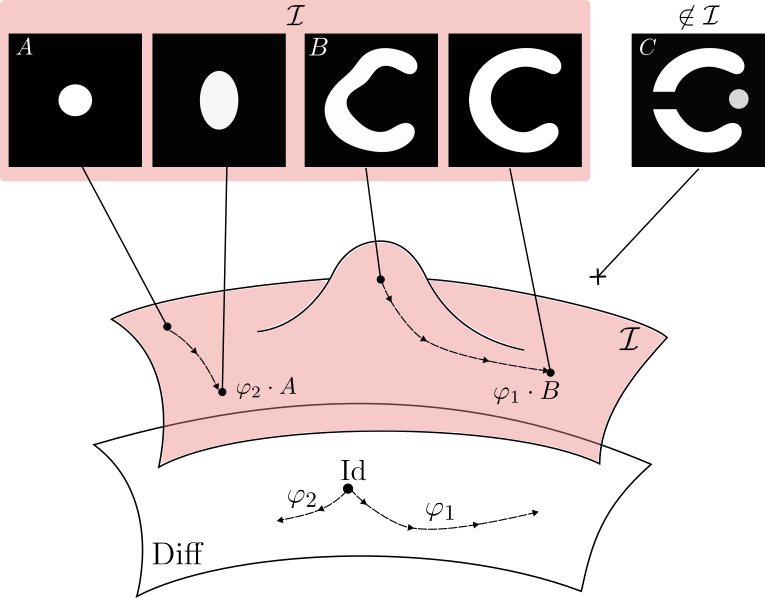
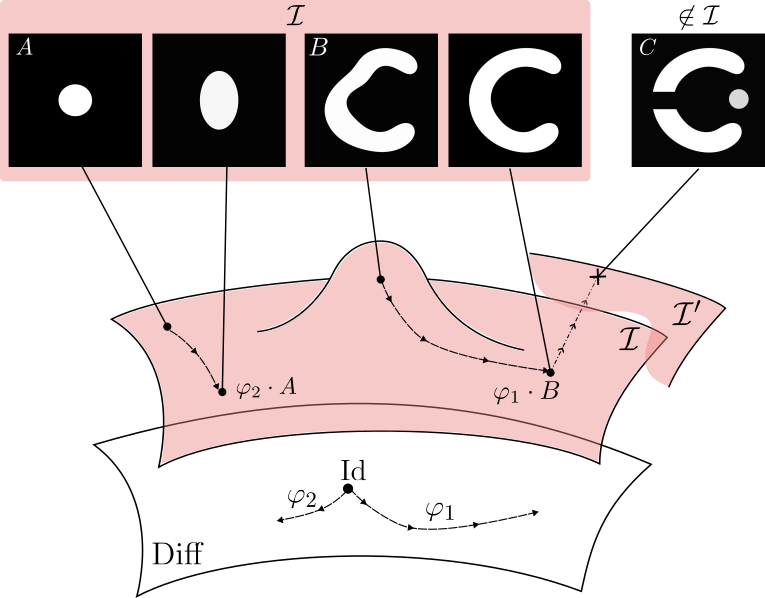
LDDMM can reach only images with same topology
Metamorphosis deforms images and adds intensity.
Making the registration of images B and C possible.
\[\partial_t I_t = v_t \cdot \nabla I_t\]
\[+ \mu z_t\]
Topology and appearances variations













Anton François - 04/06/2024

A first Example

Metamorphosis


Source
Target
LDDMM















Anton François - 04/06/2024
Metamorphosis
Implementation











Metamorphosis
A Metamorphosis on \(\mathcal I\) is a pair of curves \((\varphi_t, \psi_t)\), respectively on \(G\) and \(\mathcal I\), with \(\varphi_0 = \mathrm{Id}\).
\(G\) := Space of Deformations
\(\mathcal I\) := Space of images
\(\psi_t\) is the intensity changes evolution part: \(I_t = \psi_t \circ (\varphi_t)^{-1}\)












Anton François - 04/06/2024










Strategy overview
\(G\) := Space of Deformations
\(\mathcal I\) := Space of images












How to register in practice?
- Determine the geodesic expression by solving an exact-matching problem
- Relax the problem with inexact matching. Optimize through geodesic shooting.
Anton François - 04/06/2024










Exact matching formulation.
$$\left\{\begin{array}{rl}v_t &= -\frac{\rho}{\mu} K_\sigma \star (z_t \nabla I_t)\\ \dot z_t &= -\quad \nabla \cdot (z_t v_t) \\ \dot I_t &= -\langle v_t , \nabla I_t\rangle + \mu z_t\end{array}\right.$$
Advection equation with sourceContinuity equation

By computing the Euler-Lagrange equation of the exact matching cost :
and doing the variation with respect to \(I\) and \(v\) we obtain this set of geodesic equations:
[Trouvé & Younes, 2005]
$$ E_\mathrm M (I,v) = \frac12\int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \|z_t\|_{L_2}^2 dt \quad s.t.\ I_0 = S, I_1 = T$$











Anton François - 04/06/2024










We minimize this cost :
$$ H_\mathrm M (I,v) = \frac1 2 \left\| I_1 - T \right\|_2^2 + \frac \lambda 2\int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \|z_t\|_{L_2}^2 dt $$
$$ \Leftrightarrow H_\mathrm M (z_0) = \frac1 2 \left\| I_1 - T \right\|_2^2 + \frac \lambda 2\left( \|z_0\nabla I_0\|_V^2 + \rho \|z_0\|_{L_2}^2\right) $$
\(v_0 = - \frac \rho \mu K\star (z_0 \nabla I_0) \)
\(\|v_0\|_V+ \rho \|z_0\|_{L^2} = \|v_t\|_V +\rho \|z_t\|_{L^2} ,\forall t\in [0,1]\)
Metamorphosis Optimisation
via Geodesic shooting











Anton François - 04/06/2024










Metamorphosis Optimisation
via Geodesic shooting
$$\left\{\begin{array}{rl}v_t &= -\frac{\rho}{\mu} K_\sigma \star (z_t \nabla I_t)\\ \partial_t z_t &= -\quad \nabla \cdot (z_t v_t) \\ \partial_t I_t &= -\langle v_t , \nabla I_t\rangle + \mu z_t\end{array}\right.$$
We minimize the inexact matching cost :
$$ H_\mathrm M (I,v) = \frac1 2 \left\| I_1 - T \right\|_2^2 + \frac \lambda 2\int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \|z_t\|_{L_2}^2 dt $$
Geodesic Integration
\(z_0\)
\(I_1\)
Step 1:
Step 2:
We iterate over two steps:











\(\nabla H_M\) and adjoint equations computed
with auto differentiation.

Anton François - 04/06/2024

Lagrangian Formulation
$$x'(t) = v(t,x)$$
Lagrangian scheme
Not suitable for images
Eulerian scheme
\(I_{t+\delta_t} = I_t - \delta_t(v_t \times\nabla I_t)\)
Eulerian Formulation
$$\partial_t I(t,x) = - v(t,x) \cdot \nabla I(t,x)$$











Integration of the geodesics equations
Anton François - 04/06/2024










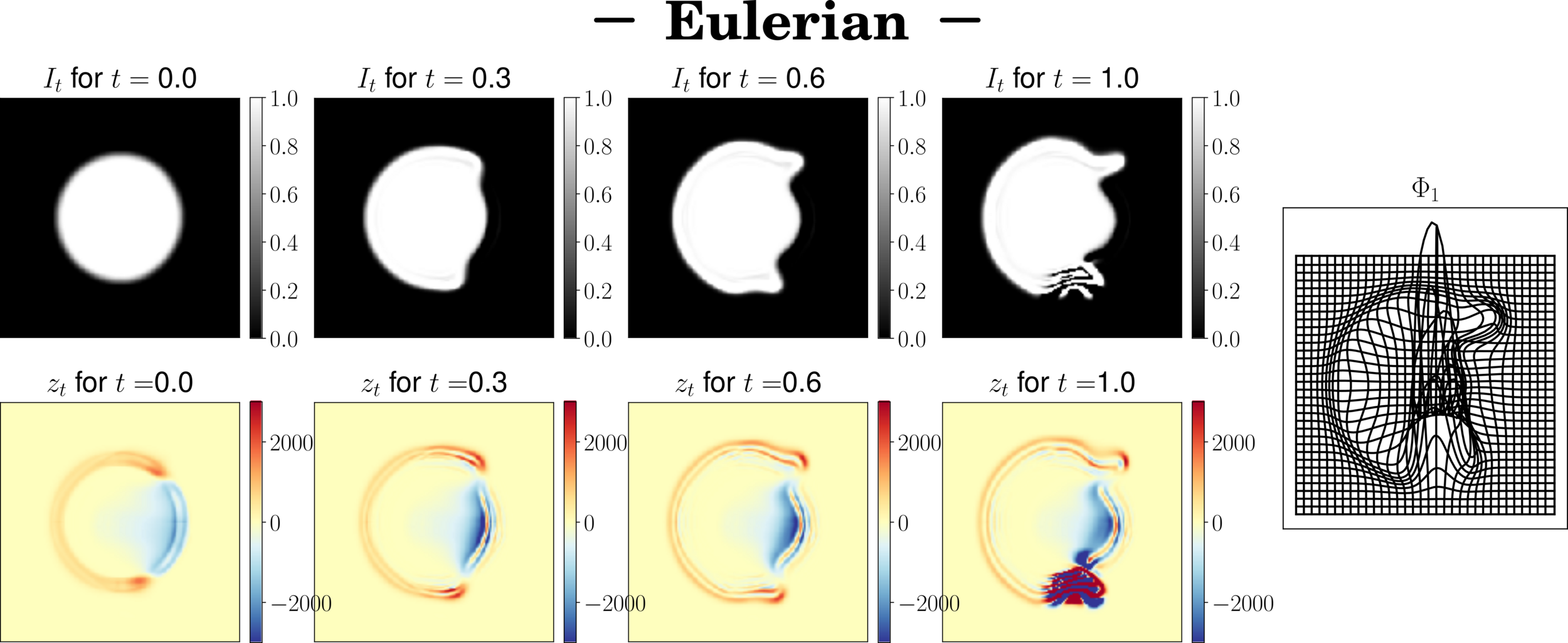
Schemes stability
Field aberations
We have to augment the number of time steps -> slow











Anton François - 04/06/2024

Semi-Lagrangian scheme principle
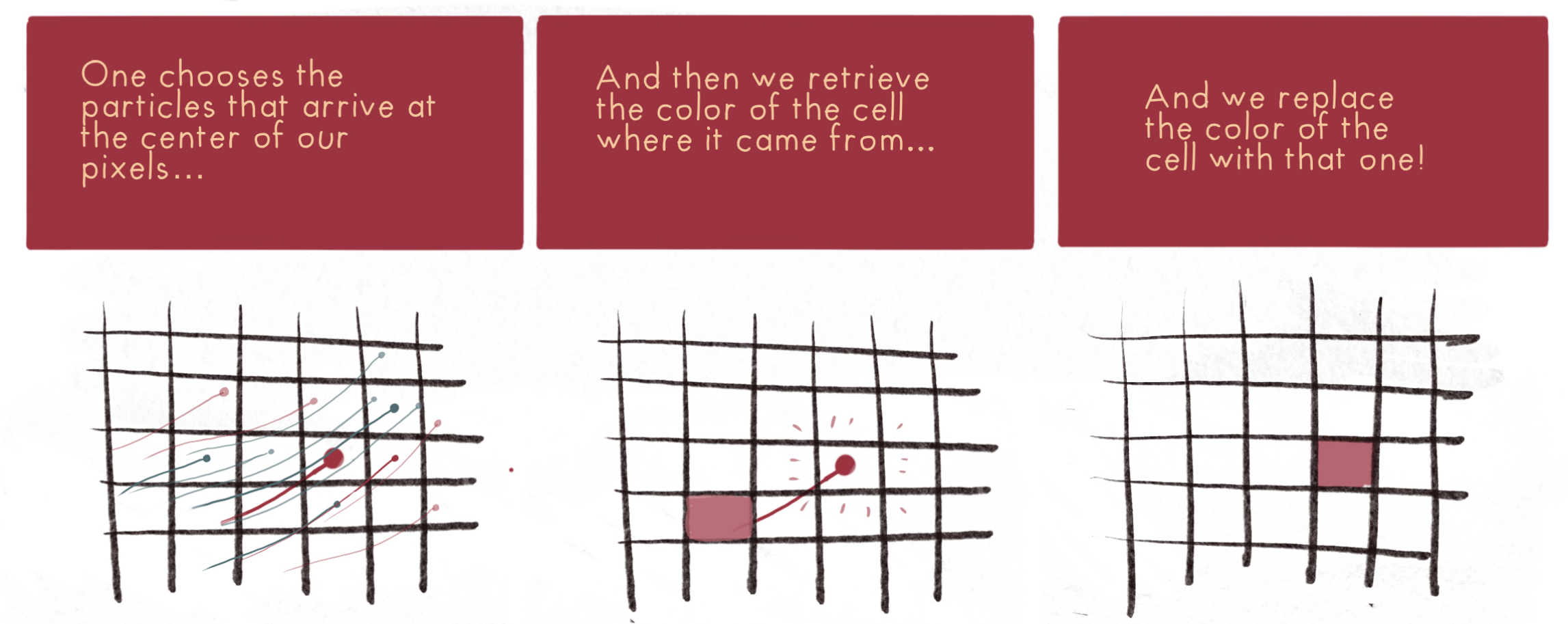
\(\partial_t I_t = v_t \cdot \nabla I_t + \mu z_t\)
Semi-Lagrangian scheme
\(I_{t+\delta_t} = \mathrm{Interp}(I_t,\varphi^{v_t}) + \delta_t \mu z_t\)











Anton François - 04/06/2024

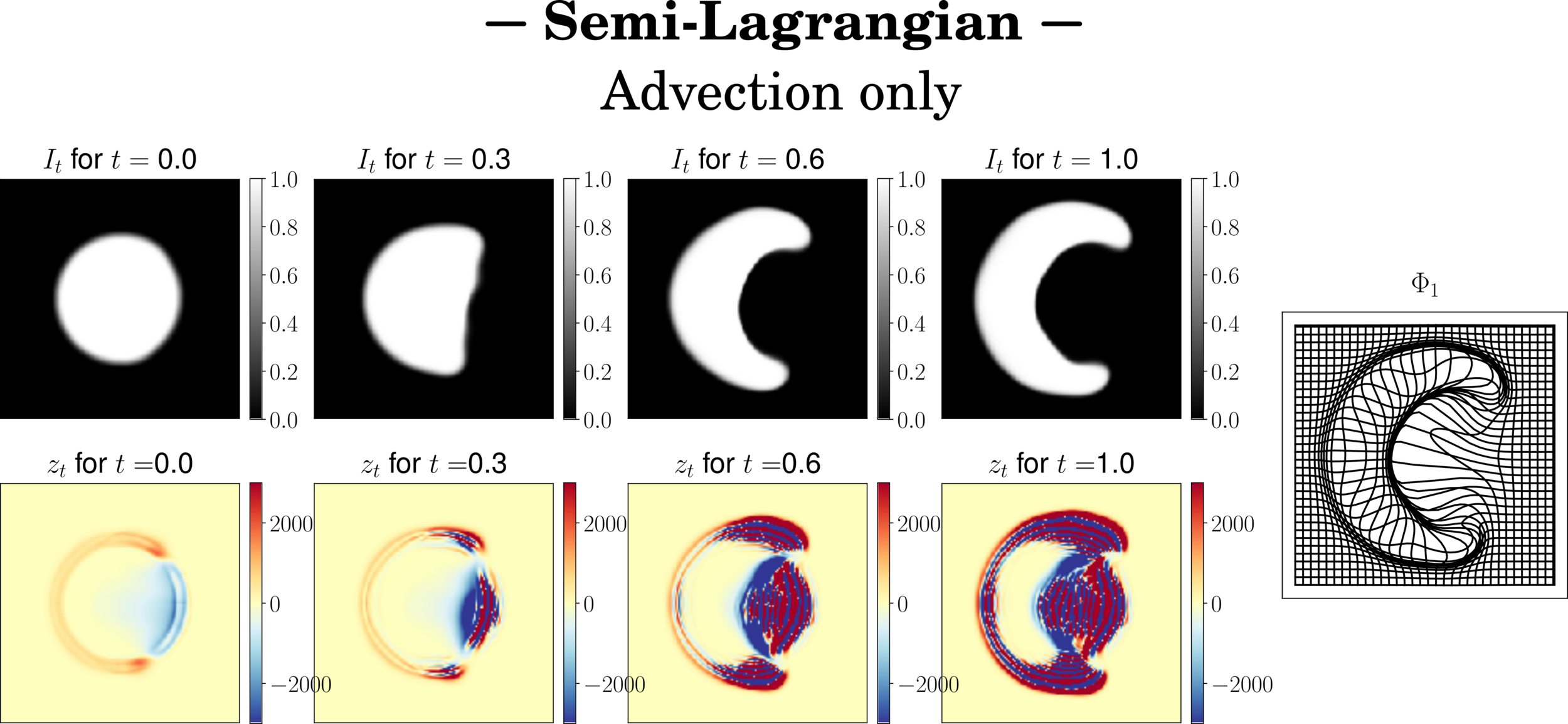
Schemes stability
Image integration more stable
residual instabilities











Anton François - 04/06/2024

Schemes stability
Stable image
Stable residual
Semi-Lagrangian scheme on residual
\(z_{t+\delta_t} = \mathrm{Interp}(z_t,\varphi^{v_t}) - \delta_t z_t \mathrm{div}(v_t)\)
\(\partial_t z_t = - \mathrm{div} (z_t v_t)\)
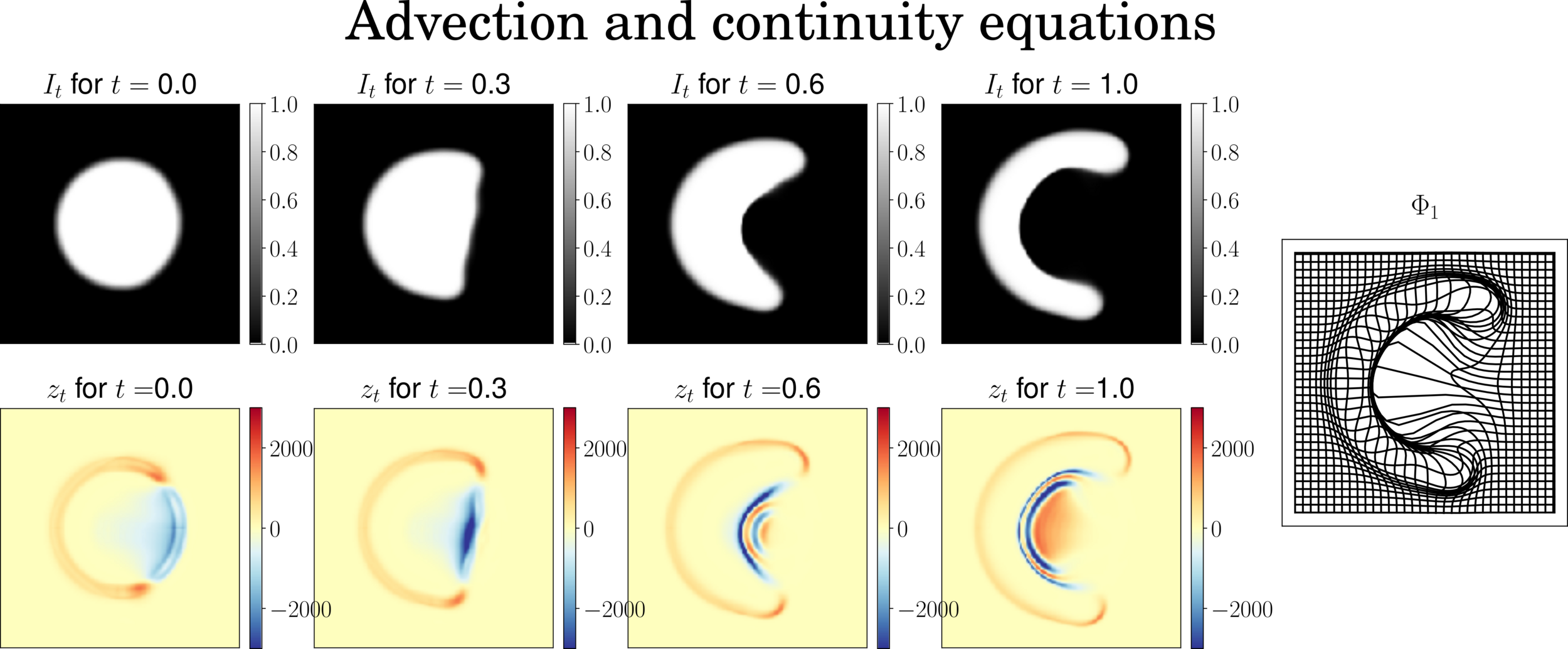
- Full semi-Lagrangian -











Anton François - 04/06/2024




github.com/antonfrancois/Demeter_metamorphosis
- The semi-Lagrangian scheme is more stable
- Open-Source Metamorphosis on the GPU, with autodiff.
- Made for prototyping











Anton François - 04/06/2024












Problem solved ?
Metamorphosis



Source
Target
LDDMM

$$\rho = 1$$
$$\rho = 80$$

$$\rho = 10$$





$$ E_\mathrm M (I,v) = \frac12\int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \|z_t\|_{L_2}^2 dt \quad s.t.\ I_0 = S, I_1 = T$$
Anton François - 04/06/2024
Constrained
Metamorphosis

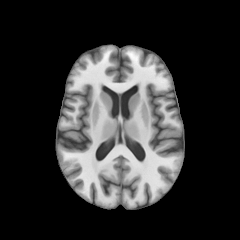
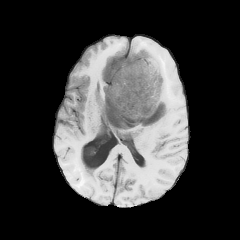
Registration with topological changes
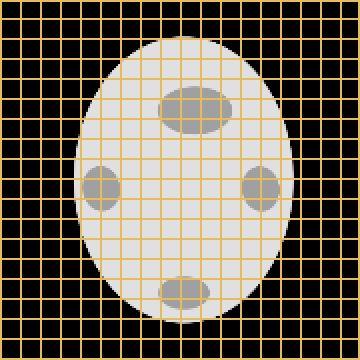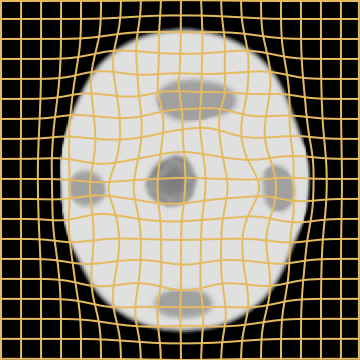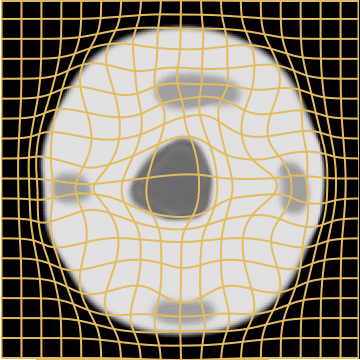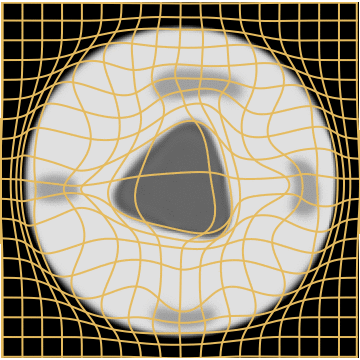
Healthy brain
Brain with a glioblastoma















Anton François - 04/06/2024
Glioma registration problem

- Necrosis : topological difference
- Mass effect : morphological difference
- Oedema : appearance difference
- Brain natural differences
MNI template
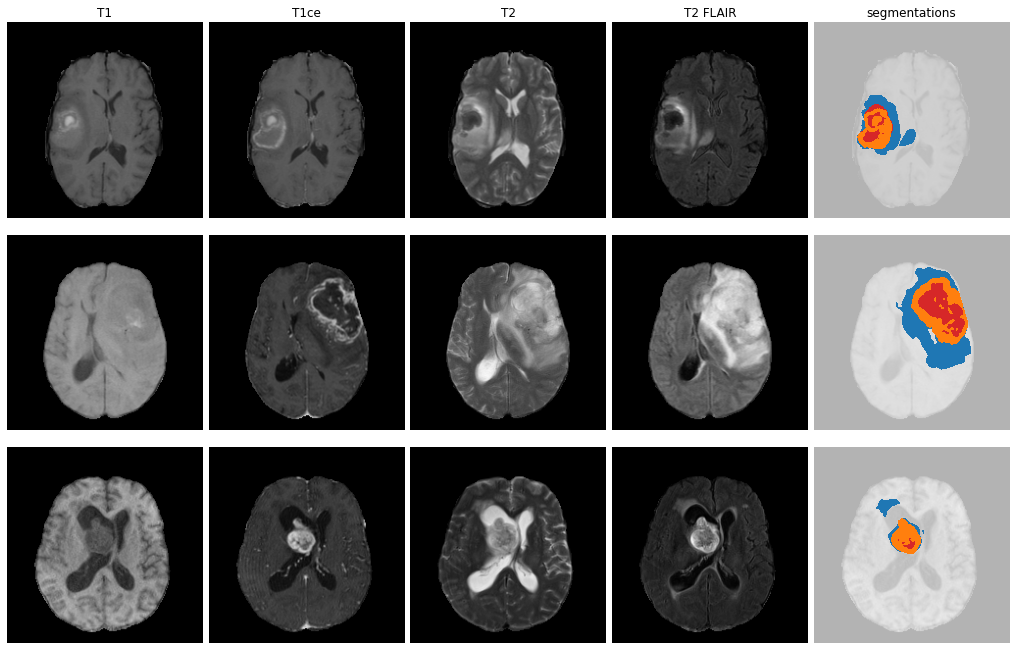



ET - GD enhancing tumour
ED - Peritumoural edematous/invaded tisue
NRC - Necrotic Tumour Core















Anton François - 04/06/2024
State of the art
For glioma registration:
- Cost-Function Masking (CFM) [Brett et al., 2001]
- Inpainting method [Sdika and Pelletier, 2009]
- Geometric Metamorphosis [Niethammer et al., 2012]
- GLISTR: biophysical models to perform registration. [Gooya et al., 2011; Ali et al., 2012]
- Deep-Learning: [Bône et al., 2020; Han et al., 2020b; Shu and et al, 2018; Wang et al., 2023]
LDDMM [Avants et al., 2008; Beg et al., 2005; Zhang and Fletcher, 2018] &
Metamorphosis [Holm et al., 2009; Trouvé and Younes, 2005]
We will base our registration on the methods:















Anton François - 04/06/2024
Problem solved ?

\(\rho\) and \(\mu\) control ratio between intensity changes and deformation
small intensity changes
big intensity changes















Anton François - 04/06/2024
Problem solved ?


small intensity changes
big intensity changes

NO !
Residual entanglement!















Anton François - 04/06/2024

Weighted Metamorphosis
$$\left\{\begin{array}{rl}v_t &= -\frac{\rho}{\mu} K_\sigma \star (z_t \nabla I_t)\\ \dot z_t &= \quad - \nabla \cdot (z_t v_t) \\ \dot I_t &= - v_t \cdot \nabla I_t + \mu M_t z_t\end{array}\right.$$
Let \((M_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) be a continuous temporal mask. By computing the Euler-Lagrange equation of the exact matching cost :
$$E_{\mathrm{WM}}(I,v) = \frac 12\int_0^1\|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho\langle z_t, M_t z_t \ \ \rangle_{L^2} dt \quad s.t.\ I_0 = S, I_1 = T $$
and doing the variation with respect to \(I\) and \(v\) we obtain this set of geodesic equations:
\(\langle z_t, M_t z_t \rangle_{L^2}\)
\(M_t\)














Anton François - 04/06/2024

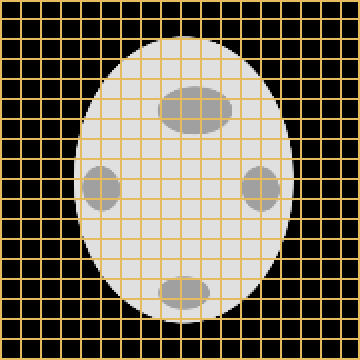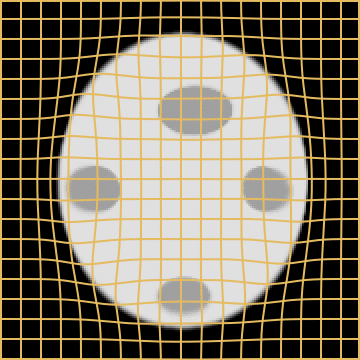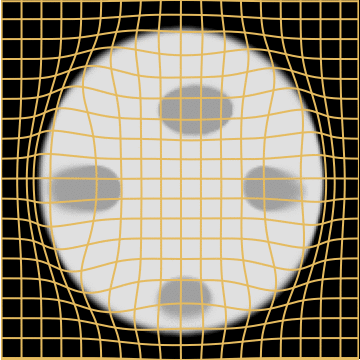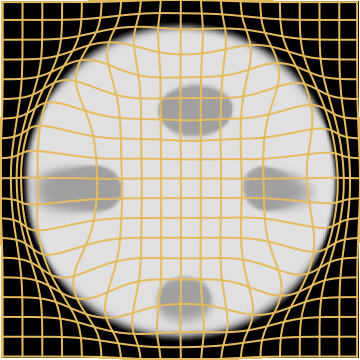
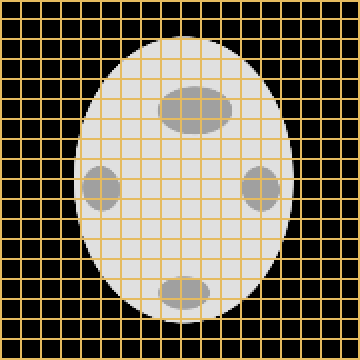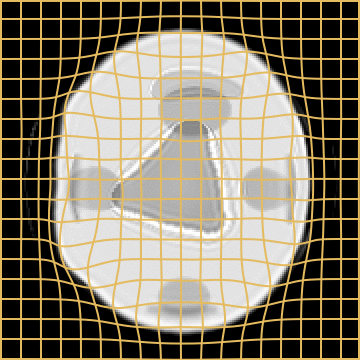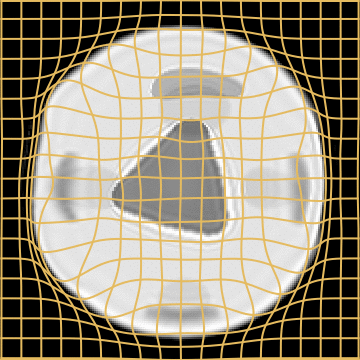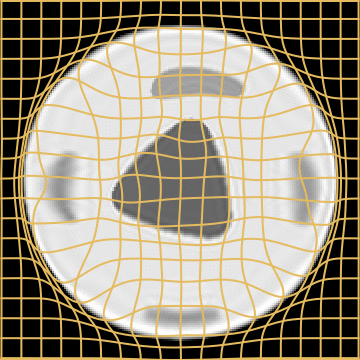


Source
Target
LDDMM
Metamorphosis
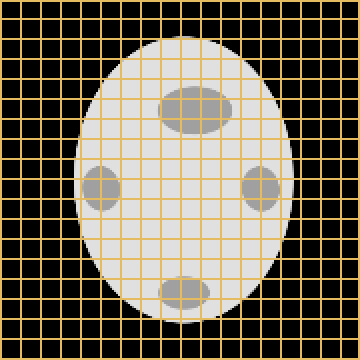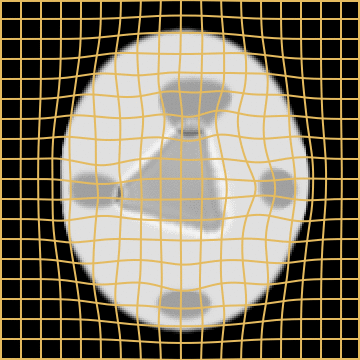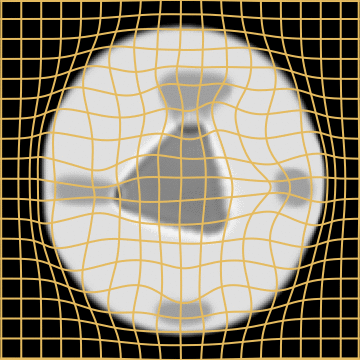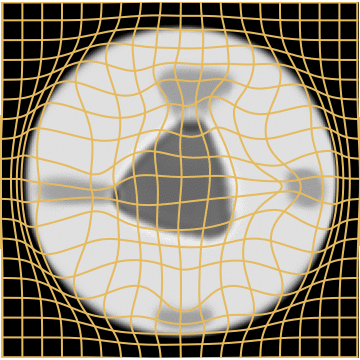
WM
A static mask gets stuck














Anton François - 04/06/2024

Weighted Metamorphosis
with a growing mask.
1. We set \(M_1\) as the topological difference segmentation.
2. We initialise \(M_0\) as a small ball at its center.


3. We register \(M_0\) to \(M_1\) using LDDMM.
Simple and realistic prior modelling:














Anton François - 04/06/2024



Source
Target

WM
WM w. Growing mask
Weighted Metamorphosis
with a growing mask.














Anton François - 04/06/2024

With textured images,
no mass effect is produced
WM fails on more realistic images

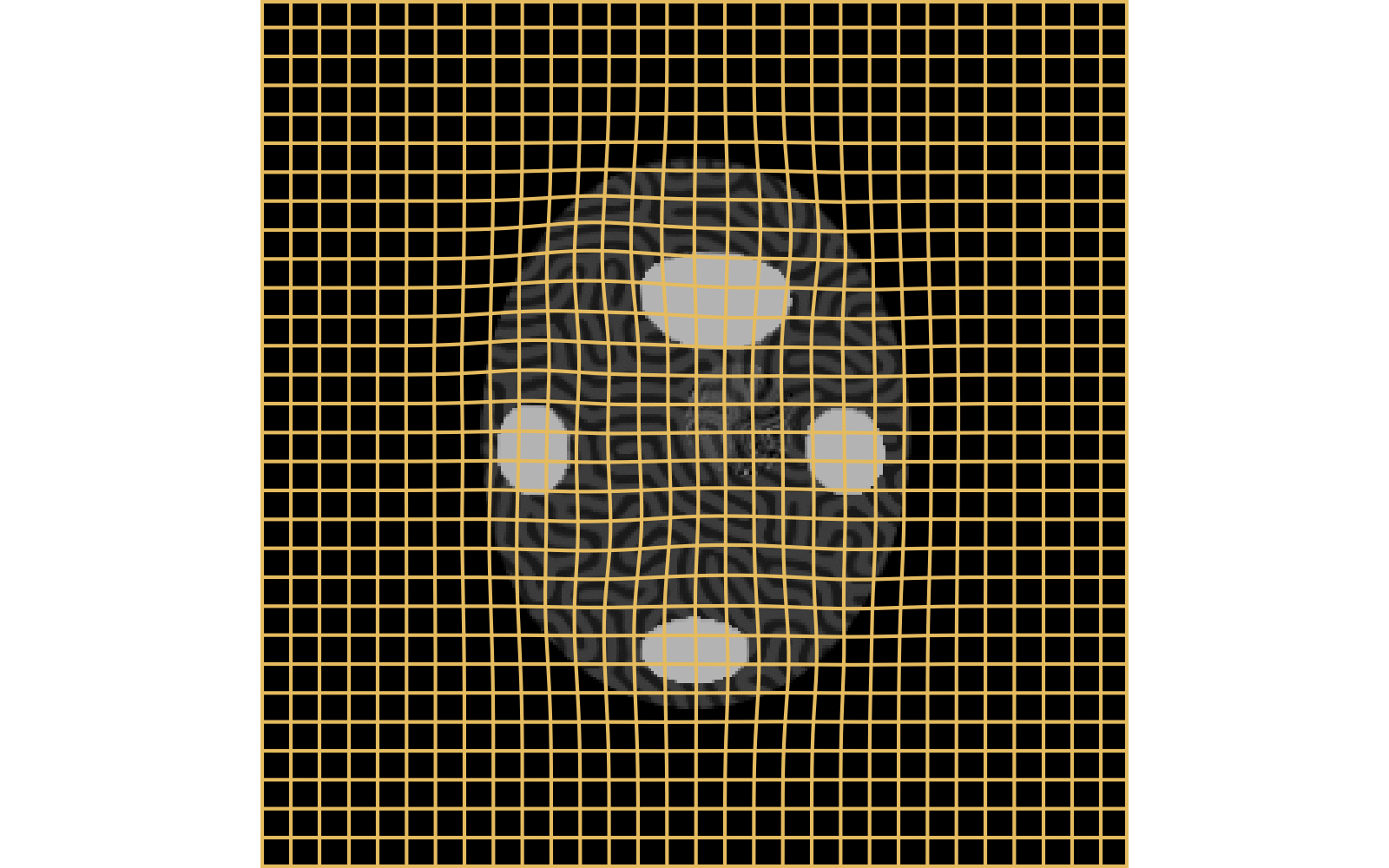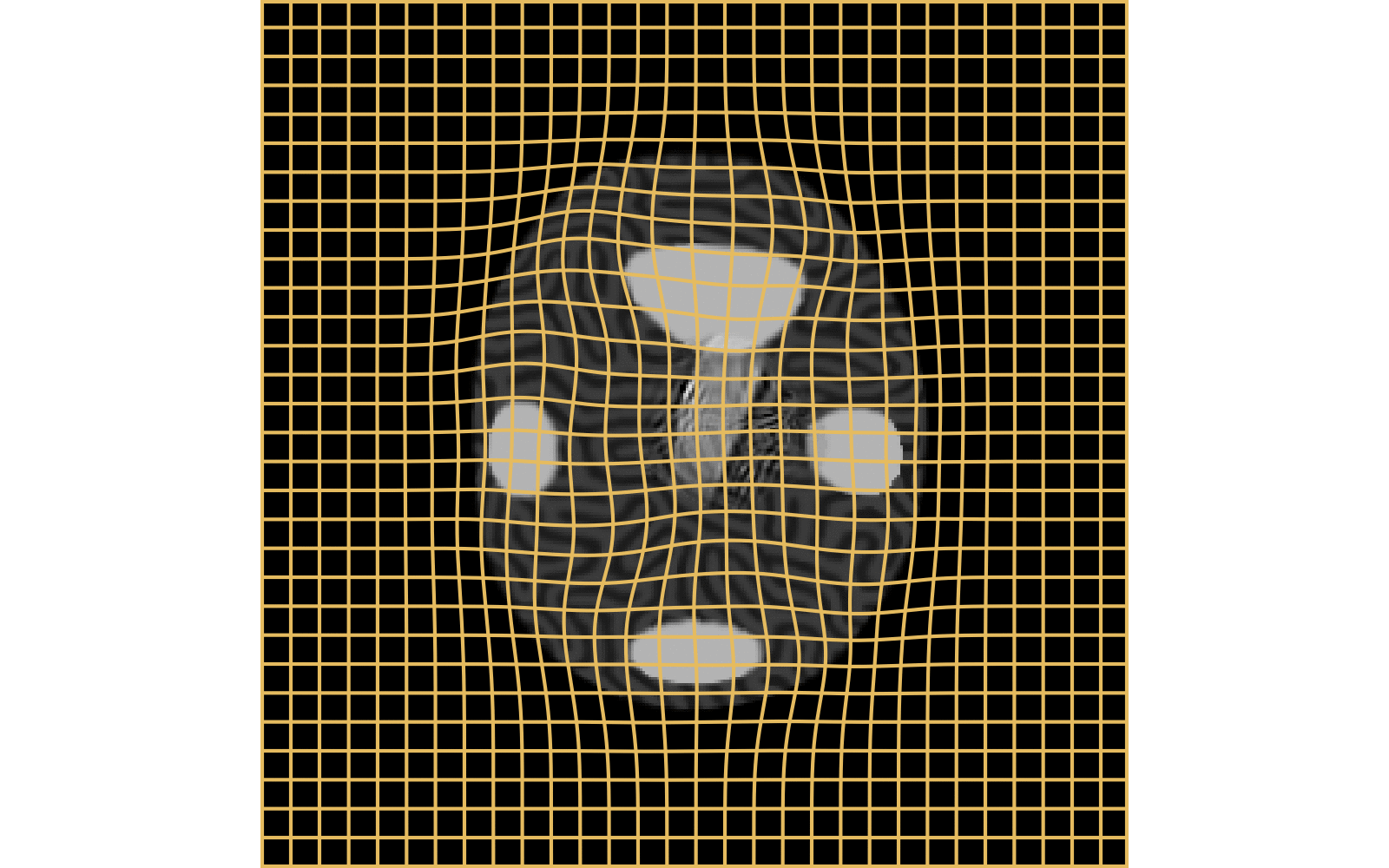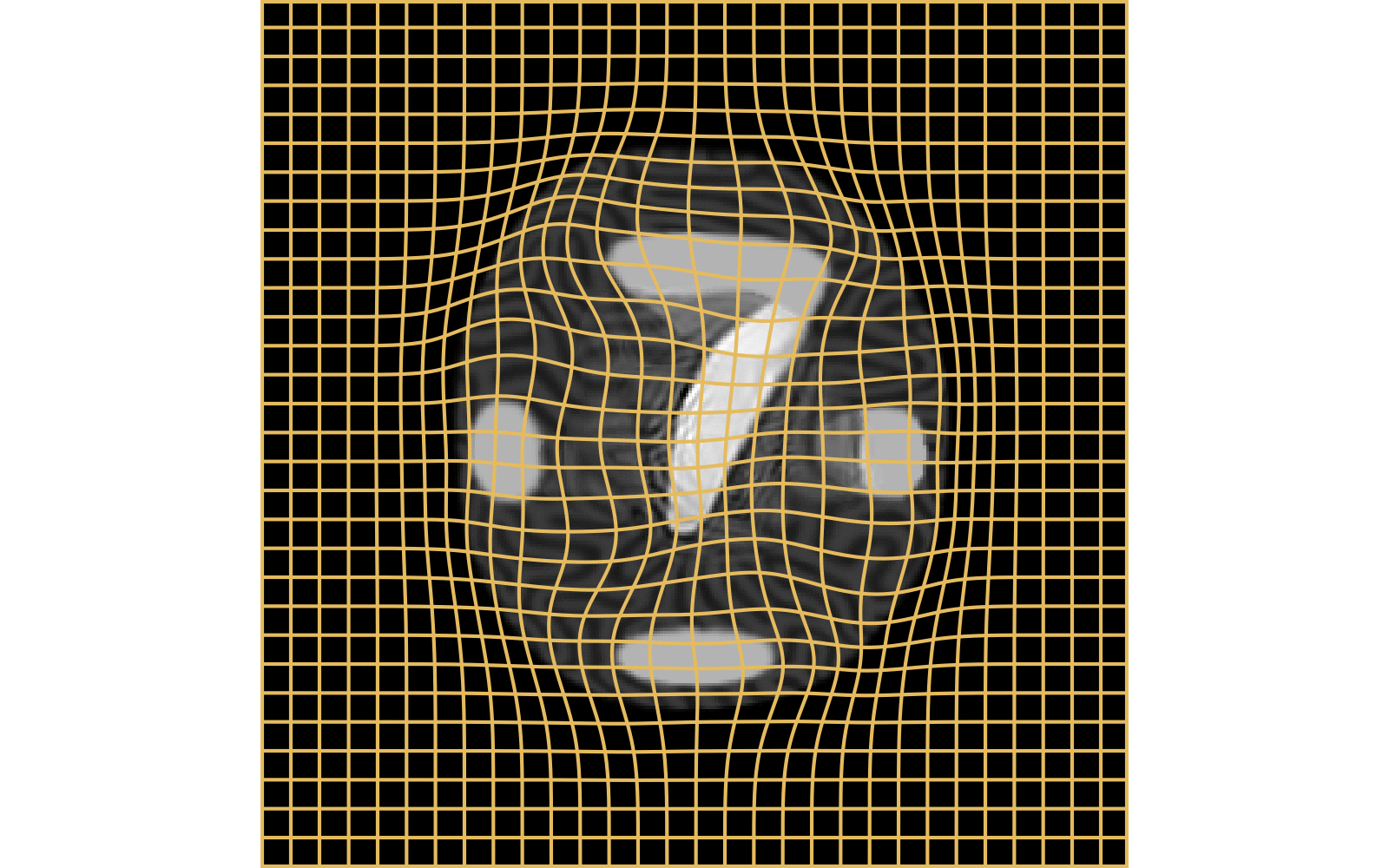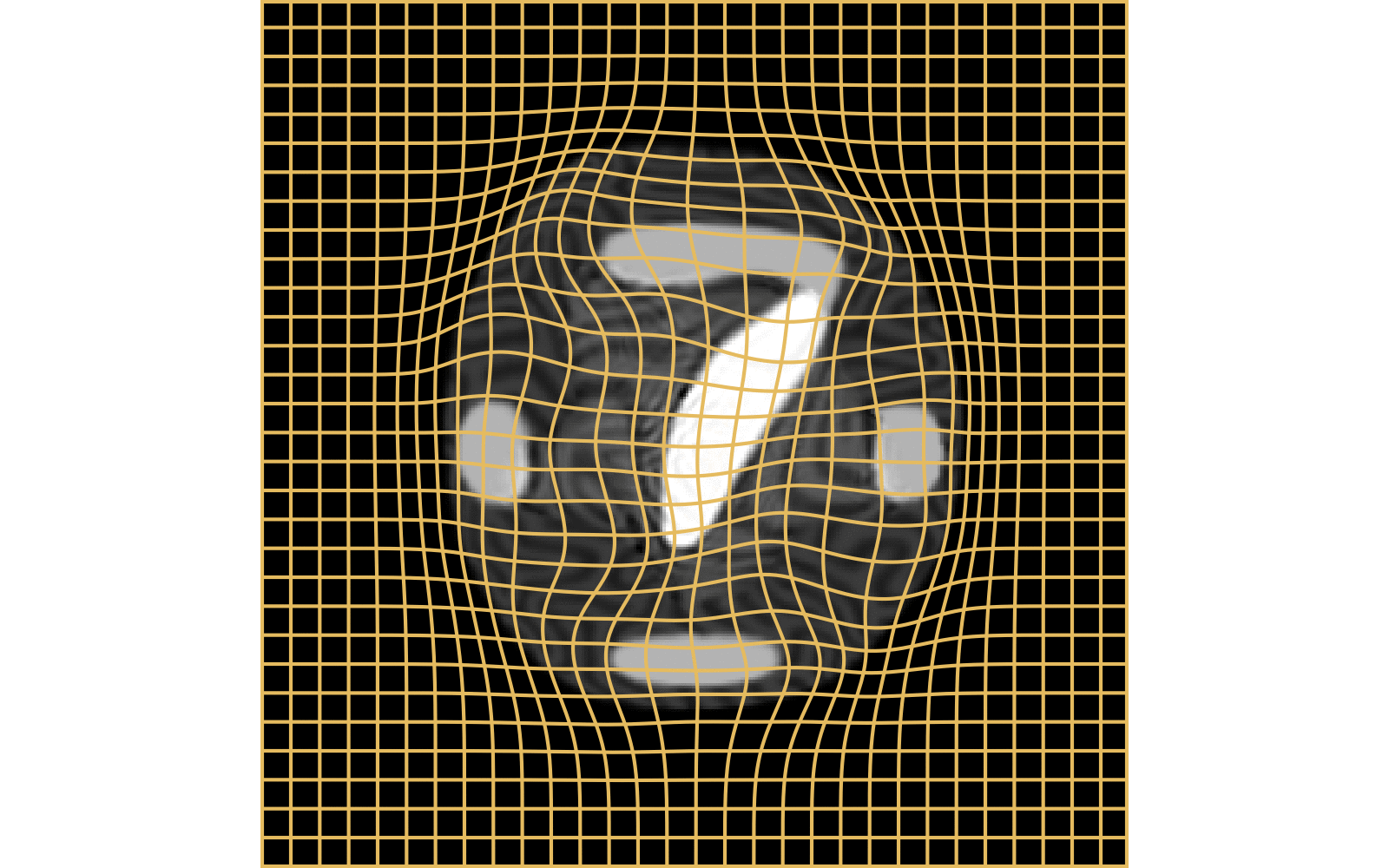














Anton François - 04/06/2024


\(M_t\) : Adding intensities
Oriented Metamorphosis
\(P_t\): Indicates where the vector field should be followed
\(w_t\): vector field to follow
We want to force the registration to follow the LDDMM field.














Anton François - 04/06/2024

Constrained Metamorphosis
Let \((M_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) and \((P_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) be two continuous temporal masks and \(w_t \in V\), an admissible vector field.
By computing the Euler-Lagrange equation of the exact matching cost:
$$ E_{\mathrm{CM}}(I,v) = \int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \langle z_t, M_t z_t \rangle_{L^2} -\gamma \langle v_t , P_tw_t\rangle_{L_2} dt $$
Oriented & Weighted
\(s.t., I_0 = S, I_1 = T\)














Anton François - 04/06/2024

Constrained Metamorphosis
Let \((M_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) and \((P_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) be two continuous temporal masks and \(w_t \in V\), an admissible vector field.
By computing the Euler-Lagrange equation of the exact matching cost:
$$ E_{\mathrm{WM}}(I,v) = \int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \langle z_t, M_t z_t \rangle_{L^2} +\gamma \langle v_t , P_tw_t\rangle_{L_2} dt $$
Oriented & Weighted
\(s.t., I_0 = S, I_1 = T\)
\[\gamma \langle v_t , P_tw_t\rangle_{L_2}\]
Oriented Norm:
We seek to estimate \(v_t\) similar to \(w_t\) where the mask \(P_t\) is positive.
Anton François - 05/03/2024















Constrained Metamorphosis
Let \((M_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) and \((P_t)_{t\in [0,1]}\) be two continuous temporal masks and \(w_t \in V\), an admissible vector field.
By computing the Euler-Lagrange equation of the exact matching cost:
$$ E_{\mathrm{CM}}(I,v) = \int_0^1 \|v_t\|_V^2 + \rho \langle z_t, M_t z_t \rangle_{L^2} -\gamma \langle v_t , P_tw_t\rangle_{L_2} dt $$
and doing the variation with respect to \(I\) and \(v\) we obtain this set of geodesic equations:
Oriented & Weighted
\(s.t., I_0 = S, I_1 = T\)
Theorem:
$$\left\{\begin{array}{rl} v_t &= K \star \left(\frac{-1}{\mu(1+\gamma P_t)} z_t\nabla I_t + \frac{\gamma P_t}{1 + \gamma P_t} w_t \right)\\ \dot z_t &= -\quad \nabla \cdot (z_t v_t) \\ \dot I_t &= - v_t \cdot\nabla I_t + \mu M_t z_t\end{array}\right.$$
\(\frac{\gamma P_t}{1+\gamma P_t}\)
$$\frac{-1}{\mu(1+\gamma P_t)}$$
Anton François - 05/03/2024
















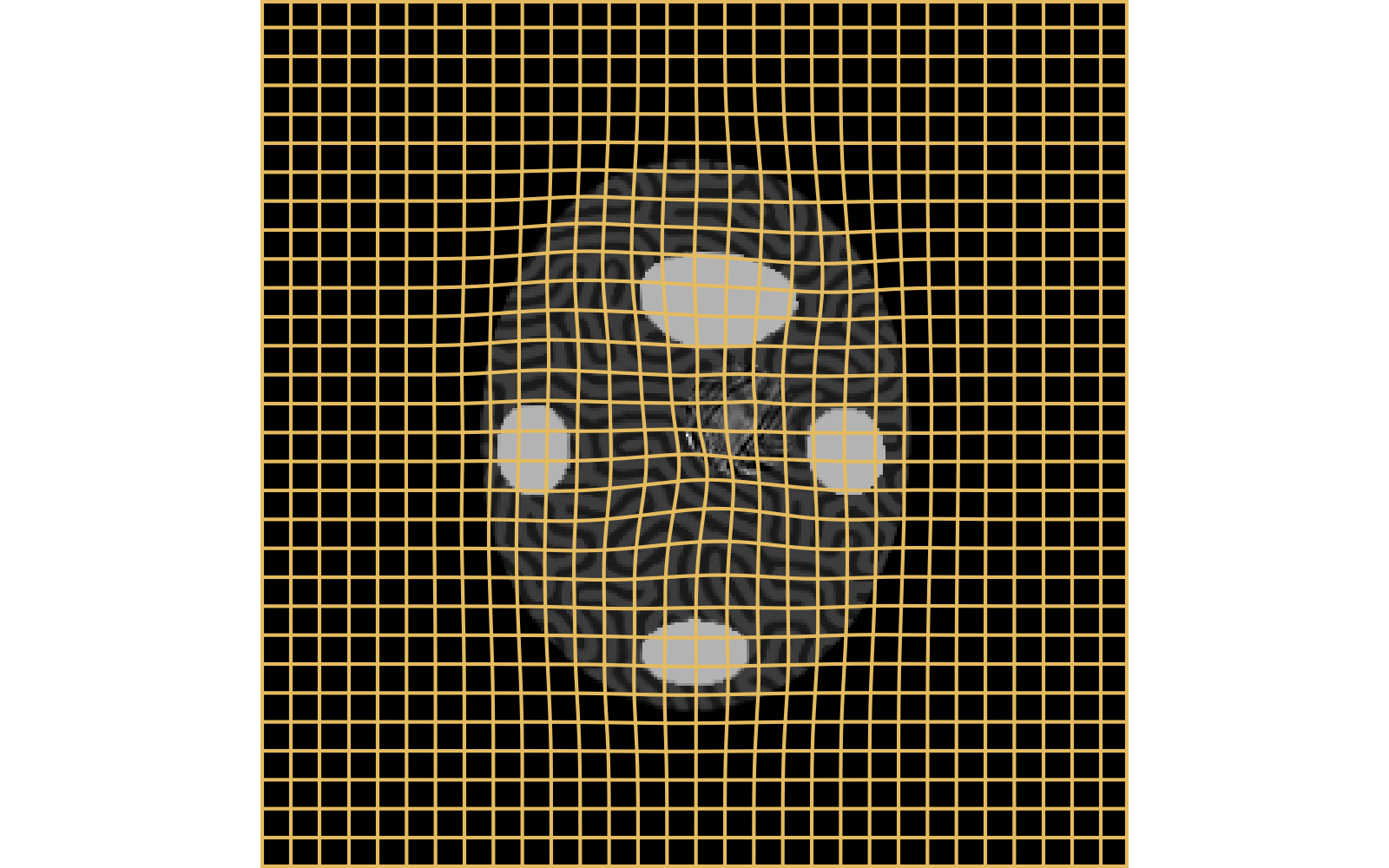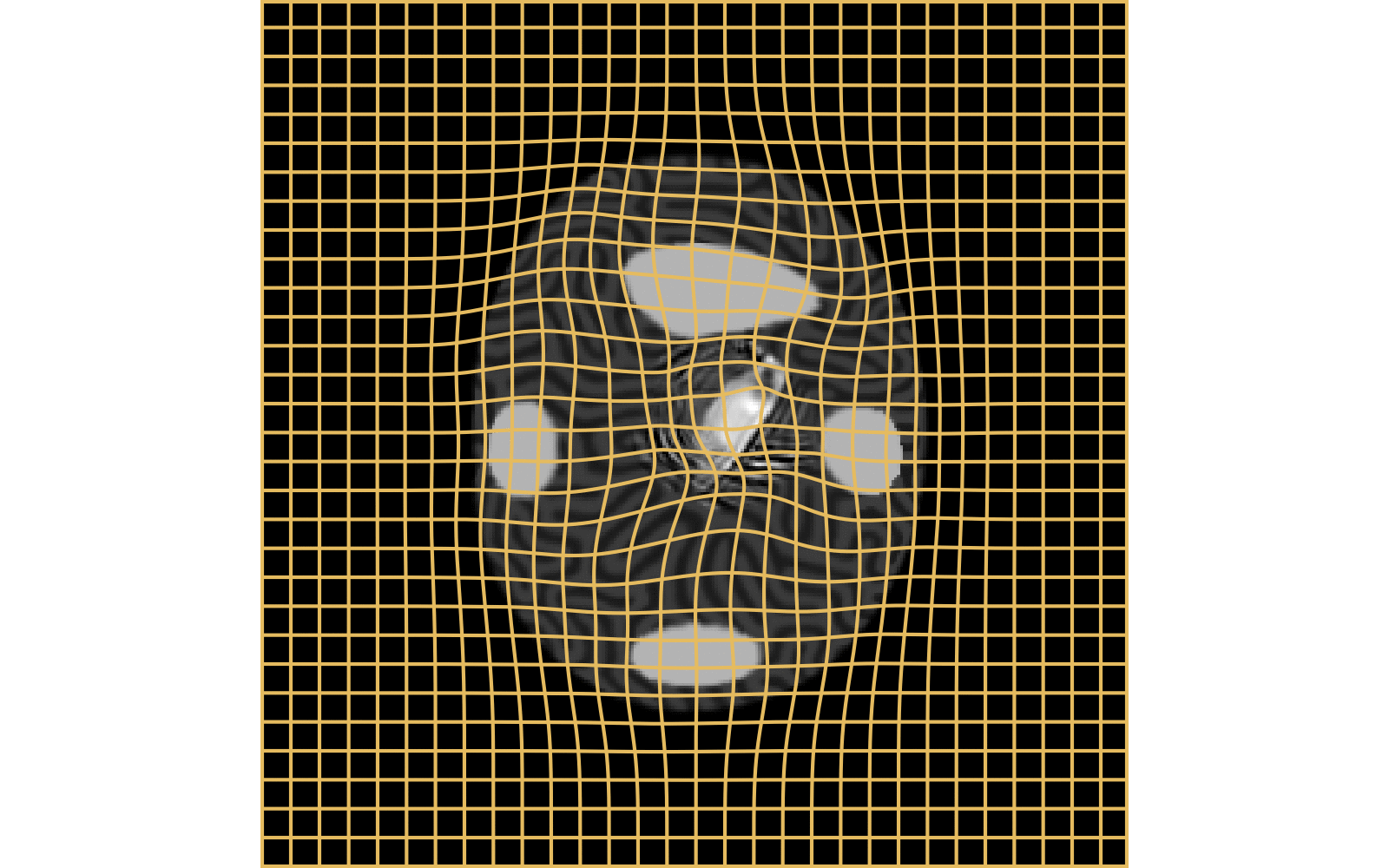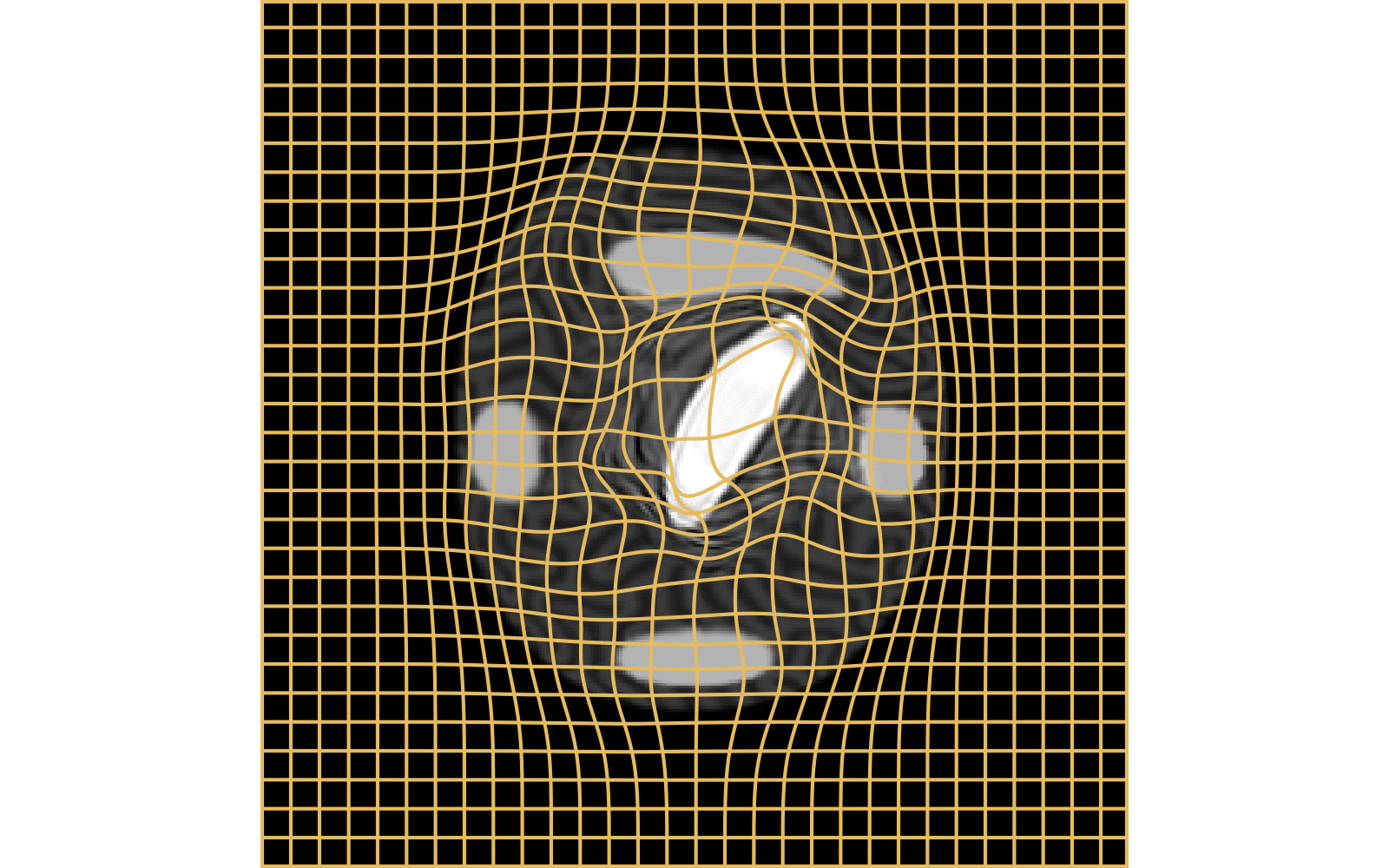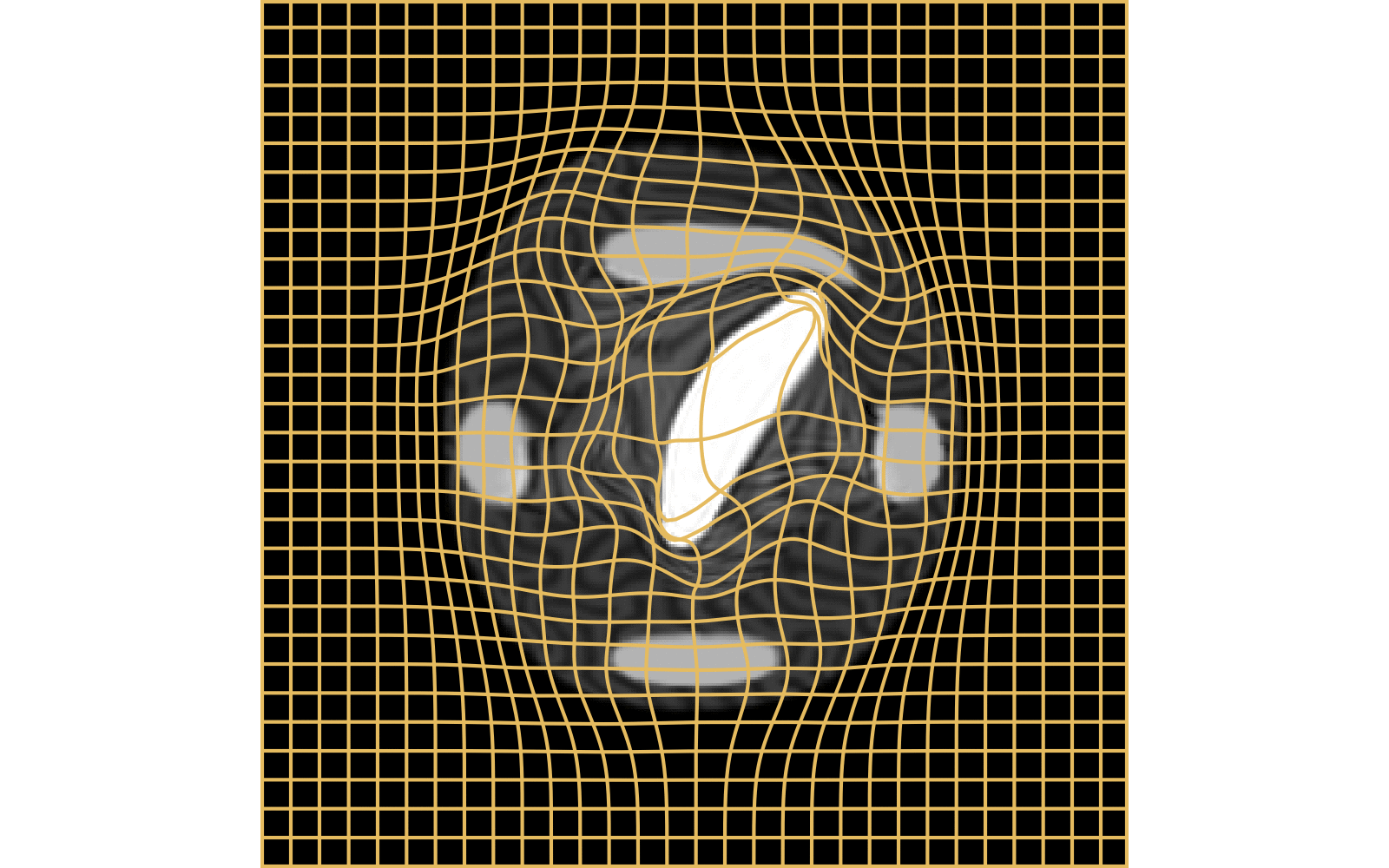

CM


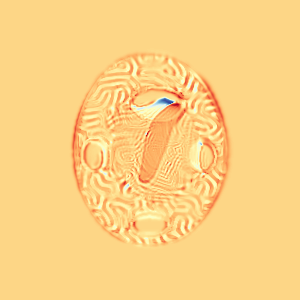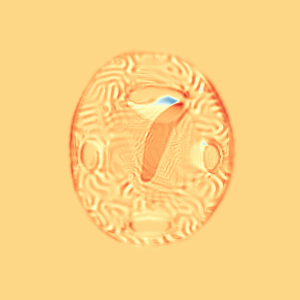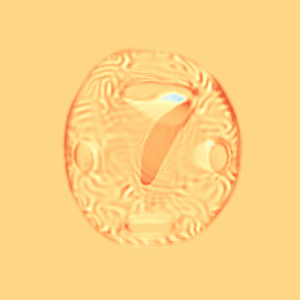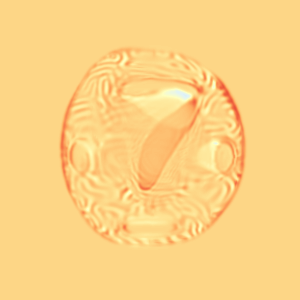
WM
\(I_t\)
\(I_t\) & \(\varphi^{v_t}\)
\(z_t\)
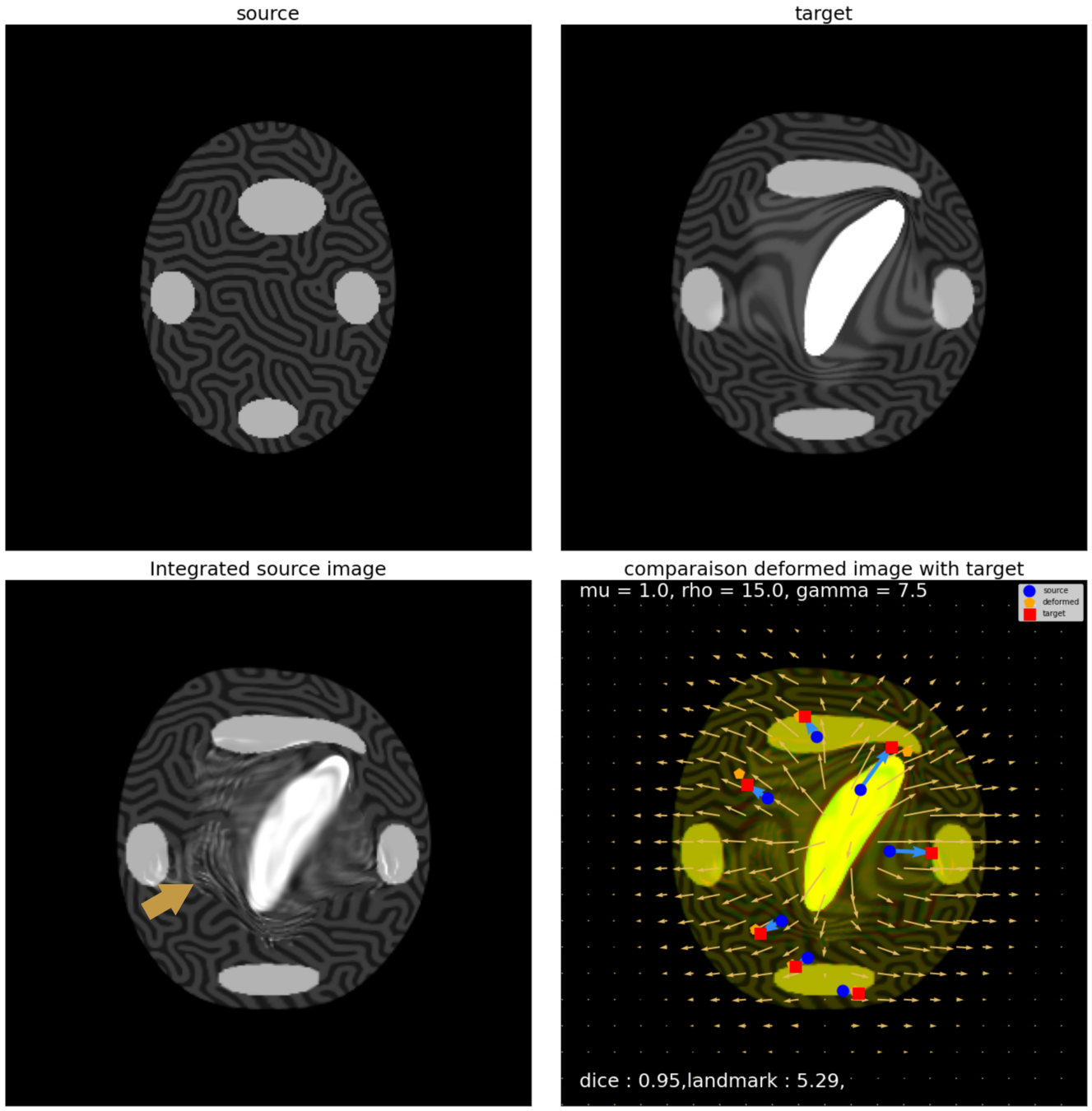
Constrained Metamorphosis
Results on ToyExamples














Anton François - 04/06/2024

On real data: BraTS 2021

- Big data-set
- 4 modalities
- Glioblastoma ground truth segmentation
Registration validation using manually segmented ventricles (40 subjects).
Registered ventricles overlap measured with DICE score.
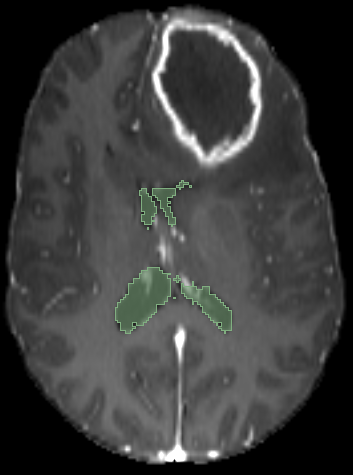
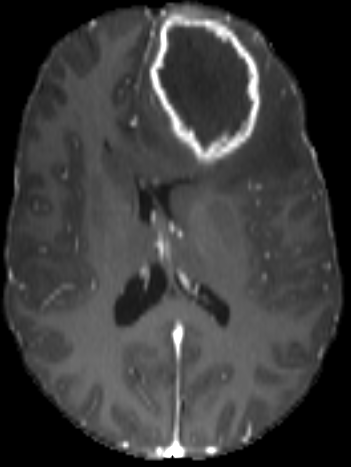














Anton François - 04/06/2024
Constrained Metamorphosis
Weighted Metamorphosis
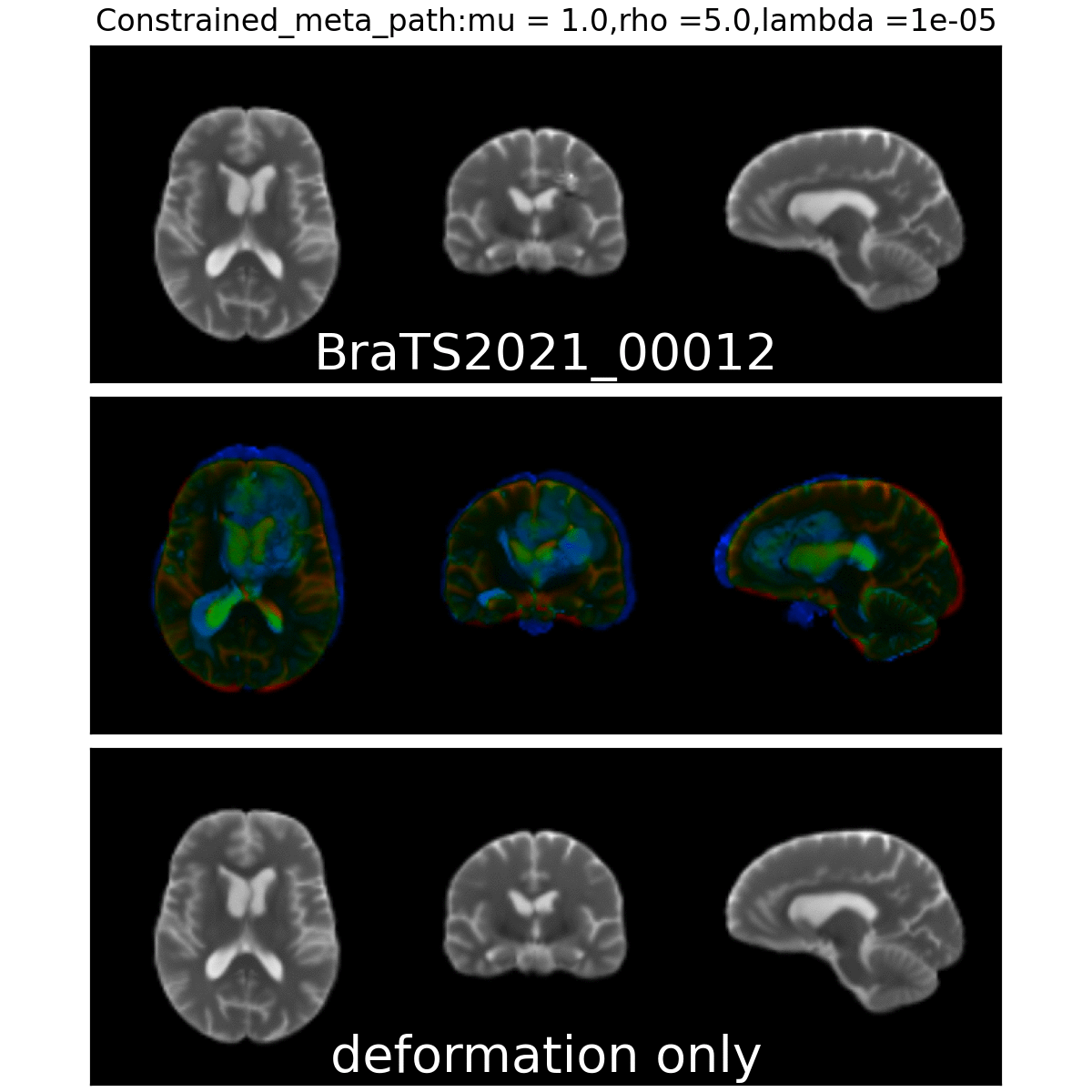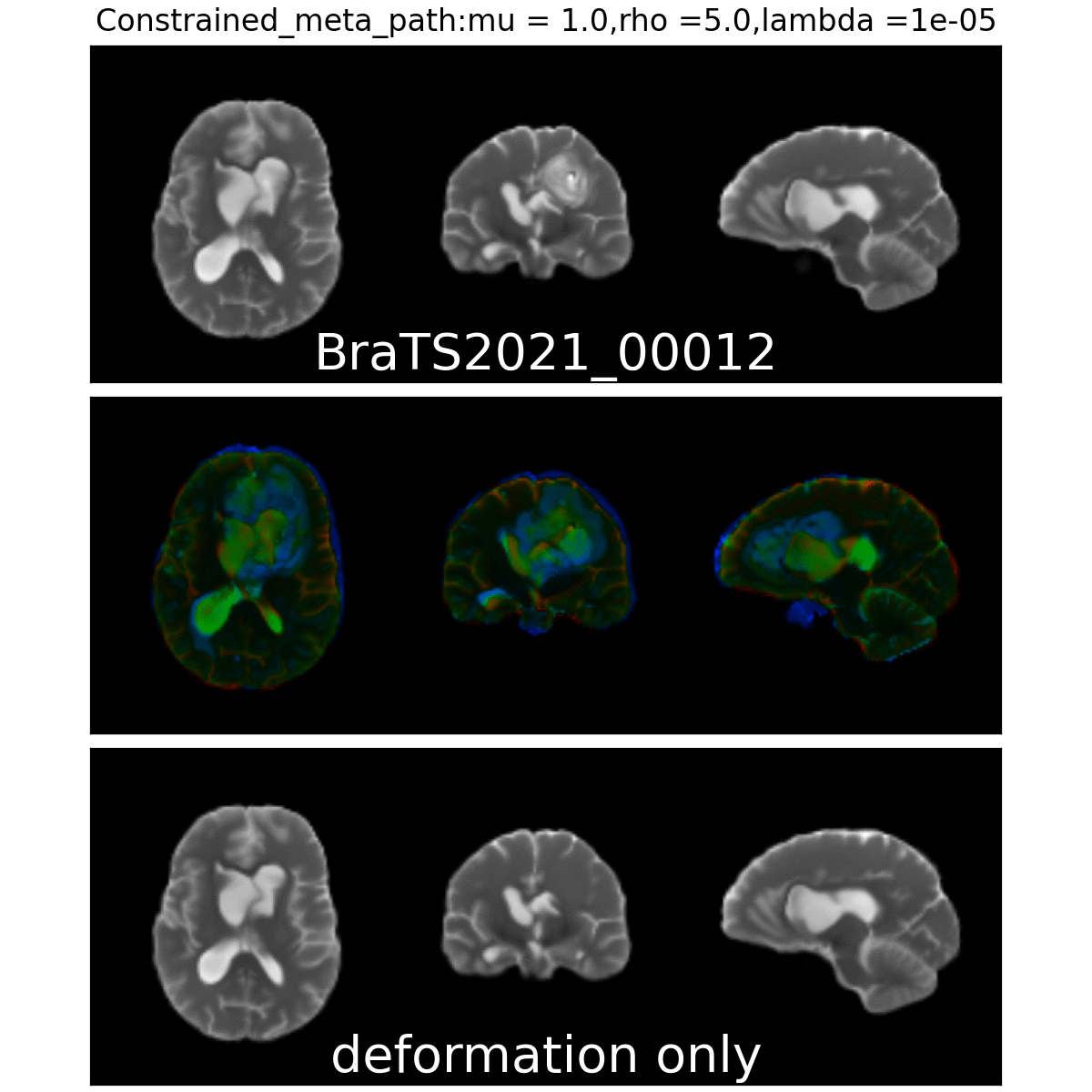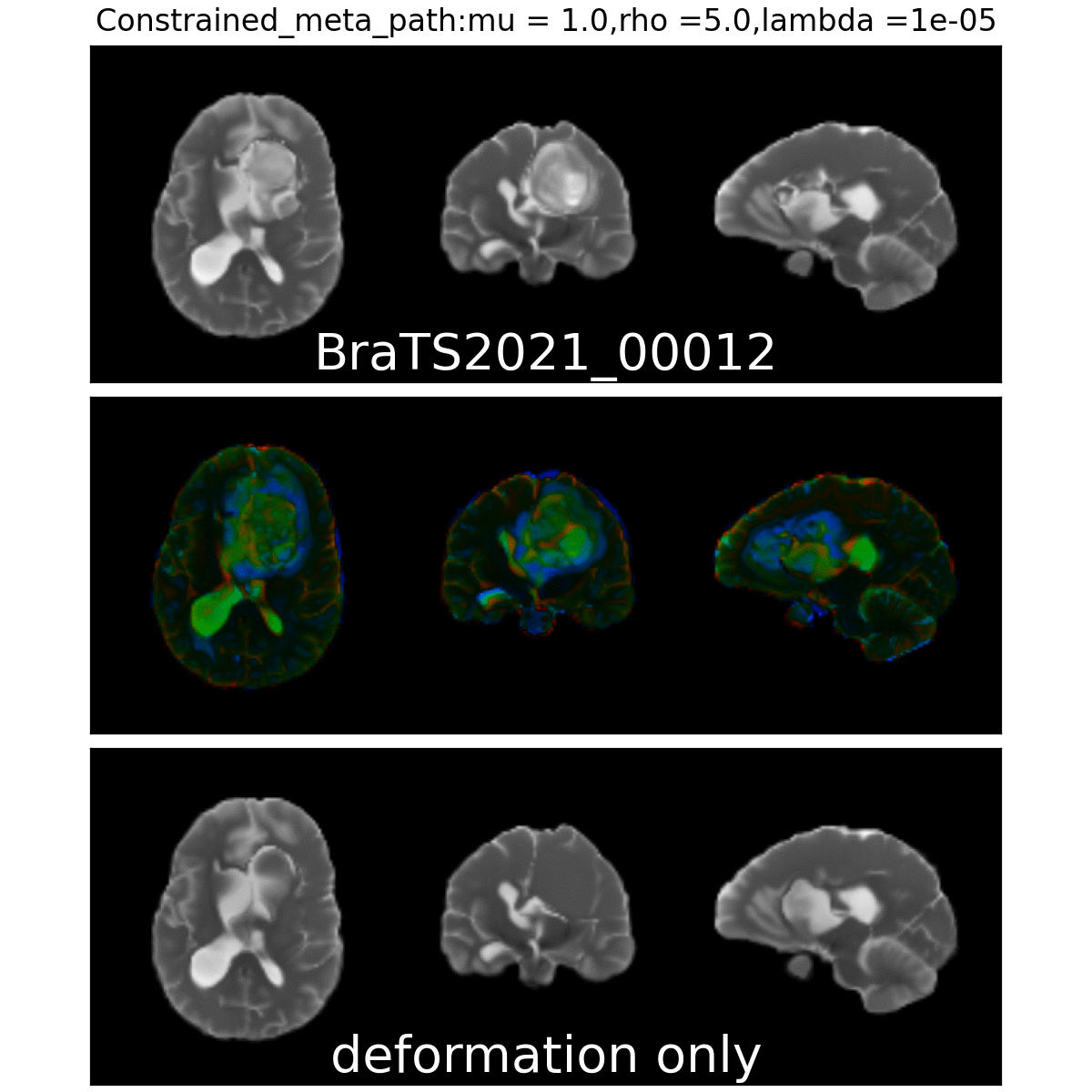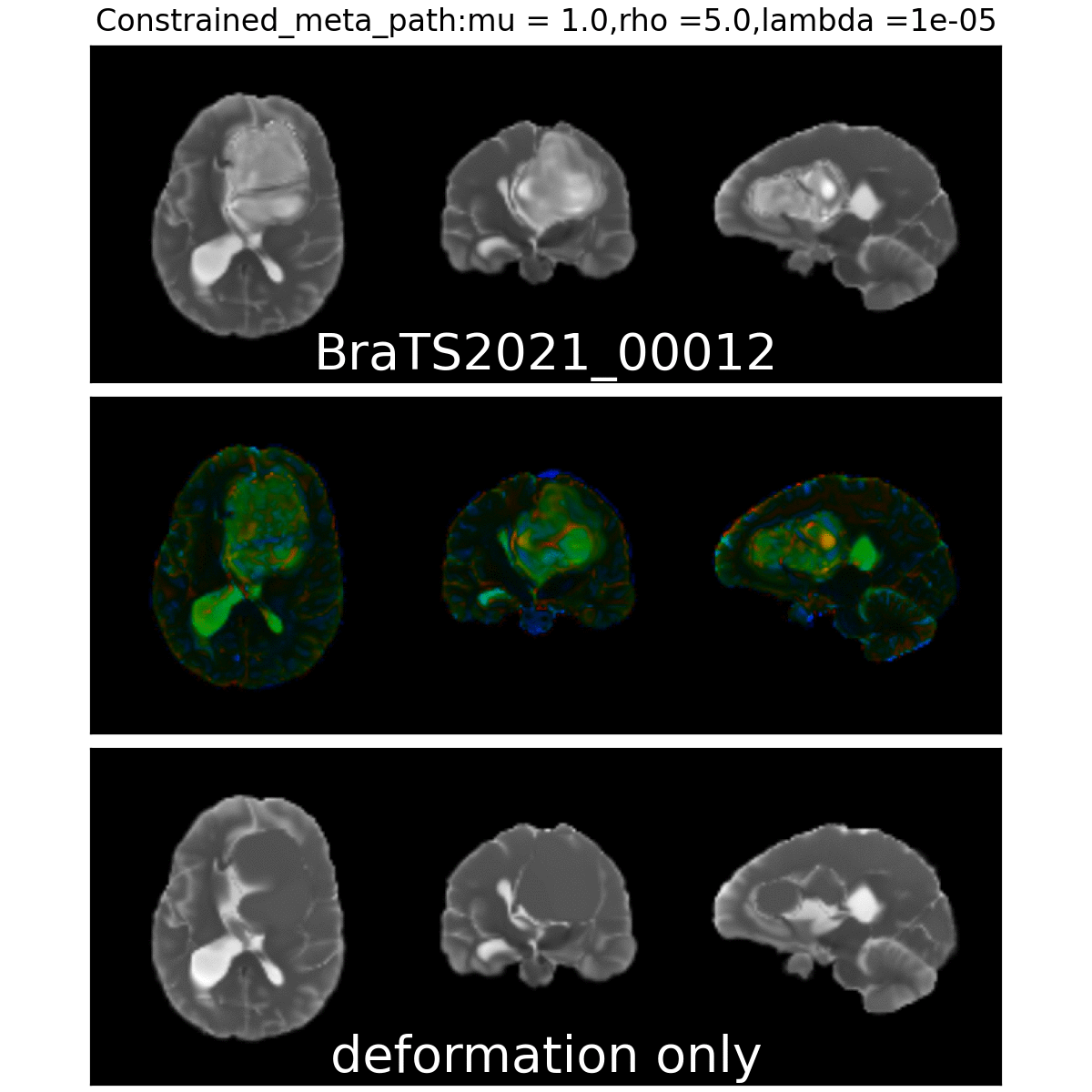
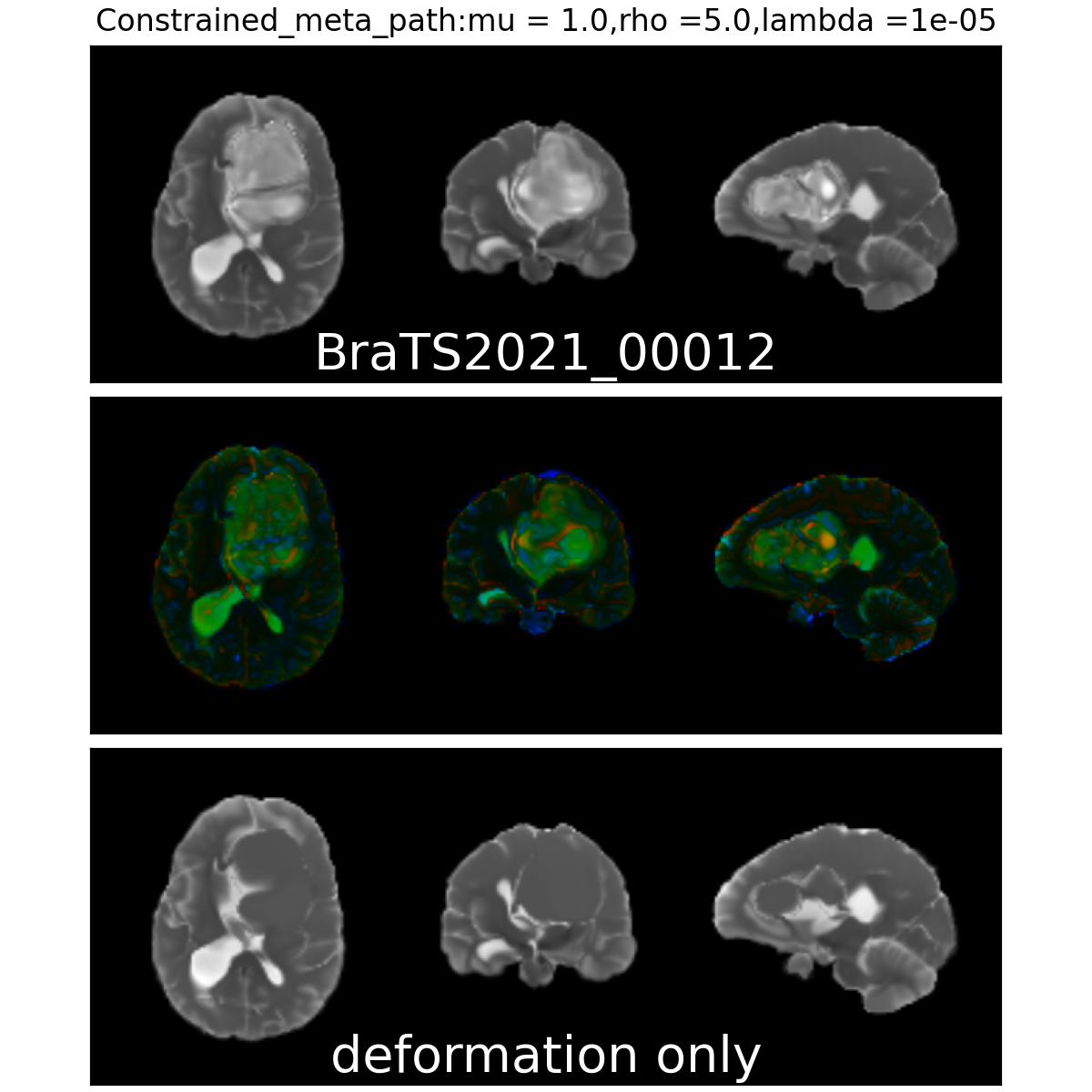
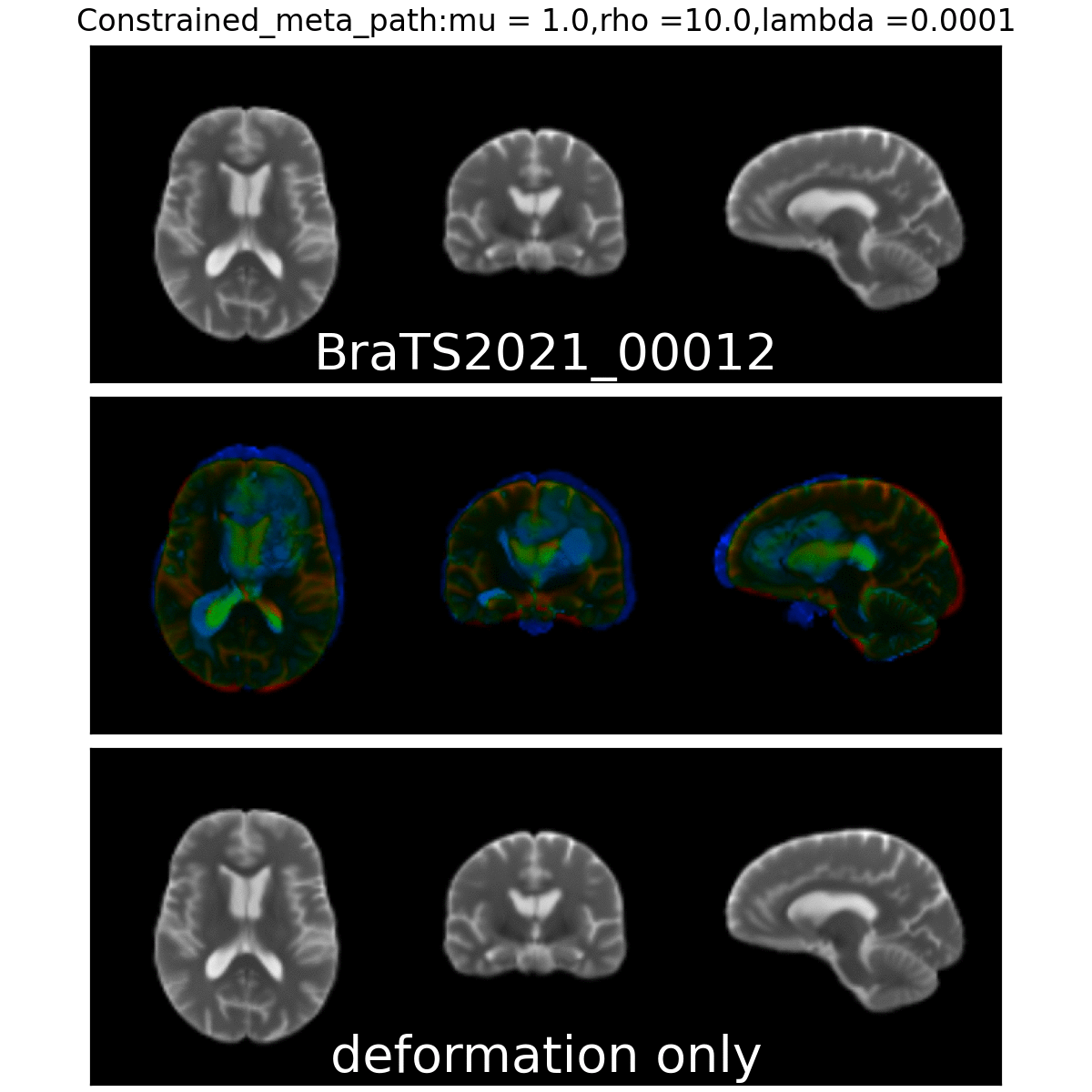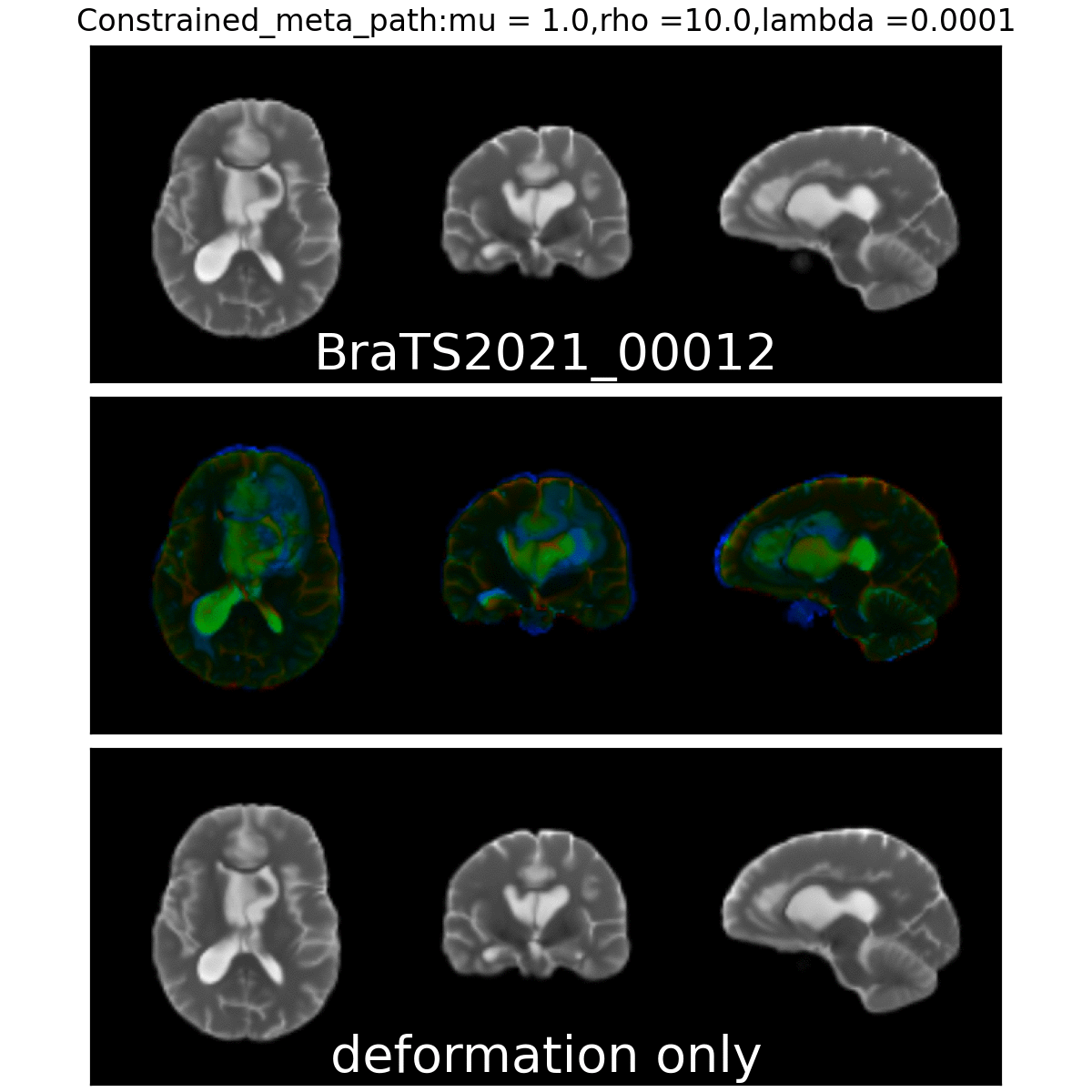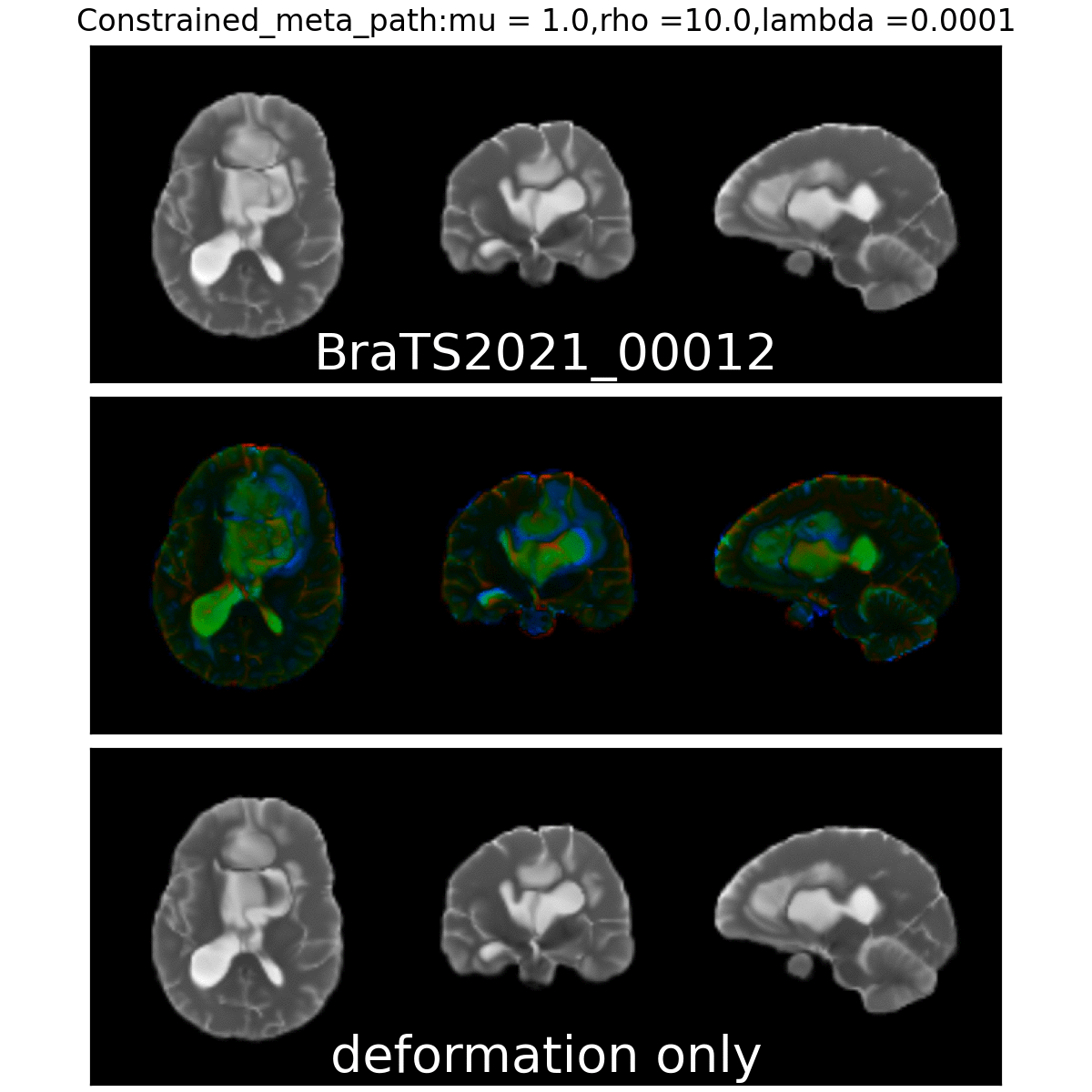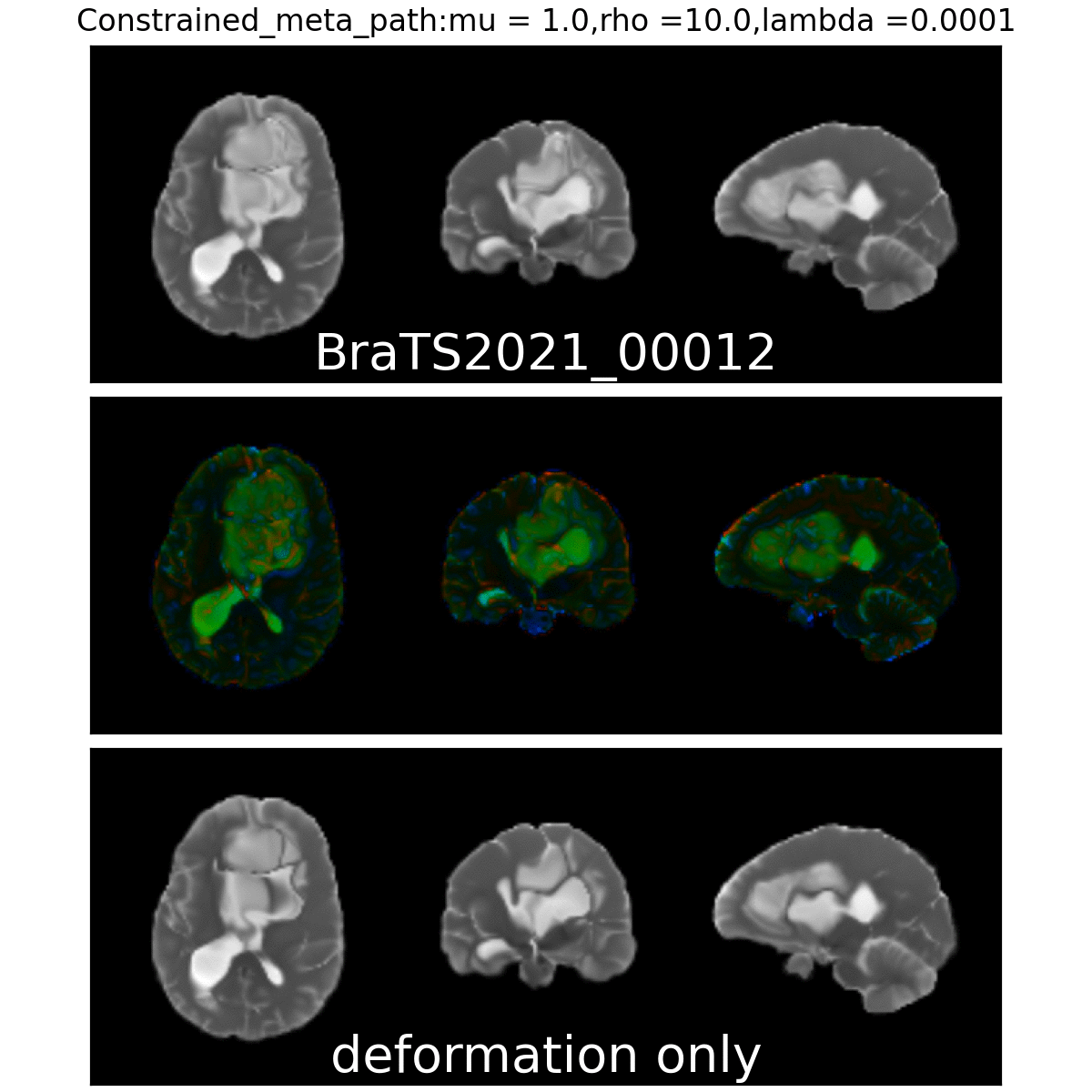
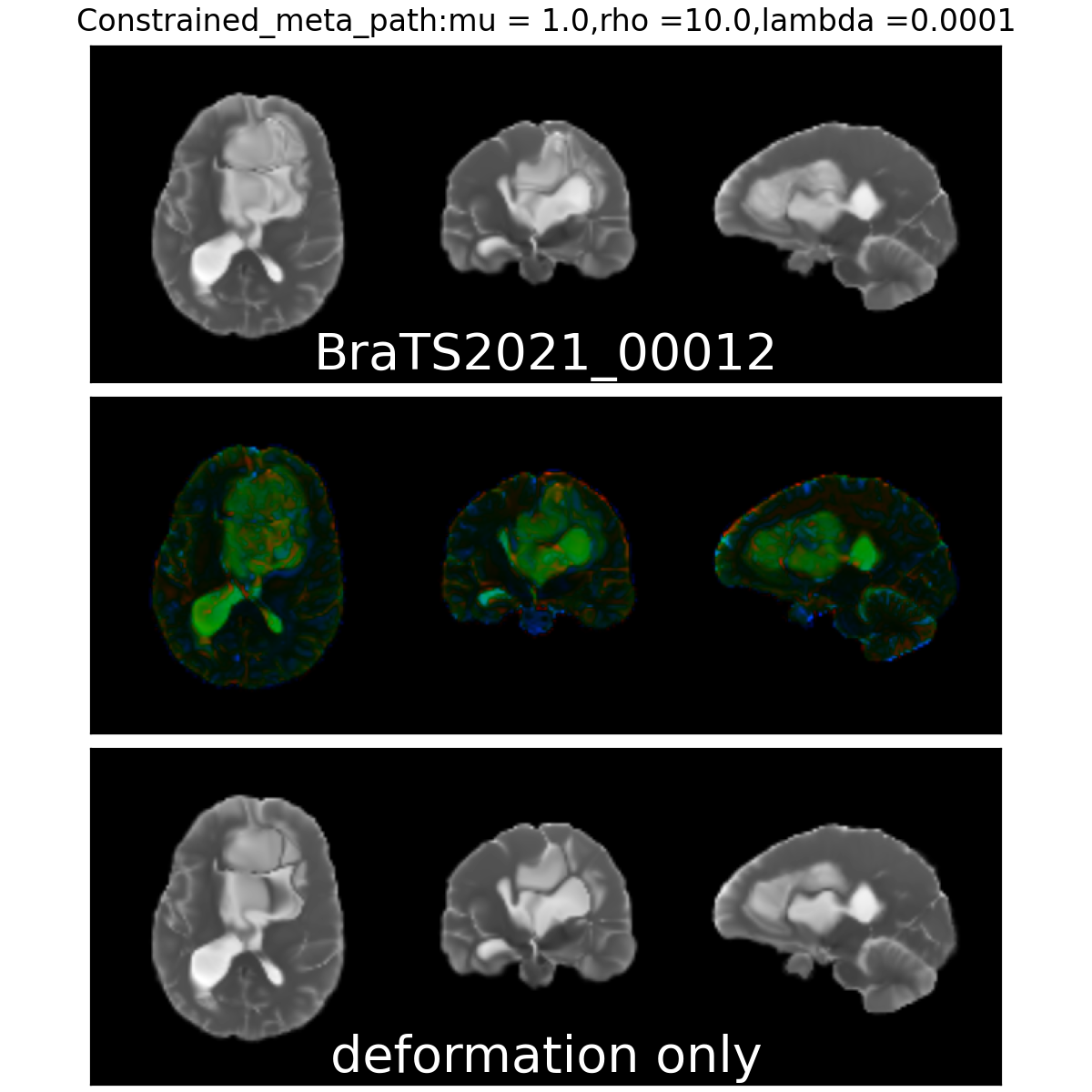













Qualitative results
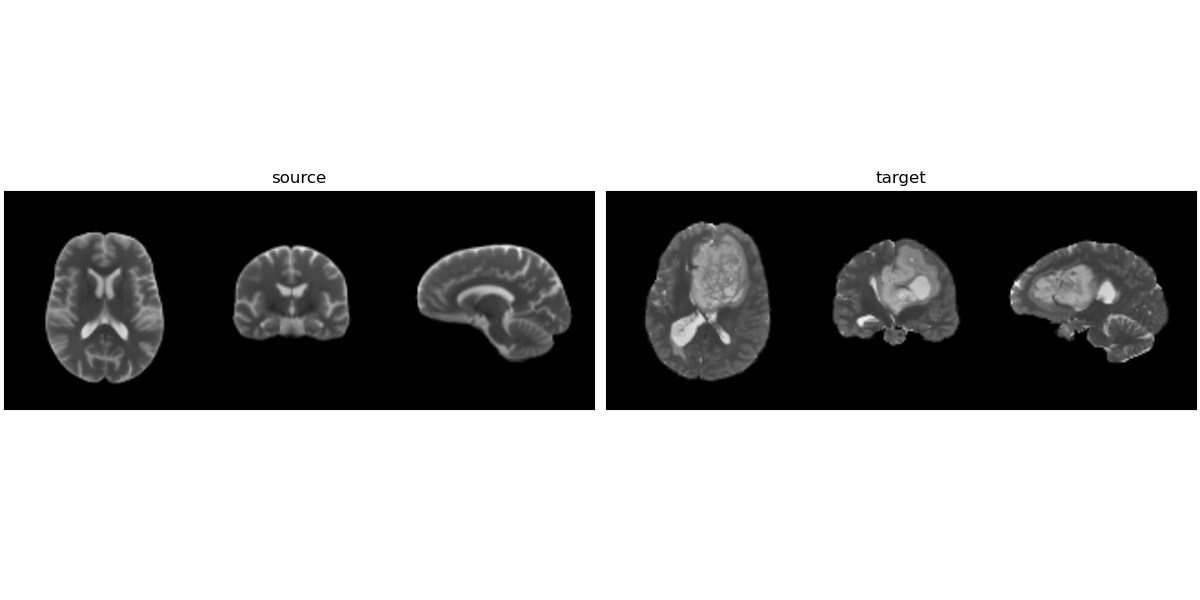














Anton François - 04/06/2024













Quantitative Results:
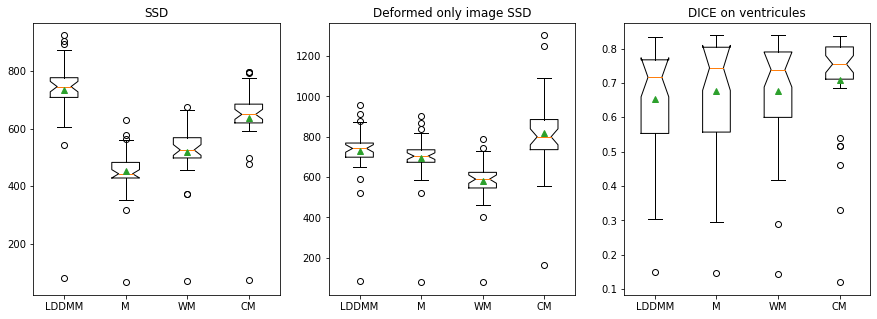
Lower the better
Higher the better
Anton François - 05/03/2024



























BraTSReg pré- to post- operative registration
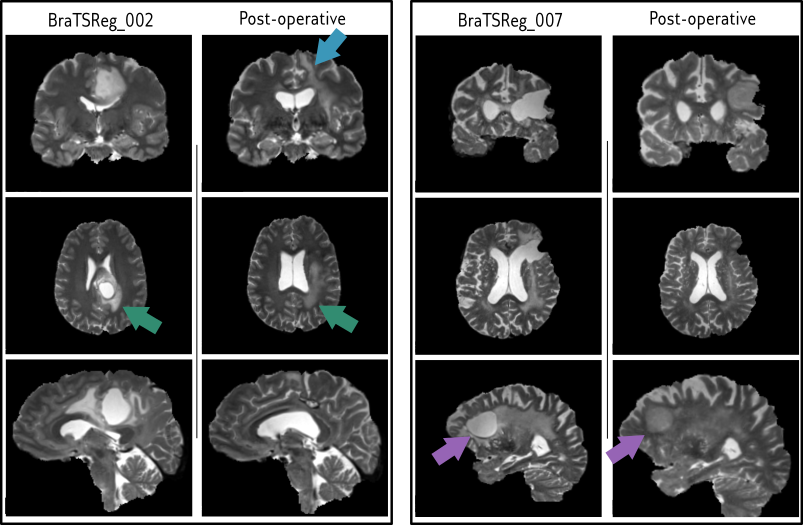
Lower the better
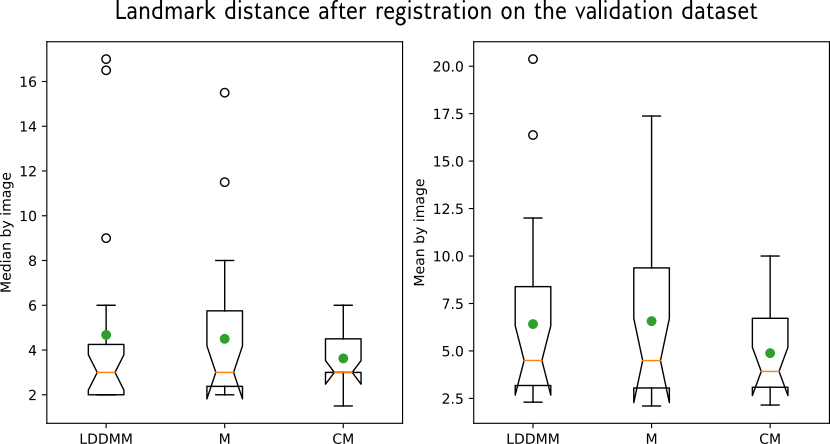
- Big datasets of the same patients before and after surgery
- Provides landmarks for registration validation
Anton François - 05/03/2024





























Constrained Metamorphosis
conclusion & perspective
Framework to add priors into Metamorphosis

Slower because of the increasing complexity
Anton François - 05/03/2024

Constrained Metamorphosis
conclusion & perspective
Framework to add priors into Metamorphosis
We have shown that growth has to drive registration
Implement Deep-Learning Version.
Prior modelisation: We can incorporate more complex glioma model (e.g., GLISTR [Gooya et al.]) or a growth model [Kaltenmark, 2016].
Versatile: can be used for healthy/pathological or pathological/pathological applications or others.
Automatic prior selection
Anton François - 05/03/2024














Future work

ANR : Radio-AIDE



Problematic: Radiotherapy (RT) is one of the most important treatments of brain tumours. A pre-analysis of 34 patients showed a cognitive degeneration for 97% of them after 1 year.
[J. Jacob, 2019; M. Ribeiro 2020]
Database: 224 + 150 patients - pre/post RT, followed for at least 12 months every 2-3 months - if survival.
Longitudinal AI-based segmentation: of post-RT white-matter hyperintensities (WHM) and their evolutions
- Will provide lesion segmentation probability map

We aim to interpolate those maps using Metamorphosis to characterize the White MH evolution patterns
Anton François - 04/06/2024
Metamorphosis on Manifolds



We can also apply Metamorphosis on objects with values into a Manifold.




Metamorphosis on the Probability simplex
The standard \(n\)-Simplex is the subset of \(\mathbb R^{n+1}\) given by
$$\Delta^n = \left\{p \in \mathbb R^{n+1} : \forall i \in \{1,\cdots,n+1\}, p_i > 0; \sum_{i=1}^{n+1} p_i = 1\right\}.$$
A path on the 2-Simplex
fig from [Jasminder, 2020]
Why the simplex rather than images:
- pixel colour does have a "meaning"
- Does not change depending on the preprocessing => Data confidence increased
- notion of uncertainty


Anton François - 04/06/2024

Let \(q\) be the "simplex image", (\(q(x) \in \Delta^n\)) and \(\tilde q : \Delta^n \mapsto S^n = \sqrt q\) the isometry from the simple on the sphere. We set its evolution such that:
\[\partial_t\tilde q = -\sqrt{\rho} \nabla \tilde q \cdot v + \sqrt{1 - \rho} z; \qquad\rho \in \mathbb R\]
Let \(H\) be the Hamiltonian defined such that,
\[H(\tilde q,p,v,z) = (p|\partial_t \tilde q) - \frac 12\|v\|_V^2 -\frac 12\|z\|_2^2\]
By computing the variations of H with respect to \(\tilde q,p,v,z\) we retrieve the geodesic equations
$$\left\{\begin{array}{rl} \dot {\tilde q_t} &= - \sqrt{\rho} \nabla \tilde q_t \cdot v_t + \sqrt{1 -\rho} z_t\\ \dot p_t &= - \sqrt{\rho} \mathrm{div}(p_t \otimes v_t) - \sqrt{1 -\rho}<p_t, \tilde q_t>z_t\\ z_t &= \sqrt{1 - \rho} (p_t - (\sum_{i=1}^{n+1} p_{t,i} \tilde q_{t,i})\tilde q_t)\\ v_t &= - \sqrt{\rho} K_V\left(\sum_{i=1}^{n+1} p_{t,i}\nabla \tilde q_{t,i} \right)\end{array}\right.$$
Metamorphosis on the Probability simplex



Metamorphosis on the Probability simplex

Conclusion & Perspective








Overall outcomes of my PhD
First open-source implementation of Metamorphosis, with novel integration scheme and GPU support.
Framework to register complex medical images with increased explainability using a simplitistic model.
Expecting better registrations using M on segmentation.
Published Articles:
- A. François, P. Gori, and J. Glaunès. Metamorphic image registration using a semi-lagrangian scheme. In SEE GSI, 2021
- A. François, M. Maillard, C. Oppenheim, J. Pallud, I. Bloch, P. Gori, and J. Glaunès. Weighted metamorphosis for registration of images with different topologies. In WBIR, pages 8–17, 2022
- M. Maillard, A. François, J. Glaunès, I. Bloch, and P. Gori. A deep residual learning
implementation of metamorphosis. In IEEE ISBI, 2022 - A. François and R. Tinarrage, Train-Free Segmentation in MRI with Cubical Persistent Homology, La Mathematica, Jan. 2024, Preprint.




Th
an
k
You !